REVISION NOTES
2.2.1 Know the colours, physical states (at room temperature) and trends in physical properties of these elements
GROUP 7 ELEMENTS
Trends in physical properties
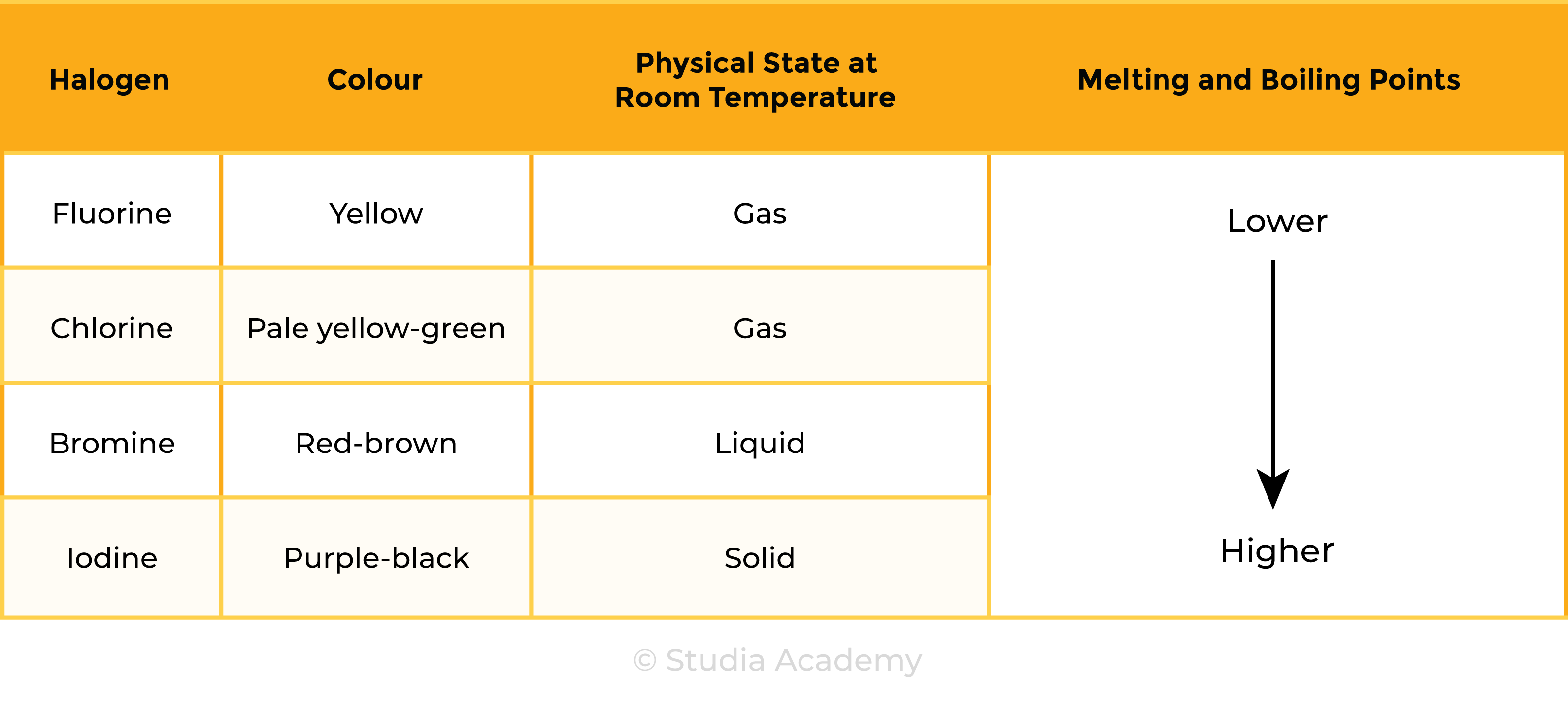
TREND 1:
Melting and boiling points increase down the group
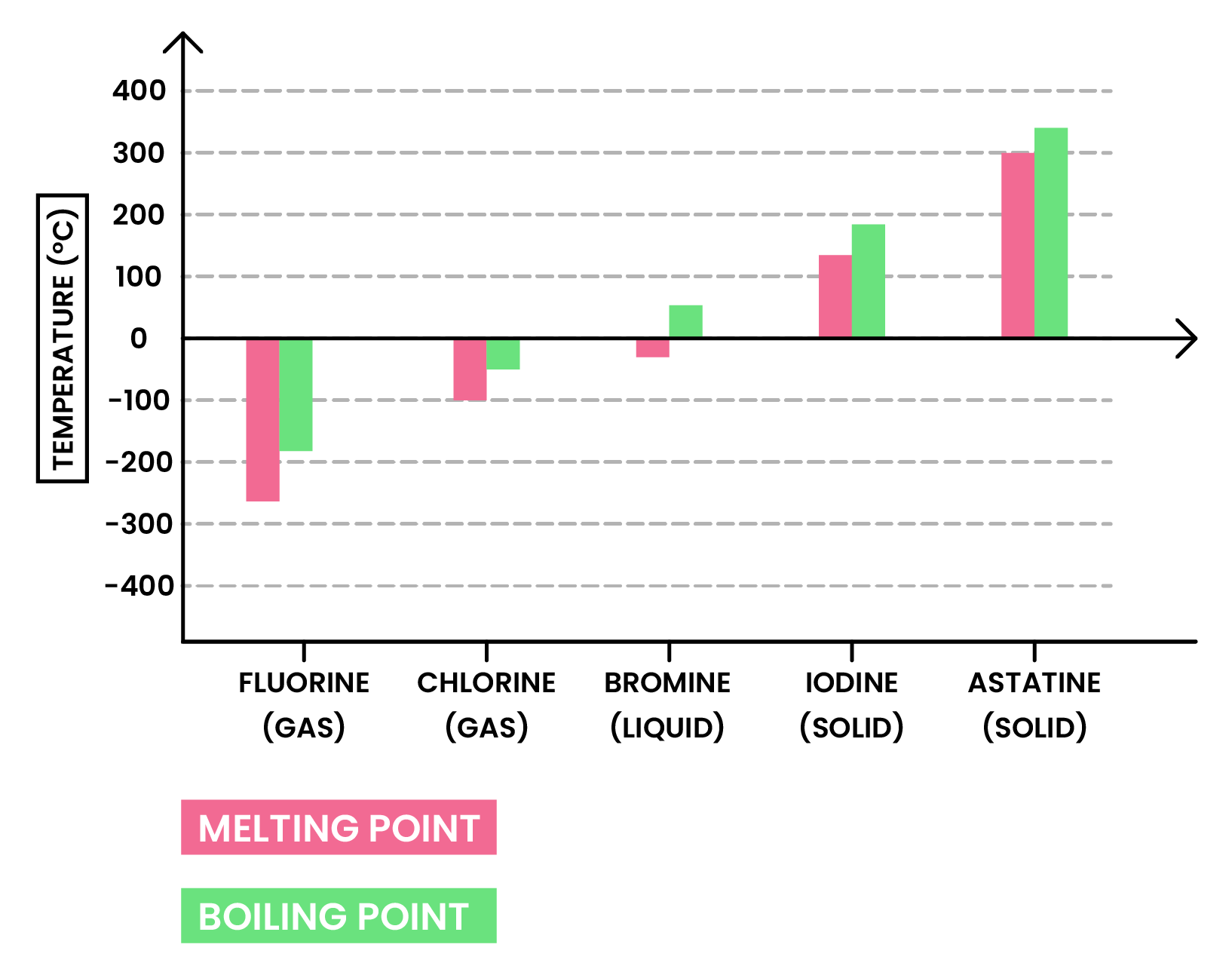
TREND 2
At room temperature, the physical state of halogens changes down the group
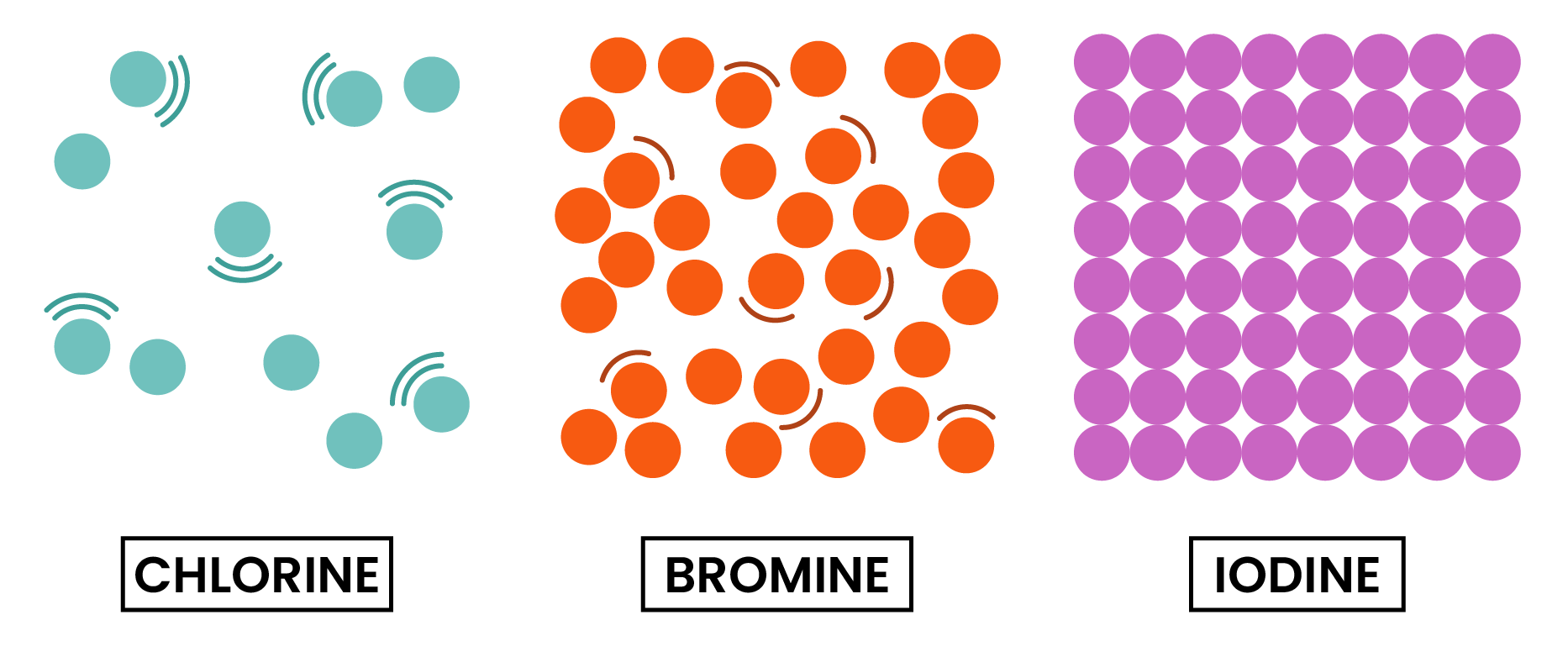
TREND 3
Colours of halogens changes down the group
2.2.2 Use knowledge of trends in Group 7 to predict the properties of other halogens
RECALL: (DOWN THE GROUP)
Halogens can also react with metals and non–metals to form compounds
REACTION 1 HALOGEN + METAL
Halogen + Metal → Metal halide (salt, ionic compound)
2Na + Cl2 → 2NaCl
Ca + Br2 → CaBr2
REACTION 2 HALOGEN + NON-MENTAL
Halogens + Non-metal → simple covalent compounds
Halogens + Hydrogen → Hydrogen halide
E.g. chlorine + hydrogen → hydrogen chloride
Cl2 + H2 → 2HCl
2.2.3 Understand how displacement reactions involving halogens and halides provide evidence for the trend in reactivity in Group 7
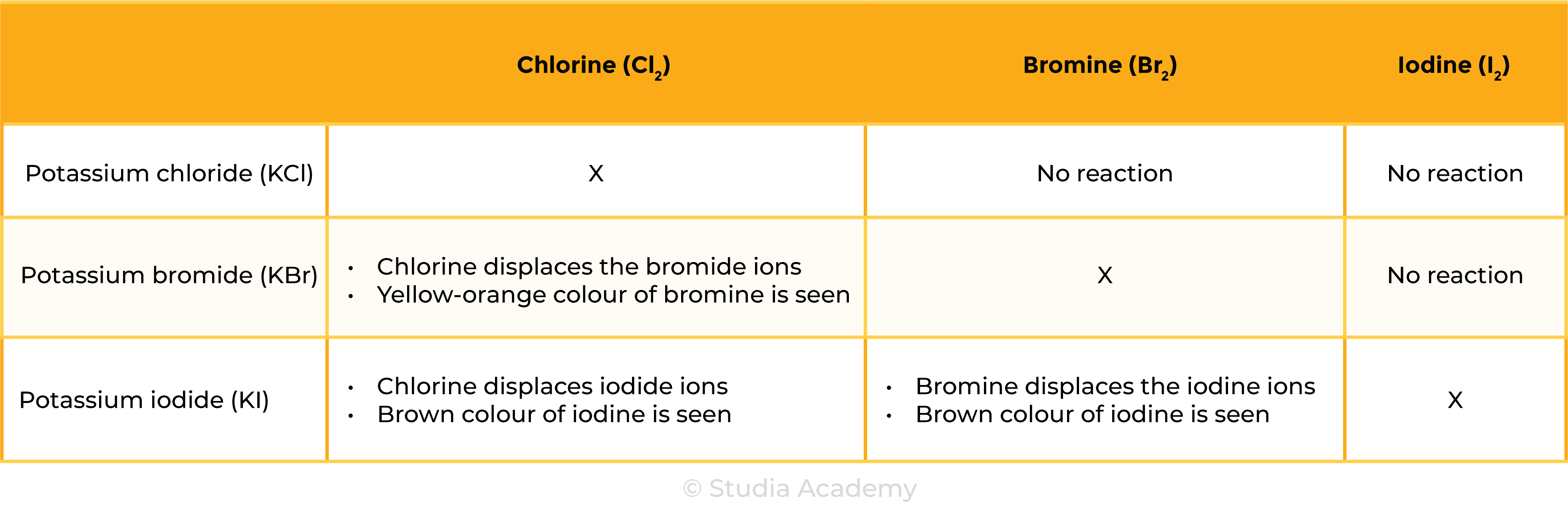
HALOGEN DISPLACEMENT REACTION
REACTIVITY OF HALOGENS
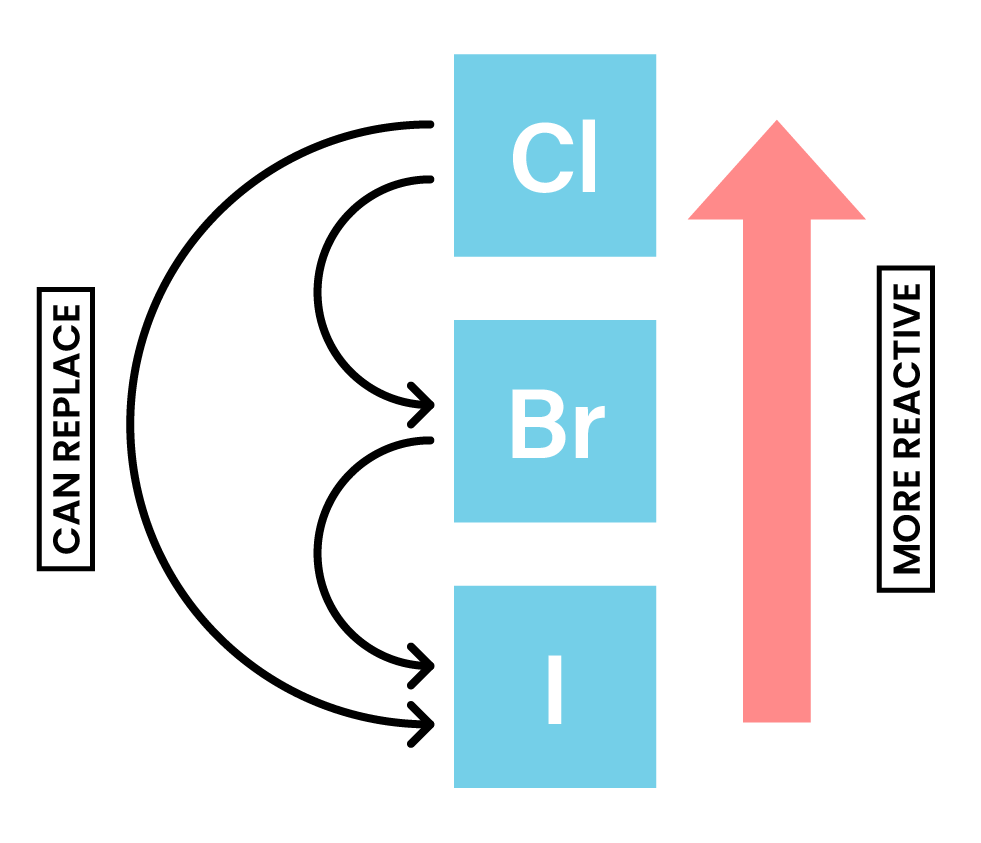
Chlorine with bromides & iodides
Cl2 + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br2
Chlorine + Potassium bromide → potassium chloride + Bromine
Cl2 + 2KI → 2KCl + I2
Chlorine + Potassium iodide→ potassium chloride + Iodine
Bromine with iodides
Br2 + 2KI → 2KBr + I2
Bromine + Potassium iodide → potassium bromide + Iodine
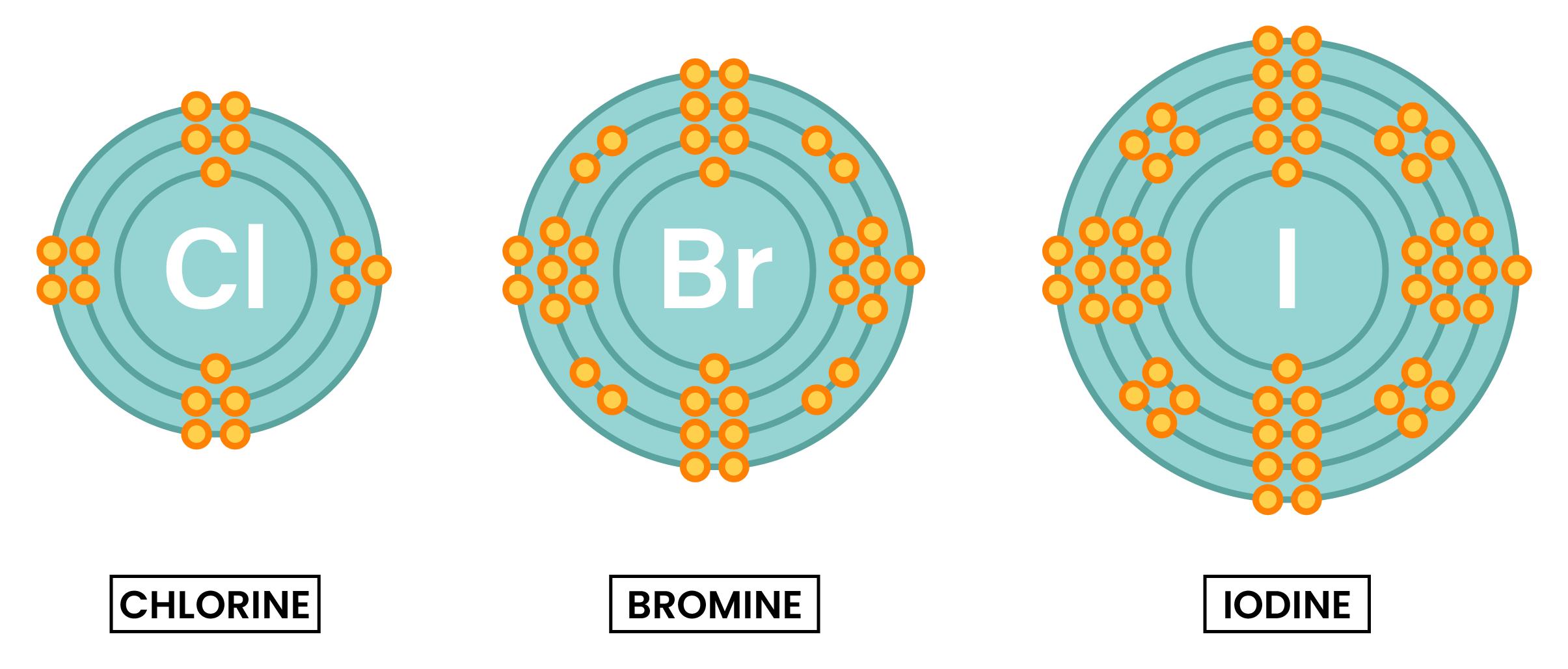
2.2.4C Explain the trend in reactivity in Group 7 in terms of electronic configurations
RECALL
WHEN HALOGENS REACT
EXPLANATION OF TREND IN REACTIVITY


© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.