REVISION NOTES
2.6.1 Understand that a balanced diet should include appropriate proportions of carbohydrate, protein, lipid, vitamins, minerals, water and dietary fibre
Balanced diet
2.6.2 Identify the sources and describe the functions of carbohydrate, protein, lipid (fats and oils), vitamins A, C and D, the mineral ions calcium and iron, water and dietary fibre as components of the diet
2.6.3 Understand how energy requirements vary with activity levels, age and pregnancy
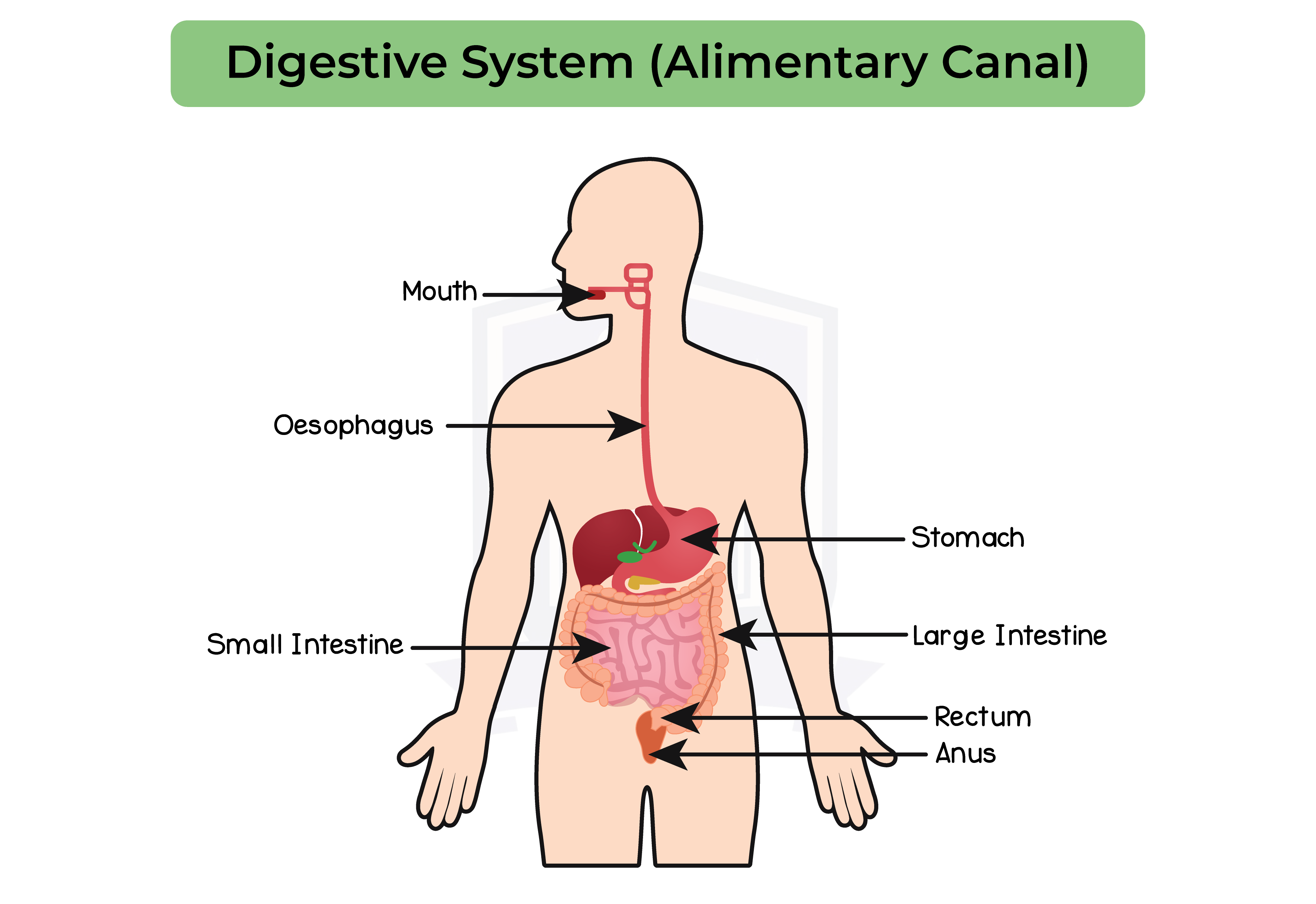
2.6.4 Describe the structure and function of the human alimentary canal, including the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine (duodenum and ileum), large intestine (colon and rectum) and pancreas
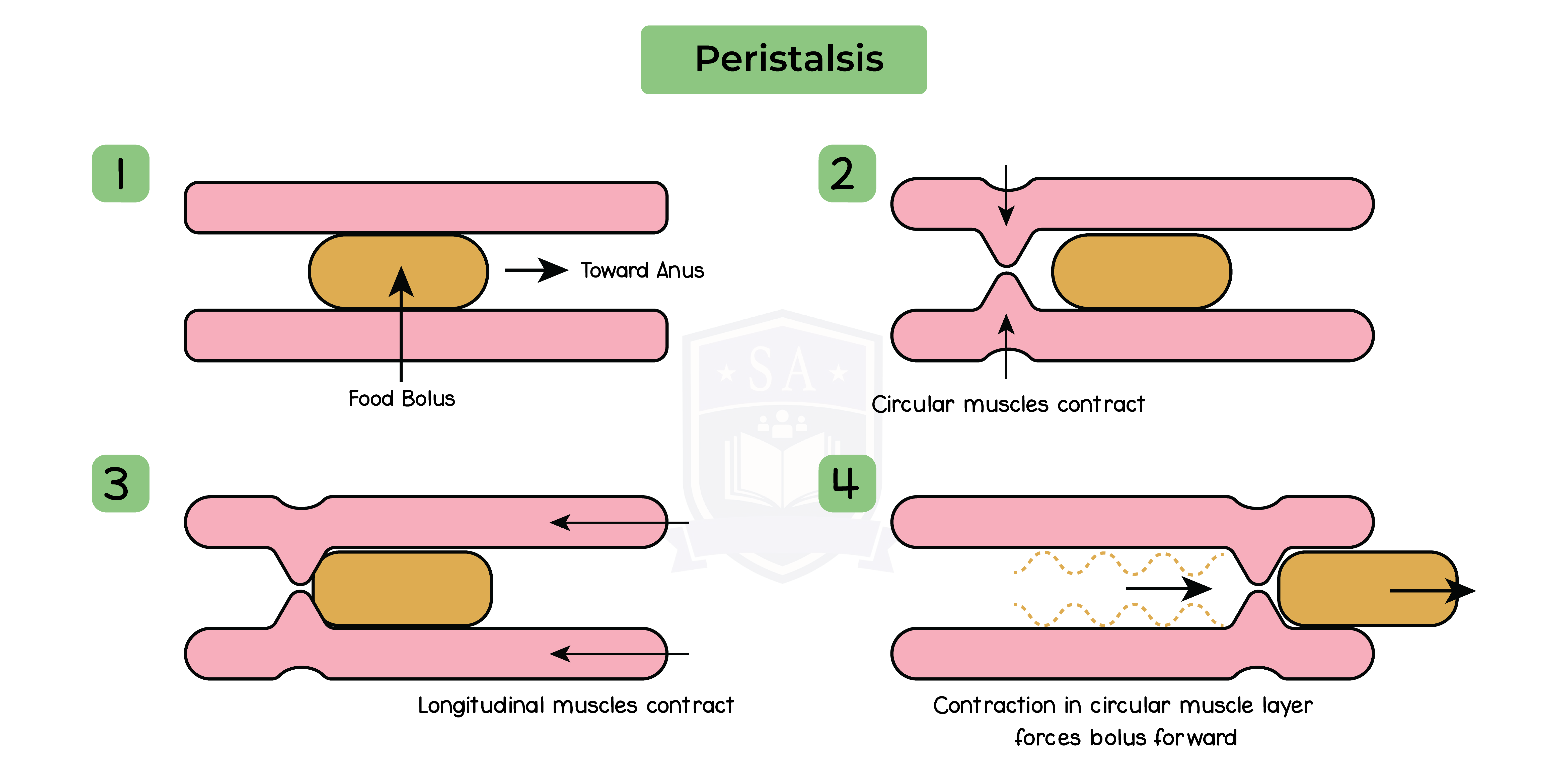
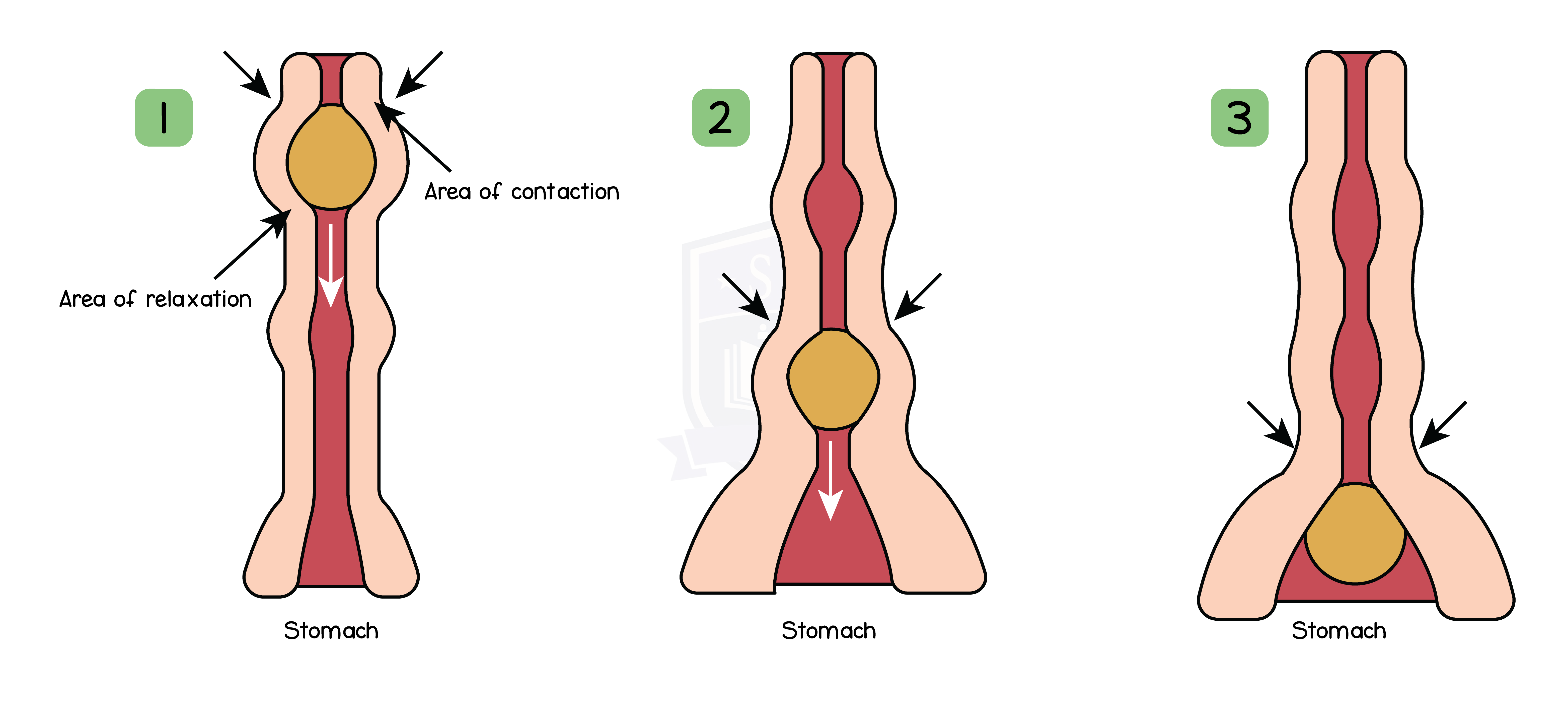
2.6.5 Understand how food is moved through the gut by peristalsis
Peristalsis
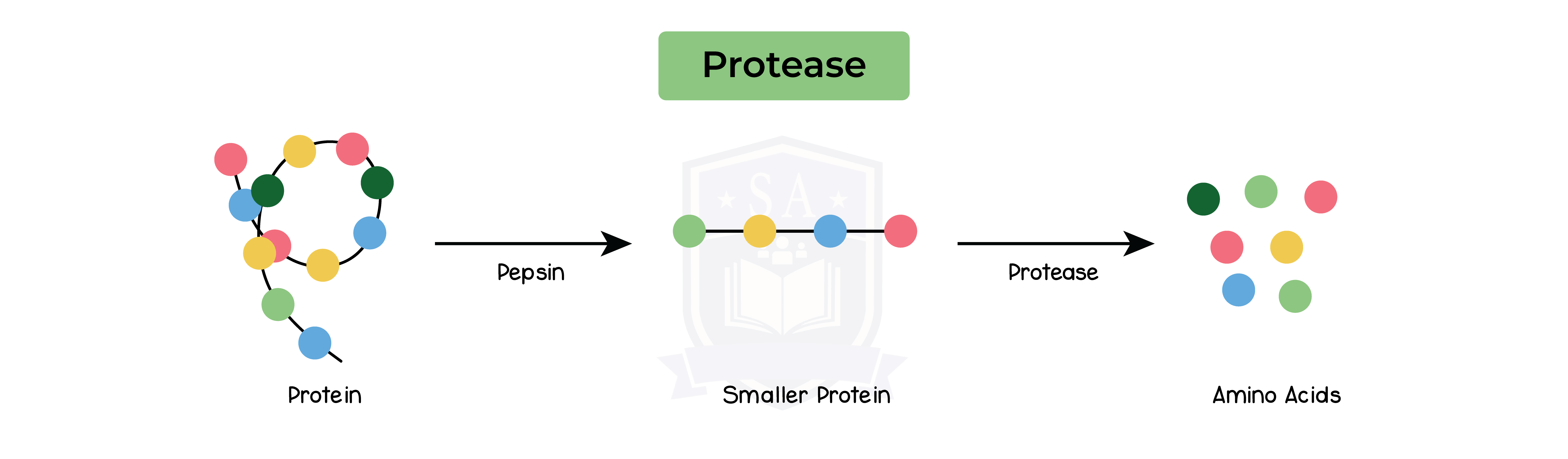
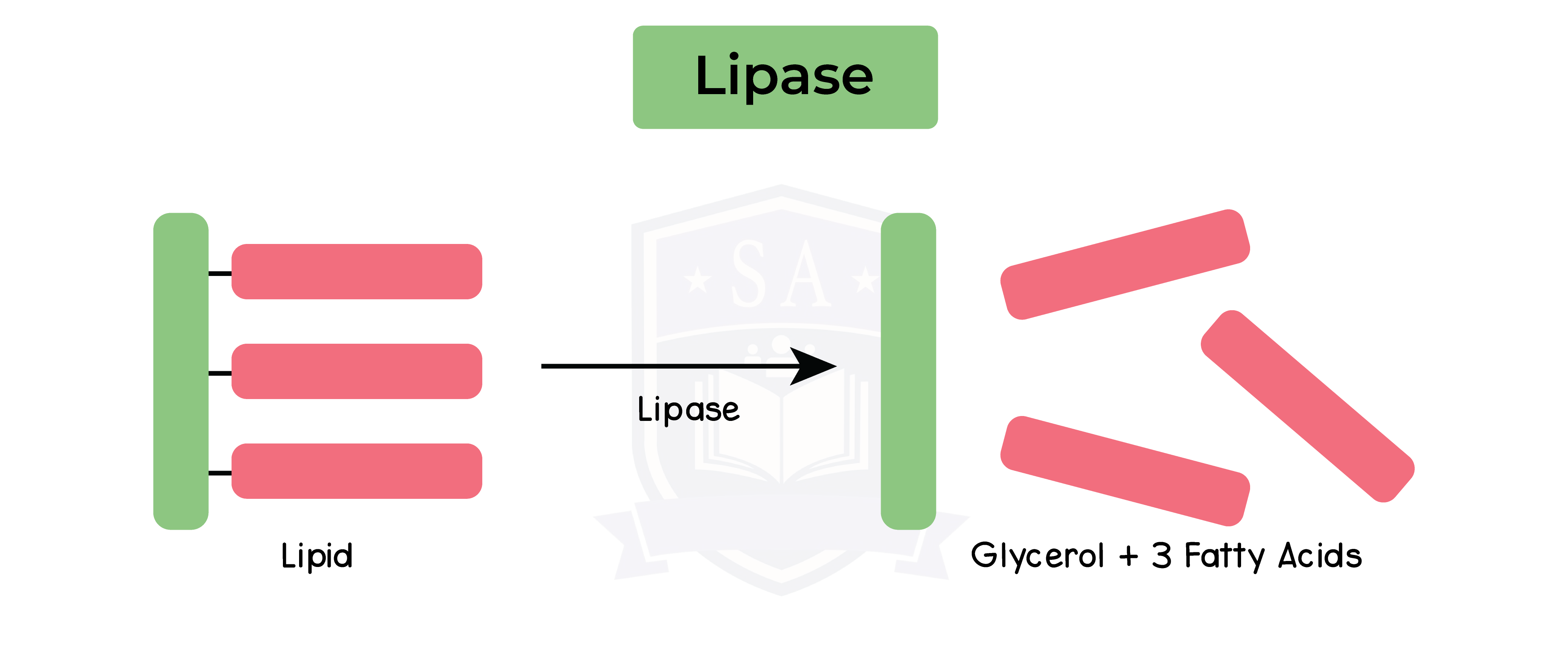
2.6.6 Understand the role of digestive enzymes, including the digestion of starch to glucose by amylase and maltase, the digestion of proteins to amino acids by proteases and the digestion of lipids to fatty acids and glycerol by lipases
Carbohydrases:
Proteases:
Lipases:

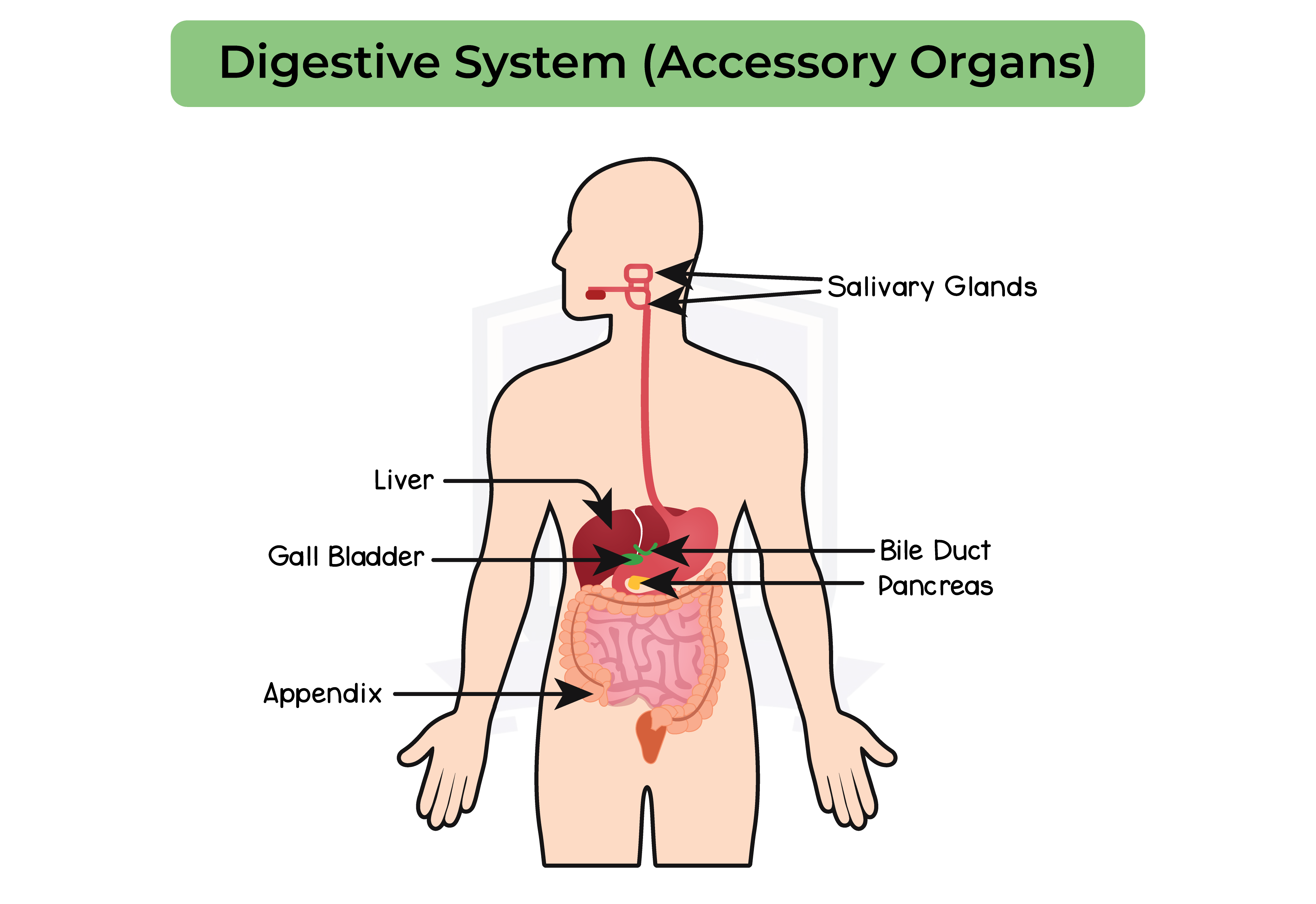
2.6.7 Understand that bile is produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder
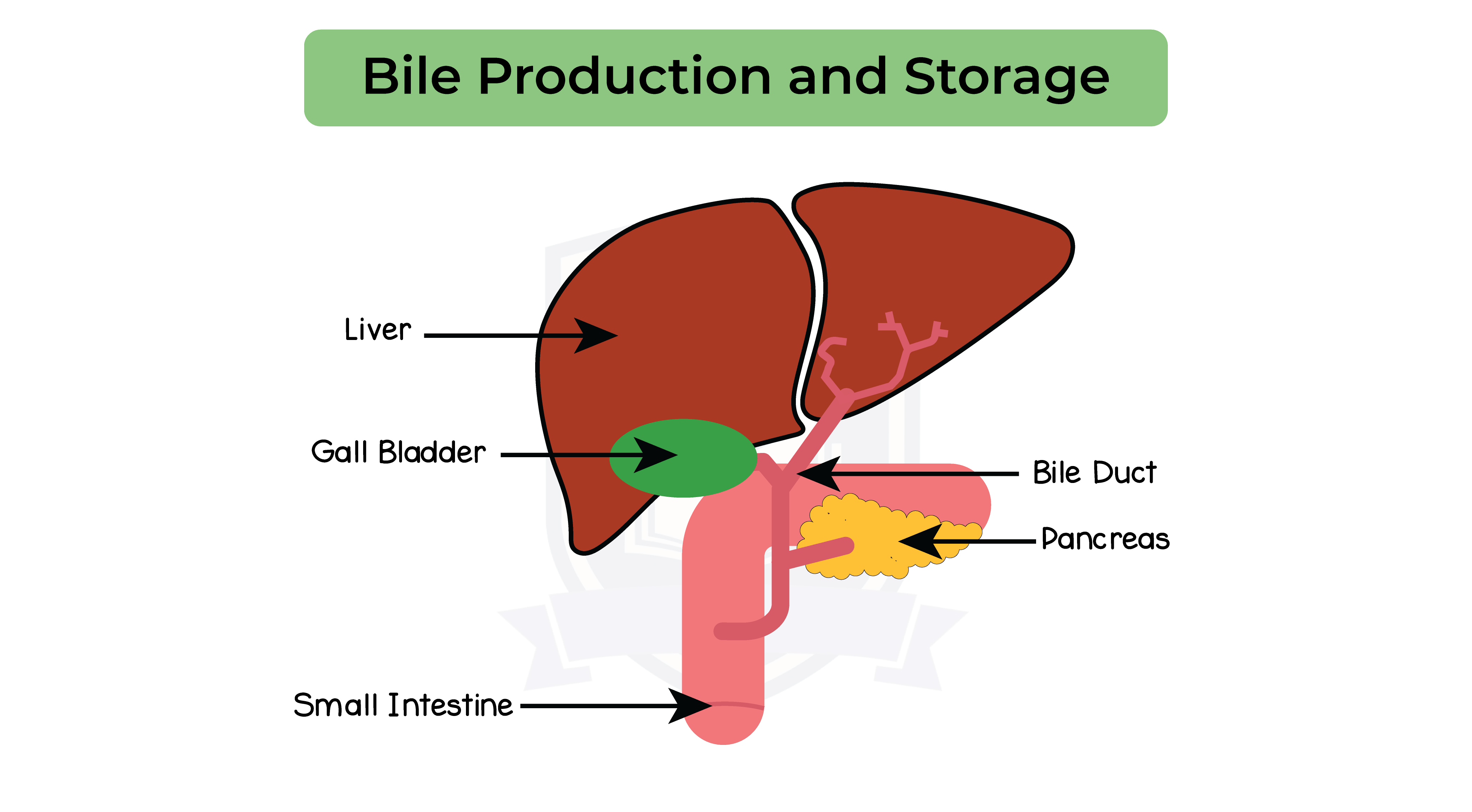
2.6.8 Understand the role of bile in neutralising stomach acid and emulsifying lipids
Role of bile
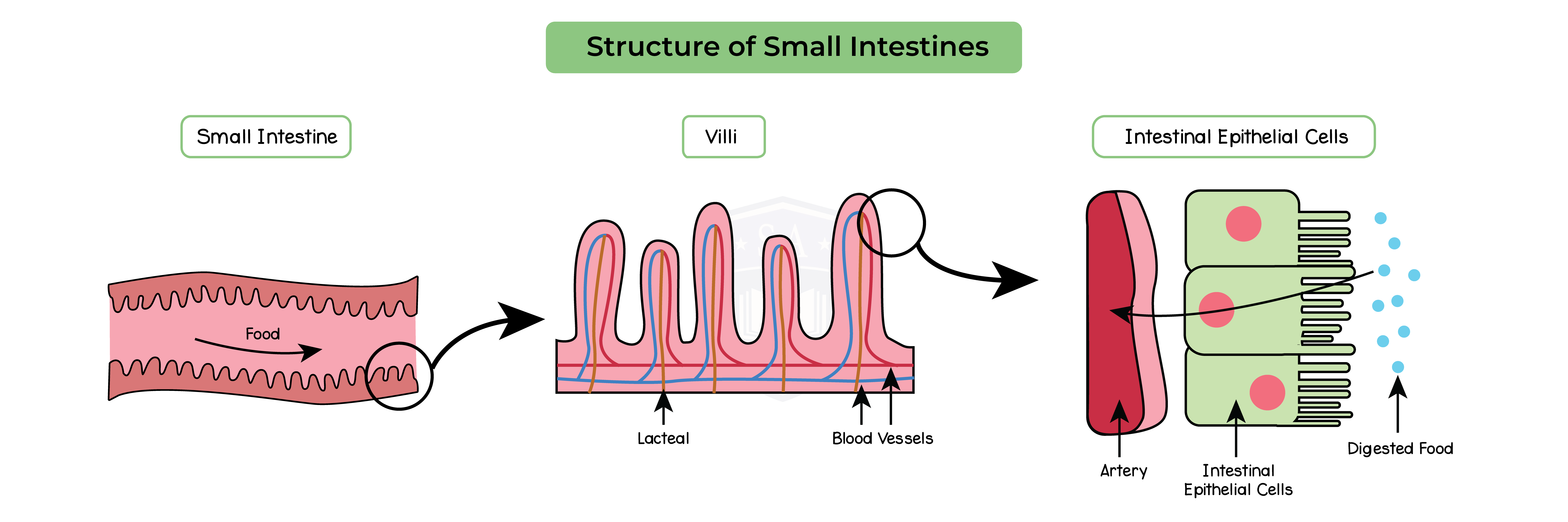
2.6.9 Understand how the small intestine is adapted for absorption, including the structure of a villus
Absorption:
Adaptations of small intestines:
Structure of villi:
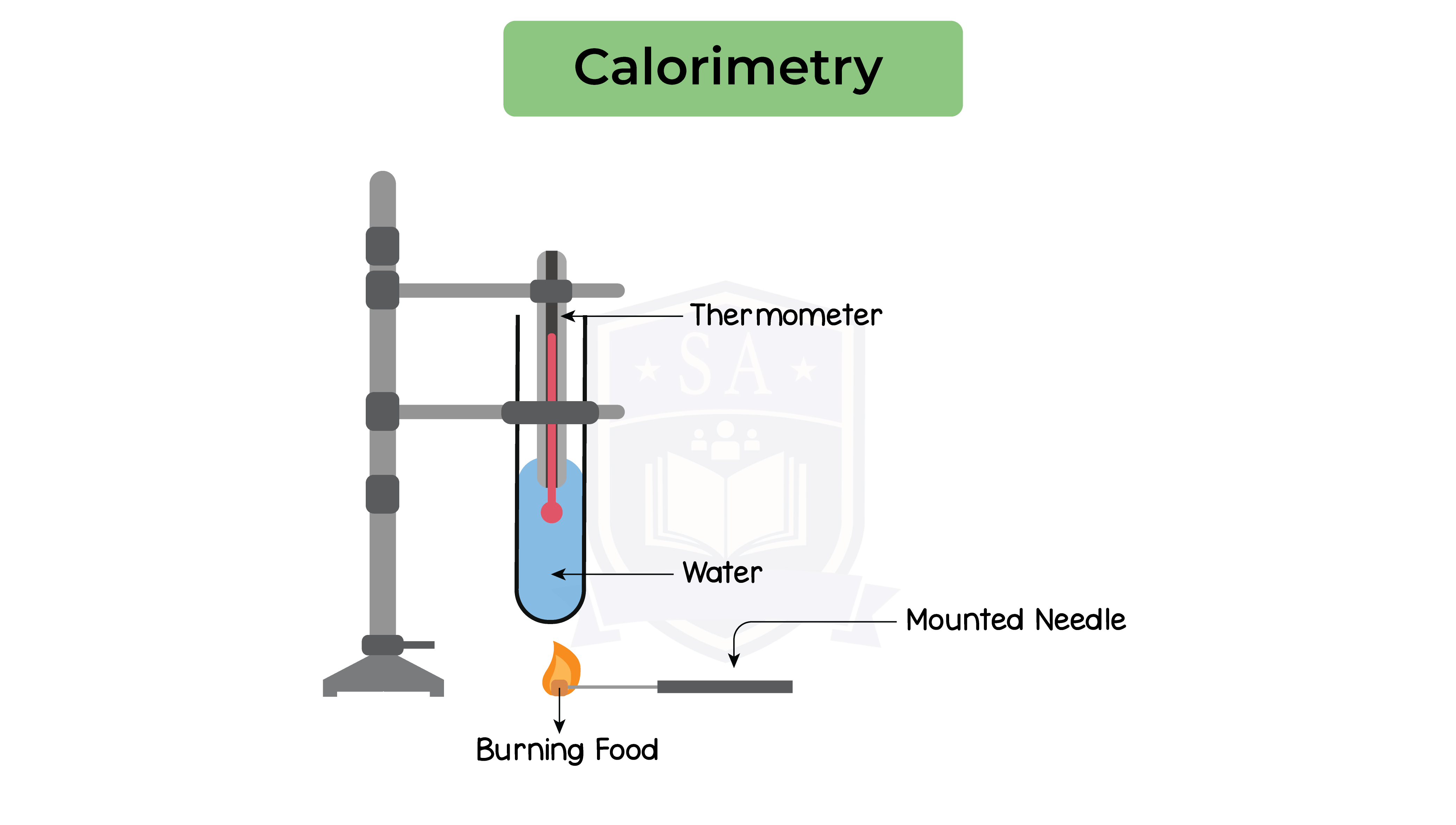
2.6.10B Practical: investigate the energy content in a food sample
Method:
Results
Energy transferred (J) =
(mass of water (g) x 4.2 x temperature increase (°C)) ÷ (mass of food (g))

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.