REVISION NOTES
4.3.1 Know the general formula for alkanes
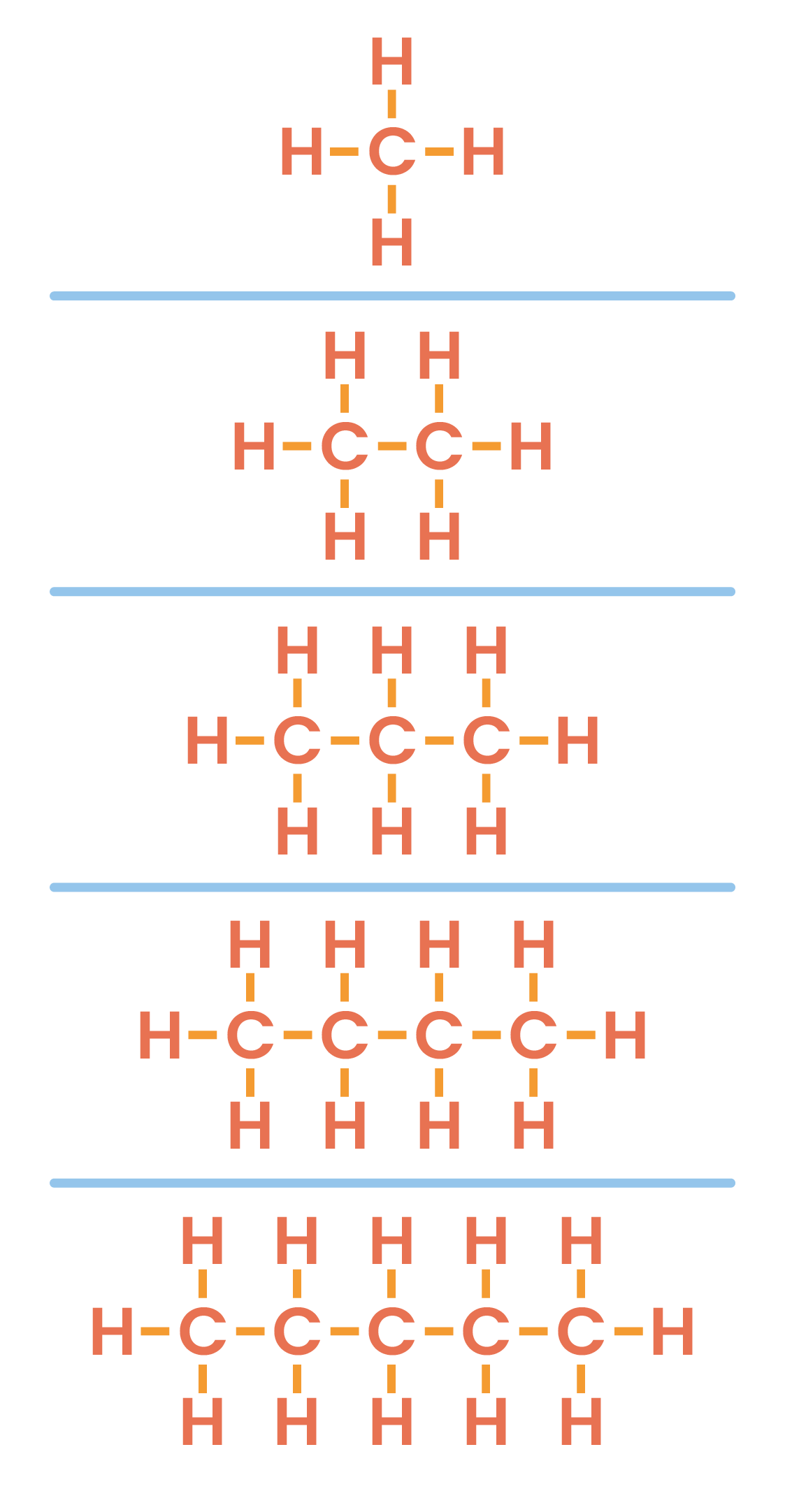
General formula for alkanes:
CnH2n+2
EXAMPLE
Ethane is a type of alkane with the formula C2H6
4.3.2 Explain why alkanes are classified as saturated hydrocarbons
ALKANES
4.3.3 Understand how to draw the structural and displayed formulae for alkanes with up to five carbon atoms in the molecule, and to name the unbranched-chain isomers
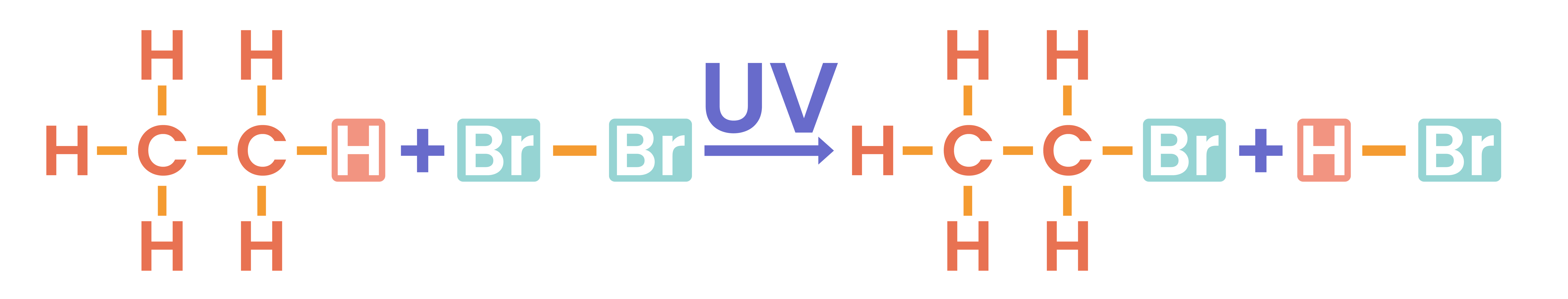
4.3.4 Describe the reactions of alkanes with halogens in the presence of ultraviolet radiation, limited to mono-substitution
knowledge of reaction mechanisms is not required
Reaction of Alkanes with Halogens
UV
alkane + halogen → halogenoalkane + hydrogen halide
UV
C2H6 + Br2 → C2H5Br + HBr

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.