REVISION NOTES
3.3.1 Interpret information presented in a range of linear and non-linear graphs
3.3.2 Understand and use conventions for rectangular Cartesian coordinates
3.3.3 Plot points (x, y) in any of the four quadrants or locate points with given coordinates


3.3.4 Determine the coordinates of points identified by geometrical information
3.3.5 Determine the coordinates of the midpoint of a line segment, given the coordinates of the two end points

3.3.6 Draw and interpret straight line conversion graphs
Linear functions may be plotted accurately by drawing a table of values.
Although two points are sufficient to define a line, it is customary to plot three points as this helps detect errors caused by a slip in the working.
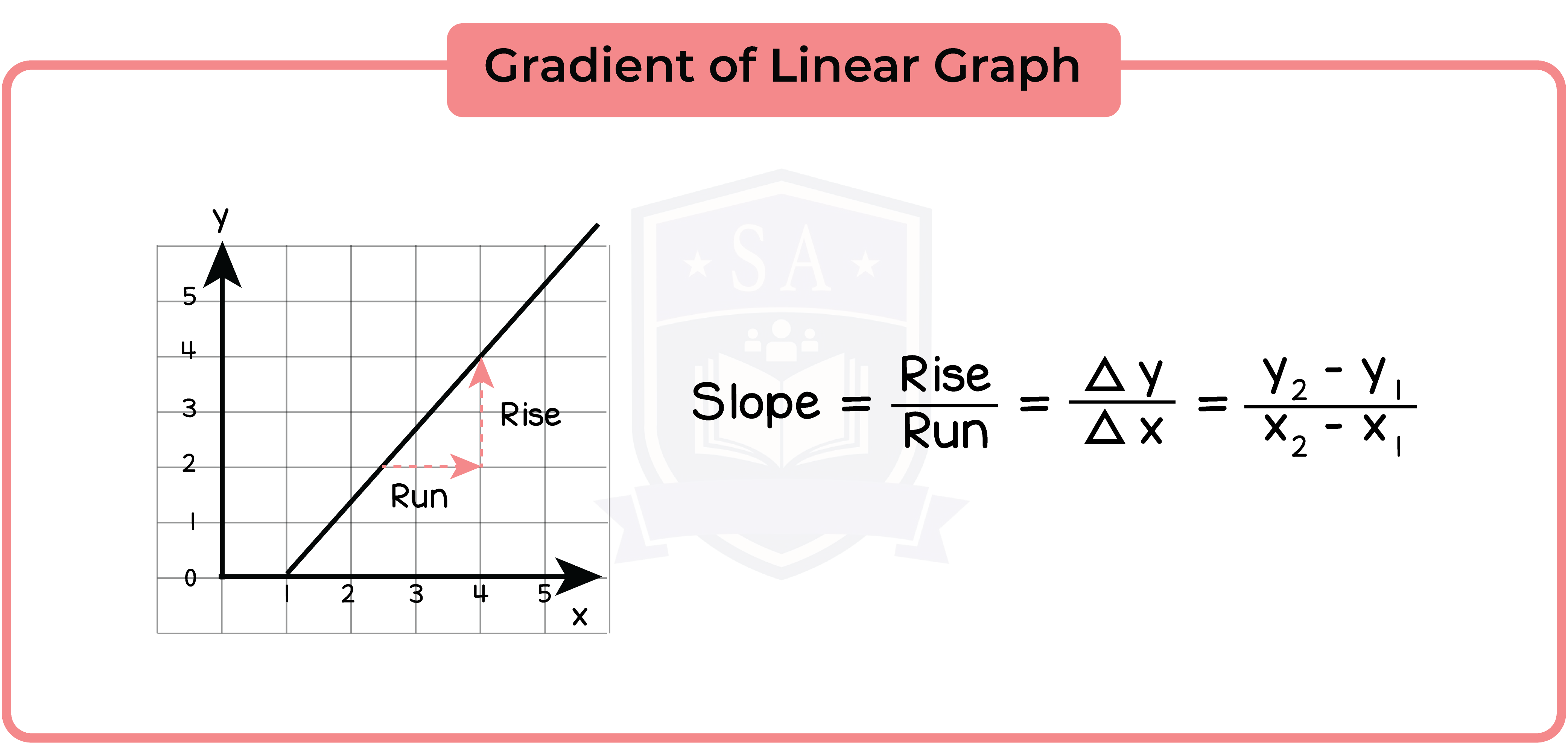
3.3.7 Find the gradient of a straight line
The gradient of a linear function is defined as the ratio of the height gained to the horizontal distance covered, or ‘rise over run’ for short.
Graphs that go down as you move to the right will have negative gradient.
3.3.8 Recognise that equations of the form y = mx + c are straight line graphs with gradient m and intercept on the y-axis at the point (0, c)
A linear graph with gradient m and y intercept c will have equation y = mx + c. This principle allows you to sketch linear functions, and to recognise the equation of a given straight line.
In order to compare the gradient of two linear functions, it is best to rearrange them into the form y= mx + c.
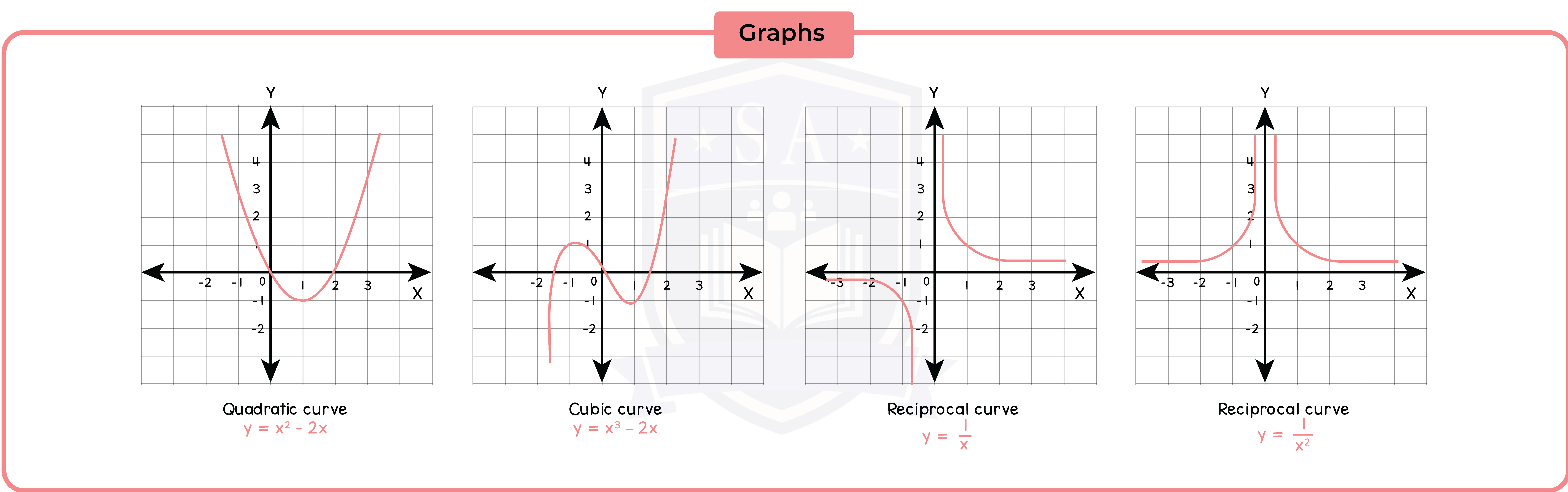
3.3.9 Recognise, generate points and plot graphs of linear and quadratic functions
3.3.10 Recognise, plot and draw graphs with equation: (Higher Tier Only)

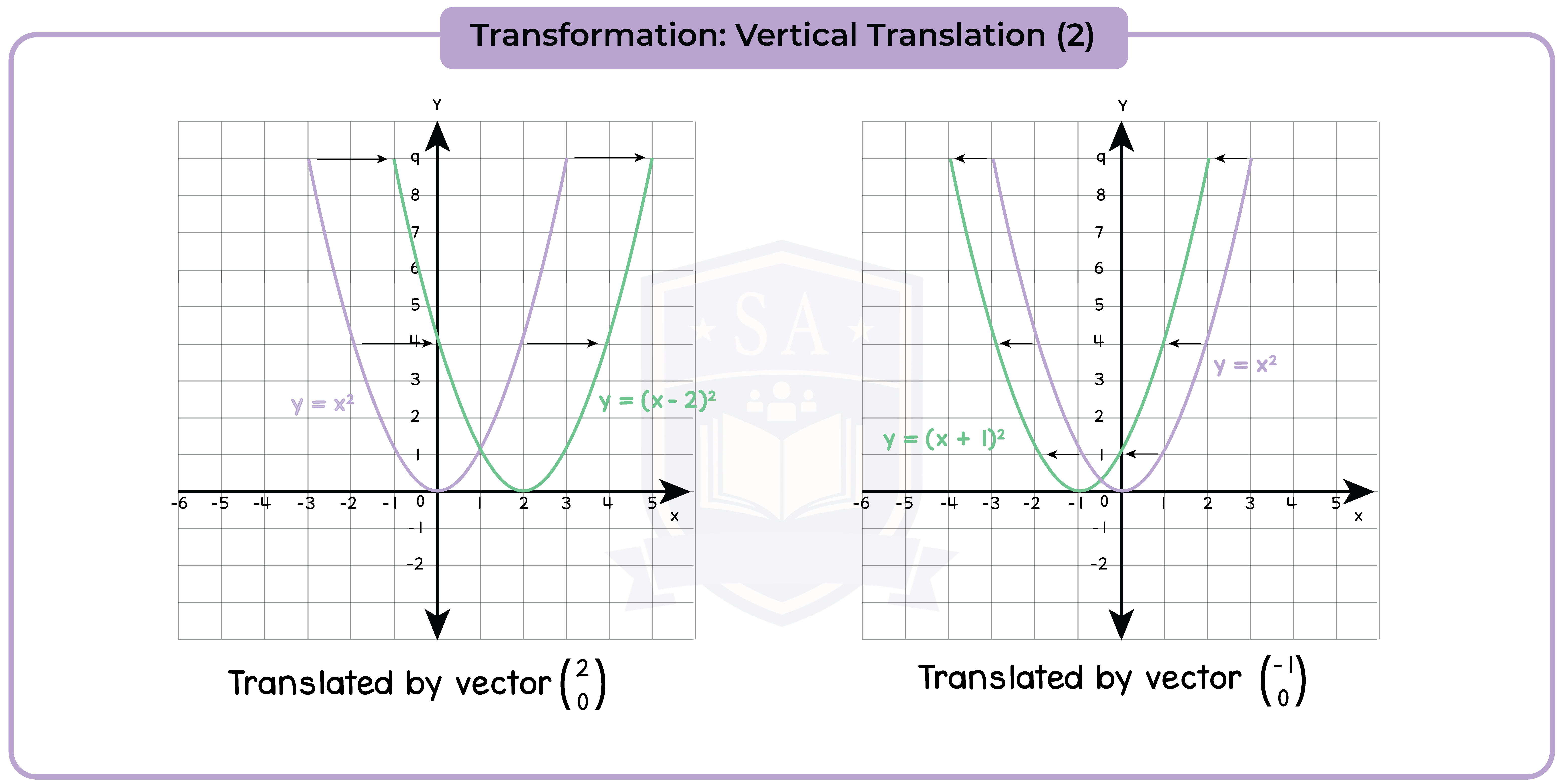
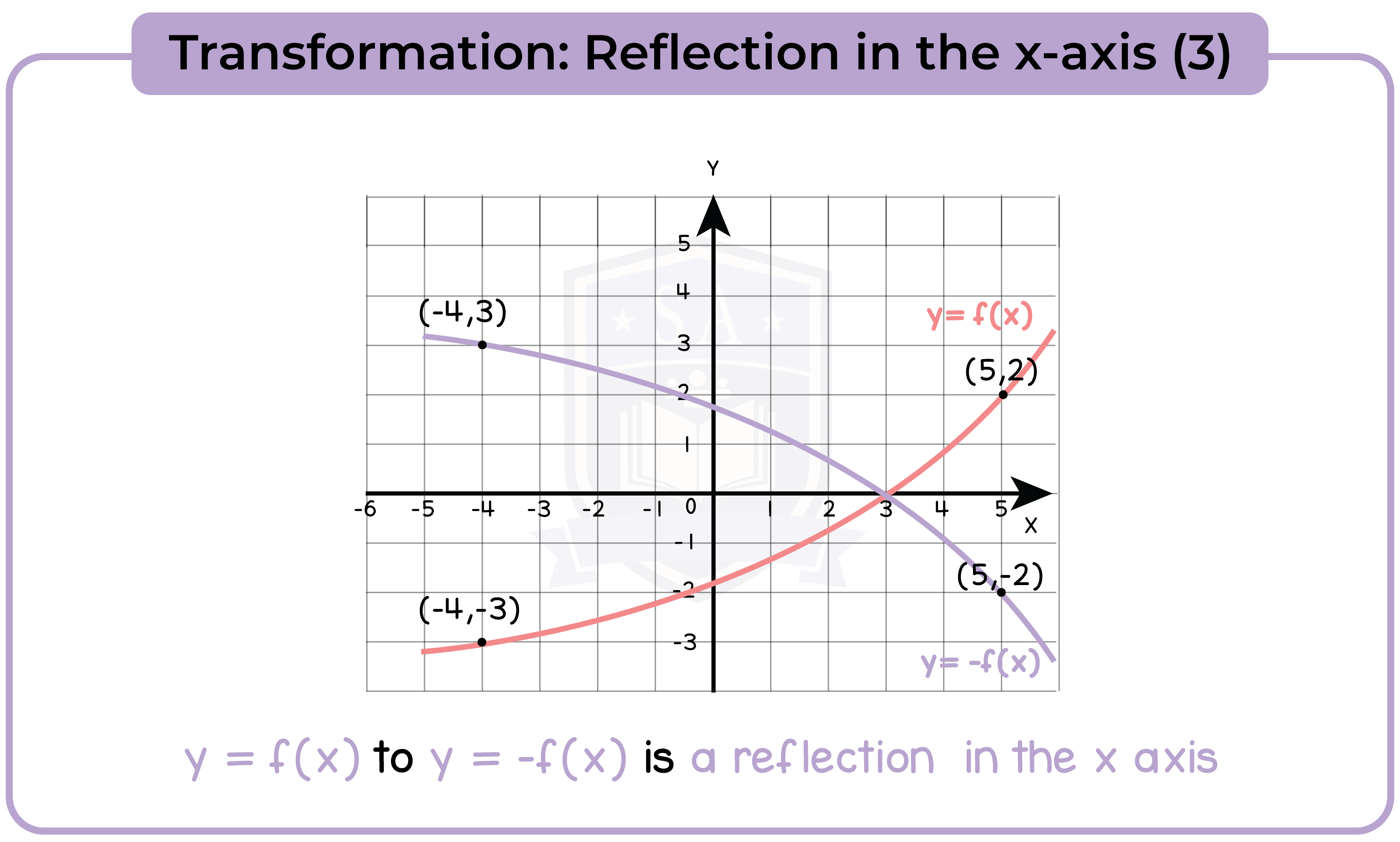
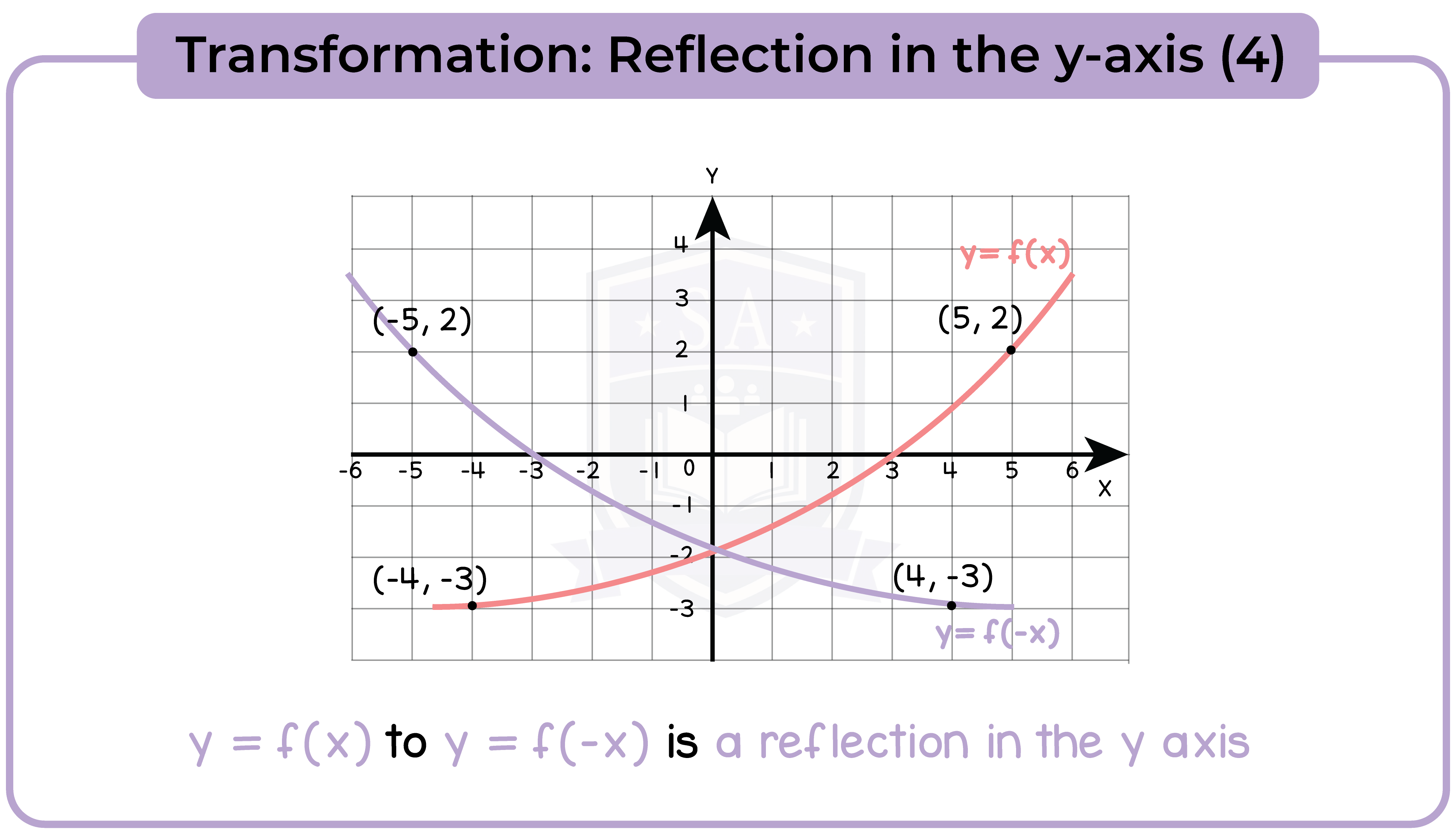
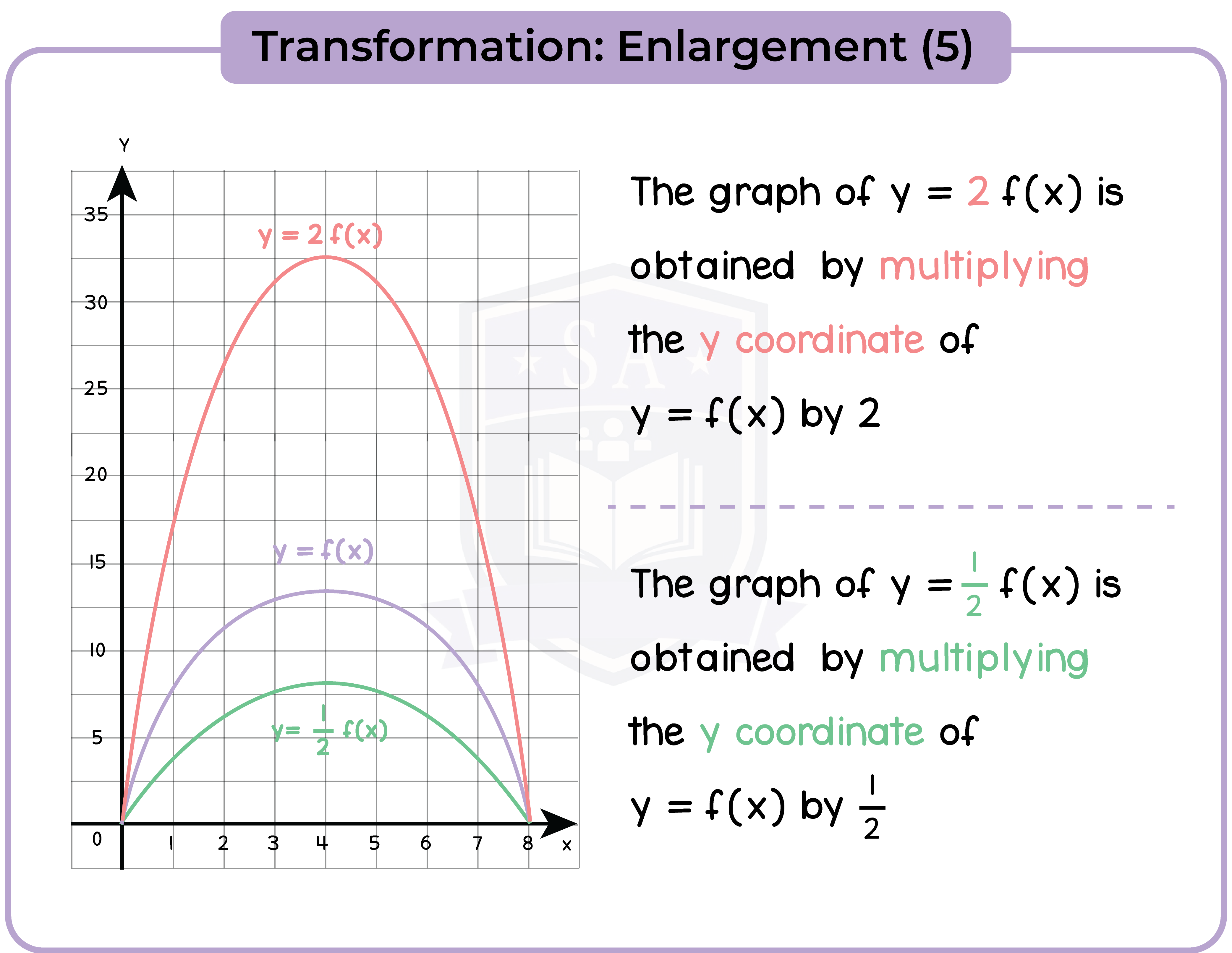
3.3.11 Apply to the graph of y = f(x) the transformations y = f(x) + a, y = f(ax), y = f(x + a), y = af(x) for linear, quadratic, sine and cosine functions (Higher Tier Only)

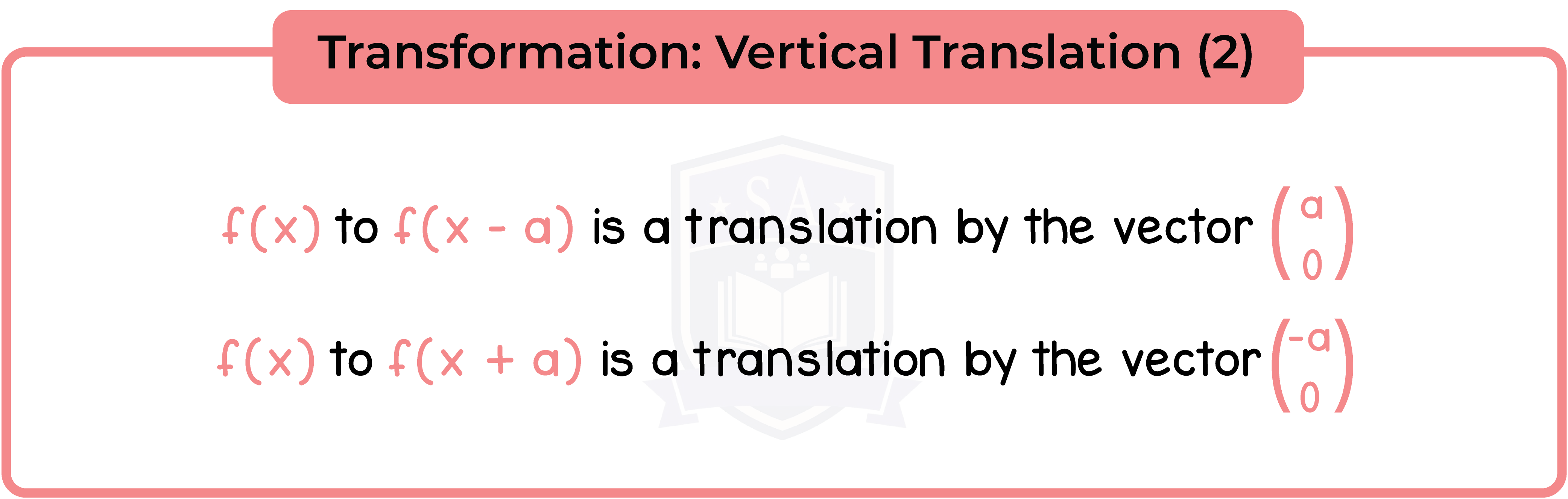

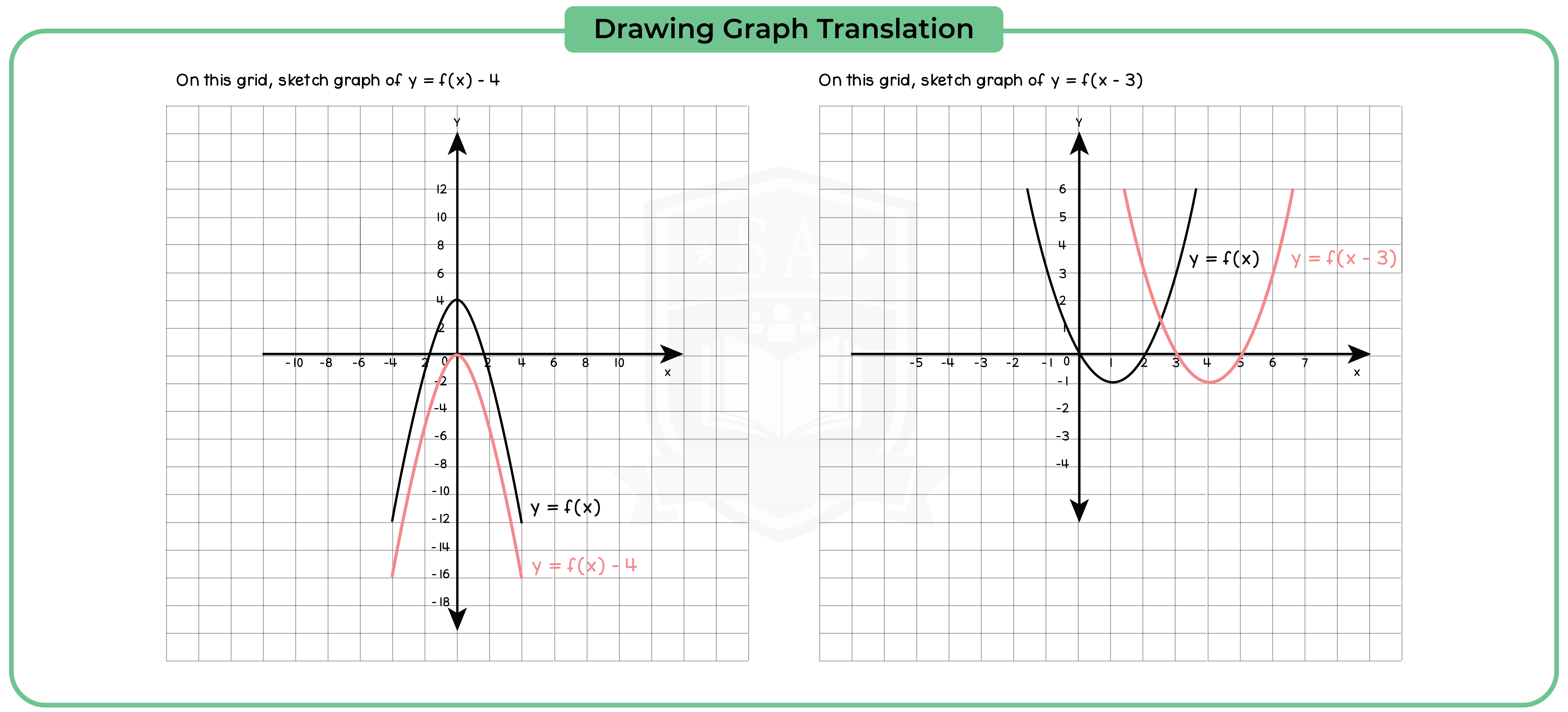
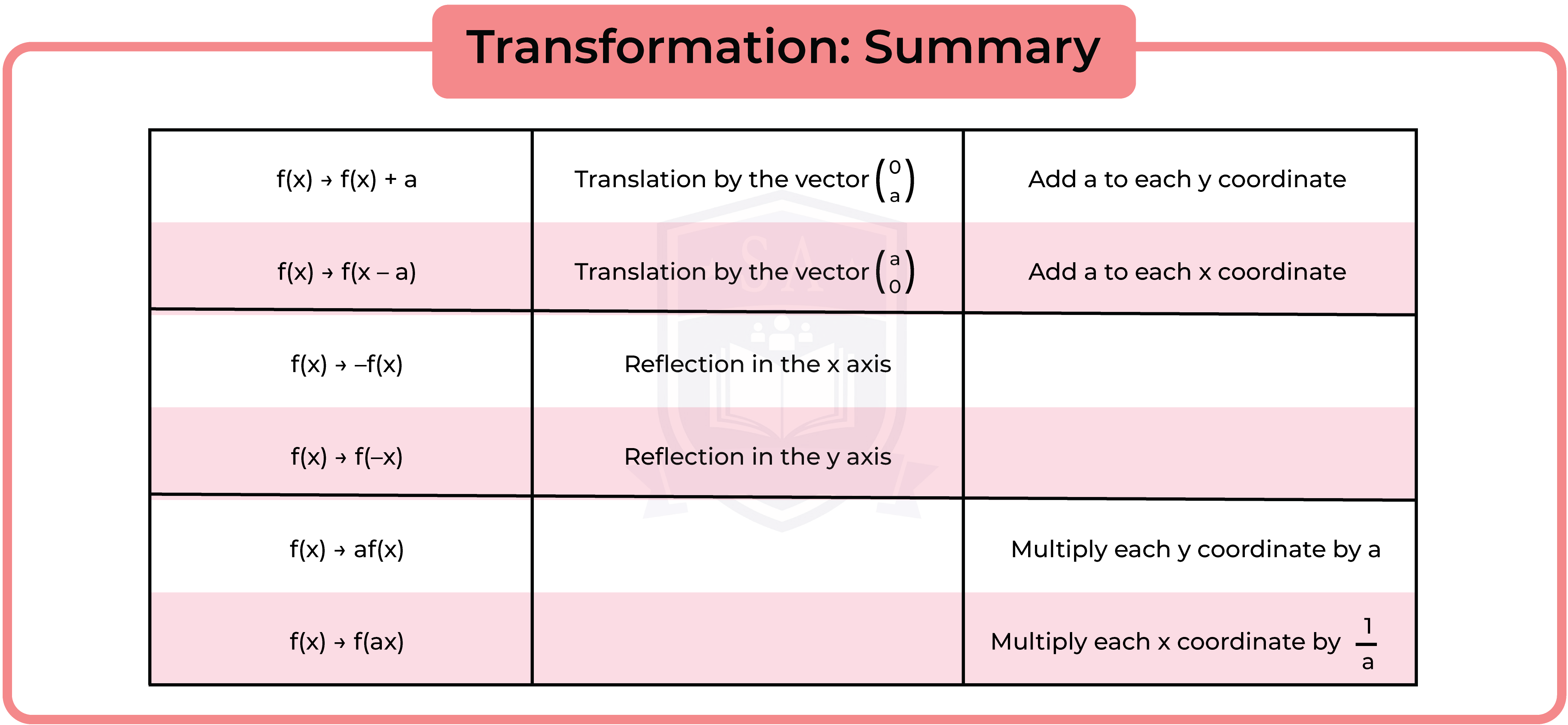
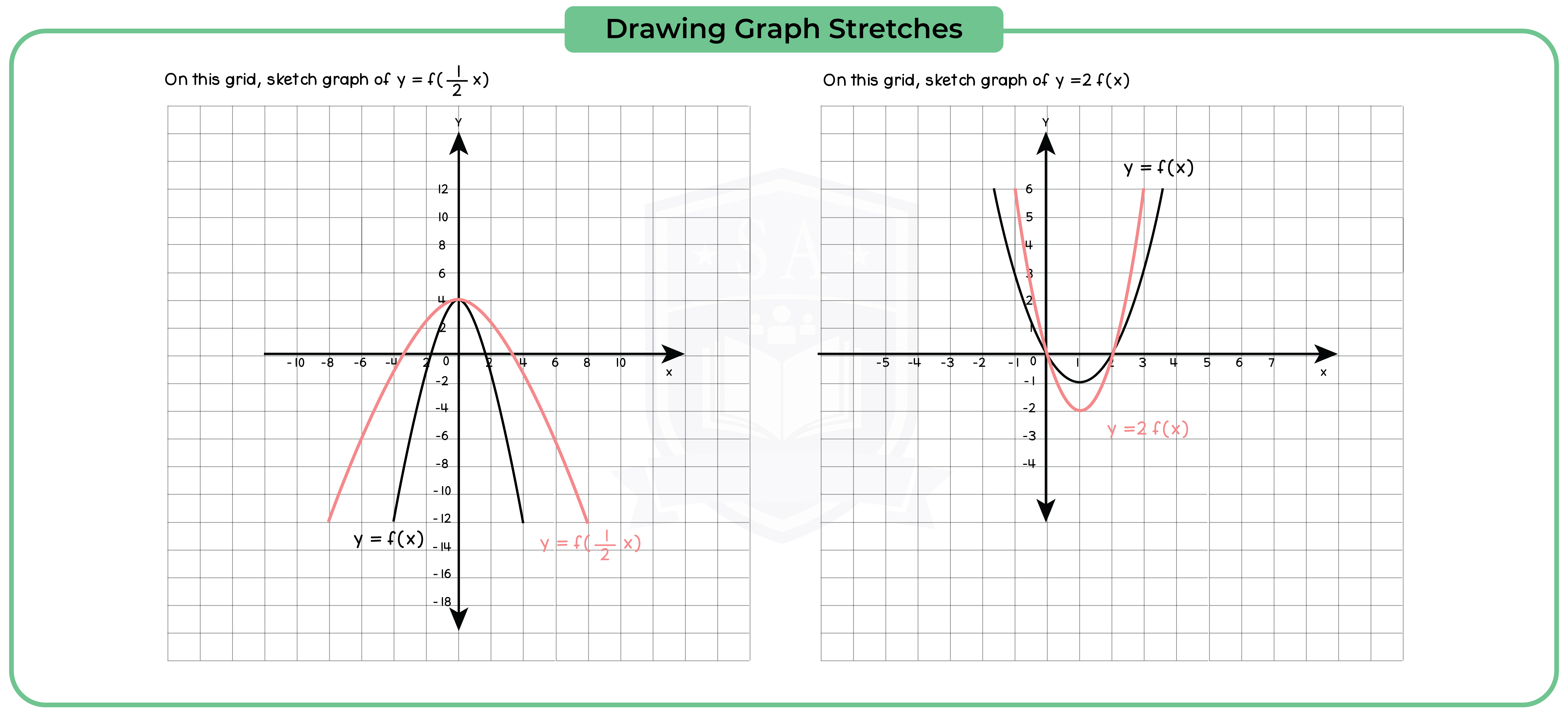
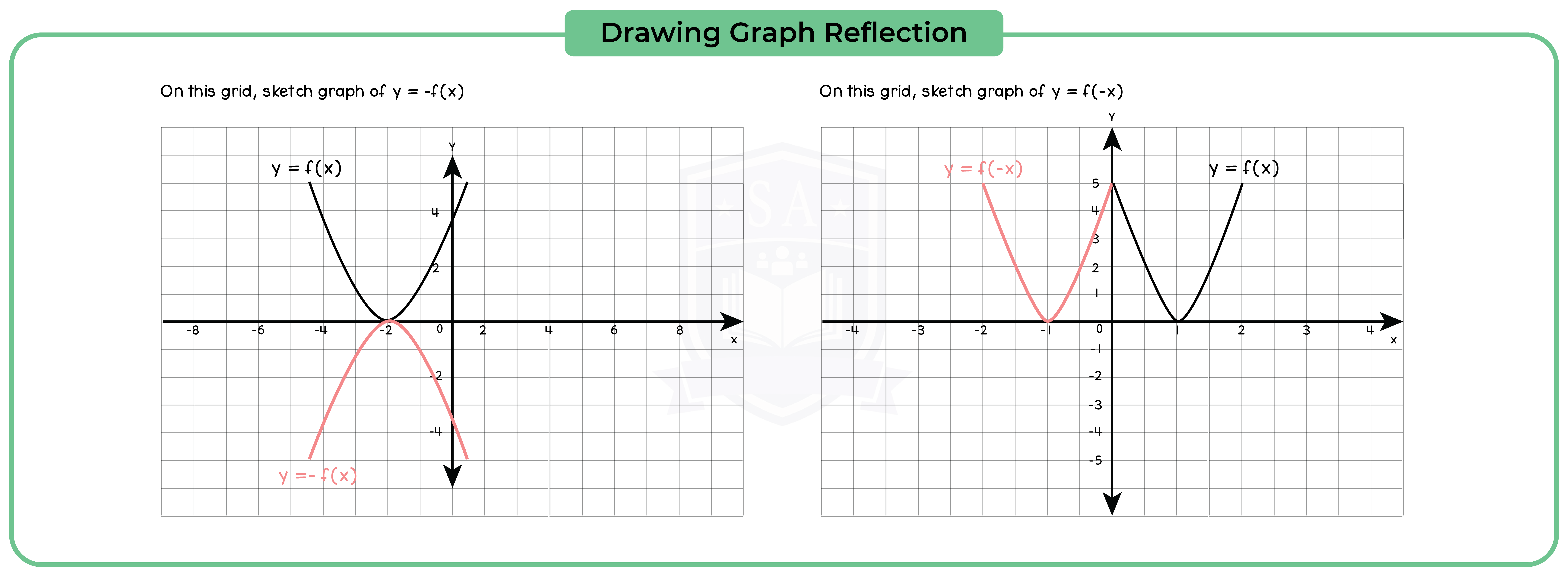
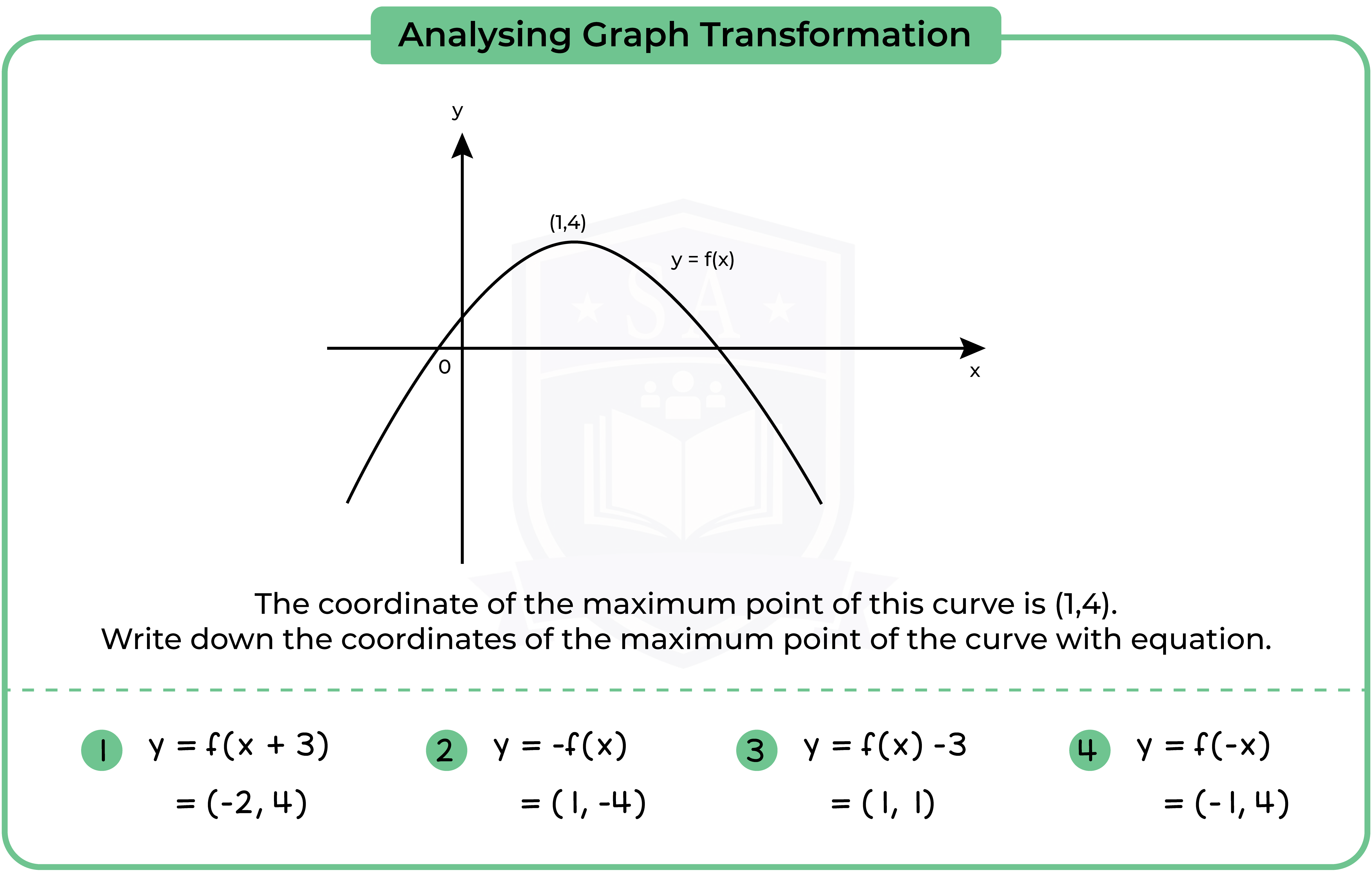
3.3.12 Interpret and analyse transformations of functions and write the functions algebraically (Higher Tier Only)

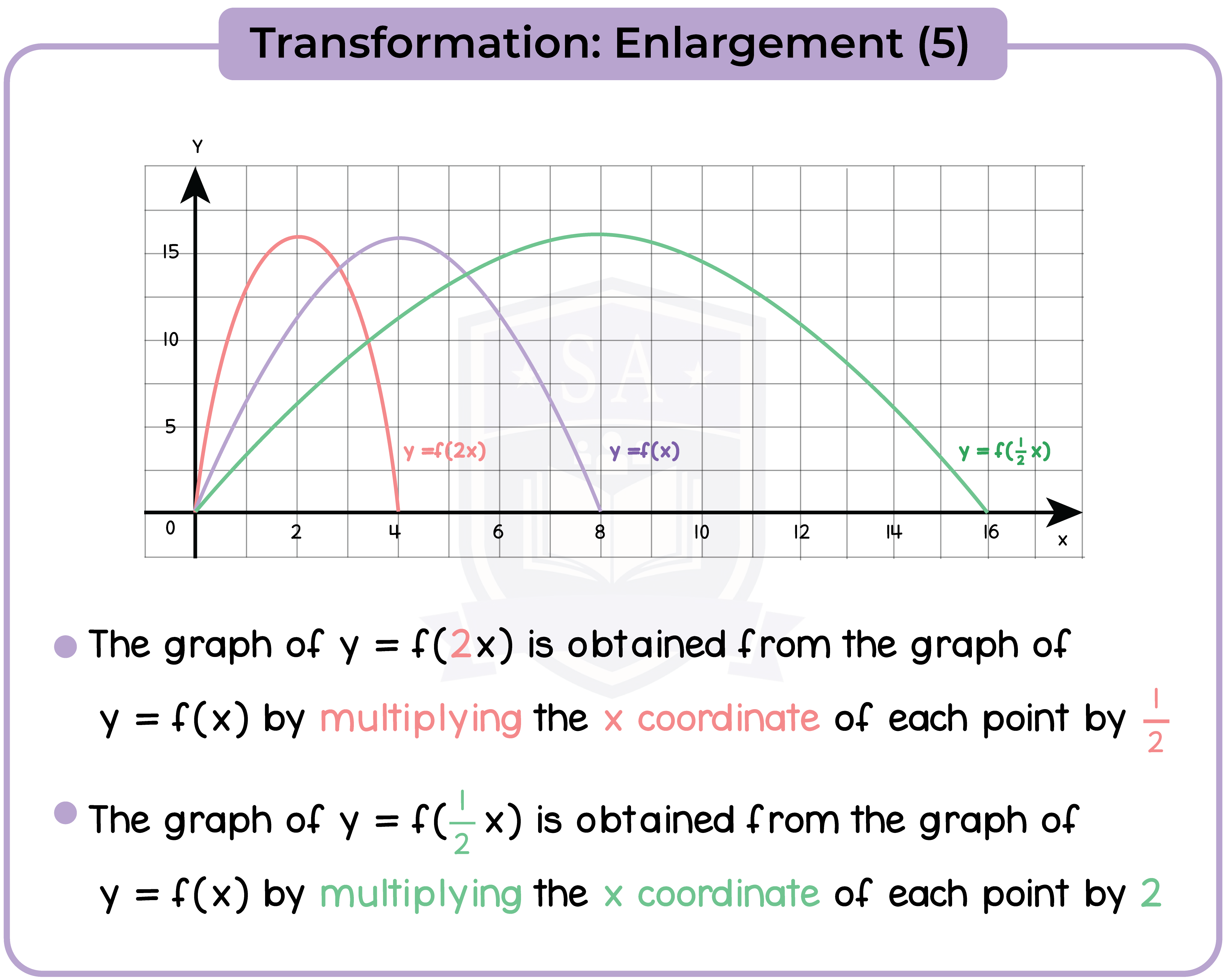

3.3.13 Find the gradients of non-linear graphs (Higher Tier Only)
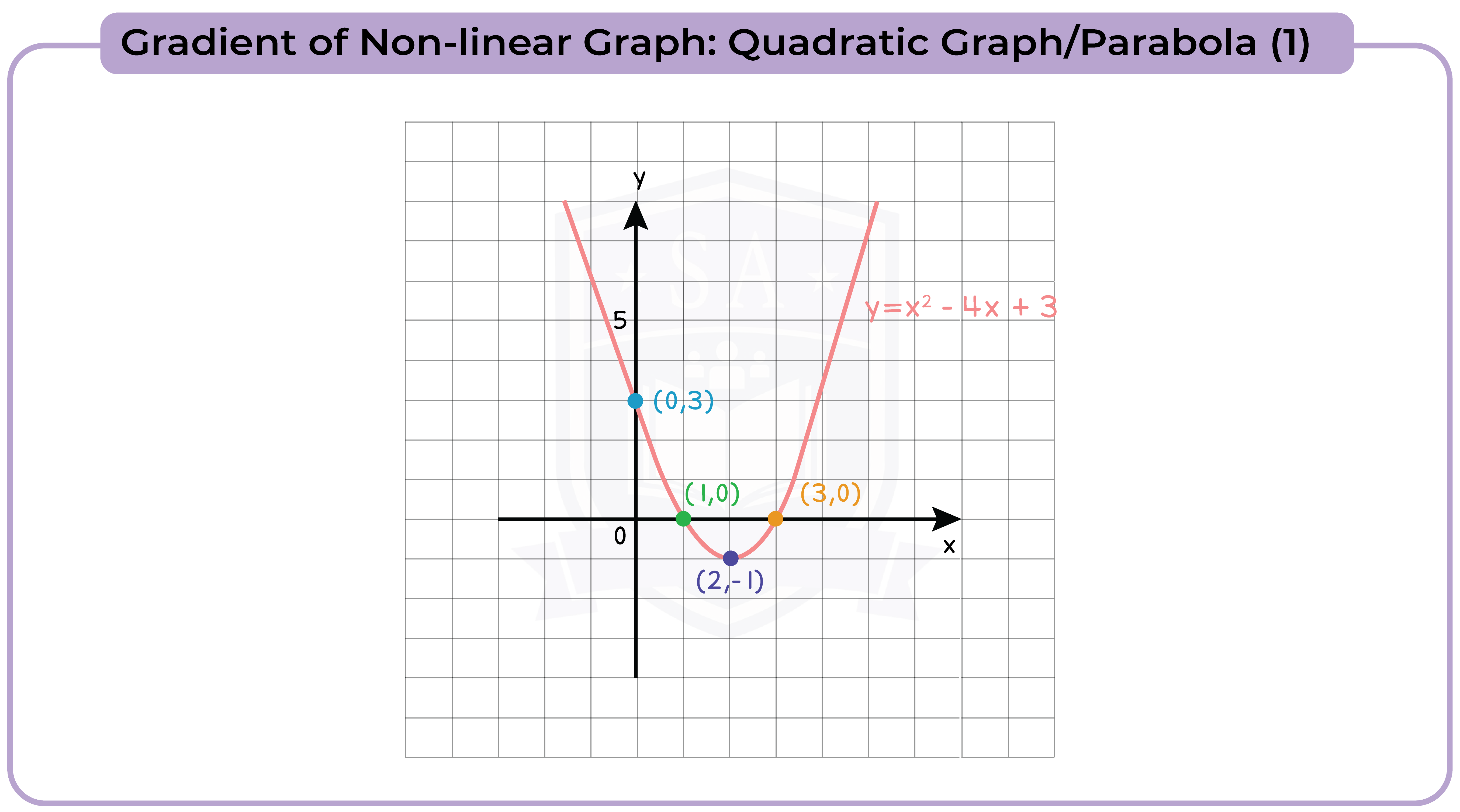
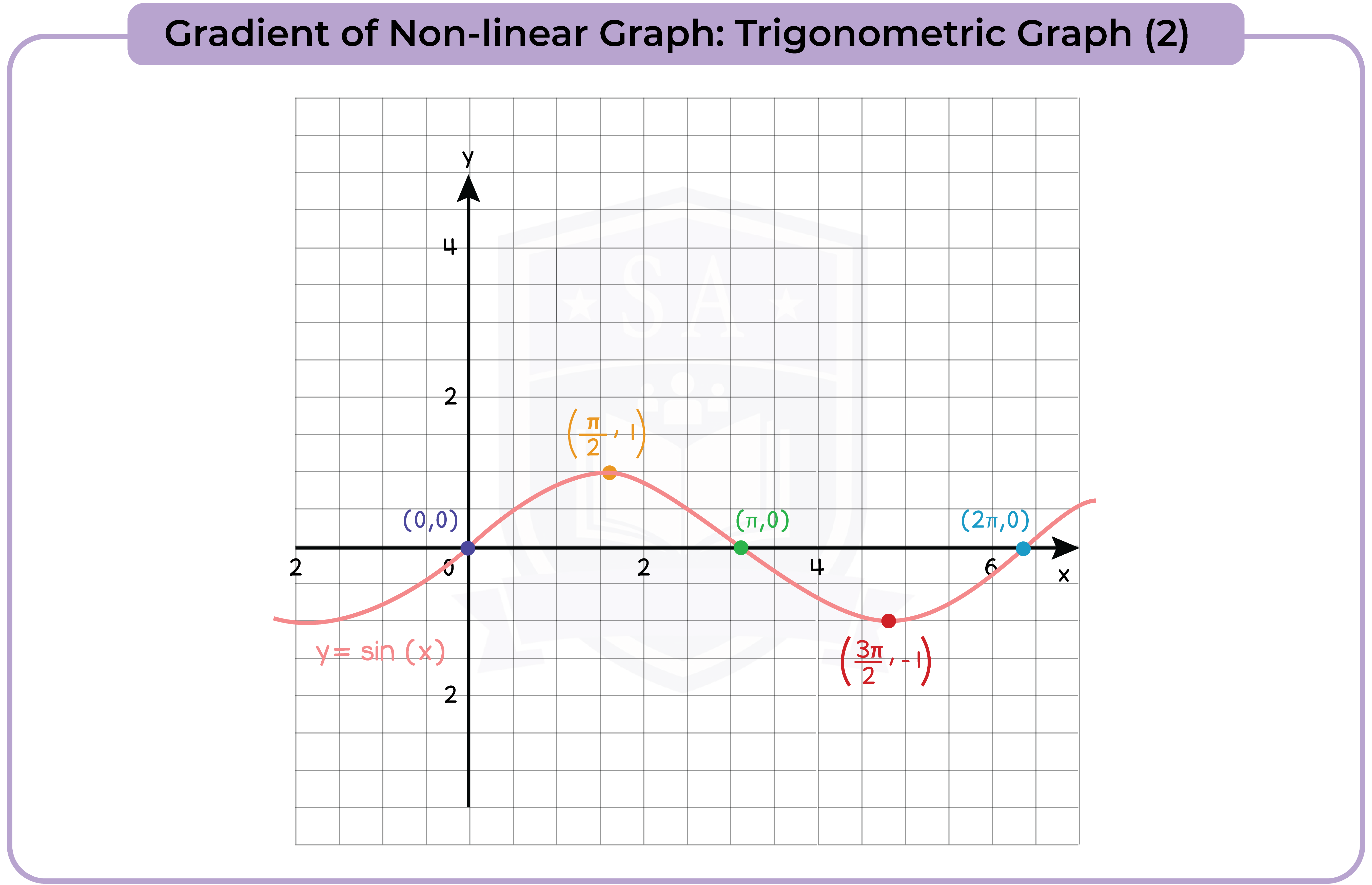
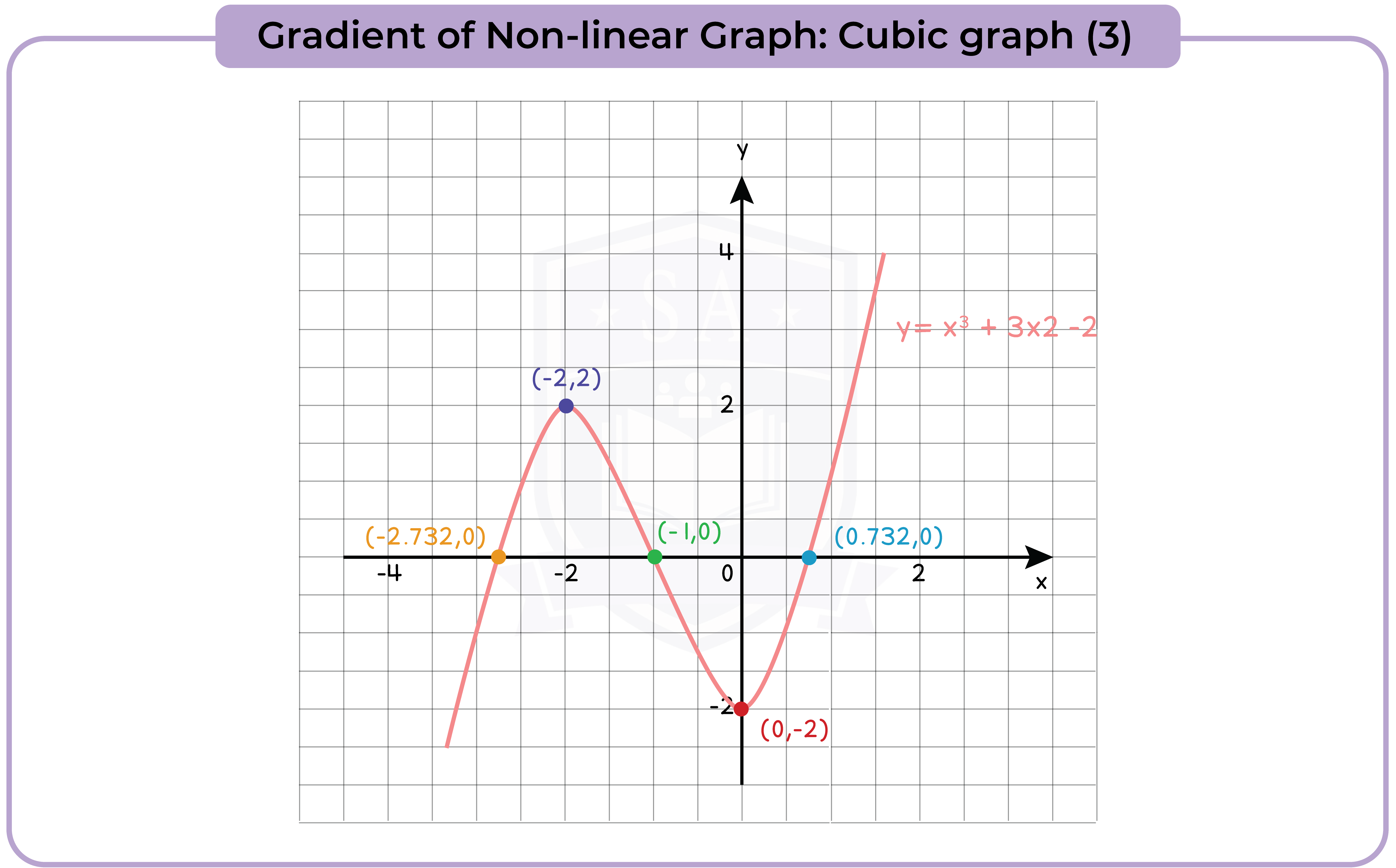

3.3.14 Find the intersection points of two graphs, on linear (y1) and one non-linear (y2), and recognise that the solutions correspond to the solutions of (y2 – y1) = 0 (Higher Tier Only)
3.3.15 Calculate the gradient of a straight line given the coordinates of two points (Higher Tier Only)
3.3.16 Find the equation of a straight line parallel to a given line; find the equation of a straight line perpendicular to a given line (Higher Tier Only)

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.