REVISION NOTES
2.15.1 Understand how organisms are able to respond to changes in their environment
Response to change:
2.15.2 Understand that homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment, and that body water content and body temperature are both examples of homeostasis
Homeostasis:
2.15.3 Understand that a co-ordinated response requires a stimulus, a receptor and an effector
Automatic control:
2.15.4 Understand that plants respond to stimuli
Plants can respond to changes in environment for survival
2.15.5 Describe the geotropic and phototropic responses of roots and stems
Tropism:
Directional growth responses made by plants in response to light and gravity
2.15.6 Understand the role of auxin in the phototropic response of stems
Auxins:
Distribution of auxins:
2.15.7 Describe how nervous and hormonal communication control responses and understand the differences between the two systems
Human control system:
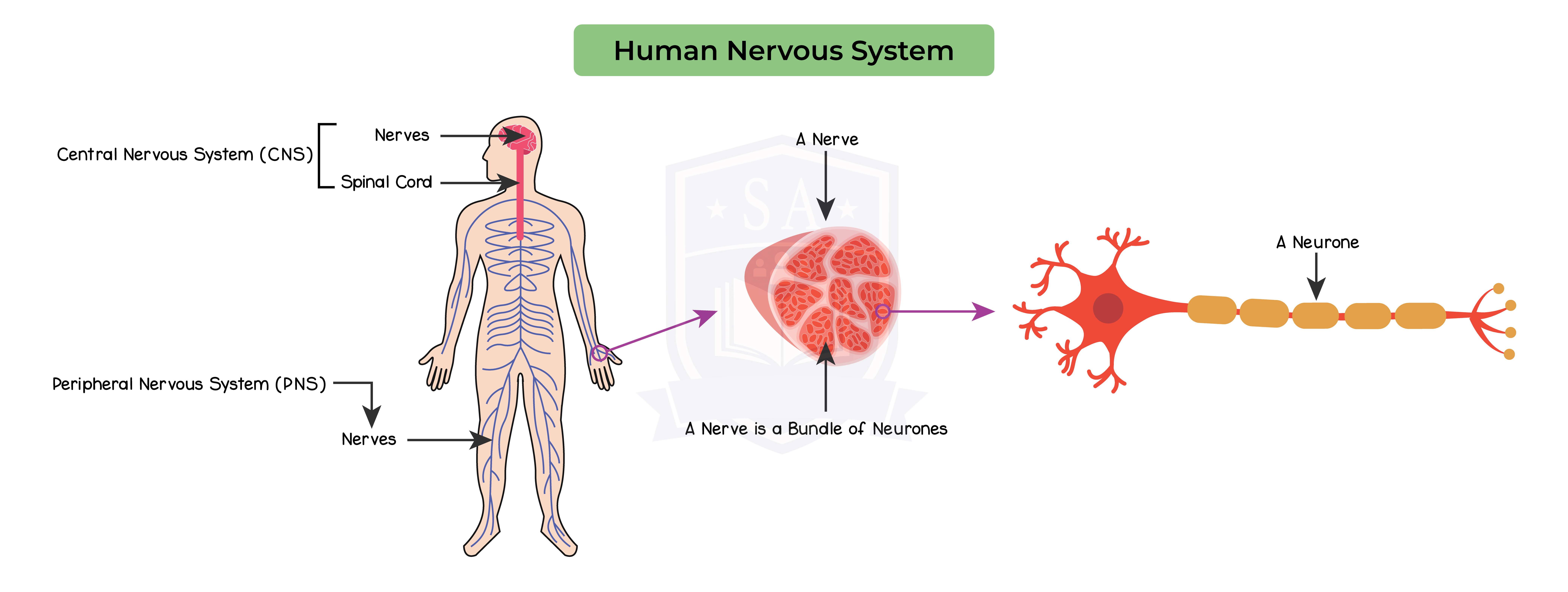
Human nervous system:
2.15.8 Understand that the central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord and is linked to sense organs by nerves
The human nervous system consists of:

2.15.9 Understand that stimulation of receptors in the sense organs sends electrical impulses along nerves into and out of the central nervous system, resulting in rapid responses
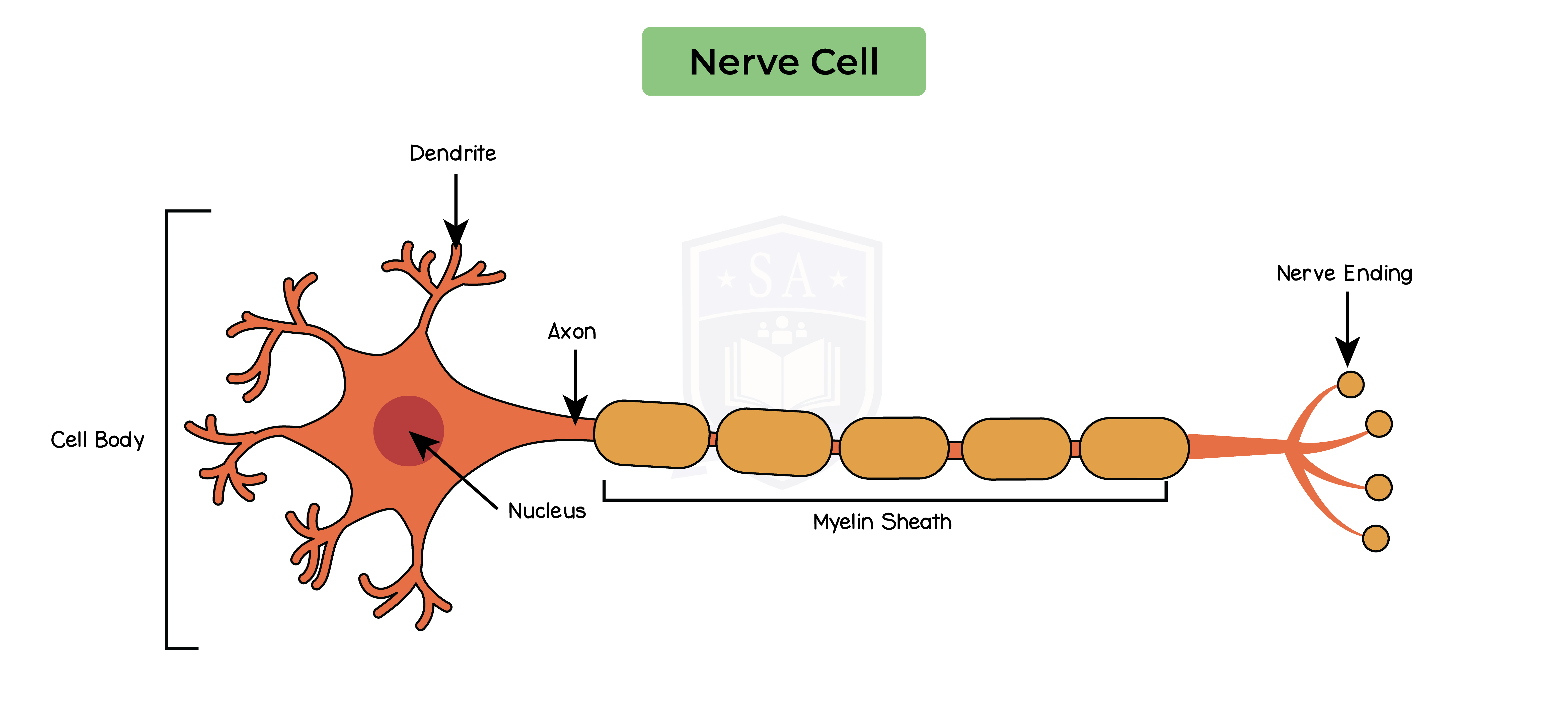
Neurons:
Adaptation of neurons:
Three main types of neurons:
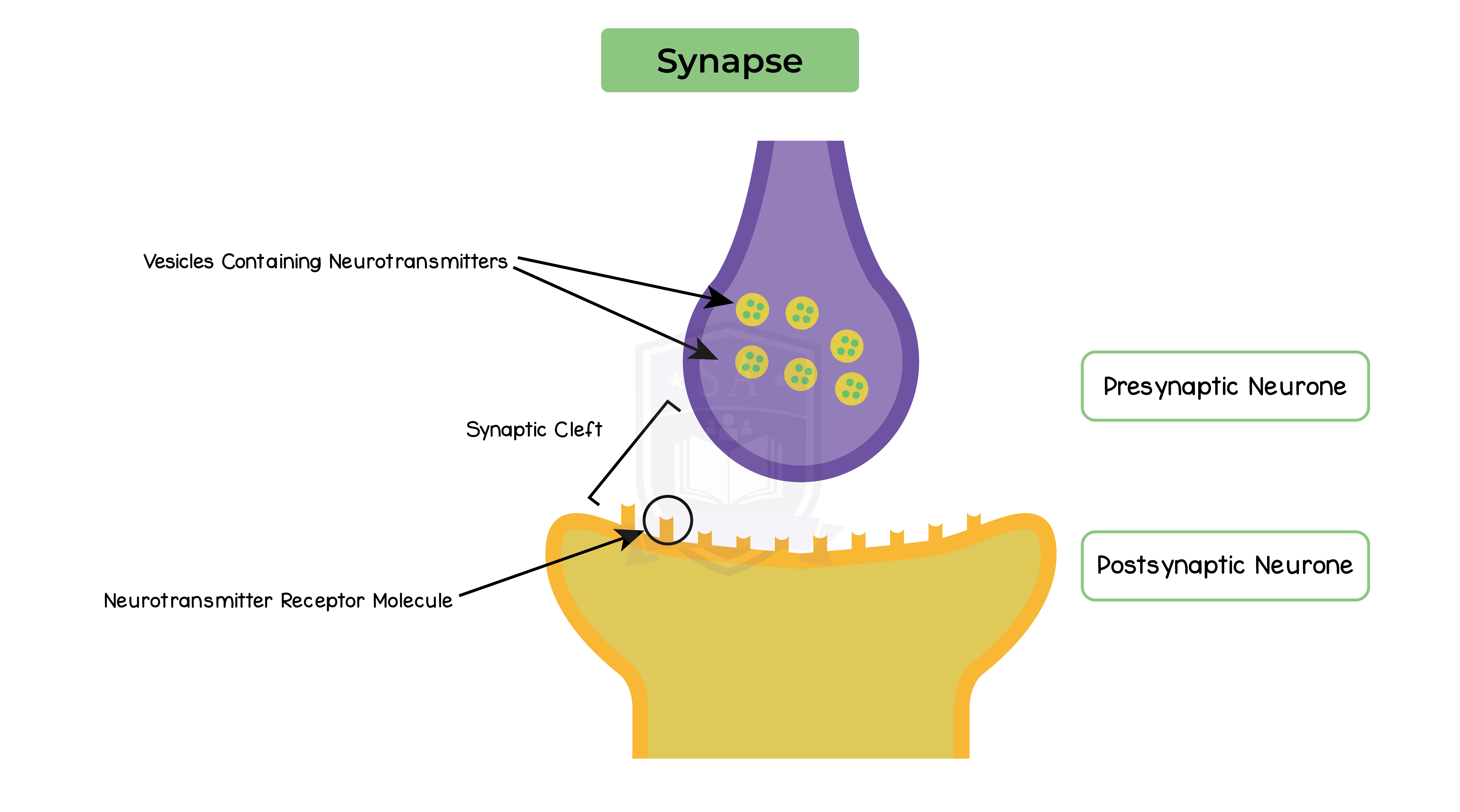
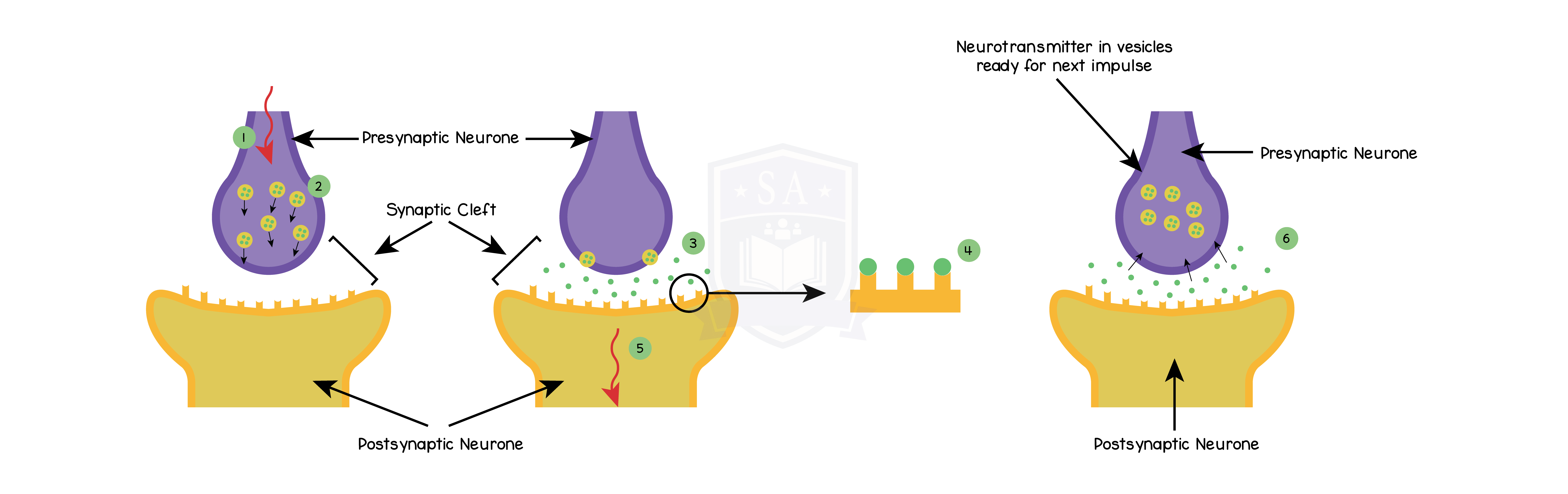
2.15.10 Understand the role of neurotransmitters at synapses
Synapse:
Role of neurotransmitters:
Since the chemical transmitter is only produced on one side of the synapse, it ensures that impulses travel in one direction through the nervous system.
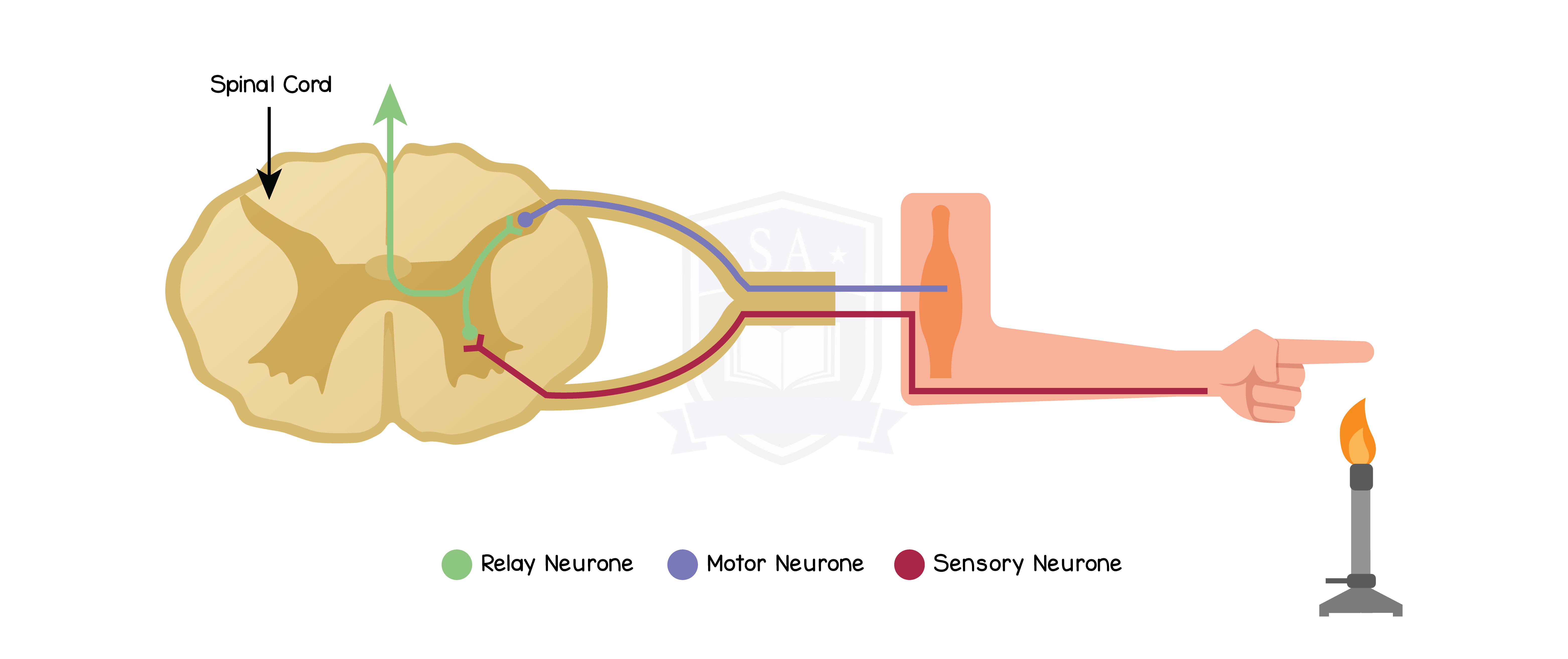
2.15.11 Describe the structure and functioning of a simple reflex arc illustrated by the withdrawal of a finger from a hot object
Reflex reaction:
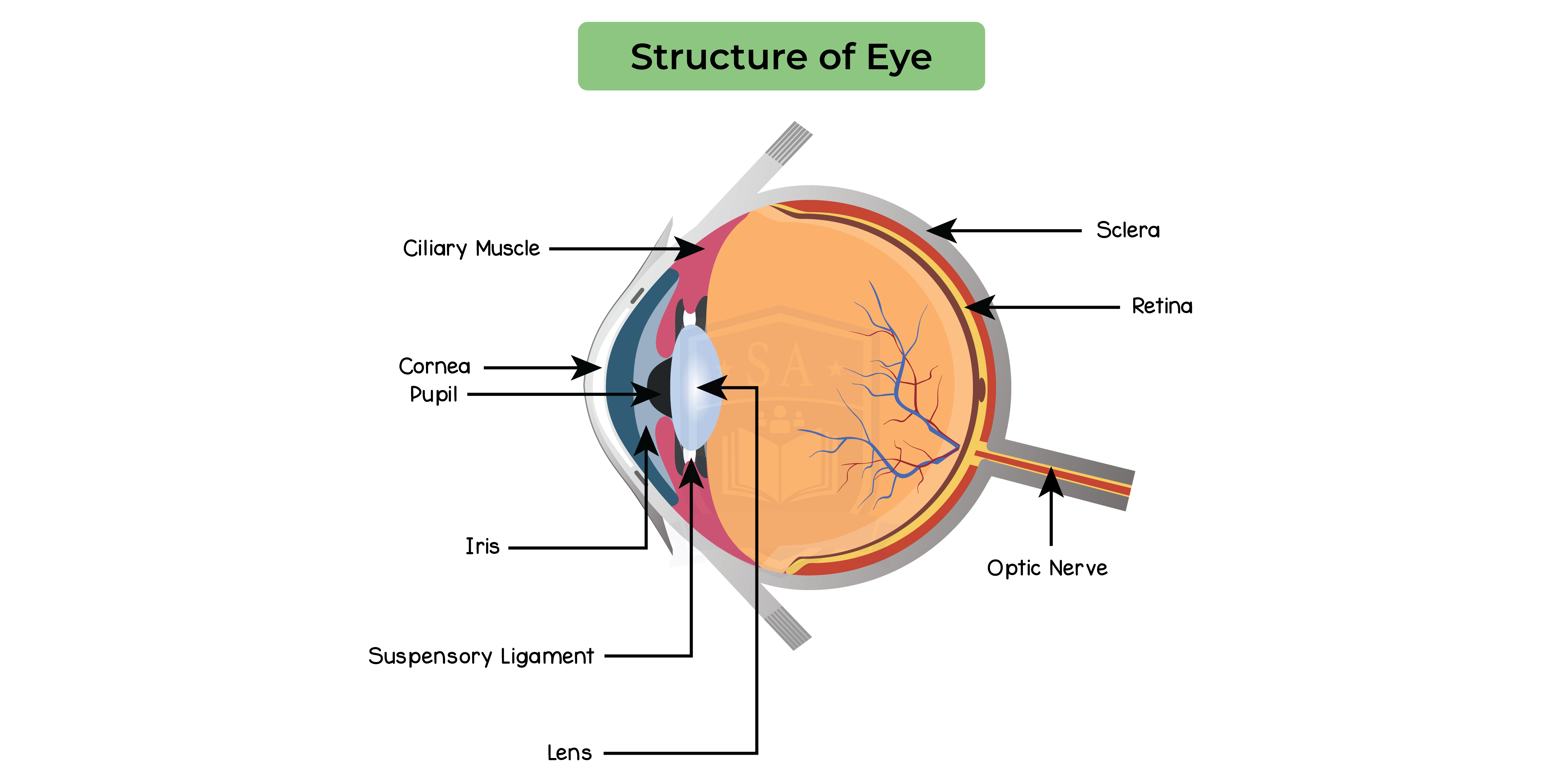
2.15.12 Describe the structure and function of the eye as a receptor
The eye is a highly specialised sense organ containing receptor cells that allow us to detect the stimulus of light
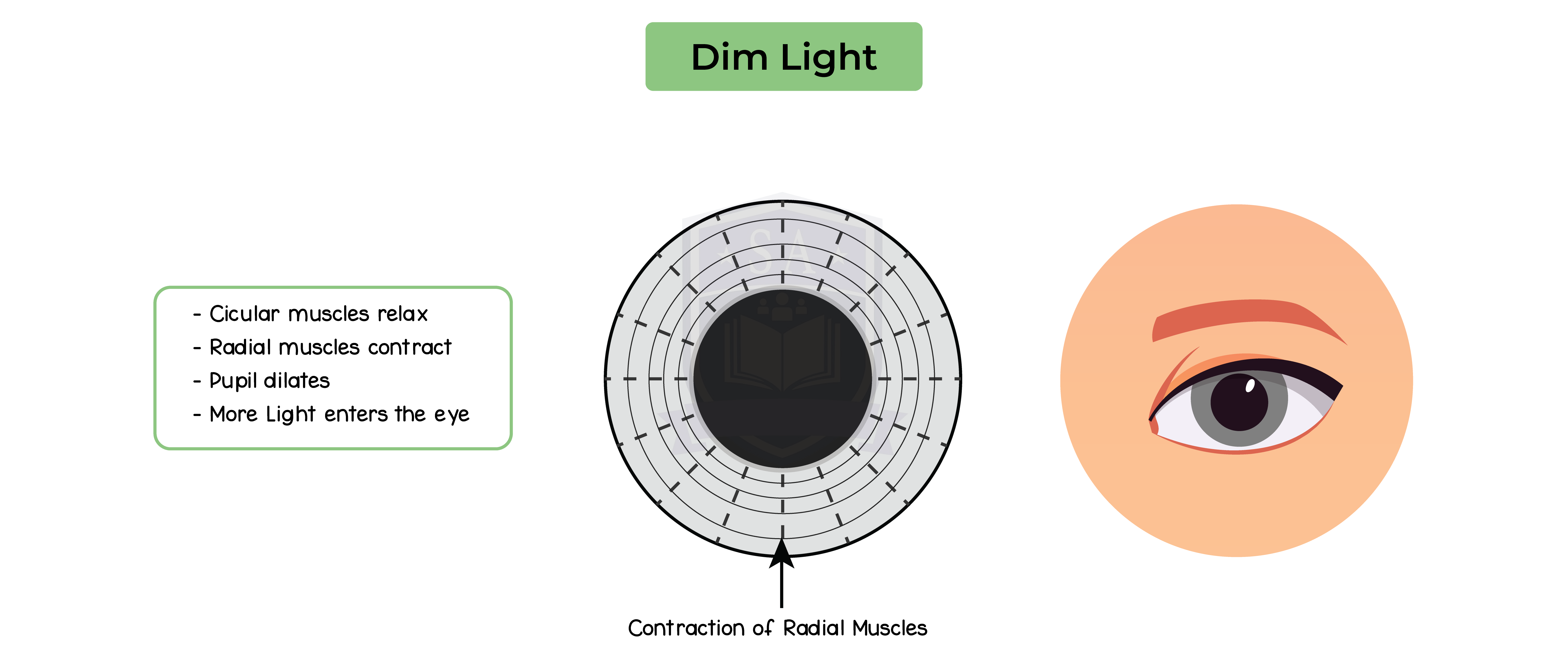
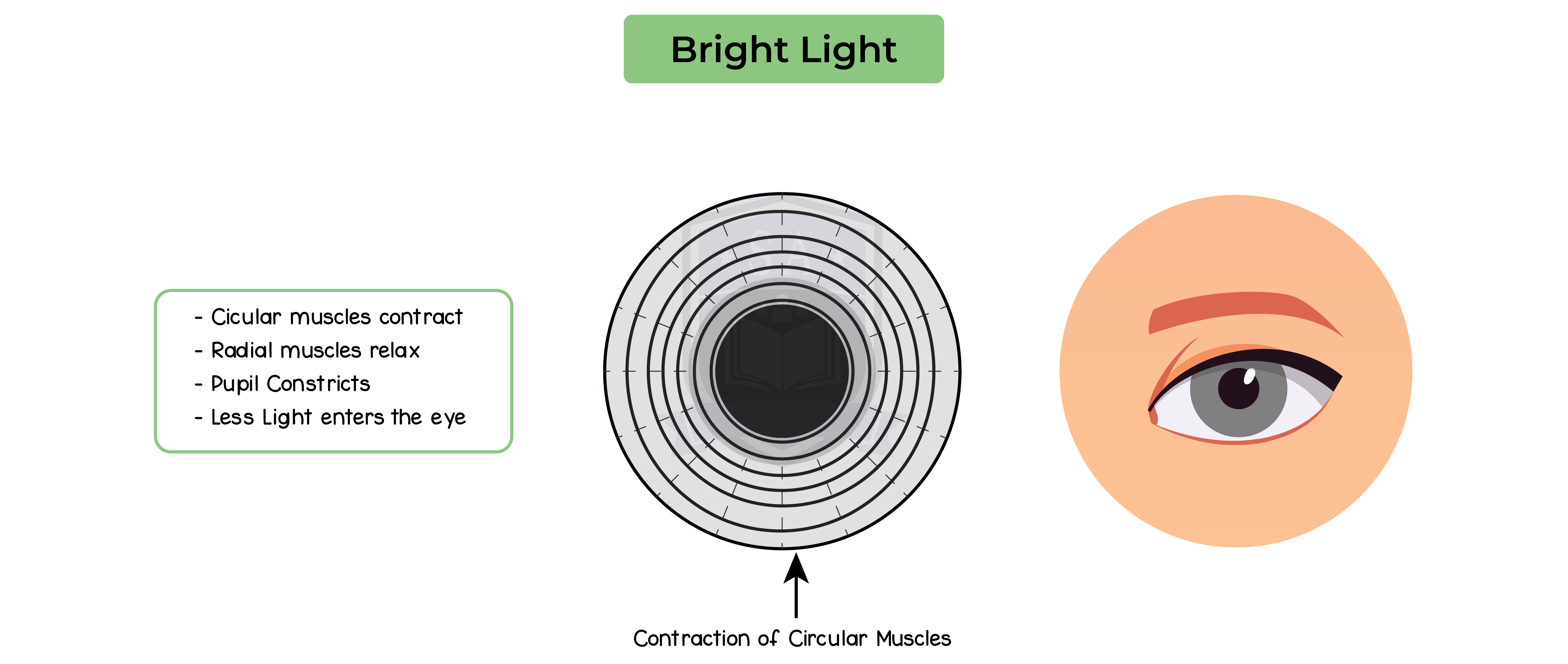
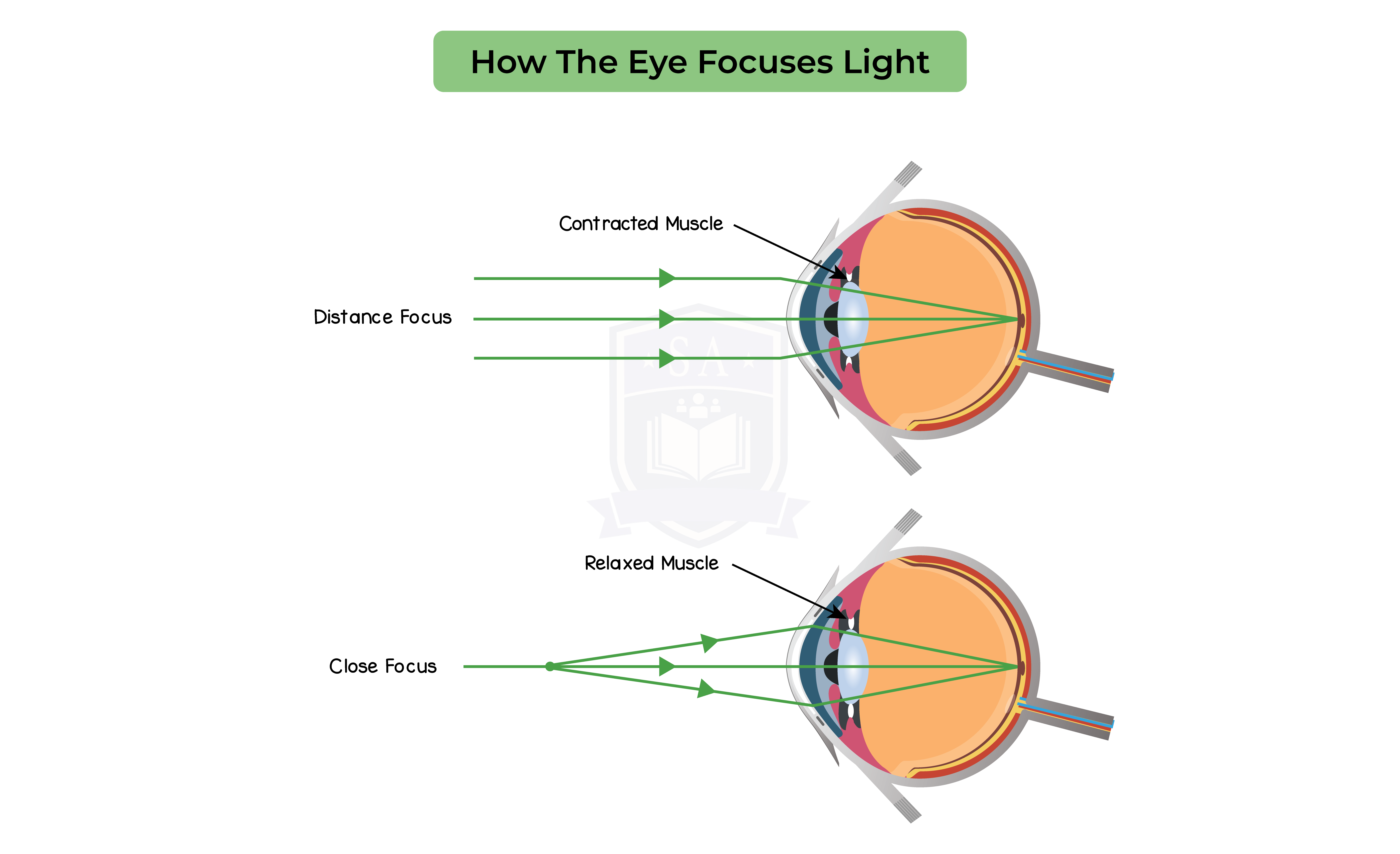
2.15.13 Understand the function of the eye in focusing on near and distant objects, and in responding to changes in light intensity
The function of the eye in focusing on near and distant objects
The pupil reflex:
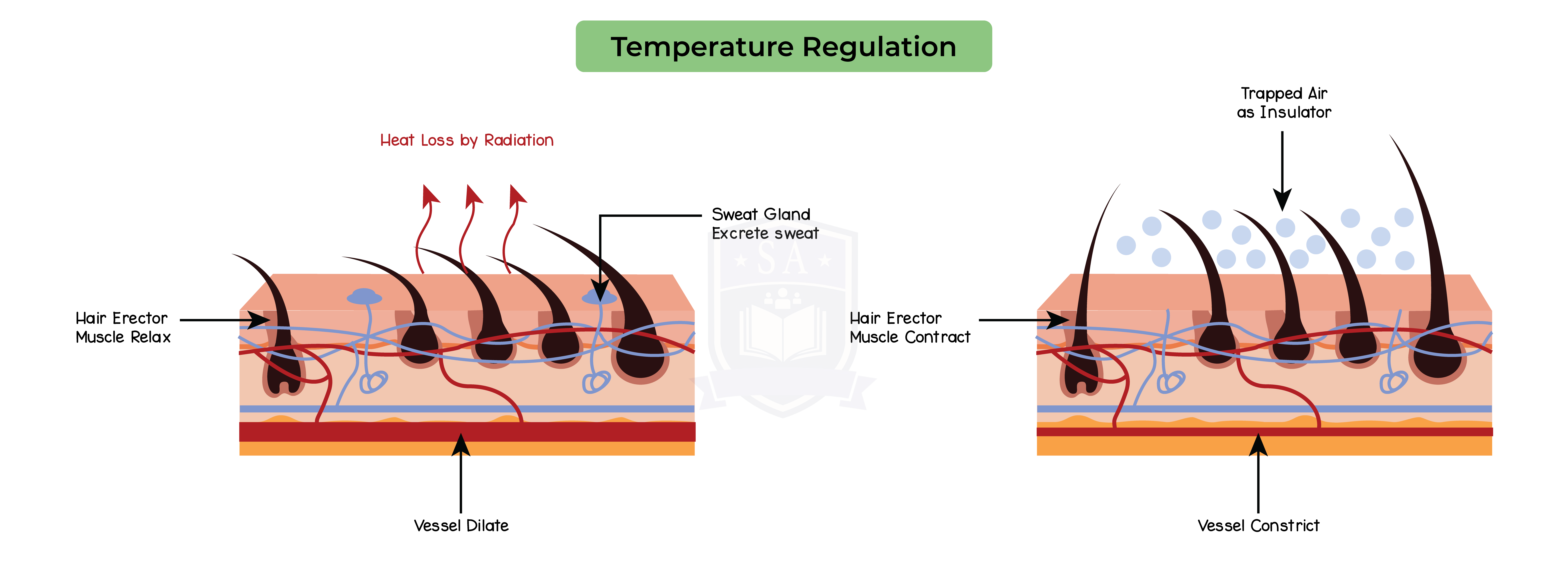
2.15.14 Describe the role of the skin in temperature regulation, with reference to sweating, vasoconstriction and vasodilation
Skin:
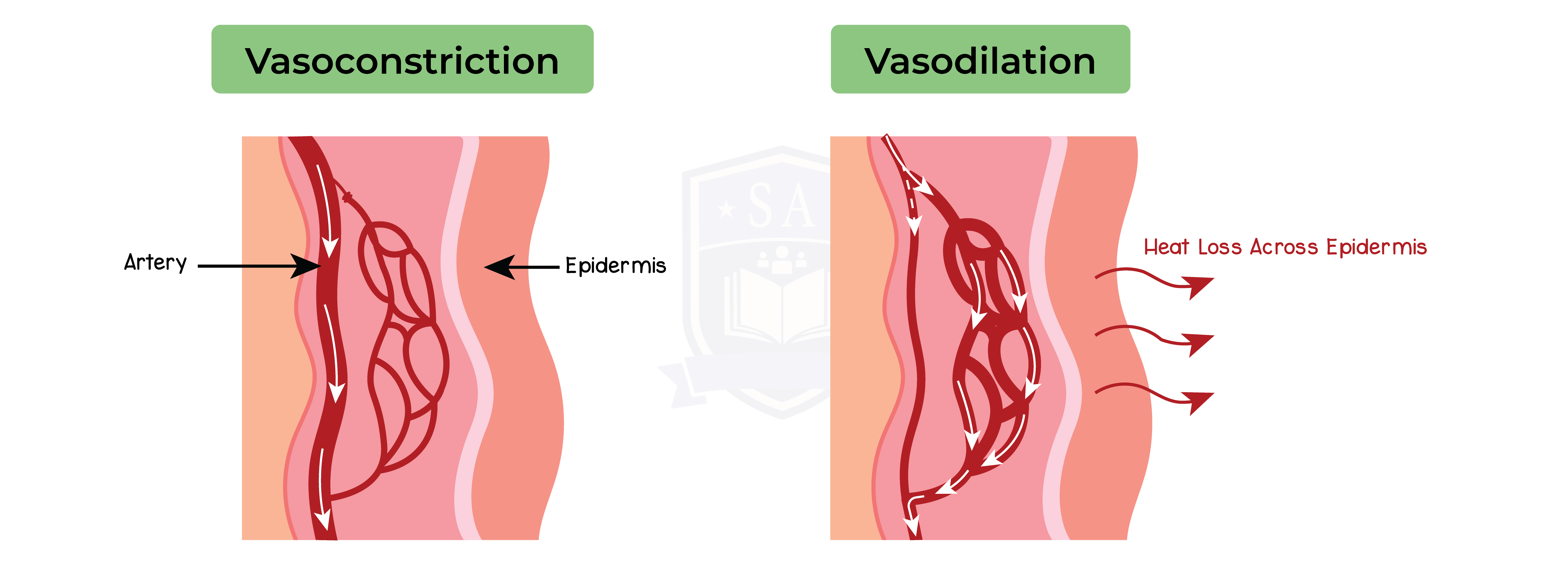
Vasoconstriction:
Vasodilation:
2.15.15 Understand the sources, roles and effects of the following hormones: adrenaline, insulin, testosterone, progesterone and oestrogen
2.15.16B Understand the sources, roles and effects of the following hormones: ADH, FSH and LH

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.