REVISION NOTES
1.2.1 Understand and use equivalent fractions, simplifying a fraction by cancelling common factors
Simplifying Fractions

1.2.2 Understand and use mixed numbers and vulgar fractions
Vulgar Fractions
Mixed Numbers
From Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
From Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
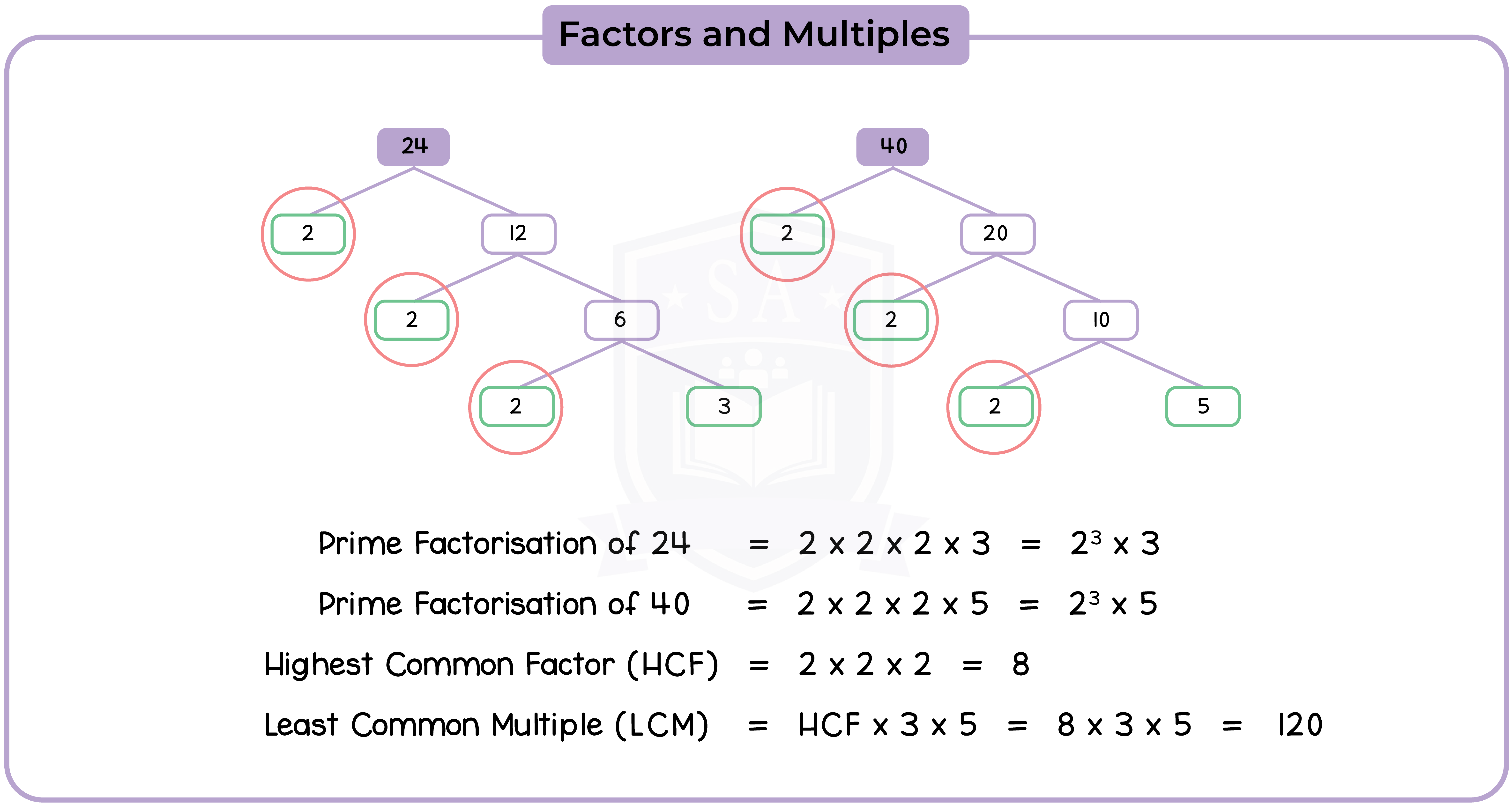
1.2.3 Identify common denominators
Common Denominators
The common denominator of ¾ and ⅔ is 4 x 3 = 12
1.2.4 Order fractions and calculate a given fraction of a given quantity
Equivalent fractions are used to compare the sizes of fractions written with a different denominator
20% = 20/100 = 1/5 = 0.2
1.2.5 Express a given number as a fraction of another number
3.45 = 345/100 = 69/20
1.2.6 Use common denominators to add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers
Type 1: Adding or Subtracting Fractions
Equivalent fractions are also used when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominator.
The fractions must be rewritten to have the same denominator before starting the addition or subtraction.
2/5 + 1/10 = 4/10 + 1/10 = 5/10 = 1/2
Type 2: Adding and Subtracting Mixed Fractions
When adding and subtracting mixed fraction, process the whole number parts separately from the fractions parts, then combine everything at the end.
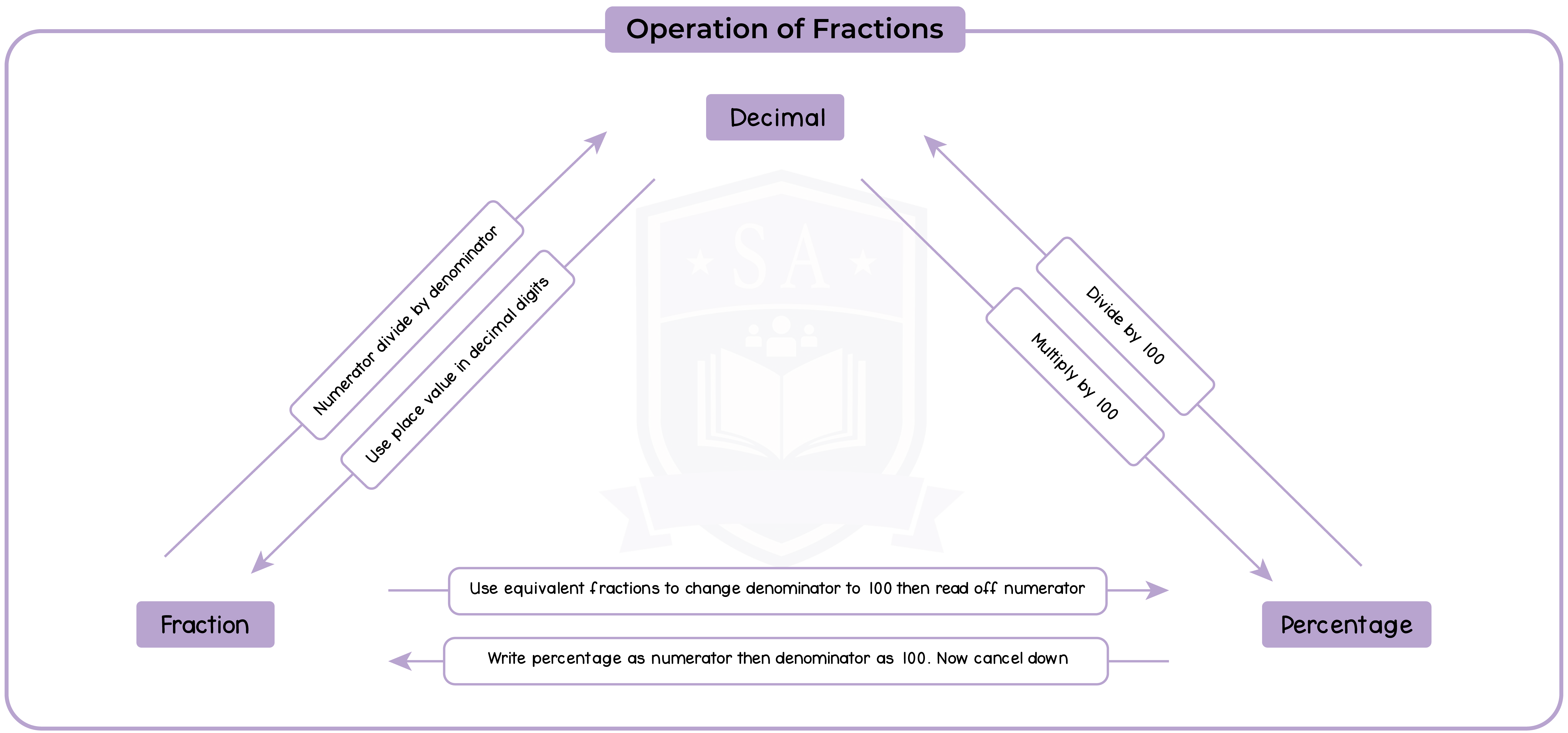
1.2.7 Convert a fraction to a decimal or a percentage
1.2.8 Understand and use unit fractions as multiplicative inverses
1.2.9 Multiply and divide fractions and mixed numbers
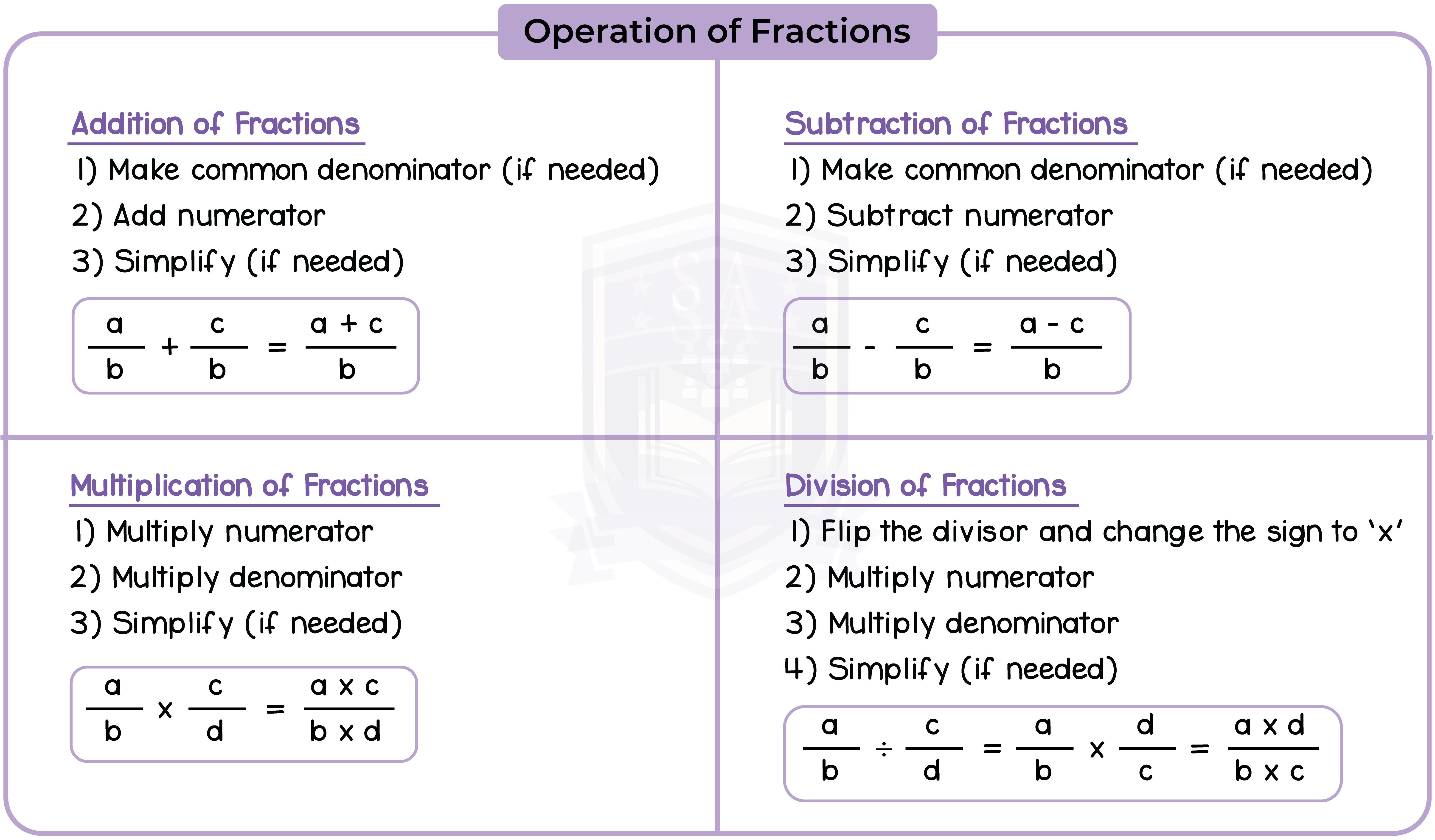
Type 1: Multiplying Fractions
Step 1: Multiply the numerator (top number)
Step 2: Multiply the denominator (bottom number)
Step 3: Simplify (optional)
Type 2: Multiplying Mixed Fractions
Step 1: Convert mixed fractions into improper fractions
Step 2: Multiply the numerator (top number)
Step 3: Multiply the denominator (bottom number)
Step 4: Simplify (optional
Type 3: Dividing Fractions
Step 1: Turn the second fraction upside down
Step 2: Multiply the numerator (top number)
Step 3: Multiply the denominator (bottom number)
Step 4: Simplify (optional)3
Type 4: Dividing Mixed Fractions
Step 1: Turn the second fraction upside down
Step 2: Convert mixed fractions into improper fractions
Step 3: Multiply the numerator (top number)
Step 4: Multiply the denominator (bottom number)
Step 4: Simplify (optional

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.