REVISION NOTES
3.2.1 Describe experiments to investigate the effects of changes in surface area of a solid, concentration of a solution, temperature and the use of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction
In combination with 3.2.7 and 3.2.8
Investigate:
Key Points
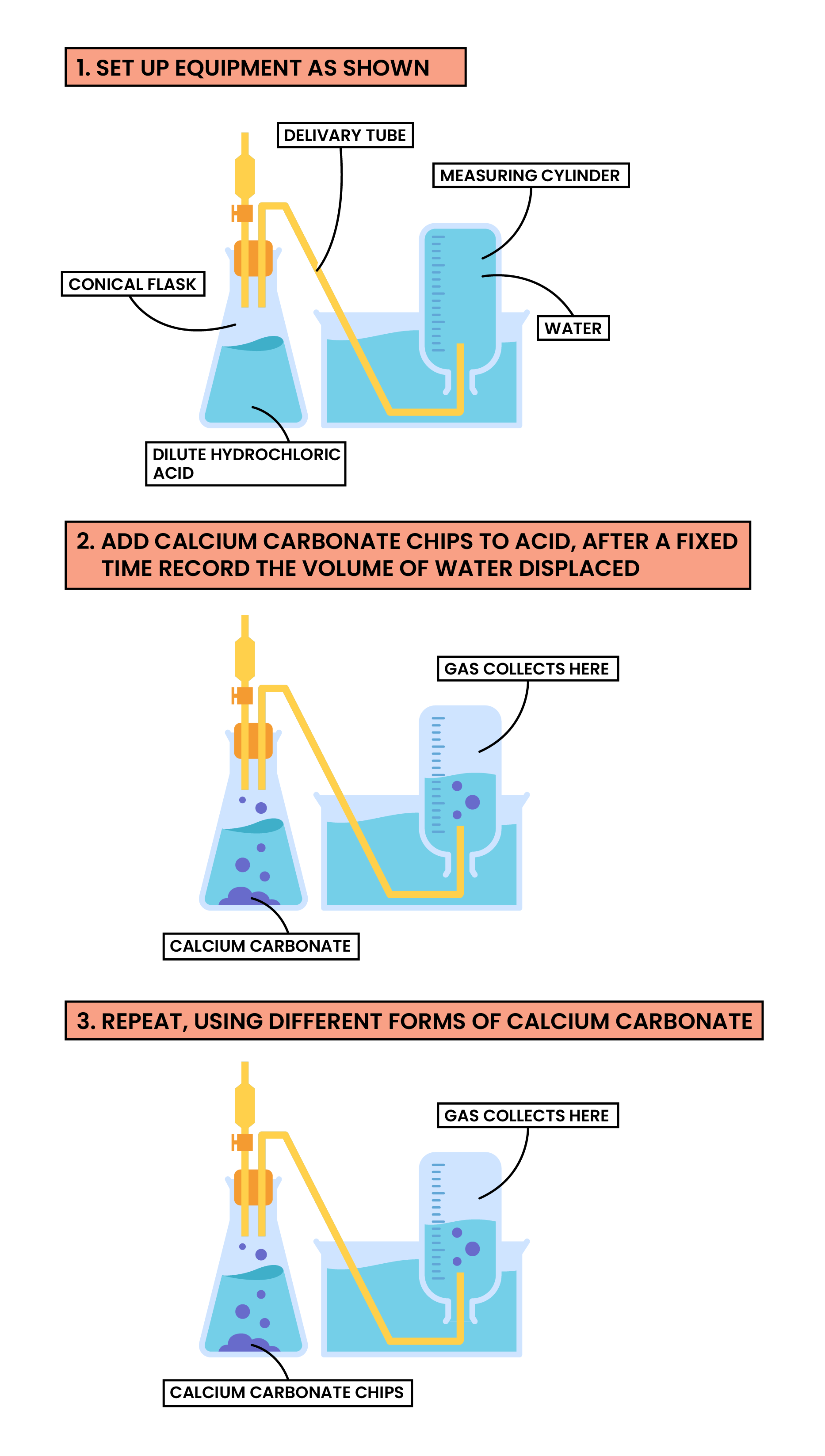
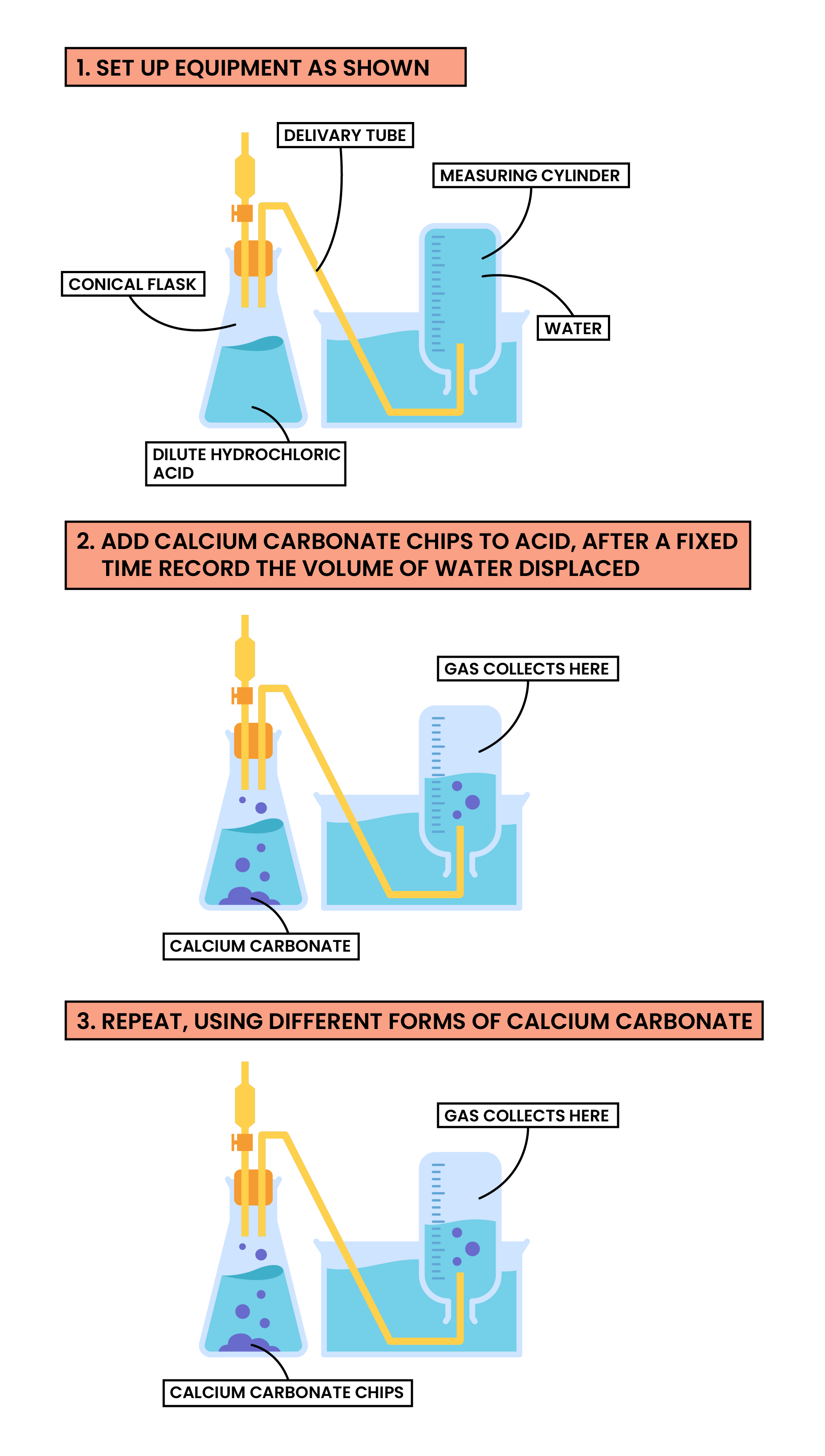
Factor 1 Surface Area of A Solid
calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → calcium chloride + carbon dioxide + water
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(l)
Methods
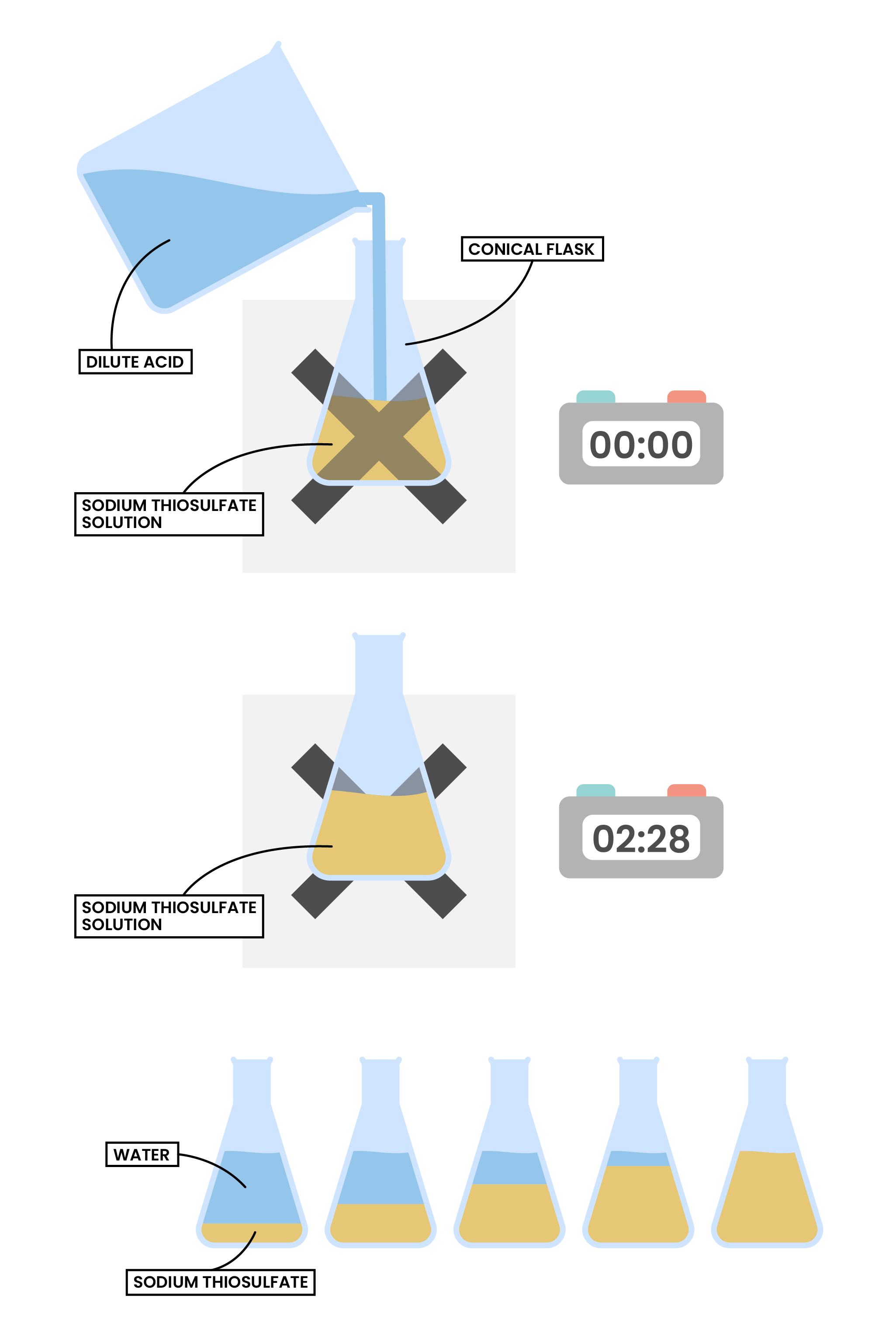
Factor 2 Concentration of A Solution
sodium thiosulfate + hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + sulphur dioxide + sulphur + water
Na2S2O3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + SO2(g) + S(s) + H2O(l)
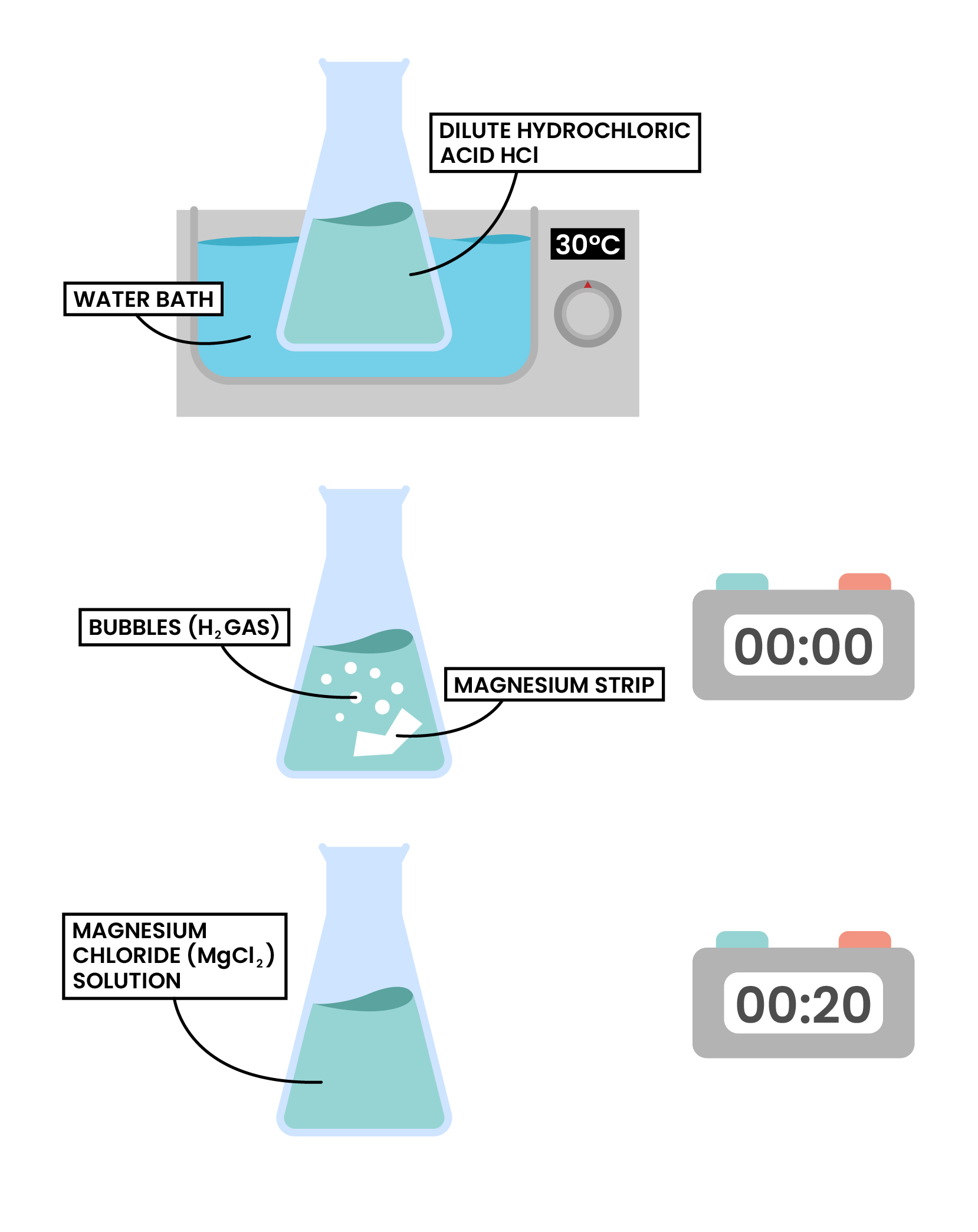
FACTOR 3 TEMPERATURE
magnesium + hydrochloric acid → magnesium chloride + hydrogen
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
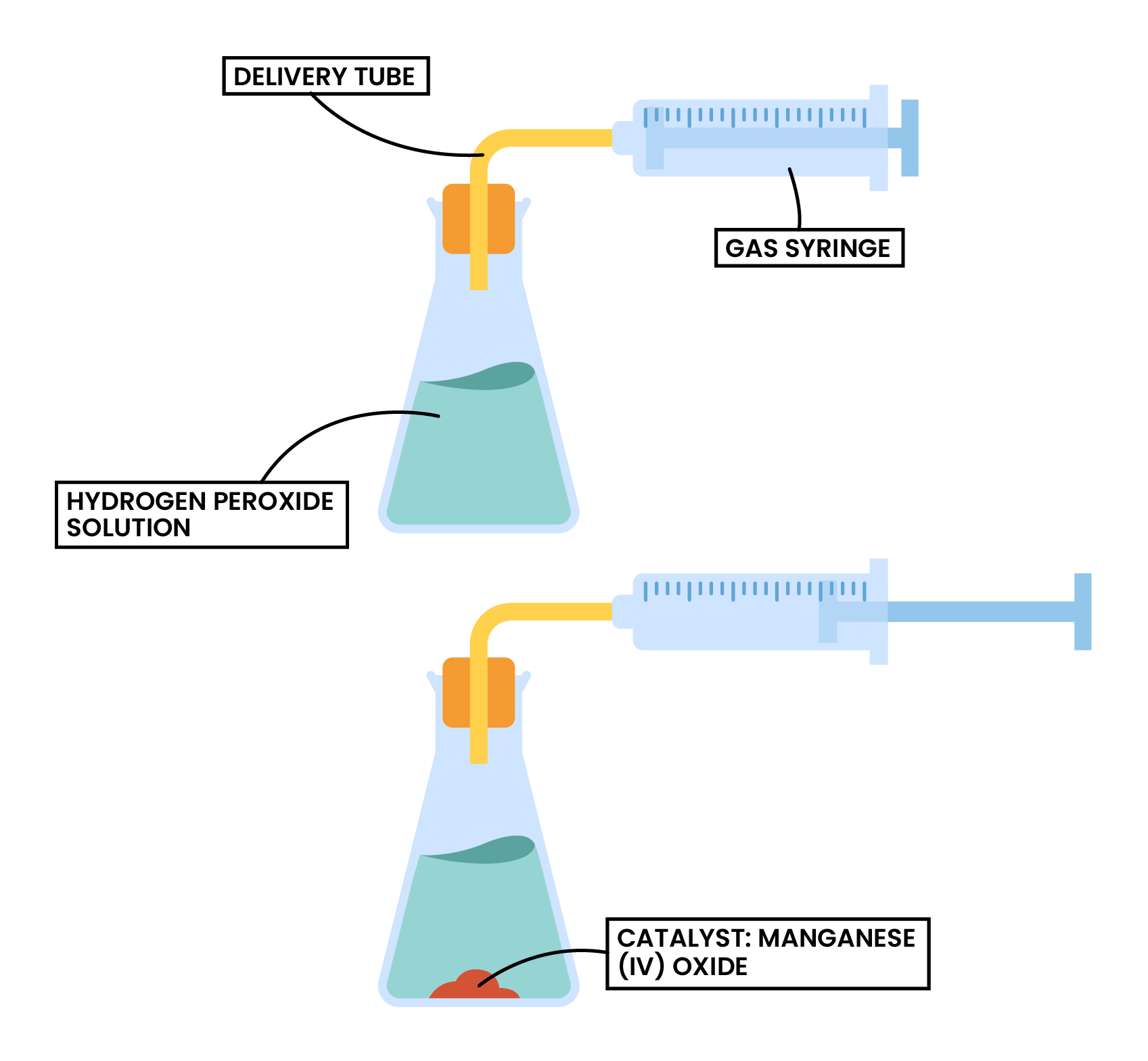
Factor 4 Catalyst
hydrogen peroxide → water + oxygen
2H2O2 (aq) → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)
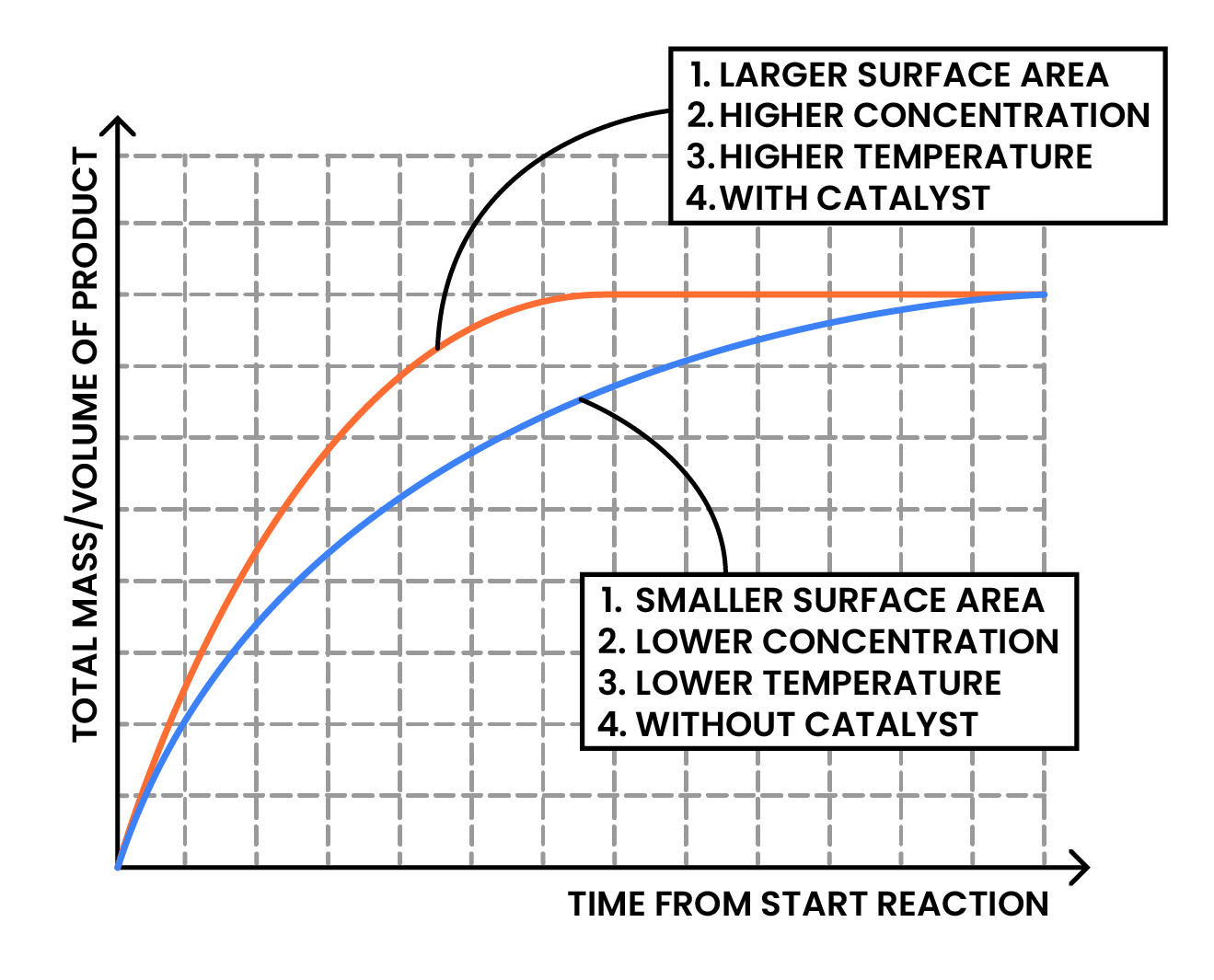
3.2.2 Describe the effects of changes in surface area of a solid, concentration of a solution, pressure of a gas, temperature and the use of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction
Factors affecting rate of reaction:
3.2.3 Explain the effects of changes in surface area of a solid, concentration of a solution, pressure of a gas and temperature on the rate of a reaction in terms of particle collision theory
PARTICLE COLLISION THEORY
Effect of Increased Concentration / Increased Pressure
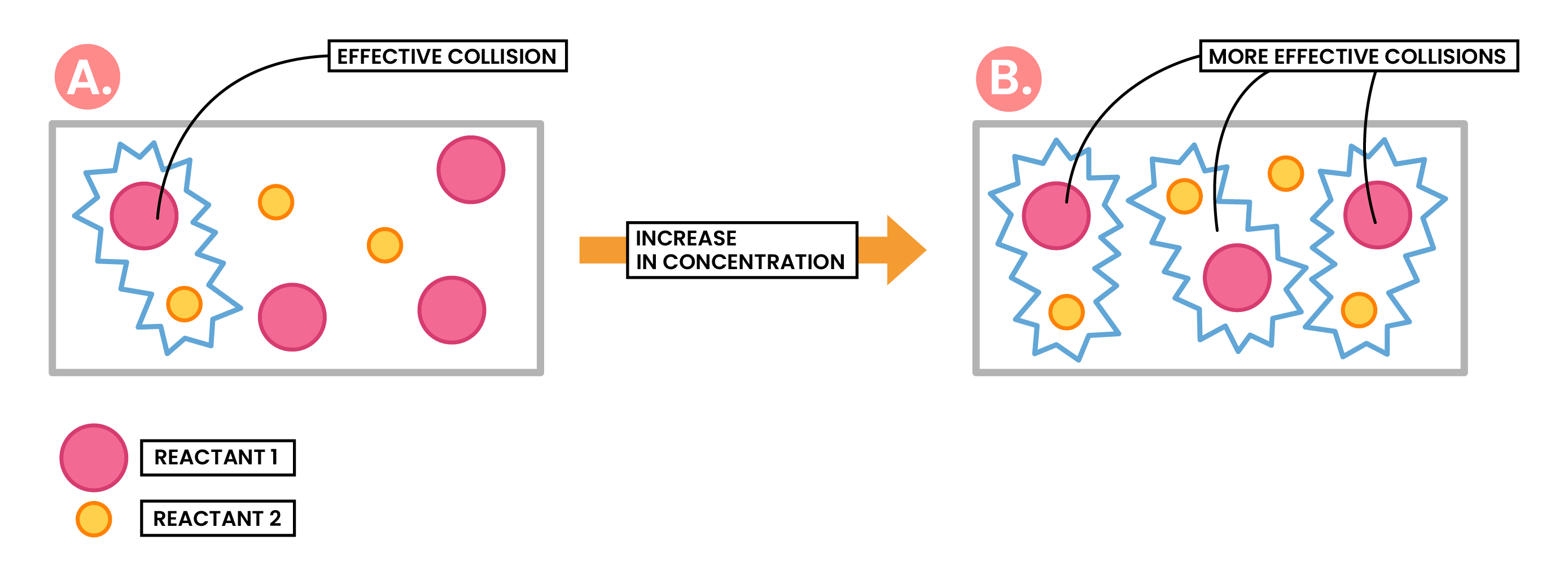
Increasing concentration of a solution
↓
More reactant particles in a given volume
↓
More frequent and successful collisions
↓
Increasing rate of reaction
Effect of Increased Temperature
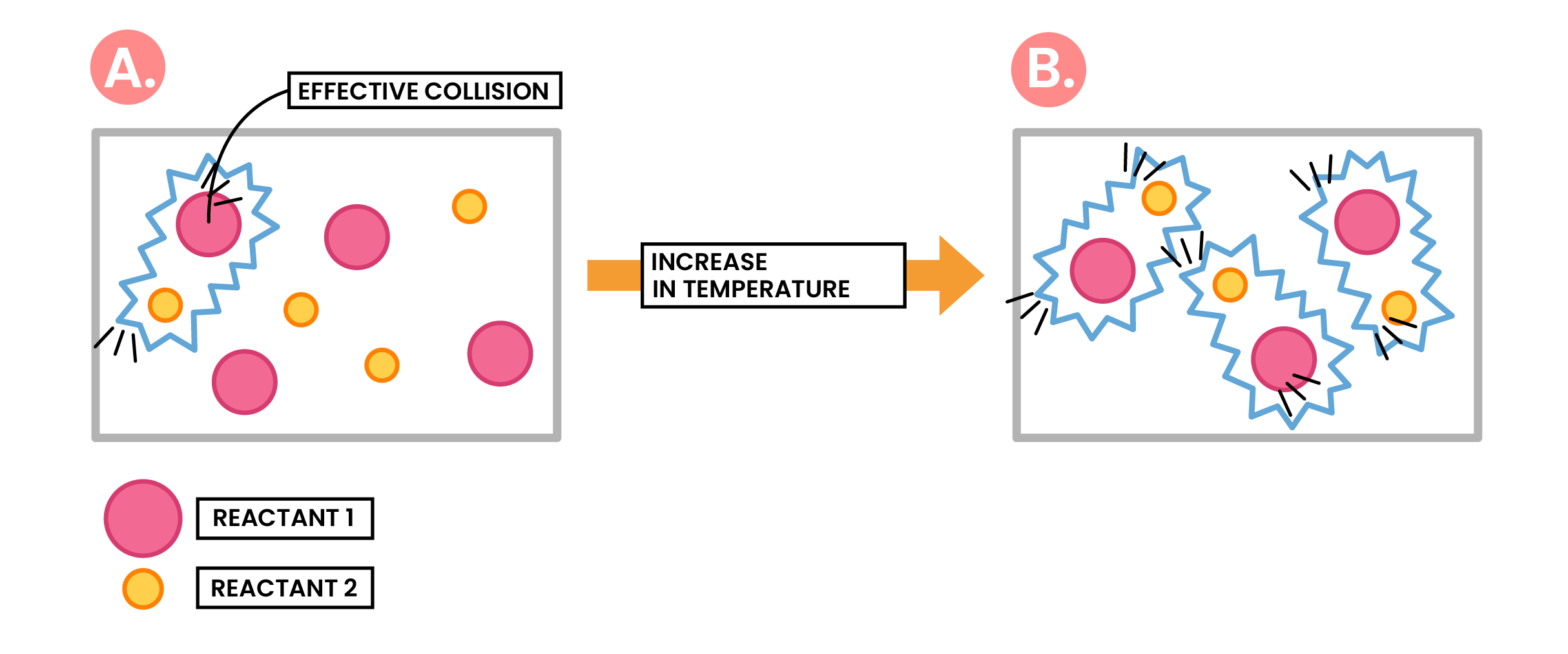
Increasing temperature
↓
Increasing average kinetic energy of particles, higher than required activation energy
↓
More frequent and successful collisions
↓
Increasing rate of reaction
Effect of Increased Surface Area
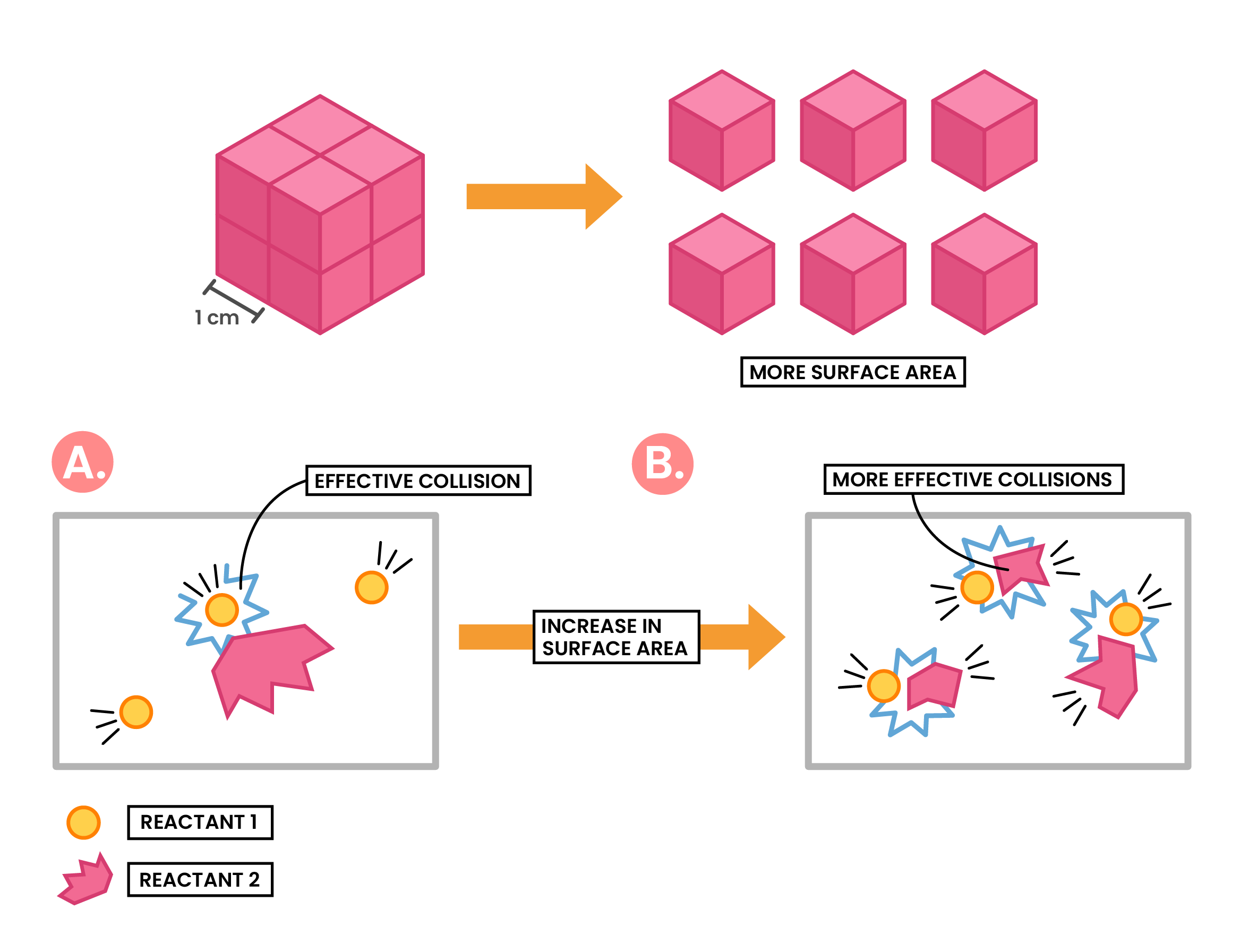
Increasing surface area of solid reactant
↓
More surface area of the particle exposed to other reactant particles
↓
More frequent and successful collisions
↓
Increasing rate of reaction
3.2.4 Know that a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a reaction, but is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction
CATALYST
3.2.5 Know that a catalyst works by providing an alternative pathway with lower activation energy
ACTIVATION ENERGY (EA)
CATALYST
3.2.6C Draw and explain reaction profile diagrams showing ΔH and activation energy
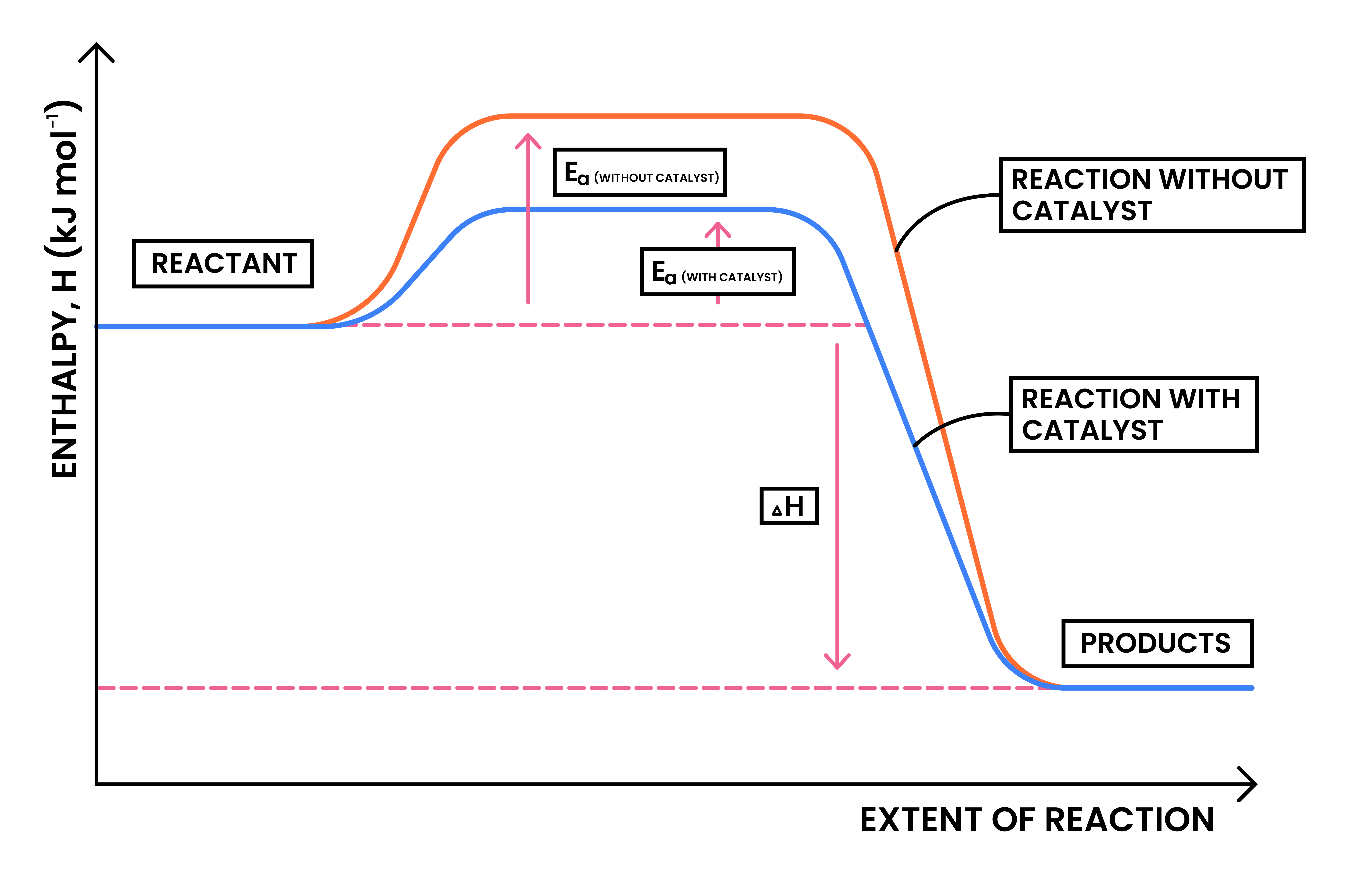
ACTIVATION OF ENERGY (EA)
ΔH
3.2.7 Practical: investigate the effect of changing the surface area of marble chips and of changing the concentration of hydrochloric acid on the rate of reaction between marble chips and dilute hydrochloric acid
Discussed in 3.1.1
3.2.8 Practical: investigate the effect of different solids on the catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide solution
Discussed in 3.1.1

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.