REVISION NOTES
4.5.1C Know that alcohols contain the functional group −OH
The functional group of alcohol is -OH
– O – H
4.5.2C Understand how to draw structural and displayed formulae for methanol, ethanol, propanol (propan-1-ol only) and butanol (butan-1-ol only), and name each compound
the names propanol and butanol are acceptable
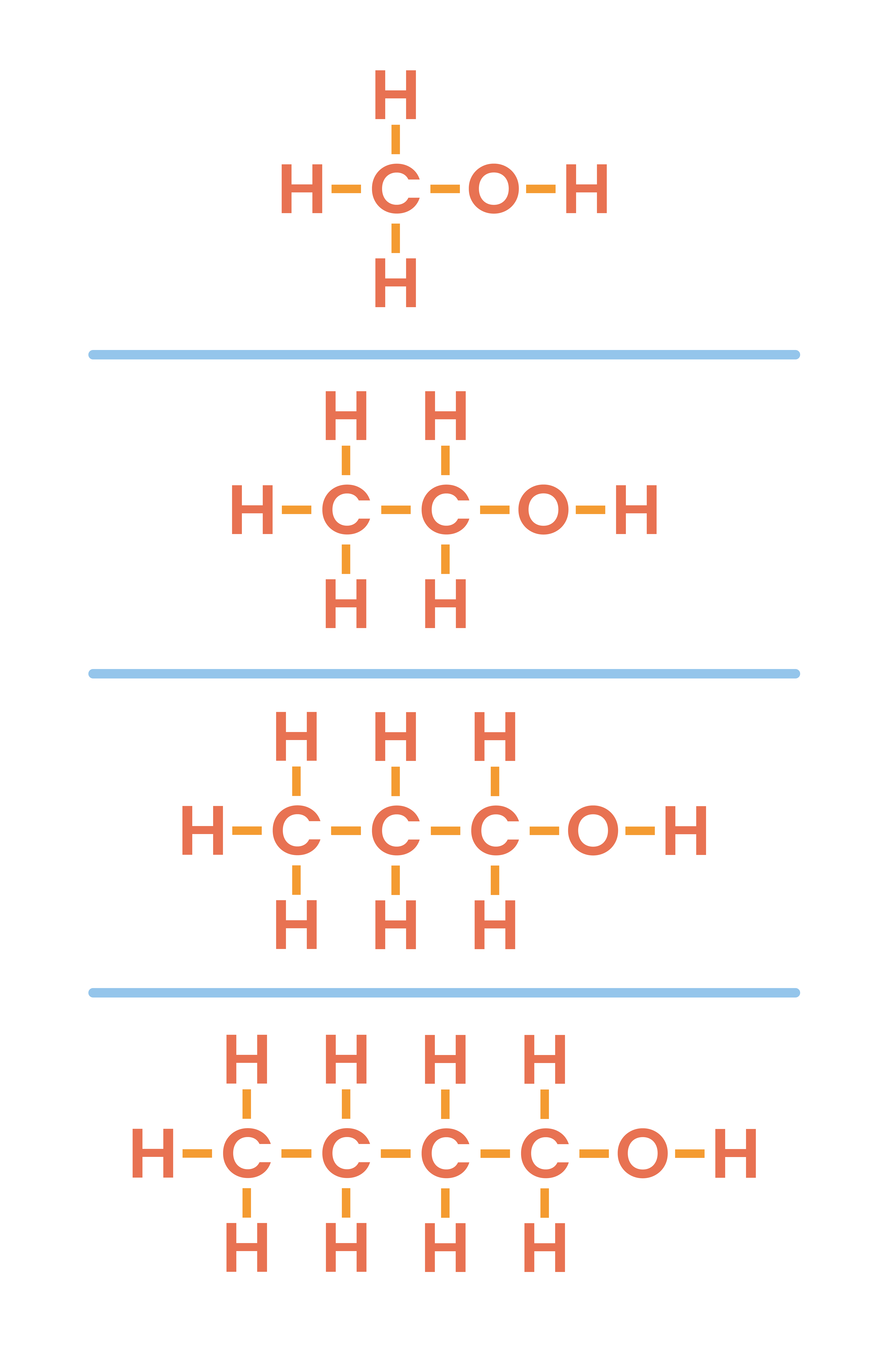
4.5.3C Know that ethanol can be oxidised by:
OXIDATION OF ETHANOL
1. Complete combustion
2. Microbial oxidation
3. Ethanol and potassium dichromate(VI)
4.5.4C Know that ethanol can be manufactured by:
Manufacture of Ethanol
1. Ethene + steam
Features
2. Fermentation of glucose
Features
4.5.5C Understand the reasons for fermentation, in the absence of air, and at an optimum temperature
Fermentation of Glucose
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.