REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics
1.9 Calculus
1.9.1 Differentiation and integration of sums of multiples of powers of x (excluding integration of 1/x),sin ax,cos ax,eax
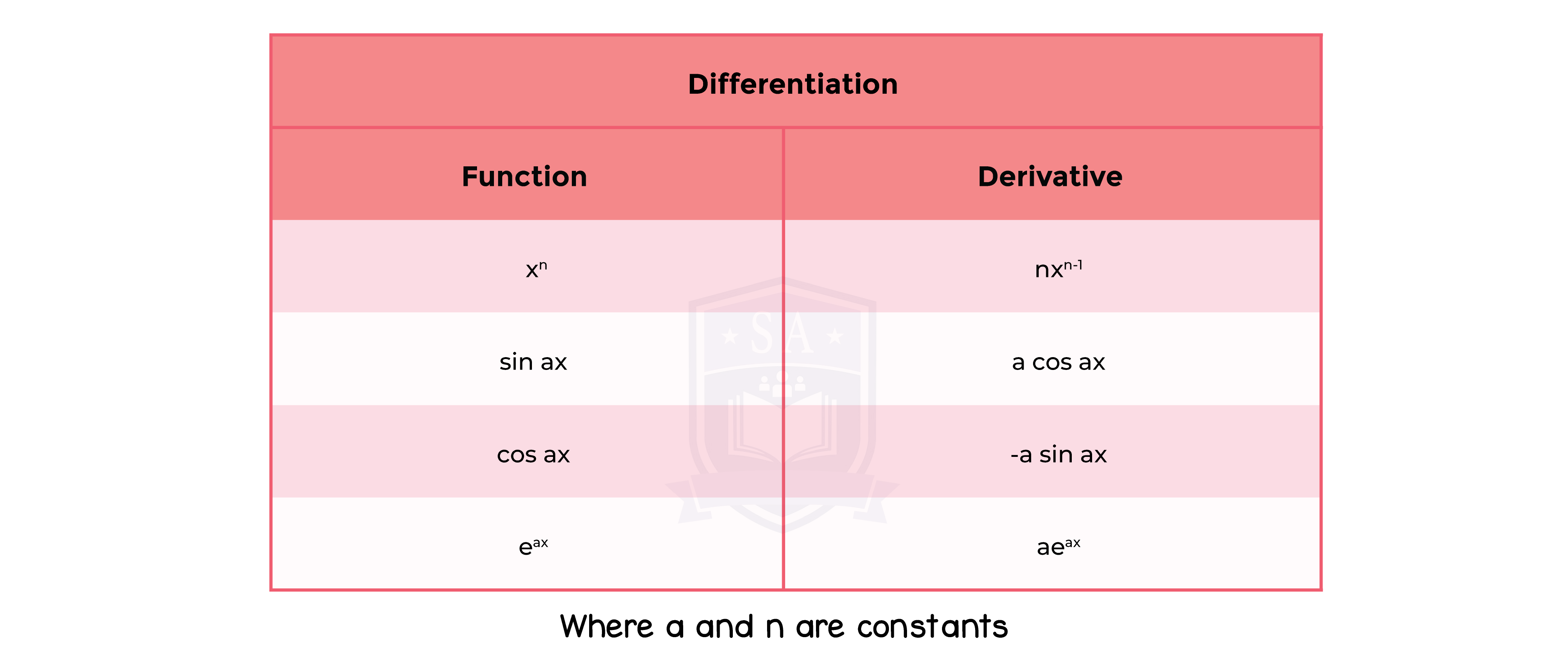
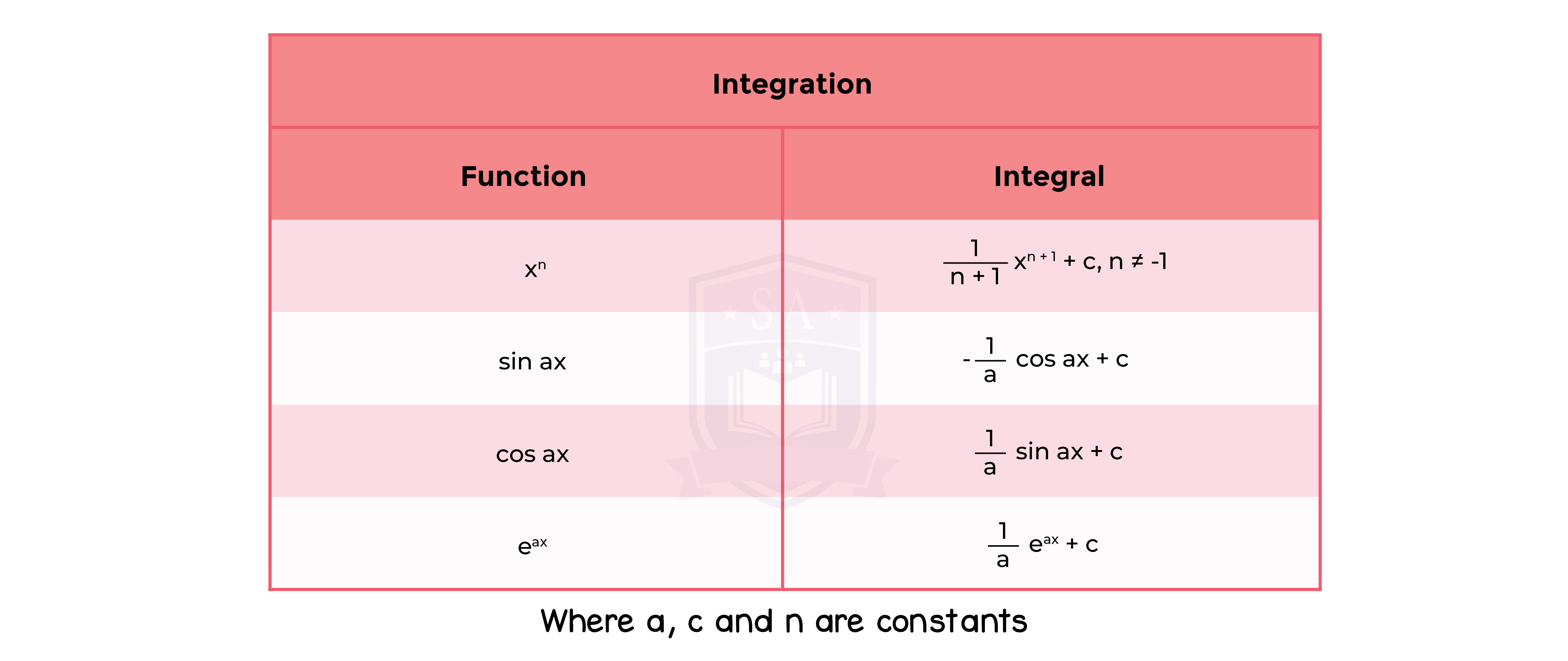
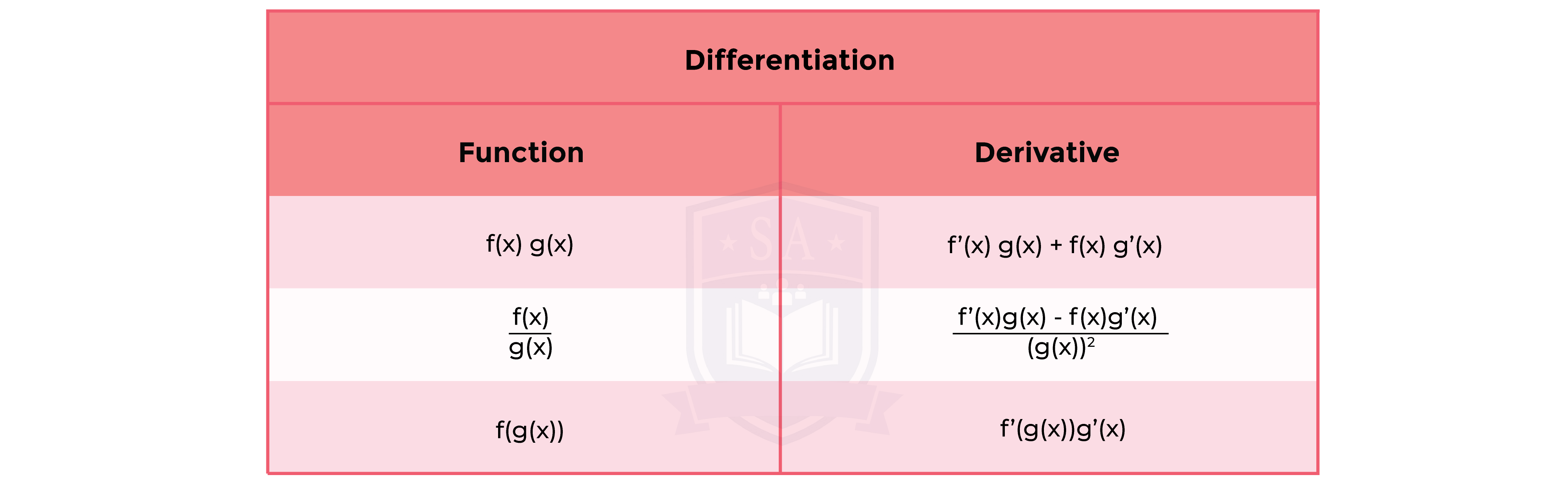
1.9.2 Differentiation of a product, quotient and simple cases of a function of a function
1.9.3 Applications to simple linear kinematics and to determination of areas and volumes
Type 1: Area between a curve and x-axis (y > 0)
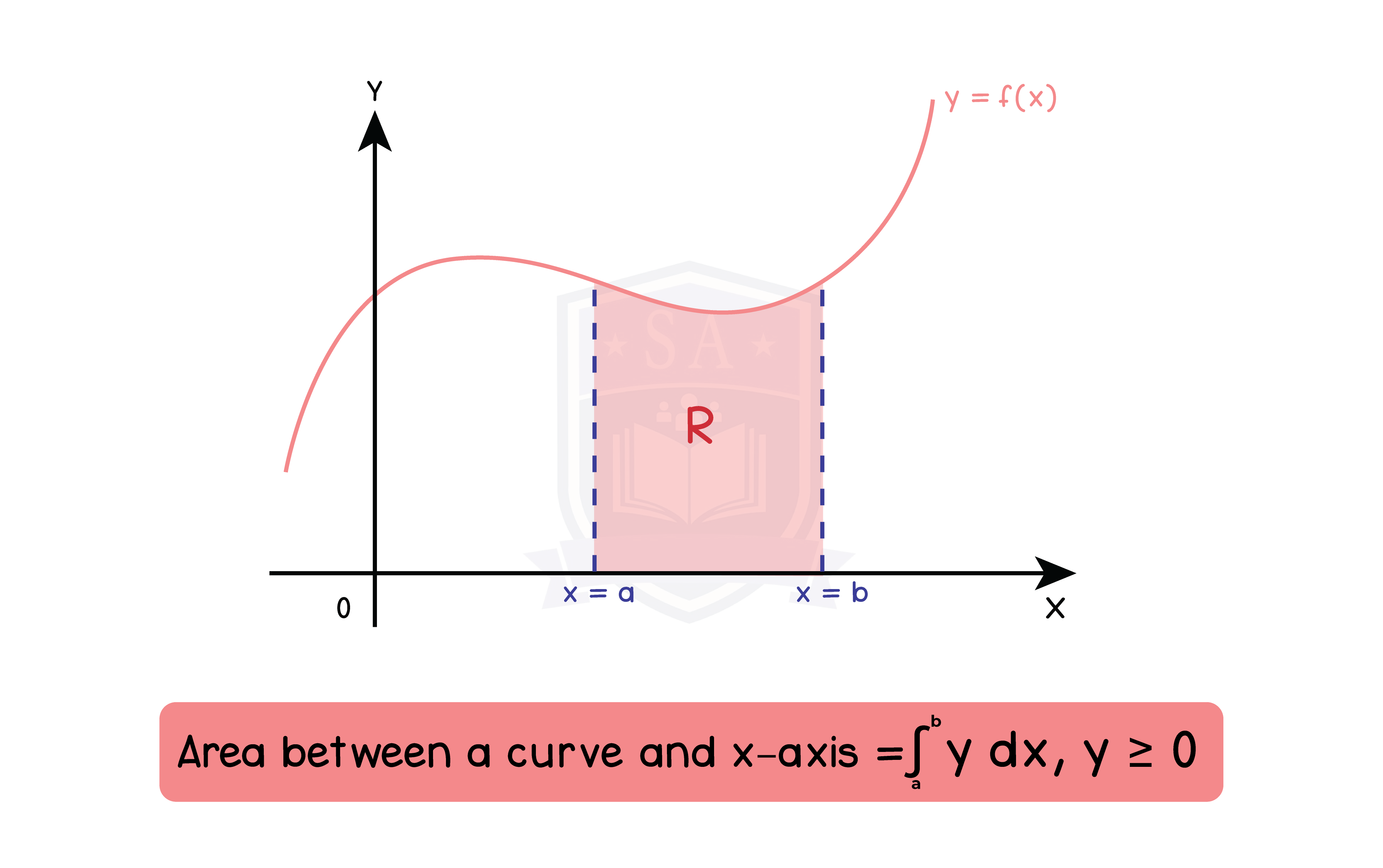
Type 2: Area between a curve and x-axis (y < 0)
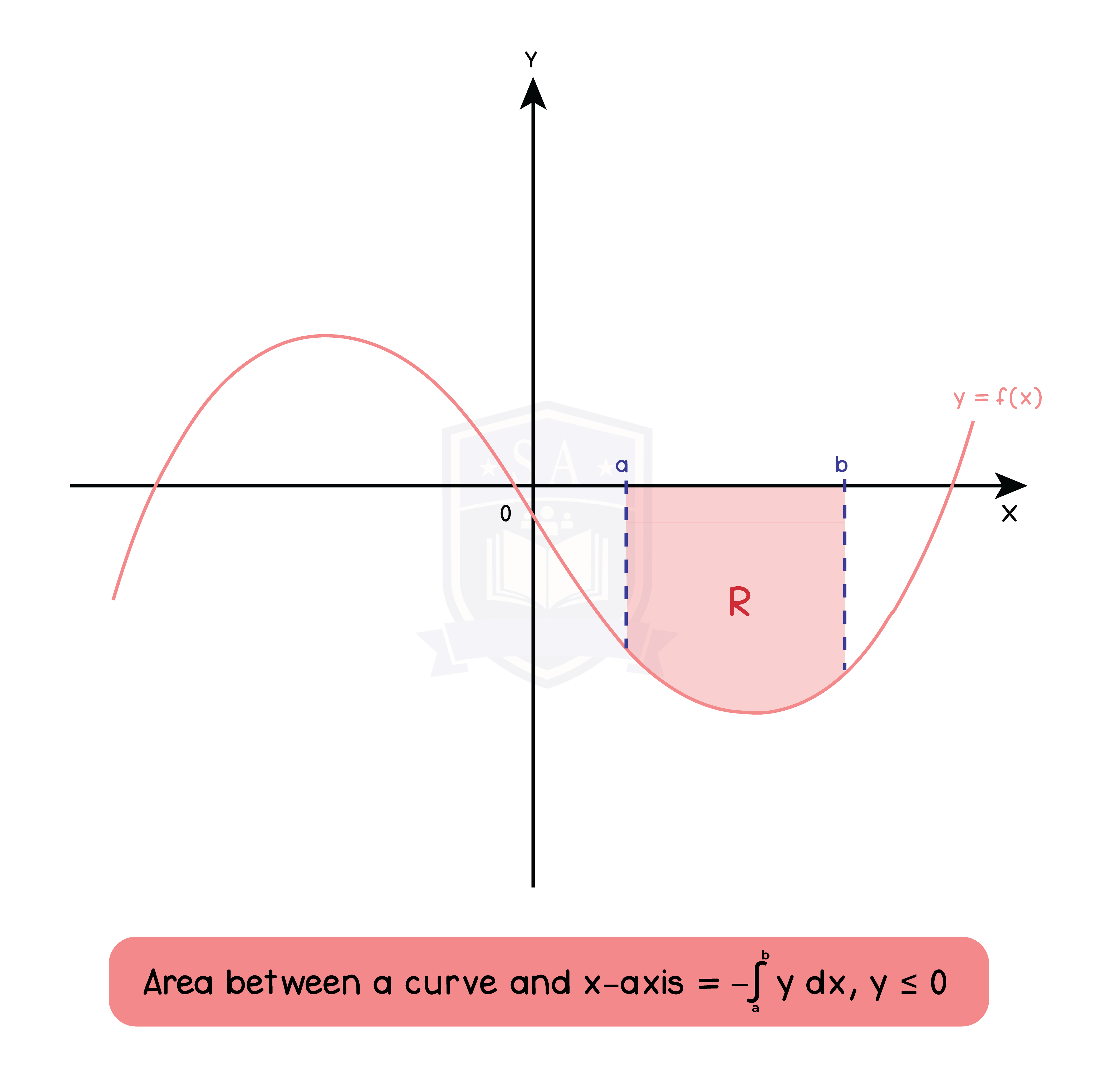
Type 3: Area between a curve and x-axis (-∞ < y <∞)
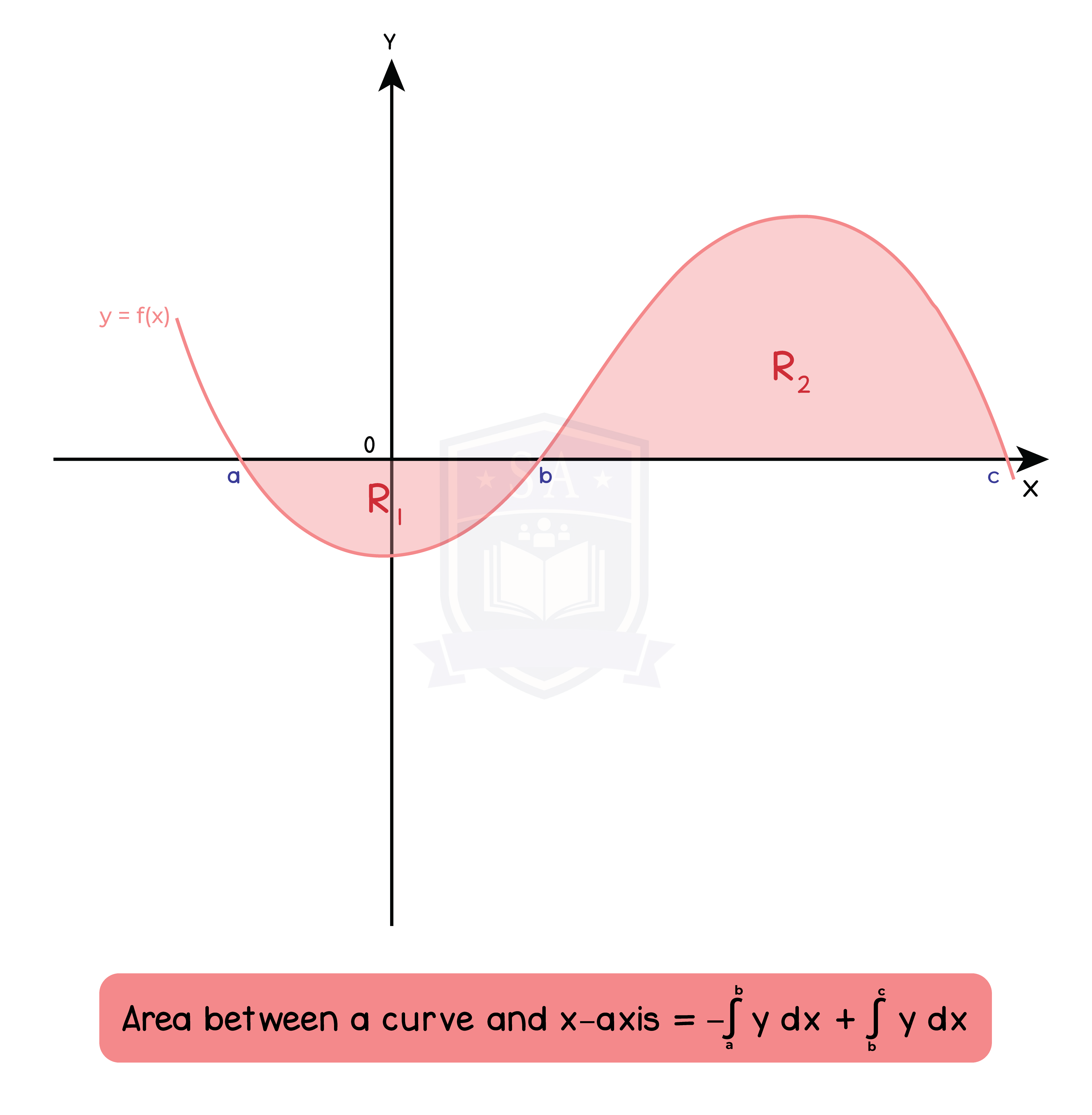
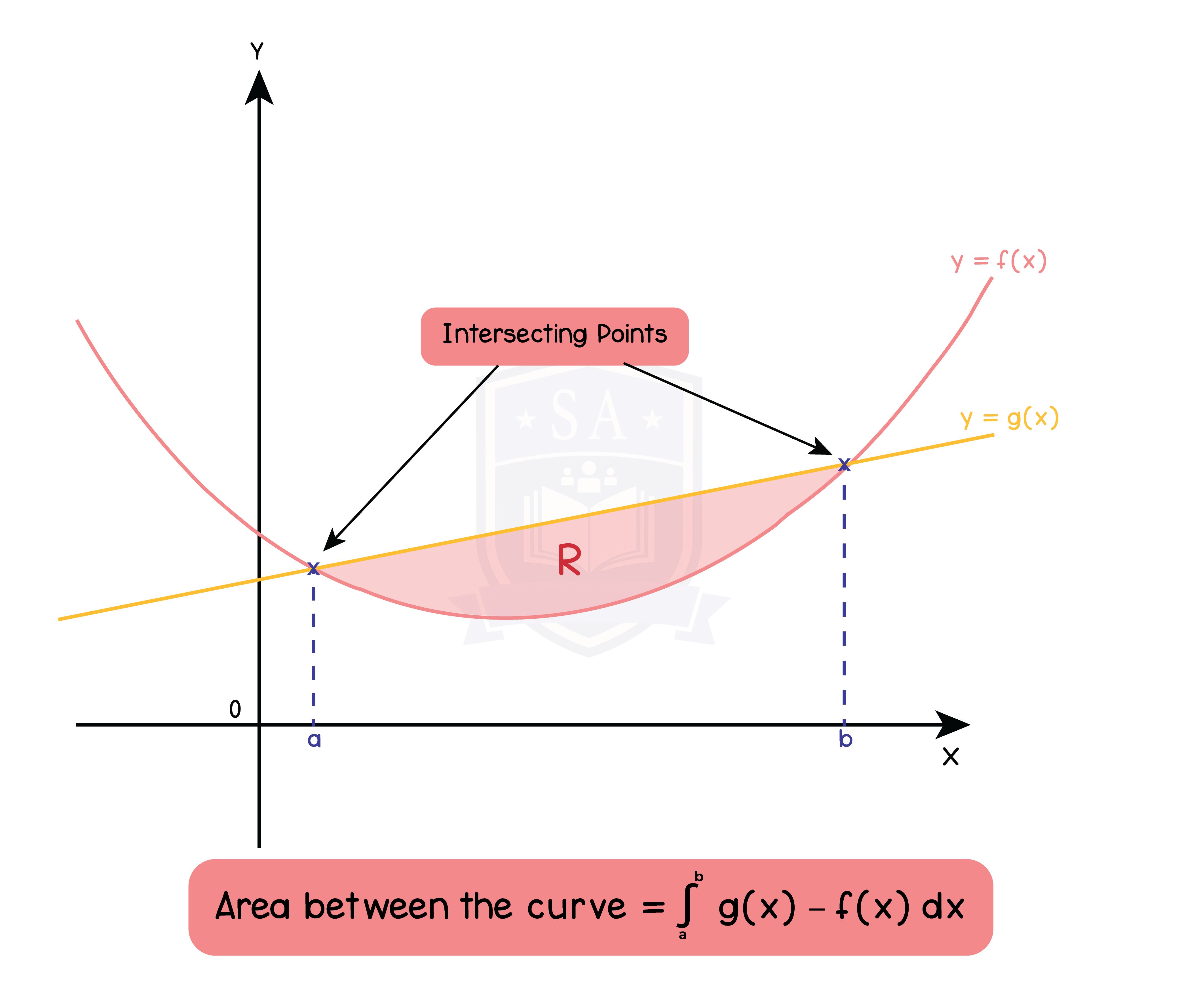
Type 4: Area between two curves
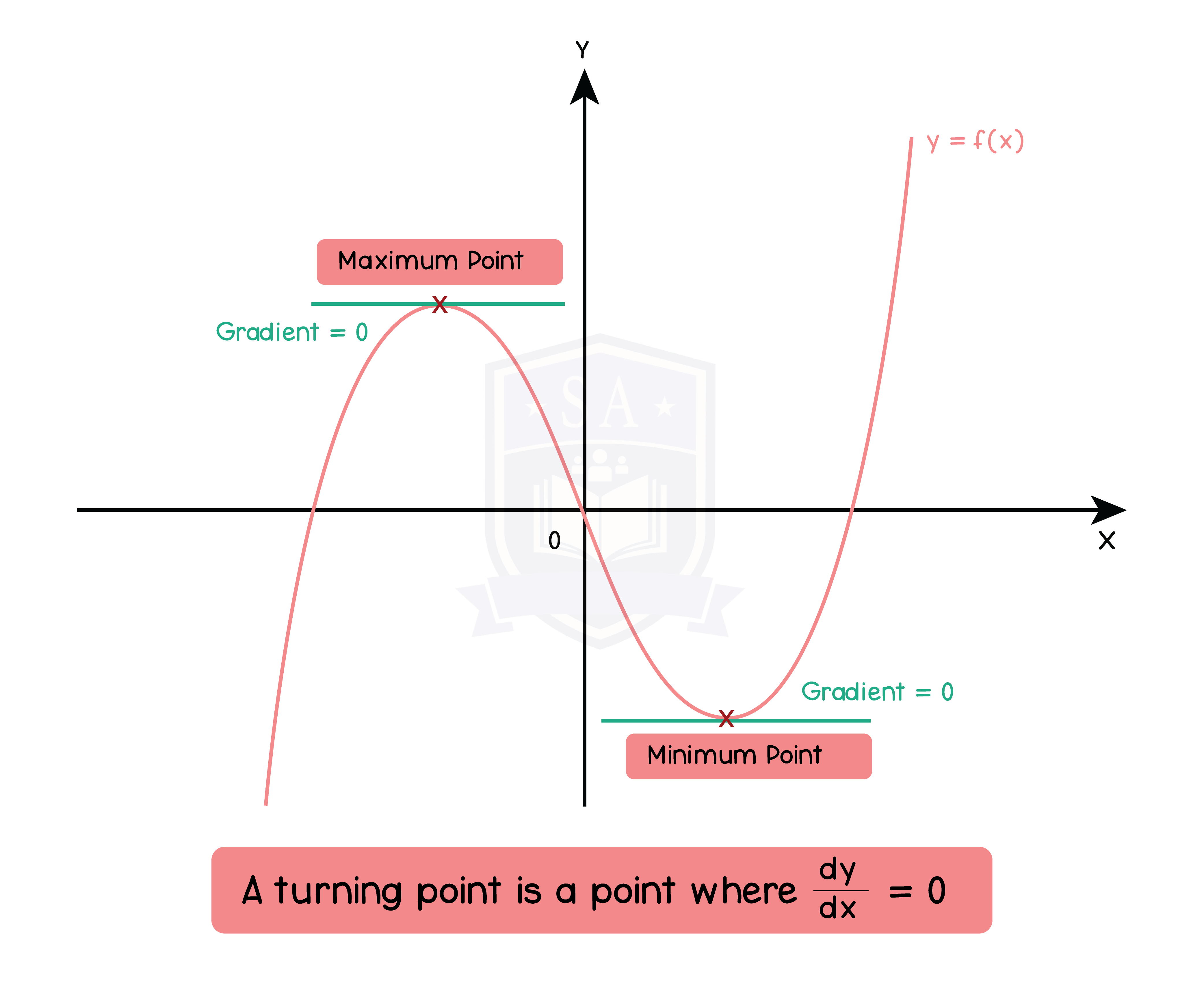
1.9.4 Stationary points and turning points
Coordinates of a Stationary Point
Step 1: Differentiate the equation and equate to 0 (f'(x) = 0)
Step 2: Substitute the value of x into the equation to find y
1.9.5 Maxima and minima

1.9.6 The equations of tangents and normals to the curve y = f(x)


1.9.7 Application of calculus to rates of change and connected rates of change
Finding rate of change of a part of a usually 3D shape (e.g. radius):
- Eg: Area of volume of cylinder info
- 50cm3/s (rate of sand poured)
- V of cone increases in a way that r of base is always 3 times the h of the cone
- Find rate of change of radius of cone, when radius is 10cm
Working:
dV/dt = 50 (given)
dr/dt = need to find
dr/dt = dV/dt x dr/dV
r = 3h (given)
h = r/3
V = 1/3πr2h
V = 1/3πr2(r/3)
V = 1/9πr3
dV/dr = 1/3πr2
dr/dt = 50 x 1/(1/3π(10)2) = 0.477 cm/s
dr/dt = 50 x 1/(1/3π(10)2) = 0.477 cm/s

