REVISION NOTES
1.7.1 Know that a covalent bond is formed between atoms by the sharing of a pair of electrons
RECALL
COVALENT COMPOUNDS
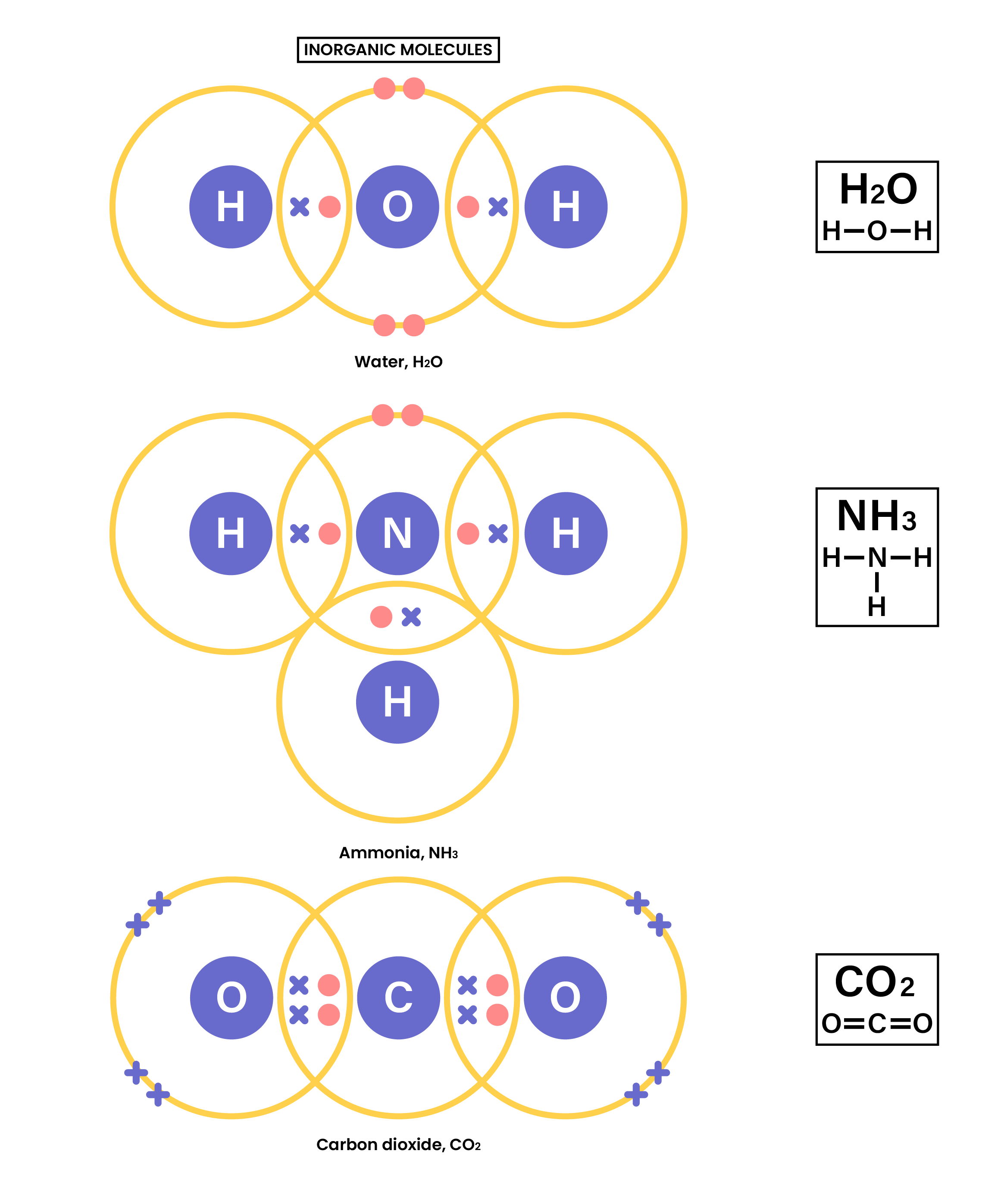
For example, in water molecules:
In a molecule:
1.7.2 Understand covalent bonds in terms of electrostatic attractions
COVALENT BONDING
Electrostatic attraction between the positive nuclei of the atoms and the shared pairs of negative electrons
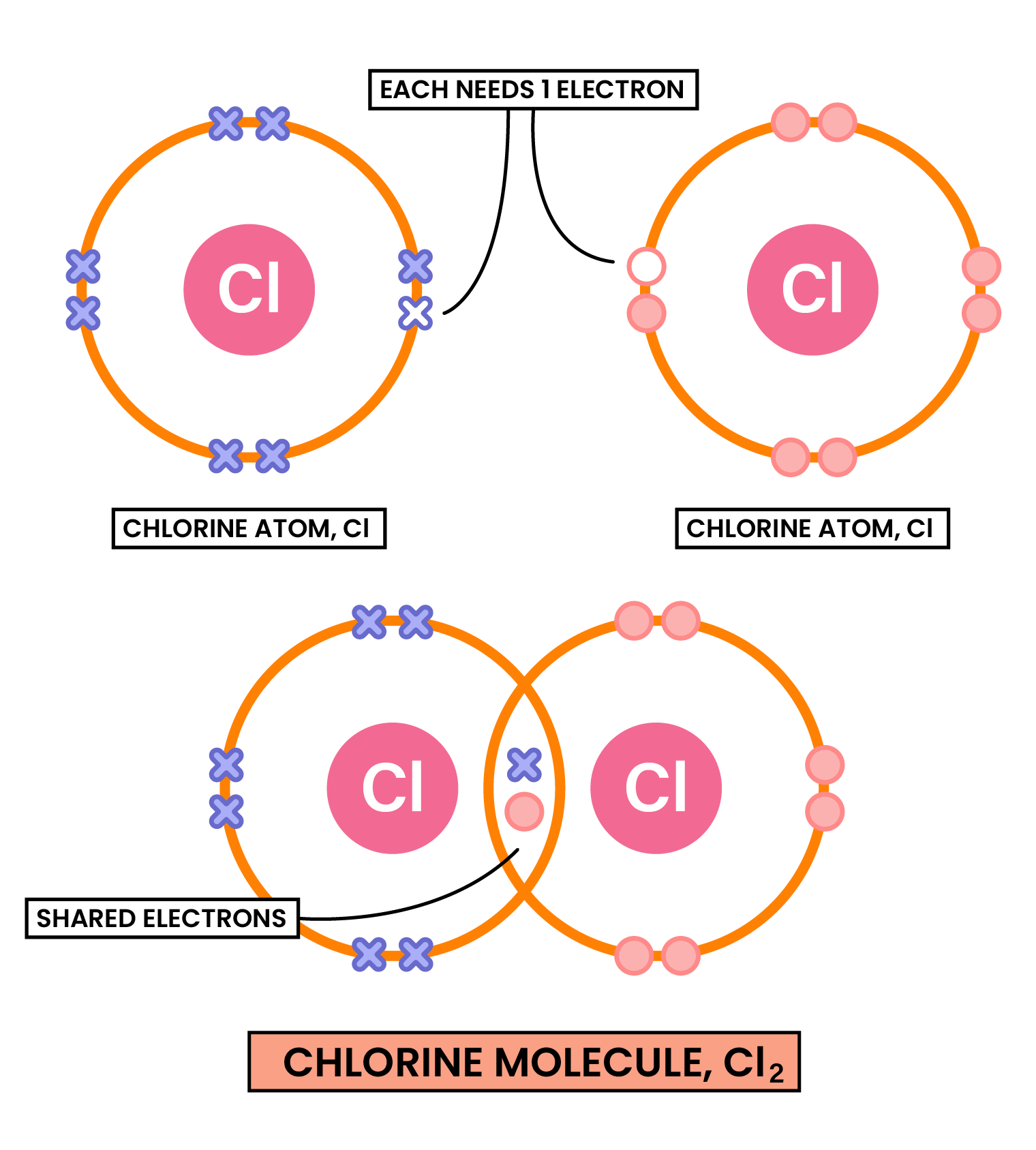
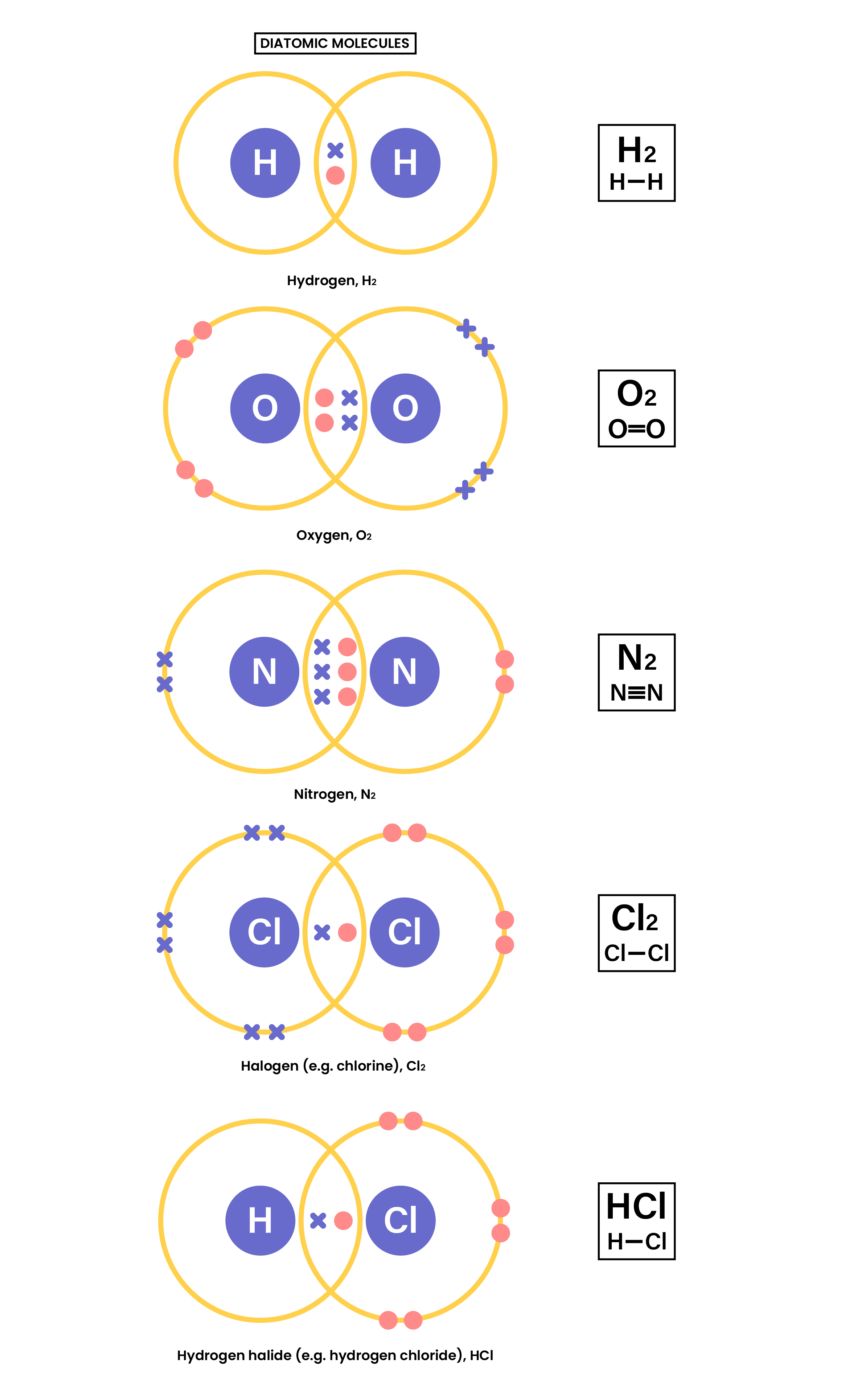
1.7.3 Understand how to use dot-and-cross diagrams to represent covalent bonds in:
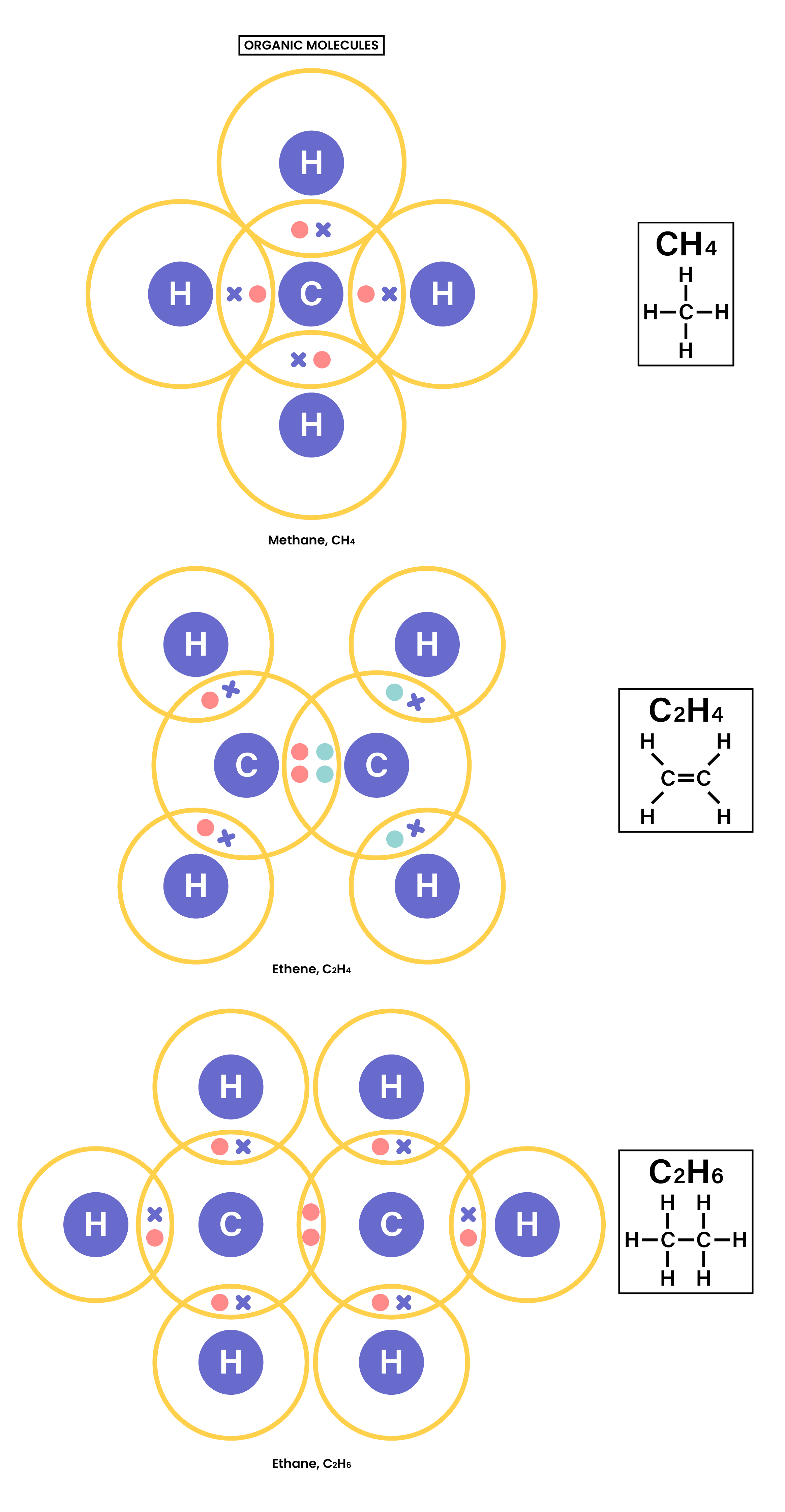
1.7.4 Explain why substances with a simple molecular structures are gases or liquids, or solids with low melting and boiling points
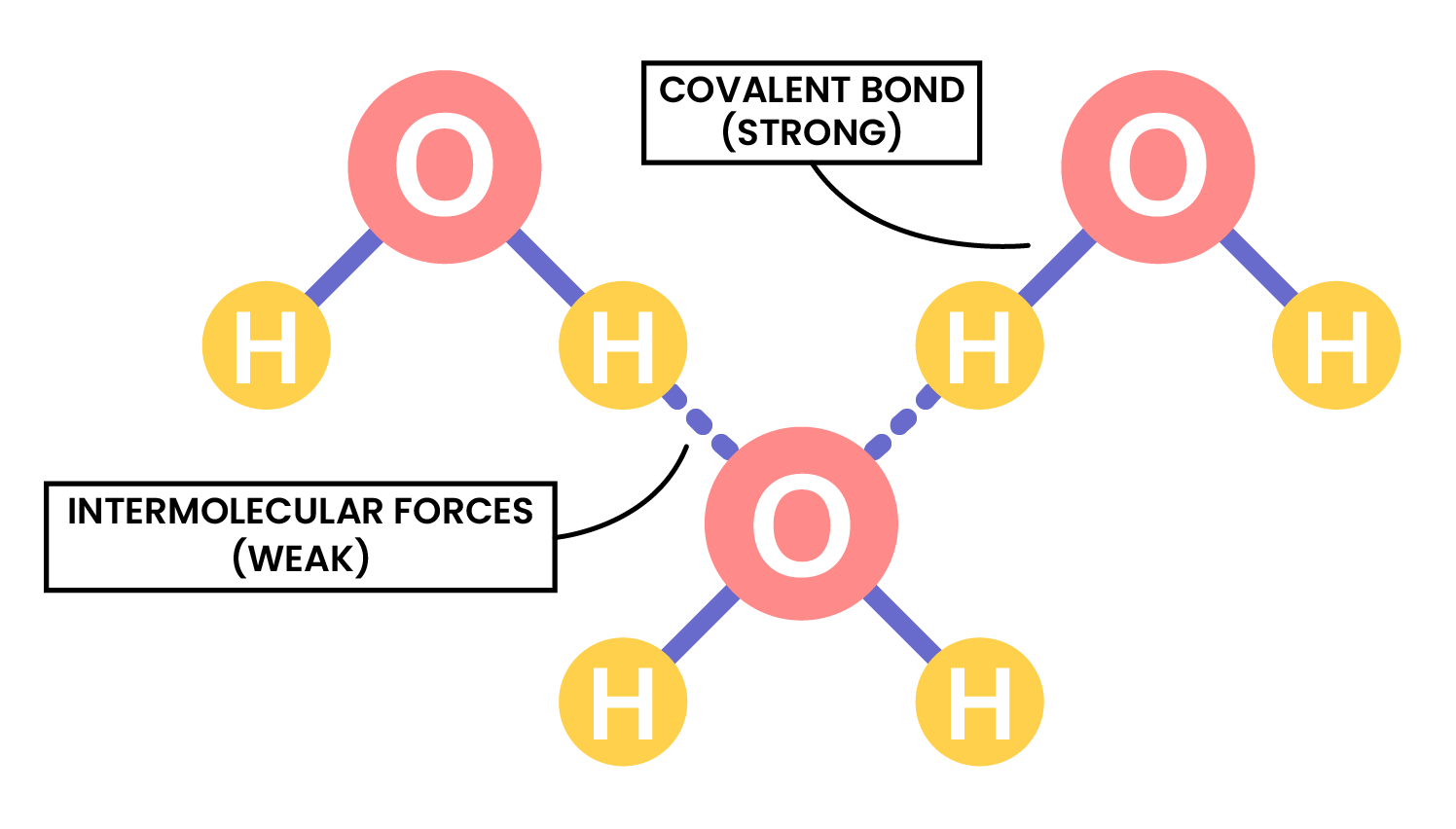
the term intermolecular forces of attraction can be used to represent all forces between molecules
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
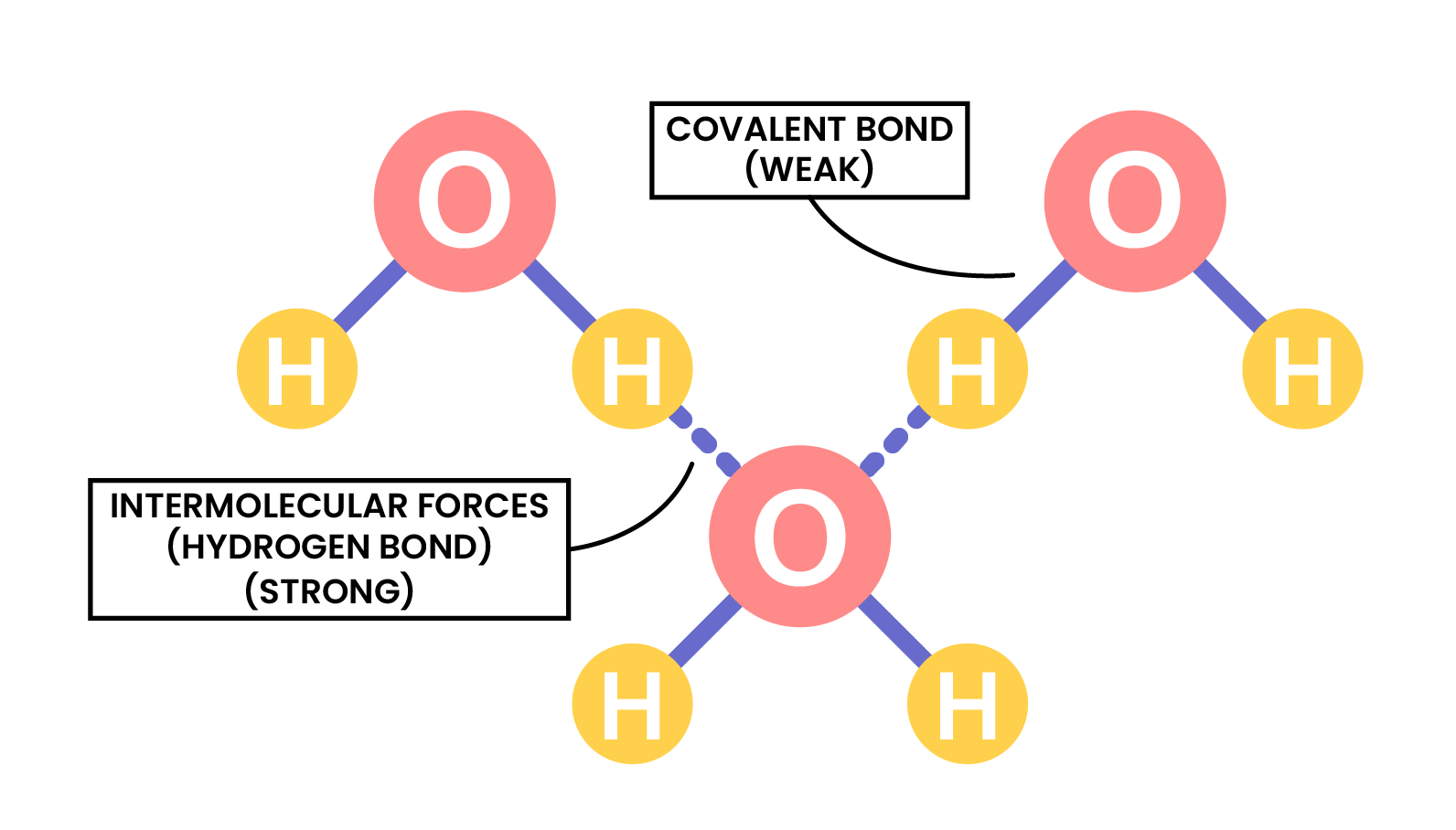
STATE OF MATTER
1.7.5 Explain why the melting and boiling points of substances with simple molecular structures increase, in general, with increasing relative molecular mass
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES INCREASE WITH THE SIZE OF THE MOLECULES
1.7.6 Explain why substances with giant covalent structures are solids with high melting and boiling points
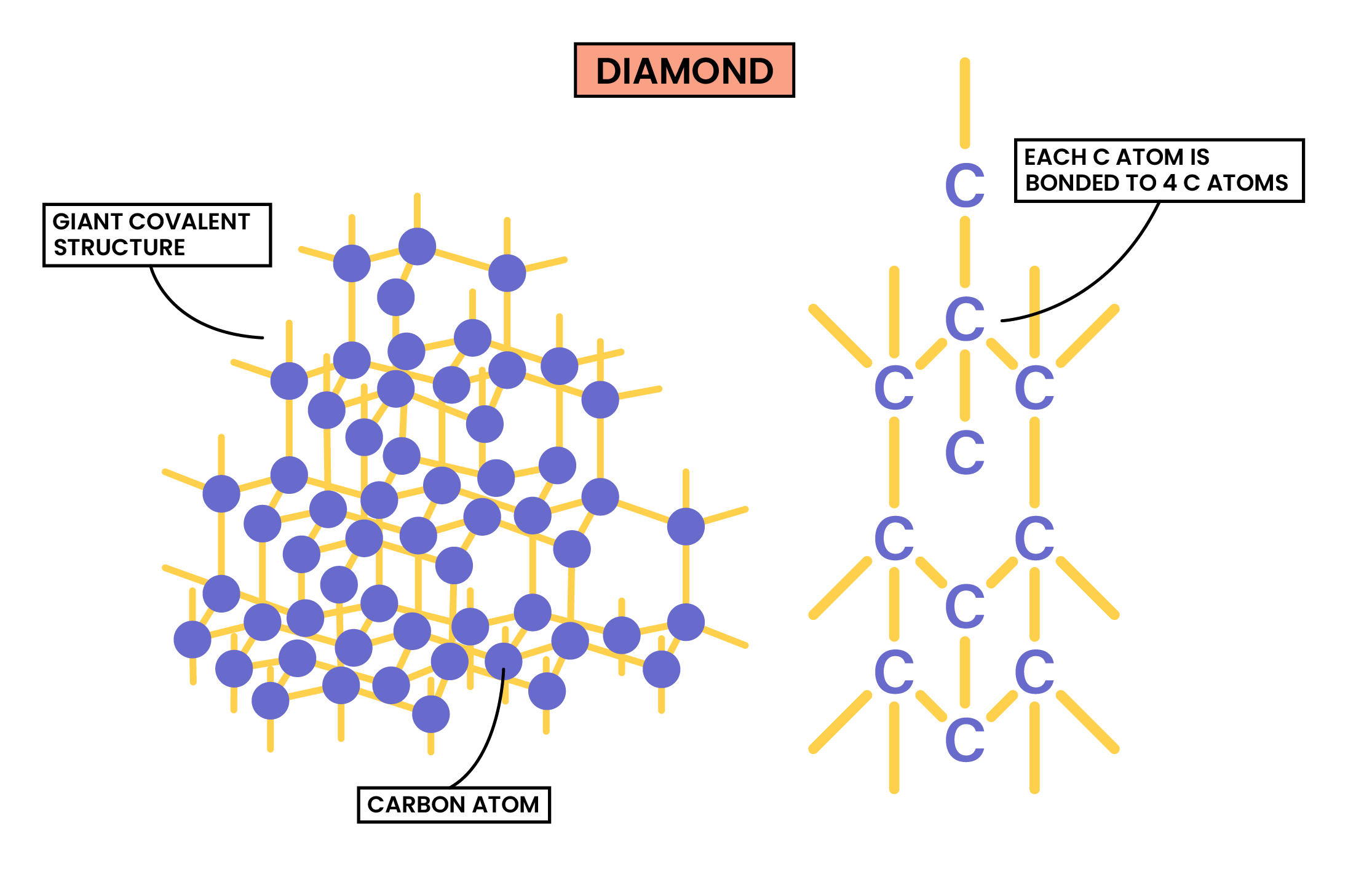
GIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES
1.7.7 Explain how the structures of diamond, graphite and C60 fullerene influence their physical properties, including electrical conductivity and hardness
DIAMOND
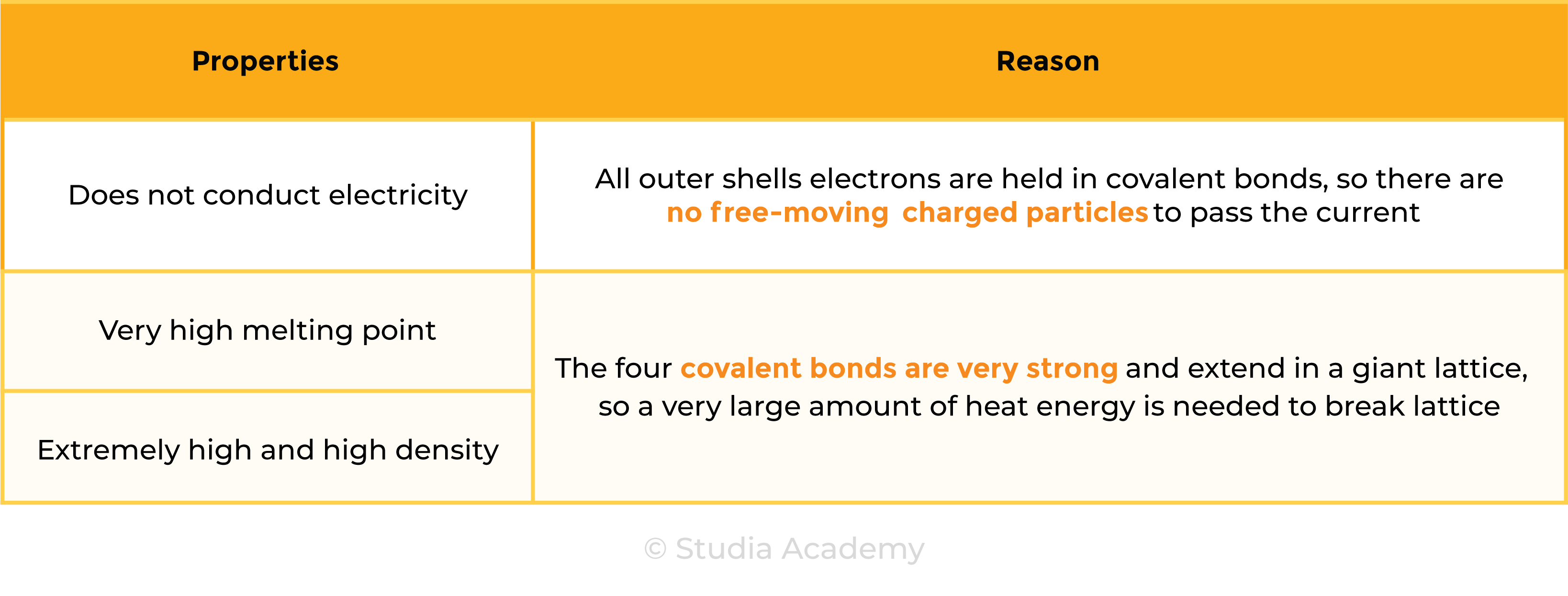
Properties of Diamond
USES OF DIAMOND
GRAPHITE
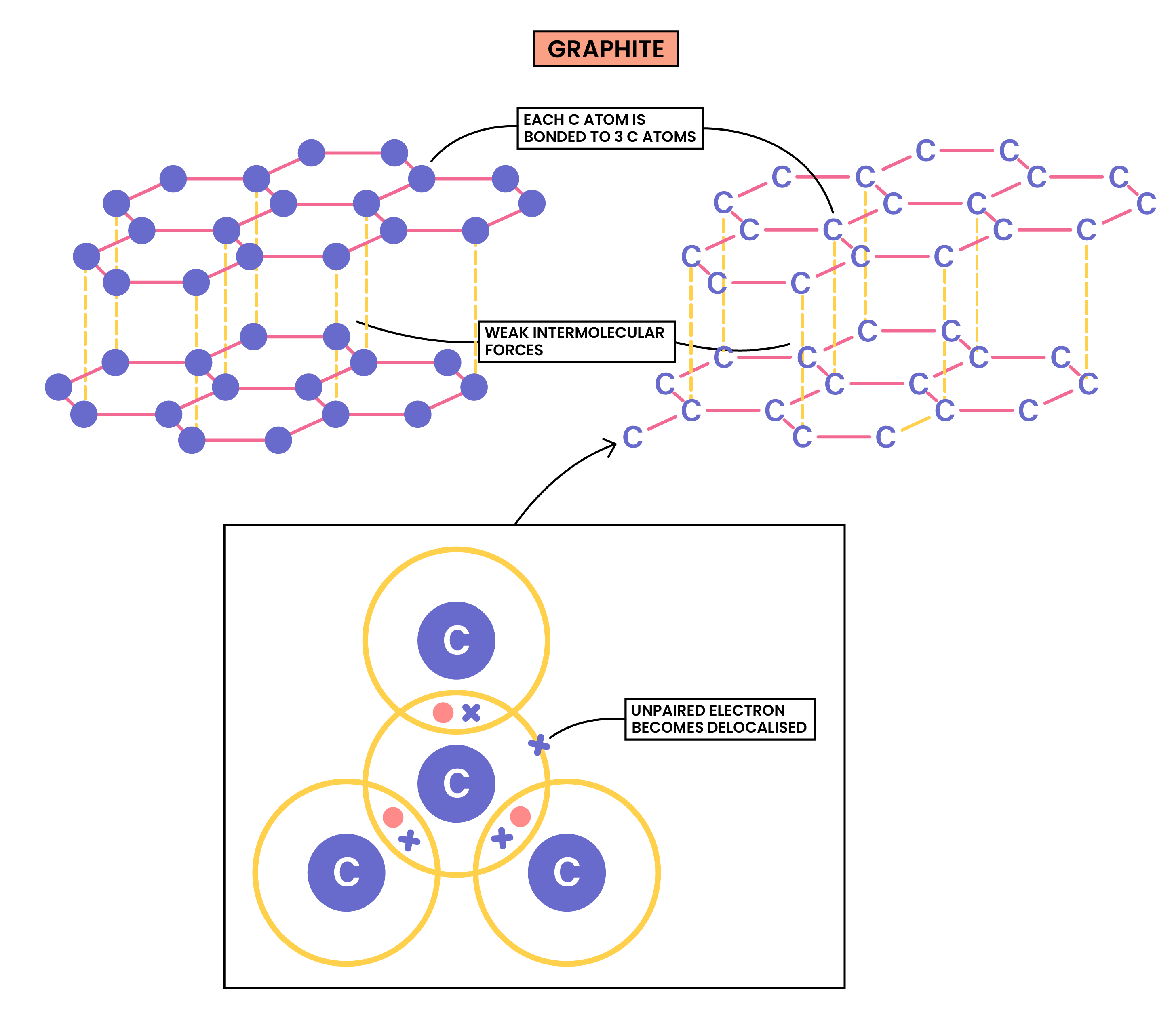
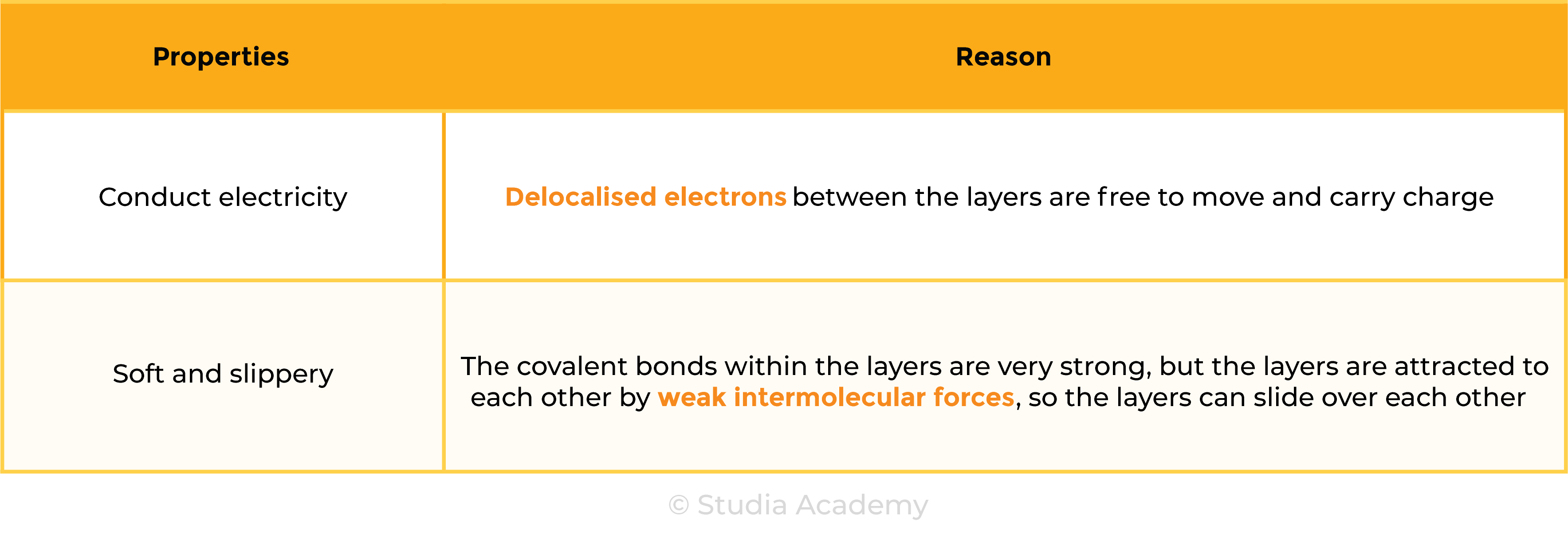
Properties of Graphite
USES OF GRAPHITE
C60 Fullerene
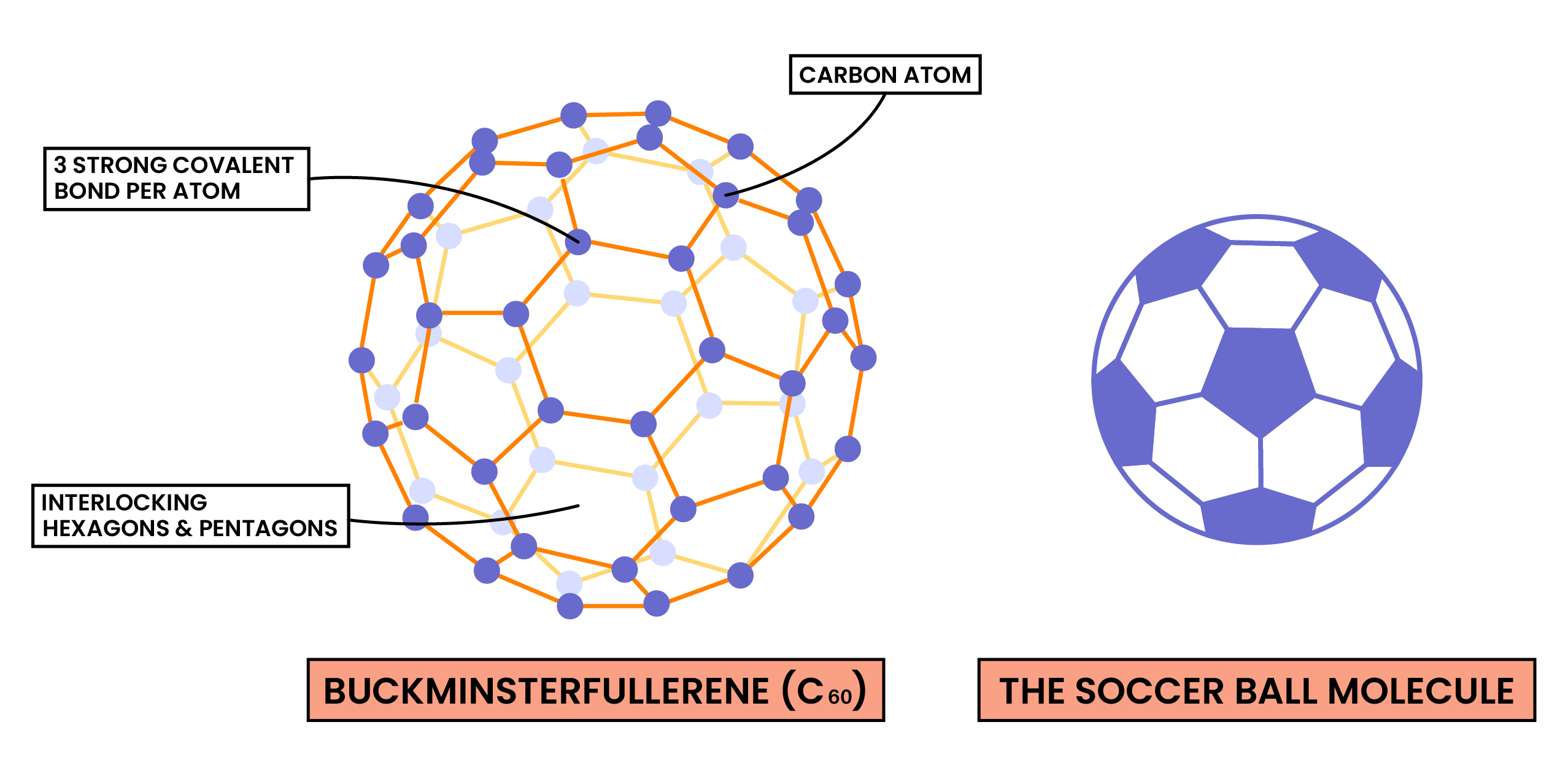
Uses of C60 fullerene
1.7.8 Know that covalent compounds do not usually conduct electricity
Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity because
Exception: graphite

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.