REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Physics
3.3 Light and Sound
3.3.1 Know that light waves are transverse waves and that they can be reflected and refracted

3.3.2 Use the law of reflection (the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection)
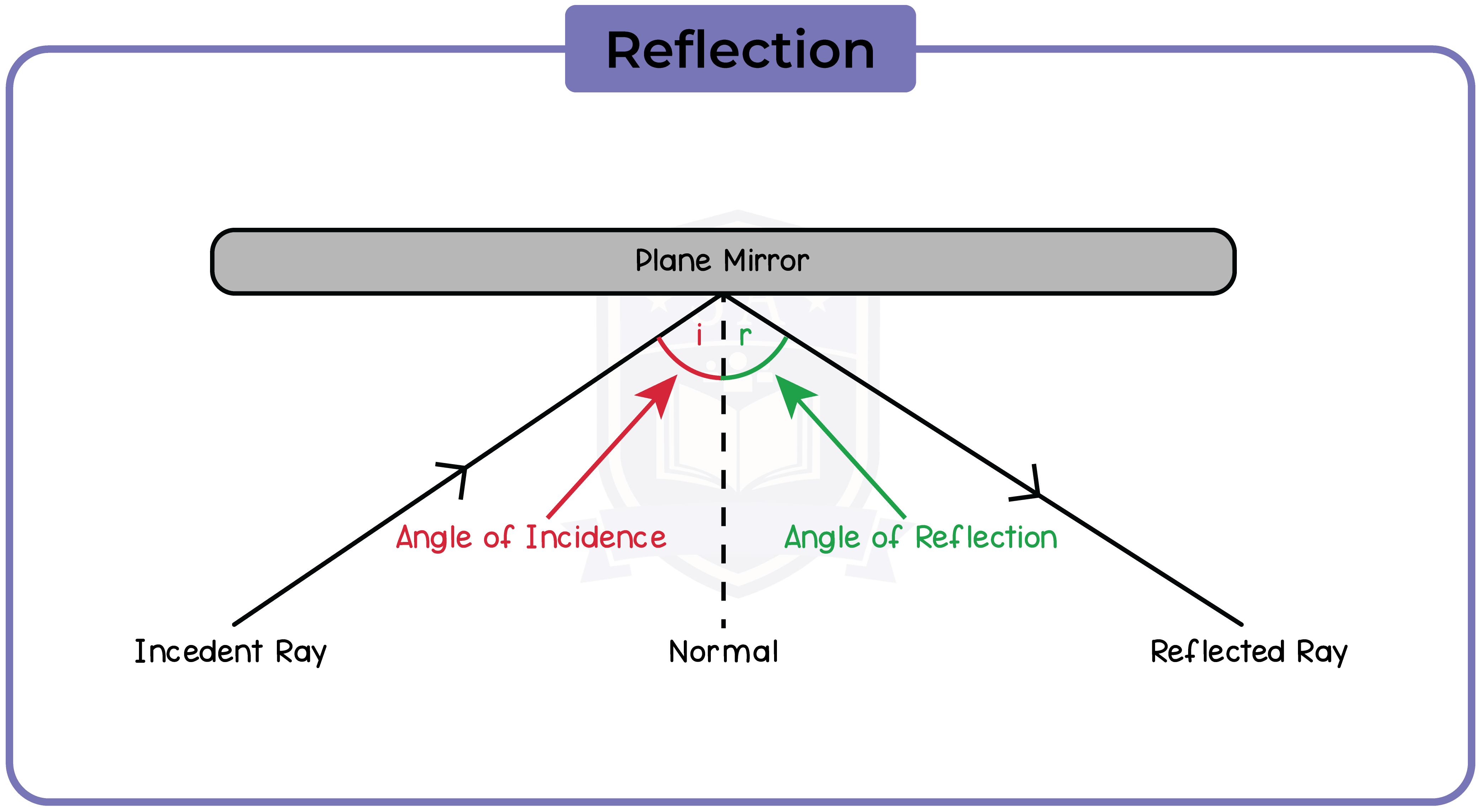
3.3.3 Draw ray diagrams to illustrate reflection and refraction
3.3.4 Practical: investigate the refraction of light, using rectangular blocks, semi-circular blocks and triangular prisms
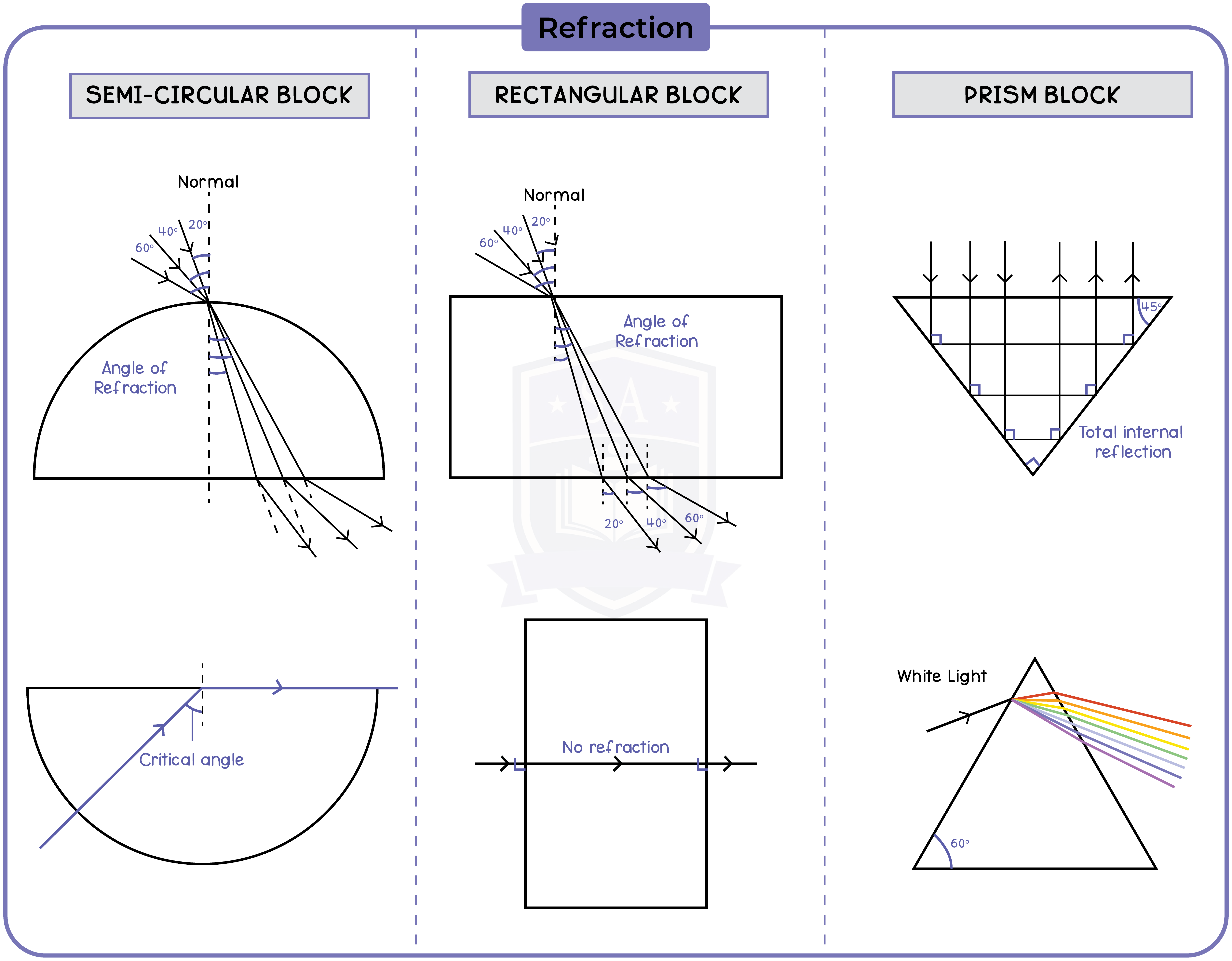
3.3.5 Know and use the relationship between refractive index, angle of incidence and angle of refraction:

3.3.6 Practical: investigate the refractive index of glass, using a glass block
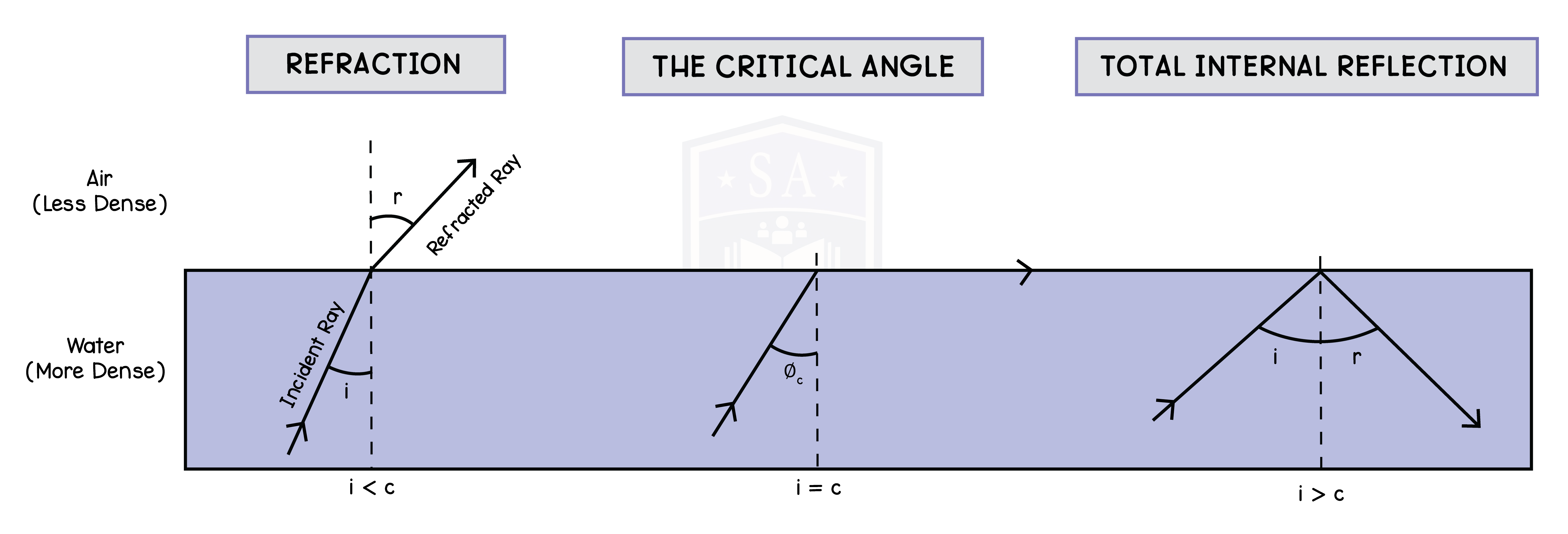
3.3.7 Describe the role of total internal reflection in transmitting information along optical fibres and in prisms
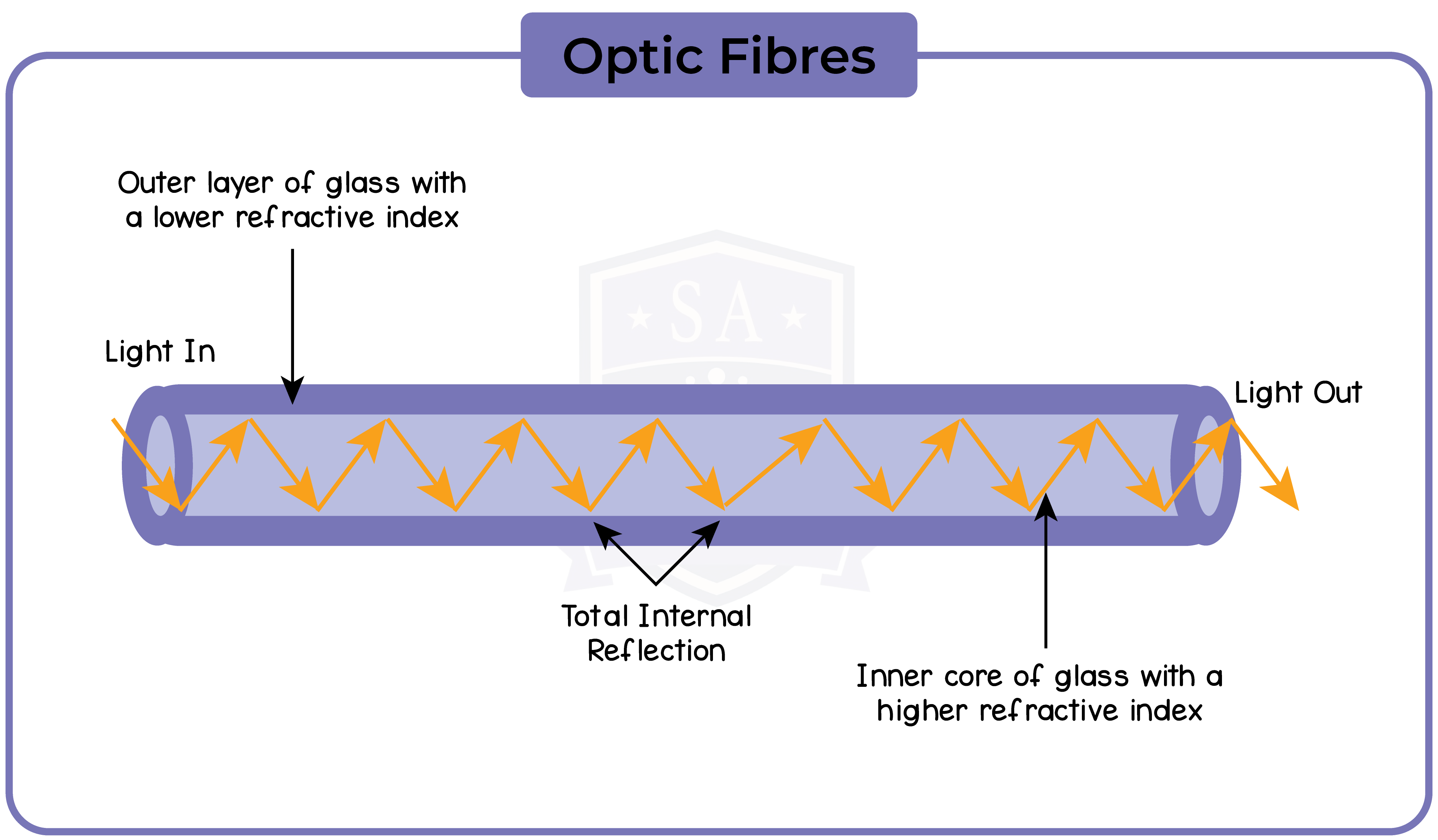
3.3.8 Explain the meaning of critical angle c
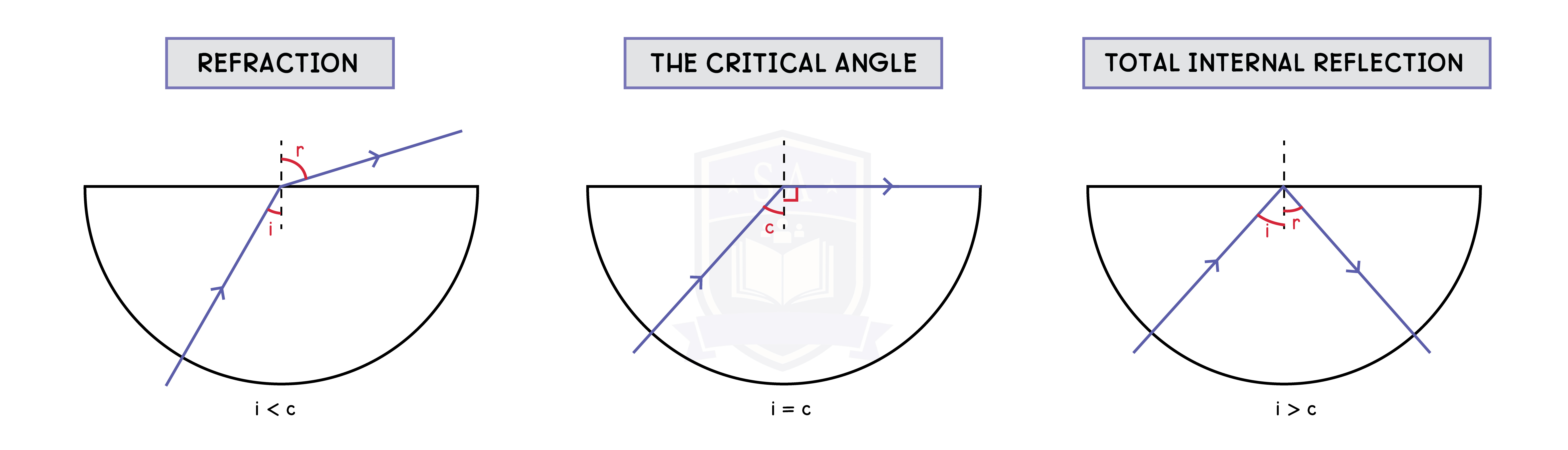
3.3.9 Know and use the relationship between critical angle and refractive index:

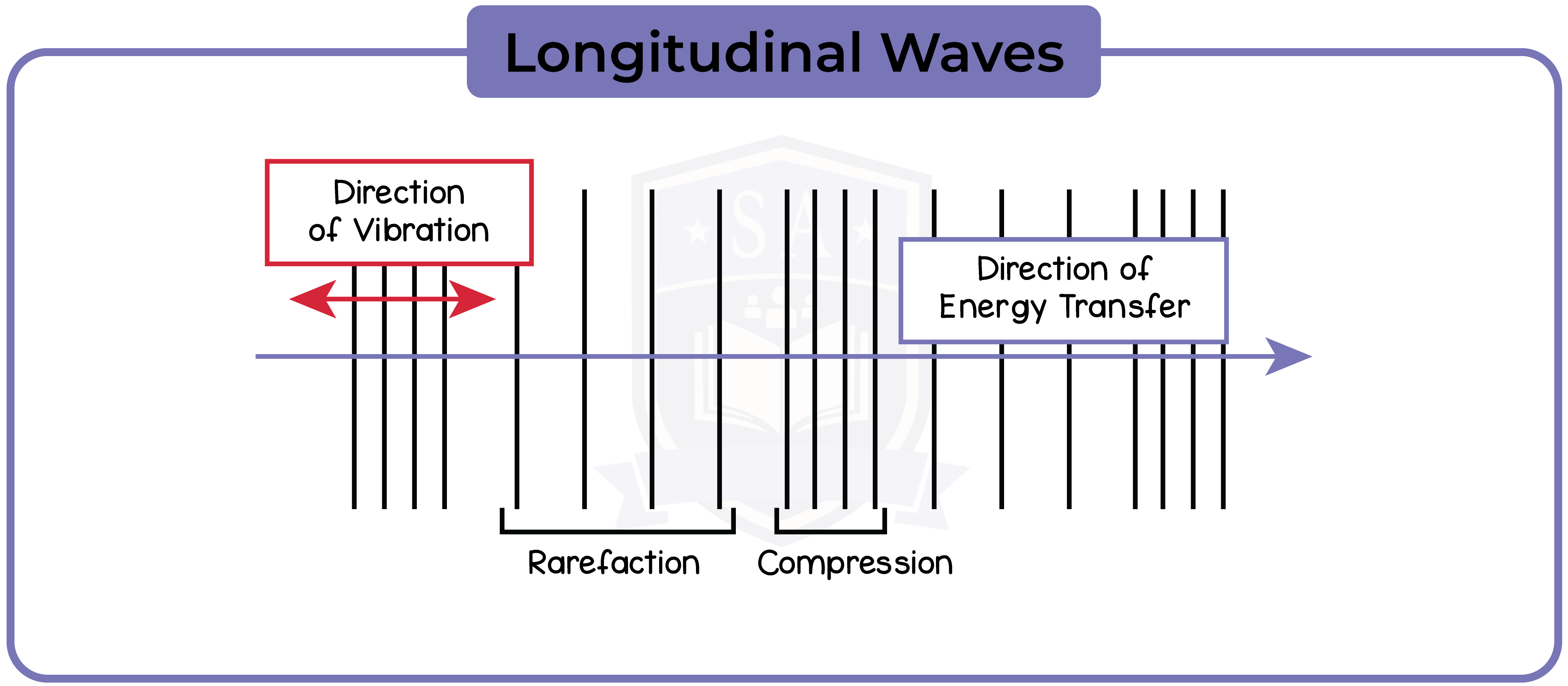
3.3.10 Know that sound waves are longitudinal waves that can be reflected and refracted

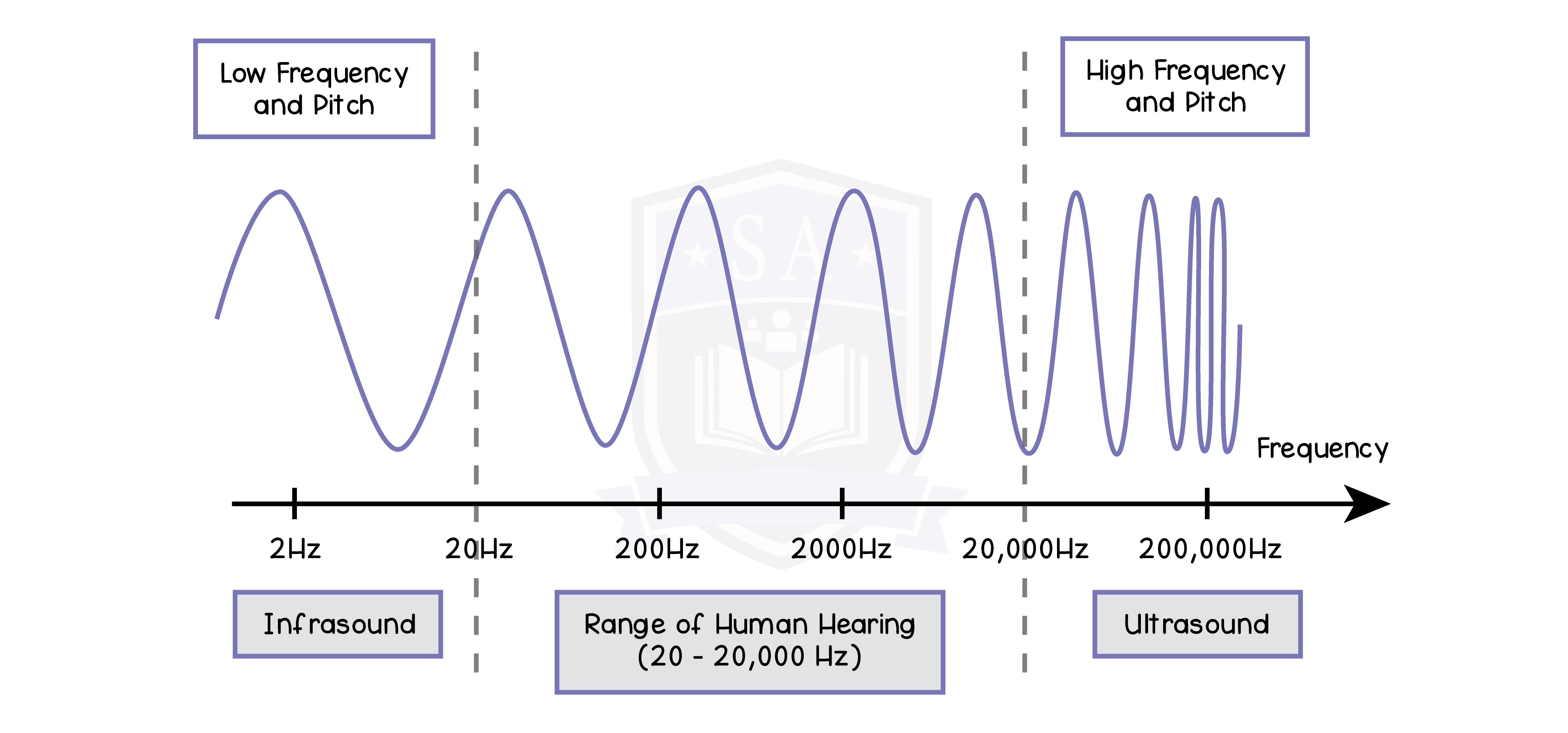
3.3.11P Know that the frequency range for human hearing is 20–20.000 Hz
3.3.12P Practical: investigate the speed of sound in air
3.3.13P Understand how an oscilloscope and microphone can be used to display a sound wave
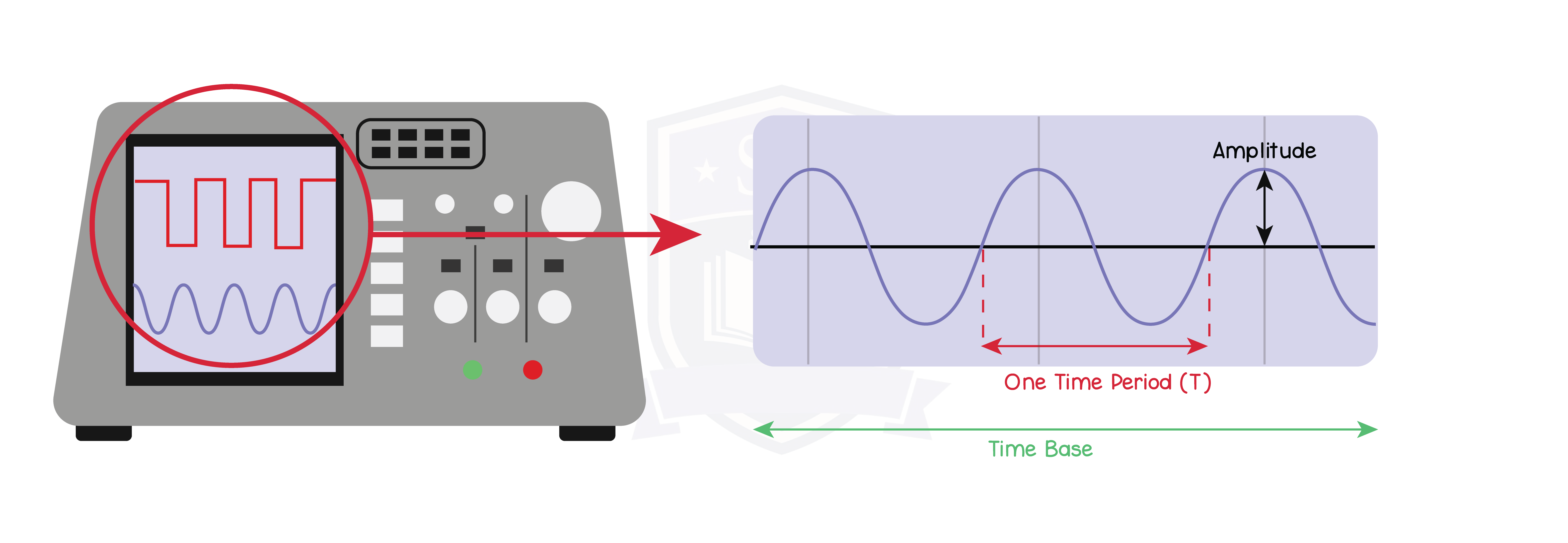
3.3.14P Practical: investigate the frequency of a sound wave using an oscilloscope
Apparatus needed:
- Measuring tape
- Microphones
- Oscilloscope
- Wooden blocks
Independent variable: Distance travelled
Dependent variable: Time taken
Method:
- Connect two microphones to an oscilloscope
- Place two microphones two metres apart
- Set up oscilloscope so that it triggers when either of the microphones detect a sound
- Set the time base of the oscilloscope small enough so that you can see the difference in time between the microphones
- Clap the wooden blocks next to one of the microphones
- Use the oscilloscope to find the time taken for the other microphone to hear
- Repeat the experiment increasing the distance by 0.5m every time until 5m
- Table results
- Calculate speed
- Average results for accuracy
Controlled variables:
- Location
- Microphones used
3.3.15P Understand how the pitch of a sound relates to the frequency of vibration of
the source
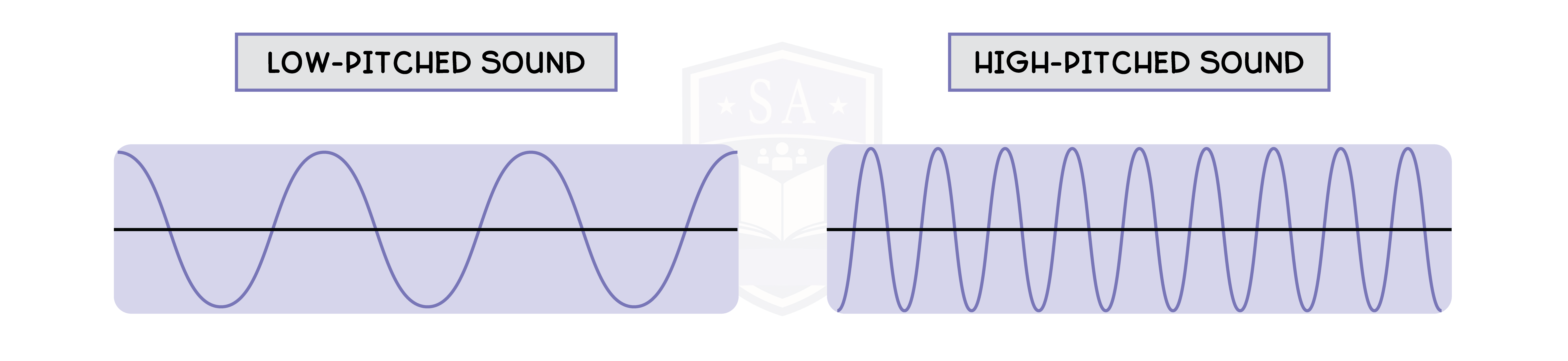
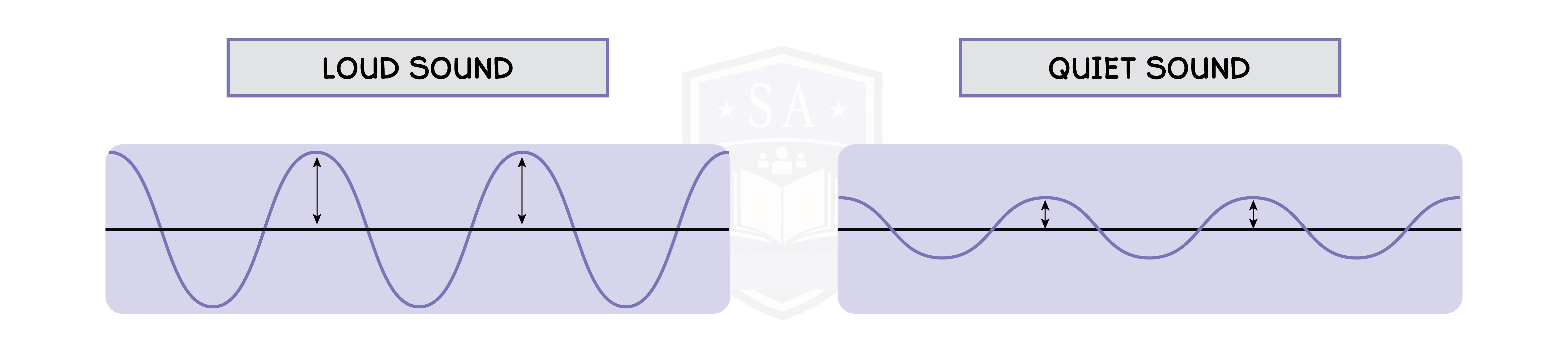
3.3.16P Understand how the loudness of a sound relates to the amplitude of vibration of the source