REVISION NOTES
1.8.1C Know how to represent a metallic lattice by a 2-D diagram
RECALL
Metal ions are held together strongly by metallic bonding
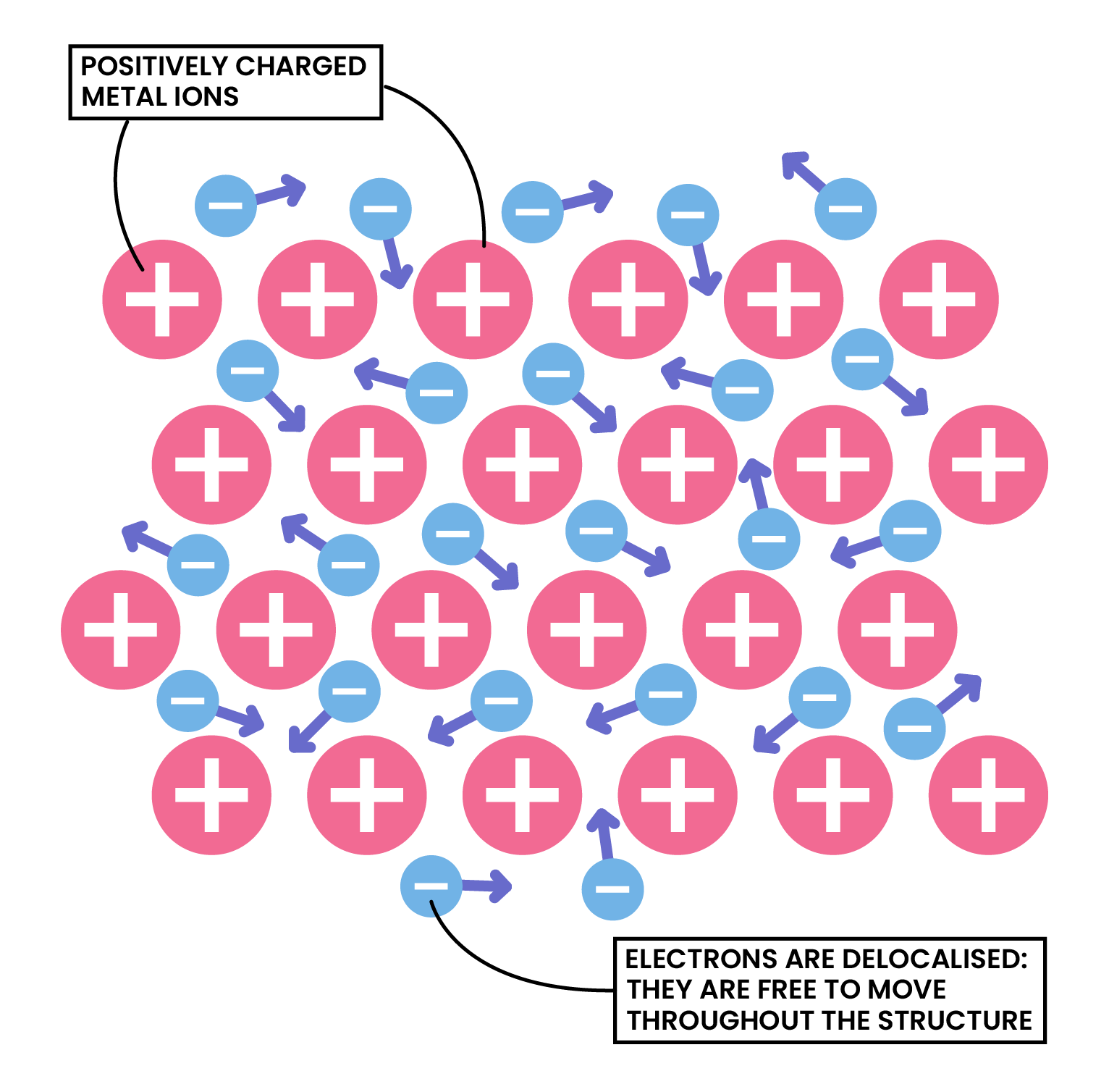
1.8.2C Understand metallic bonding in terms of electrostatic attractions
Metallic Bonding
Electrostatic attraction forces between positive metal ions lattice and negative delocalised electrons
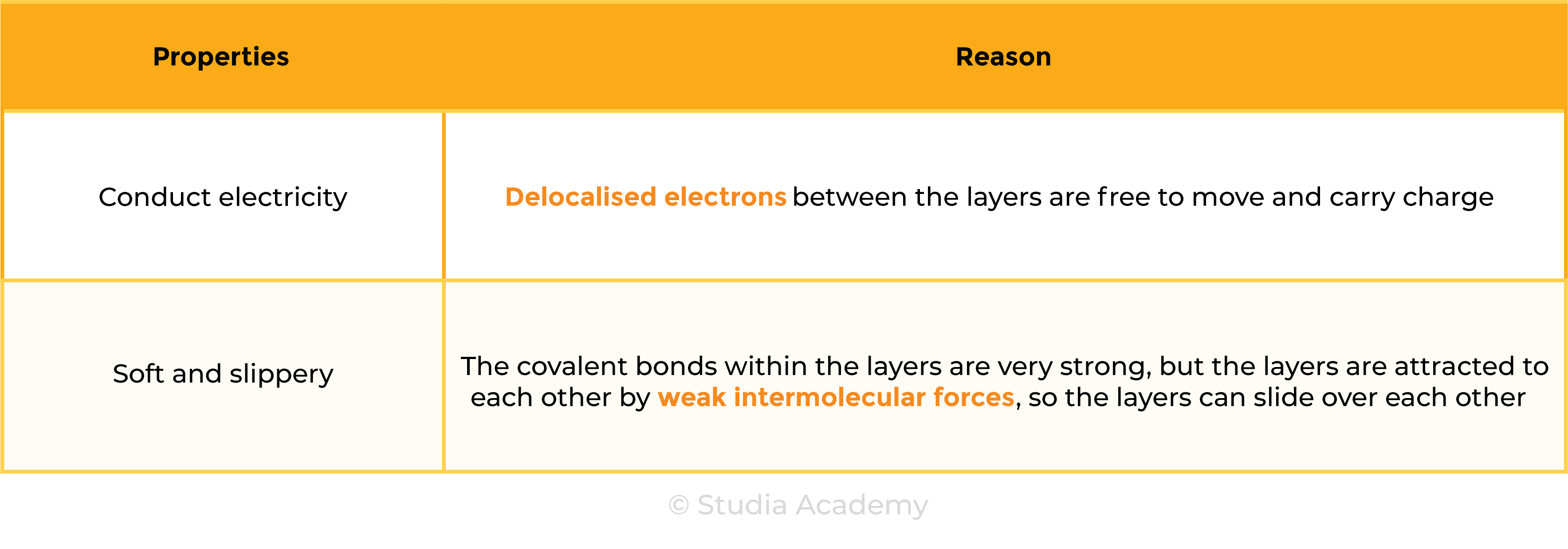
1.8.3C Explain typical physical properties of metals, including electrical conductivity and malleability

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.