REVISION NOTES
1.6.1 Understand how ions are formed by electron loss or gain
IONS
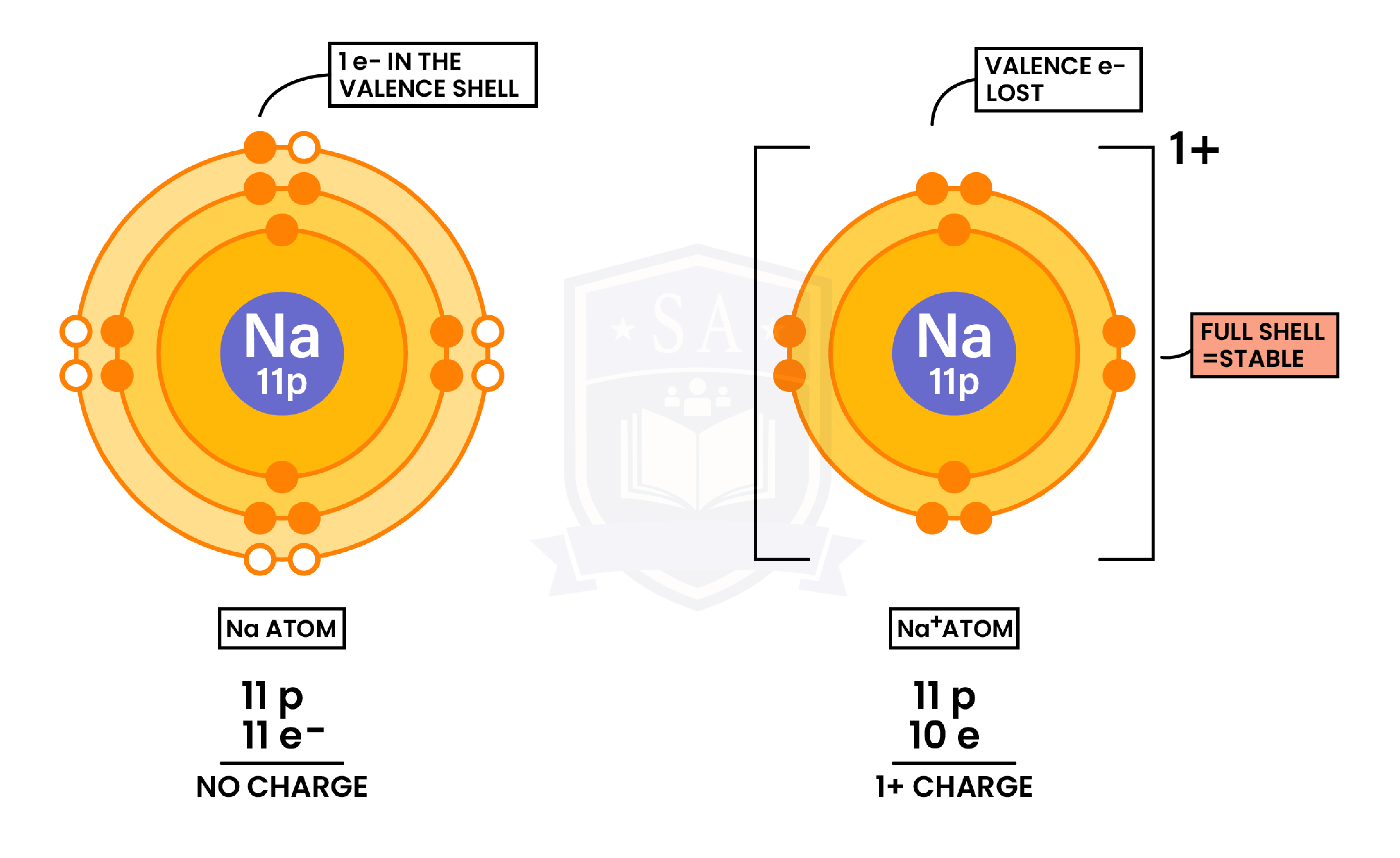
Formation of Cations (Metal Losing Electrons)
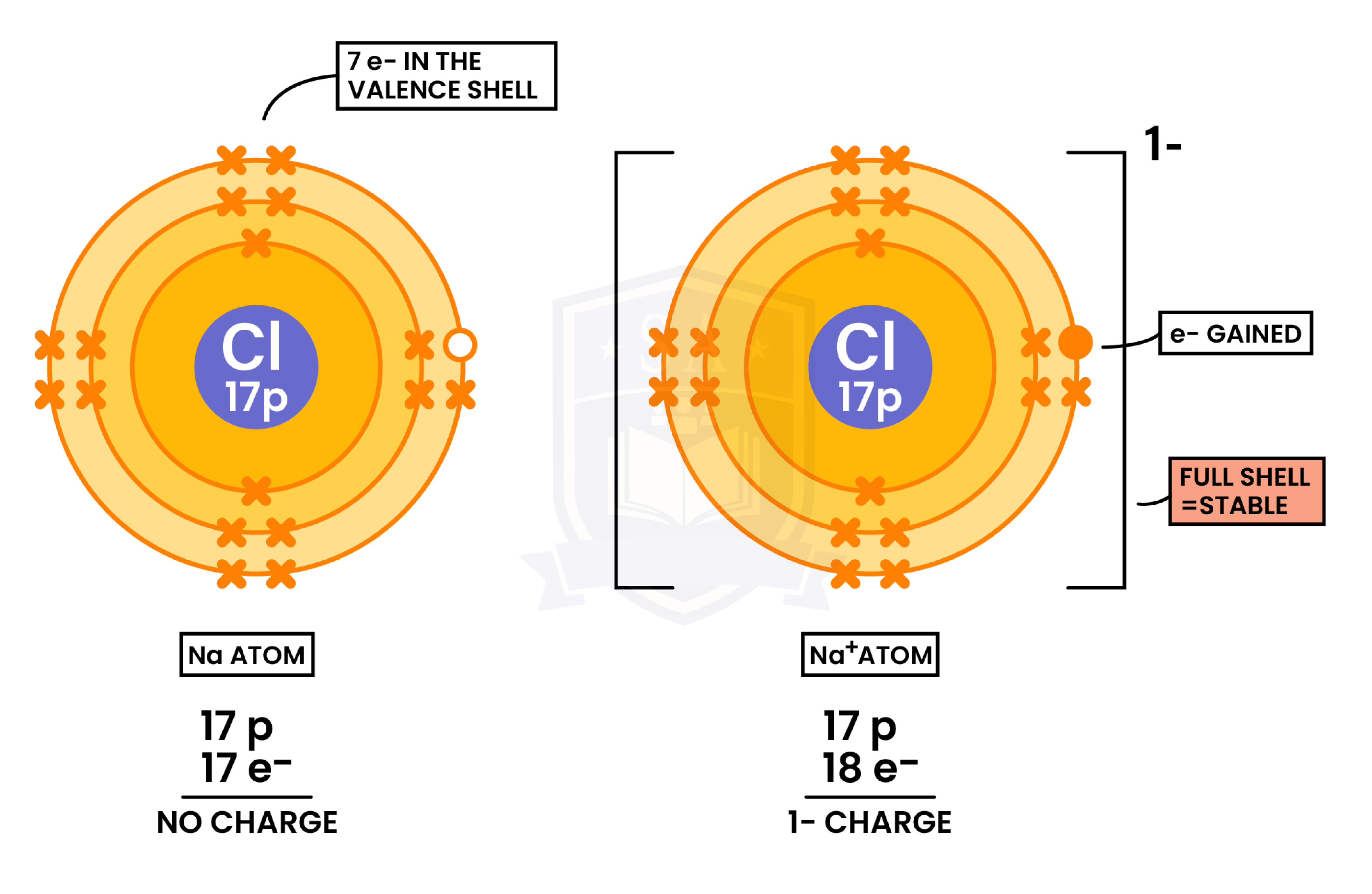
Formation of Anions(Nonmetal Gaining Electrons)
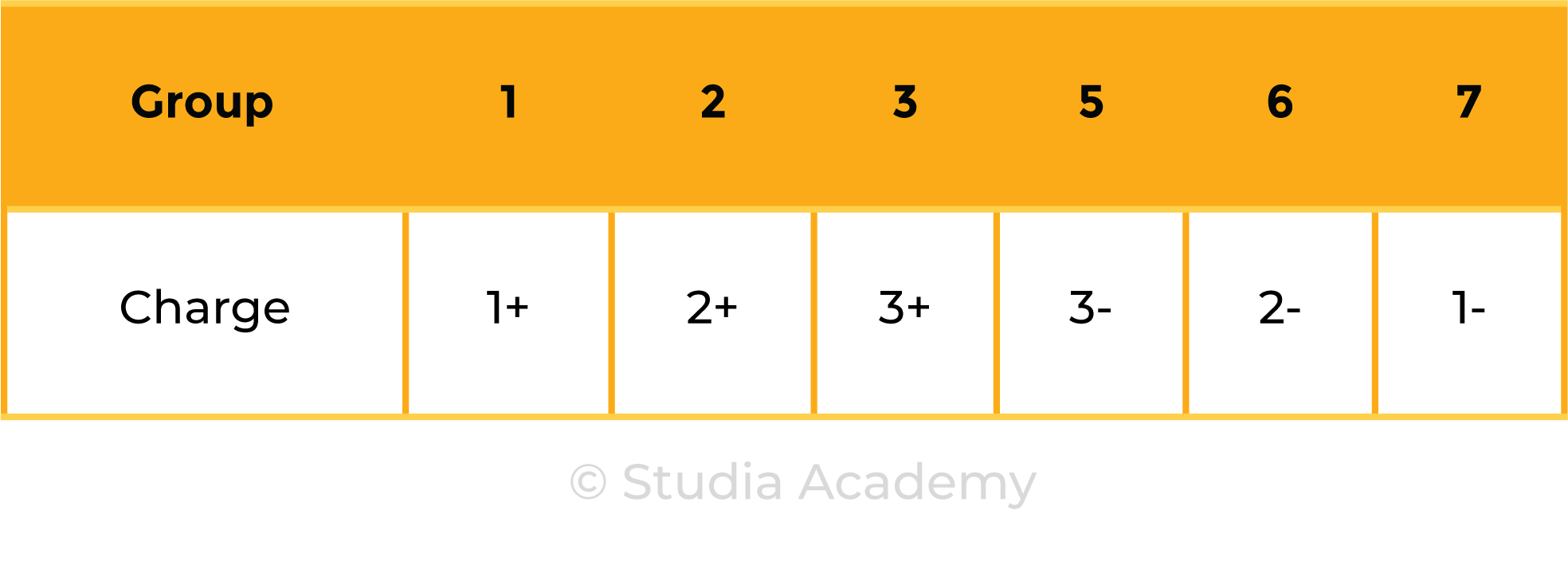
1.6.2 Know the charges of these ions:
Metals and Nonmetals in Group 1, 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7:
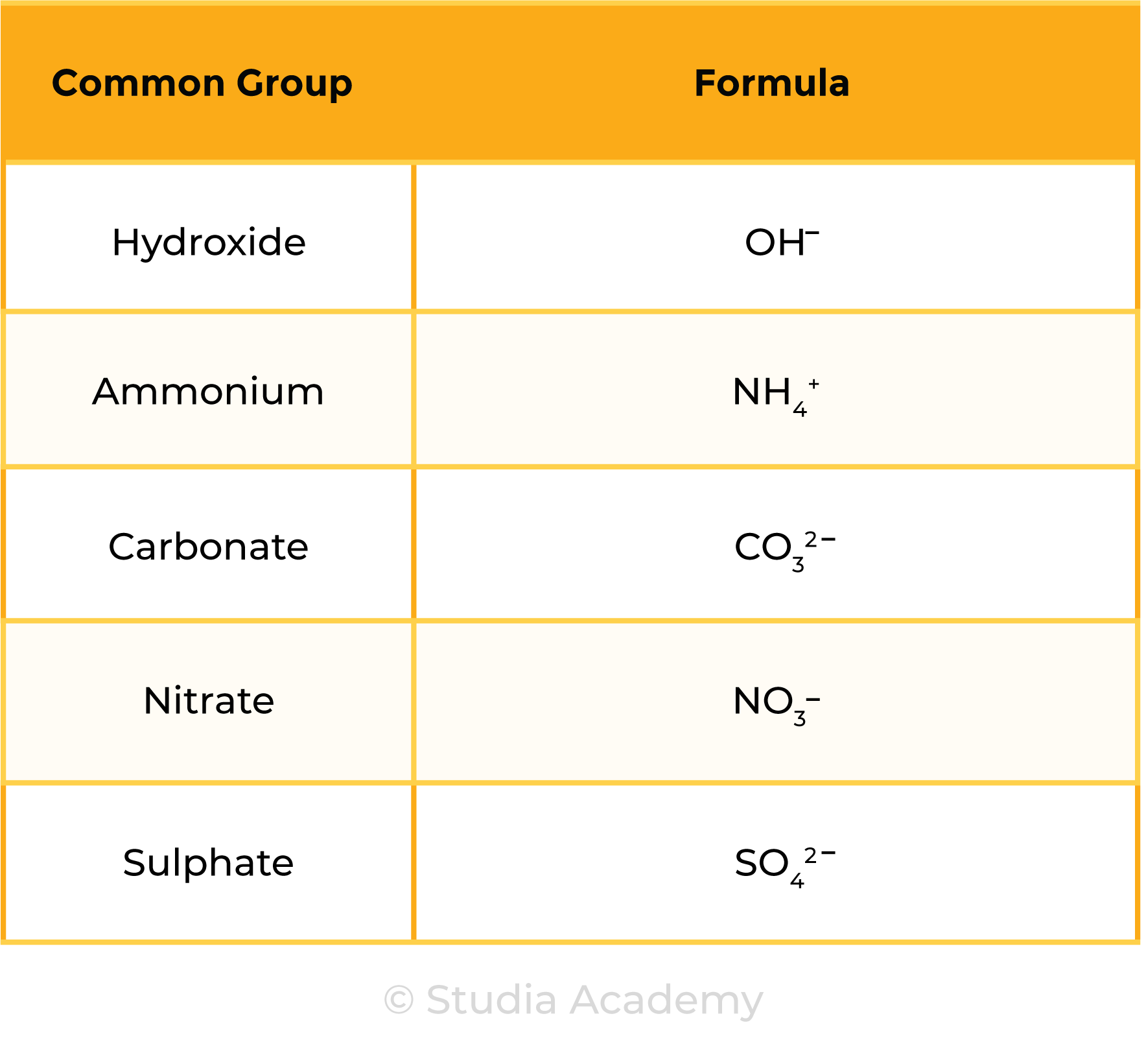
Common Groups (Polyatomic Ions):
1.6.3 Write formulae for compounds formed between the ions listed above
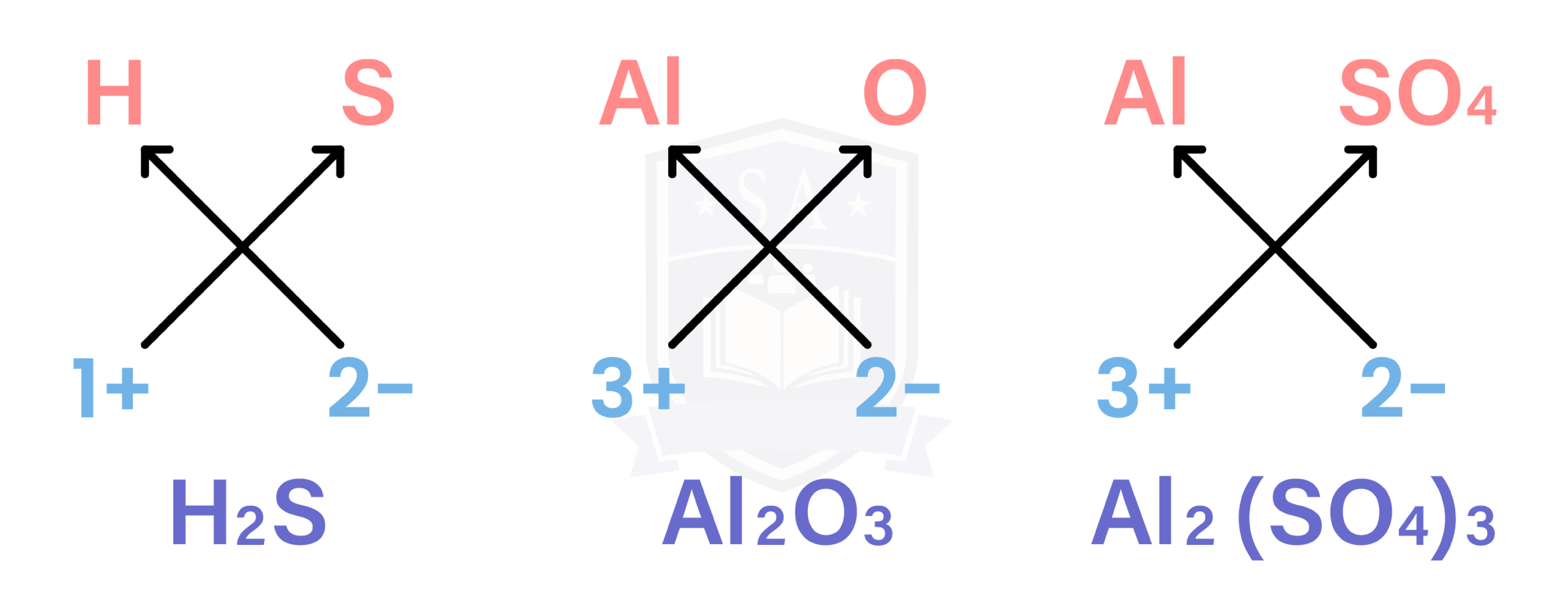
IONIC COMPOUNDS
EXAMPLE
What is the formula of aluminium sulphate?
Al is in group III
→ charge = 3+
→ Al3+
Sulphate is a common ion
→ SO42-
1.6.4 Draw dot-and-cross diagrams to show the formation of ionic compounds by electron transfer, limited to combinations of elements from Groups 1, 2, 3 and 5, 6, 7 only outer electrons need be shown
Ionic compounds are formed when there is electron transfer between metals and nonmetals
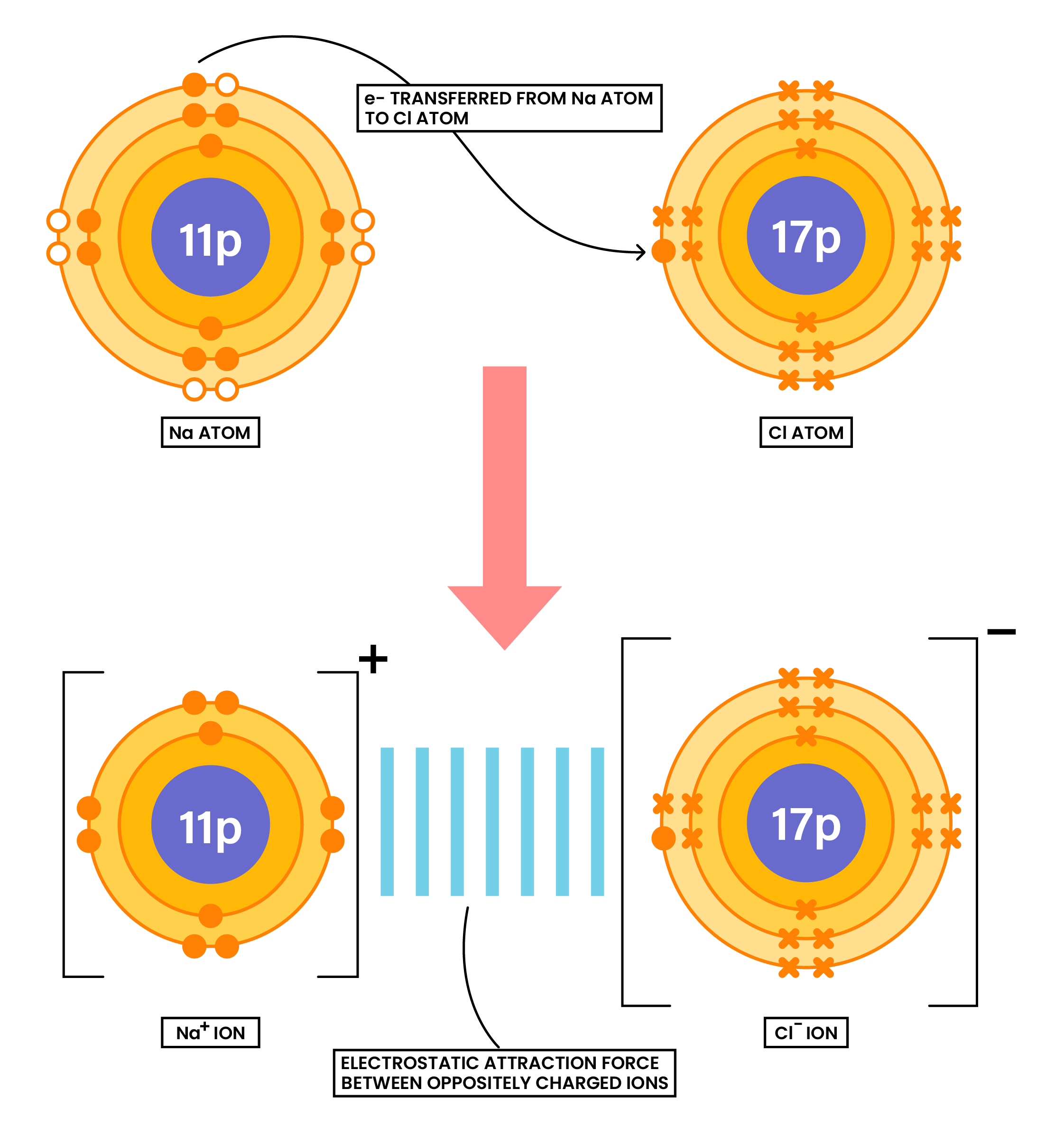
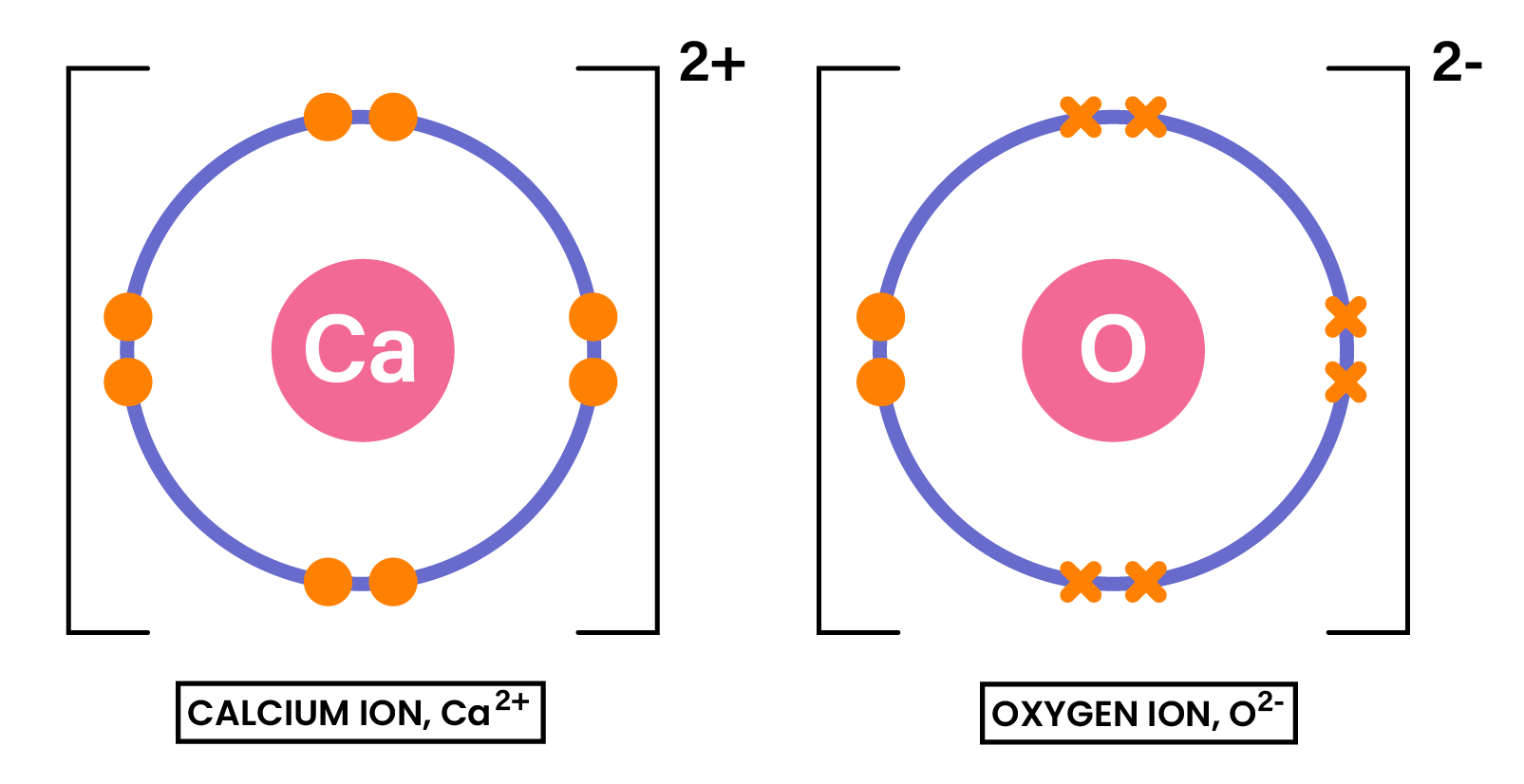
EXAMPLE
Draw the dot-and-cross diagram to show the formation of the compound CaO
1.6.5 Understand ionic bonding in terms of electrostatic attractions
IONIC BONDING
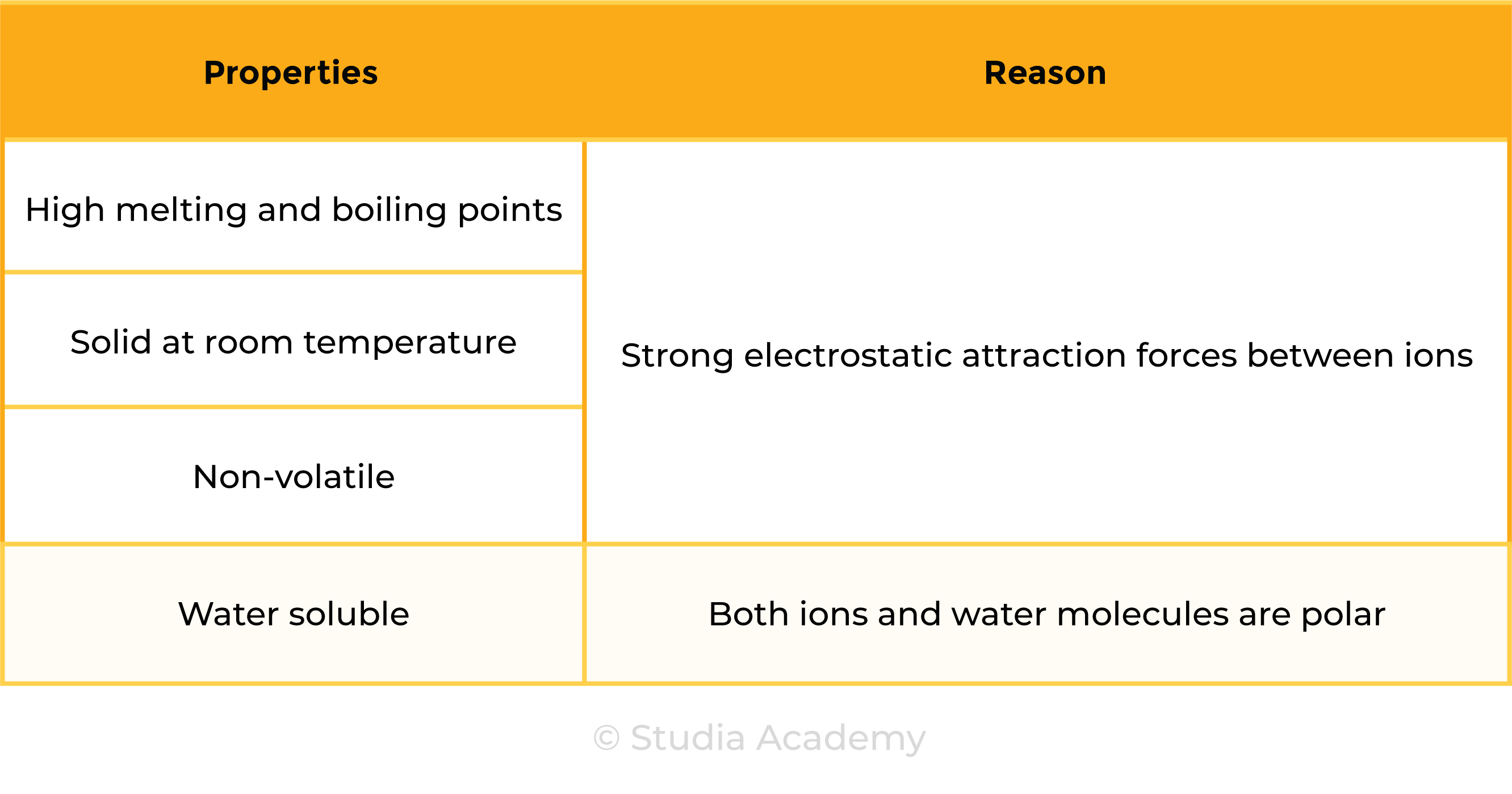
1.6.6 Understand why compounds with giant ionic lattices have high melting and boiling points
STRUCTURE OF IONIC COMPOUNDS
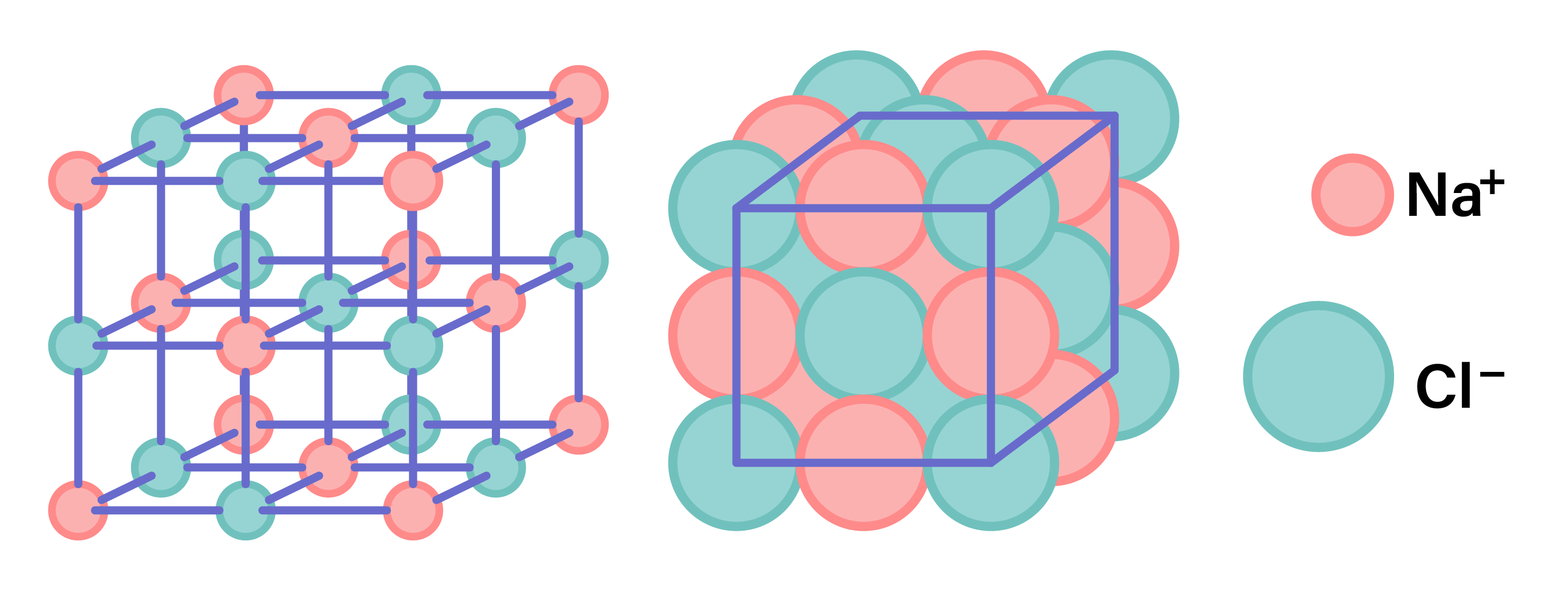
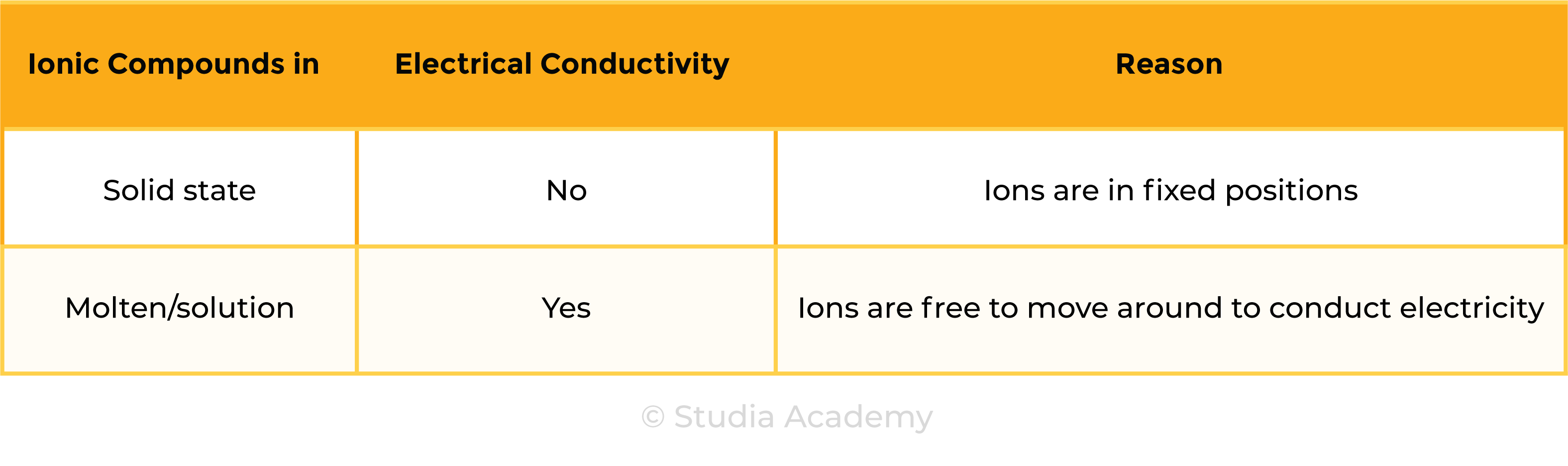
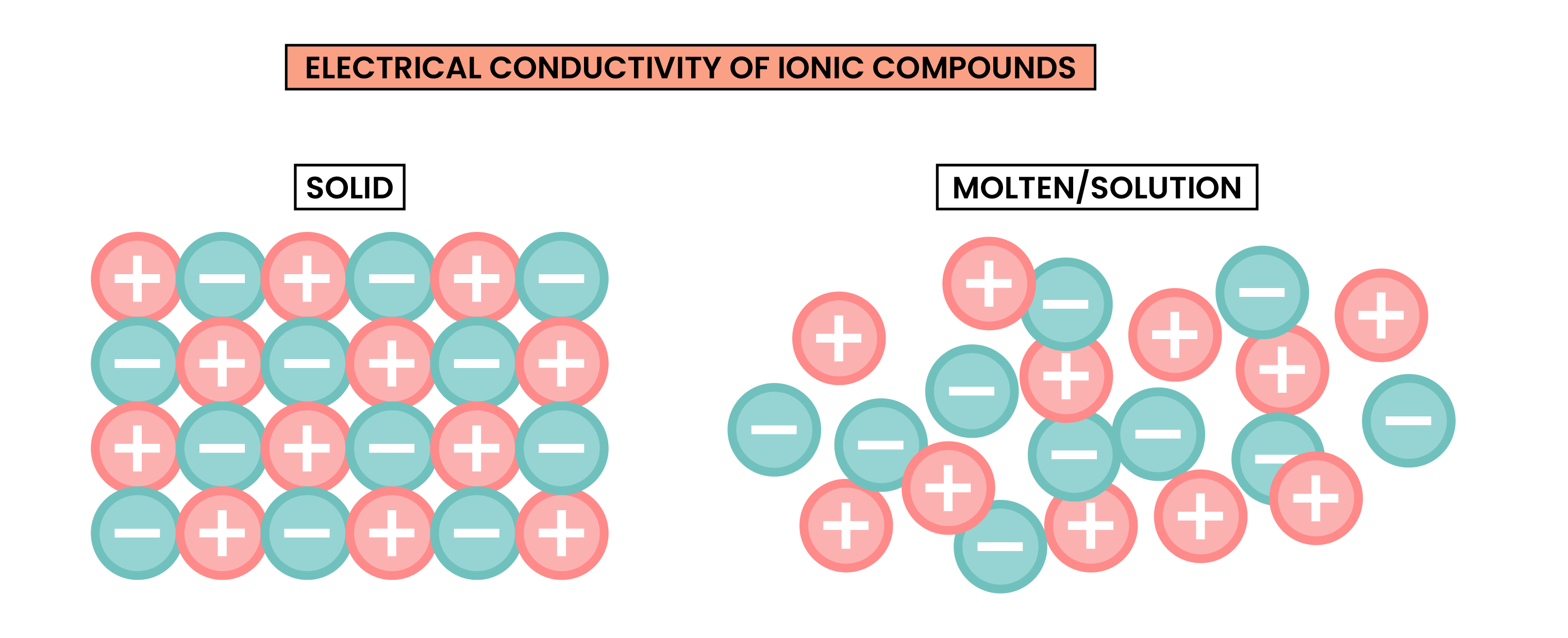
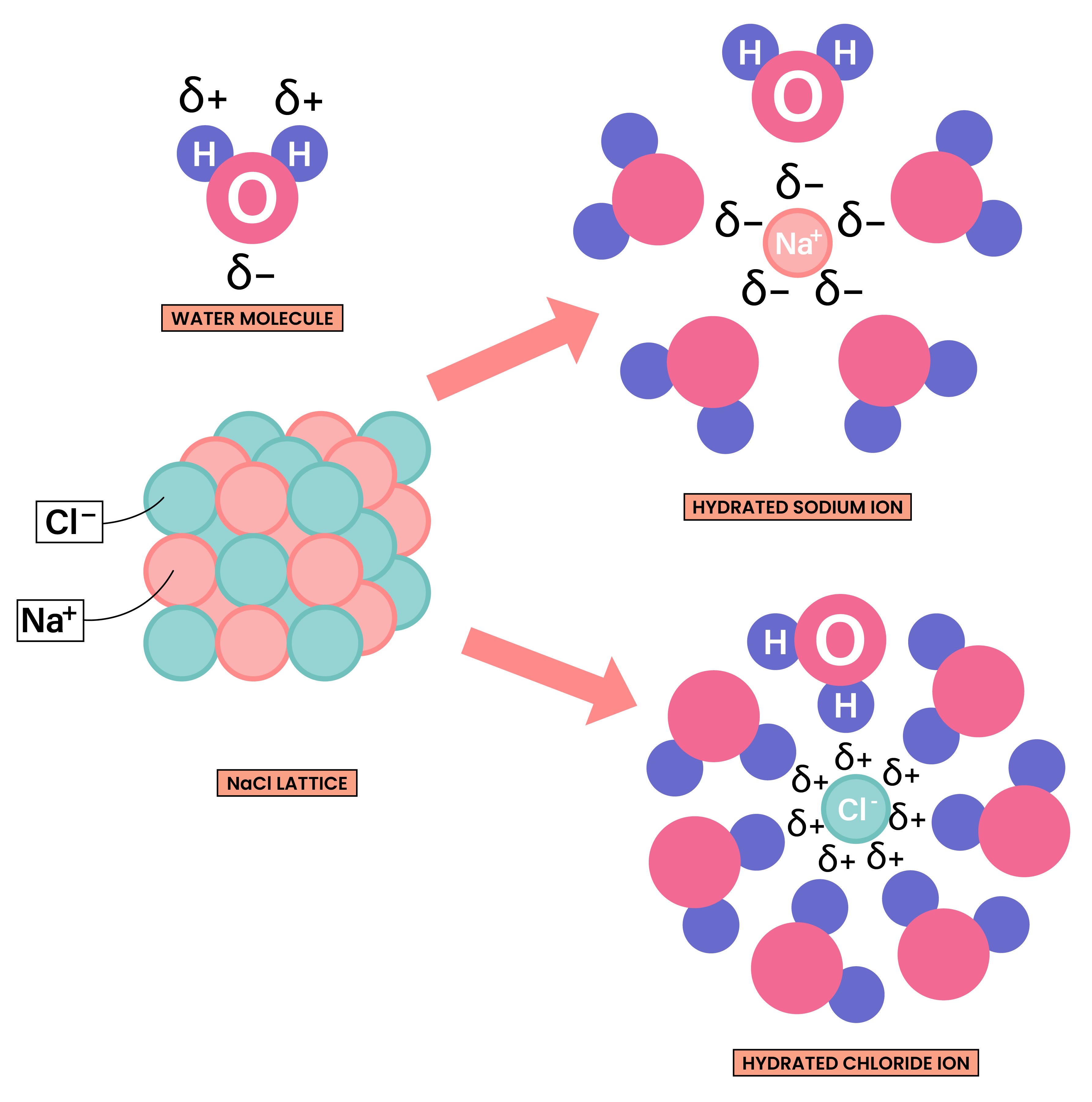
1.6.7 Know that ionic compounds do not conduct electricity when solid, but do conduct electricity when molten and in aqueous solution
ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITY OF IONIC COMPOUNDS
For a substance to conduct electricity, there should be free-moving, charged particles, for example:

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.