REVISION NOTES
2.12.1 Understand the origin of carbon dioxide and oxygen as waste products of metabolism and their loss from the stomata of a leaf
Excretion:
Waste products of metabolism in a plant:
2.12.2 Know the excretory products of the lungs, kidneys and skin (organs of excretion)
Excretion in humans:
Skin excretes excess mineral ions and water through sweat
2.12.3B Understand how the kidney carries out its roles of excretion and Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation
dehydrating effect and cell death
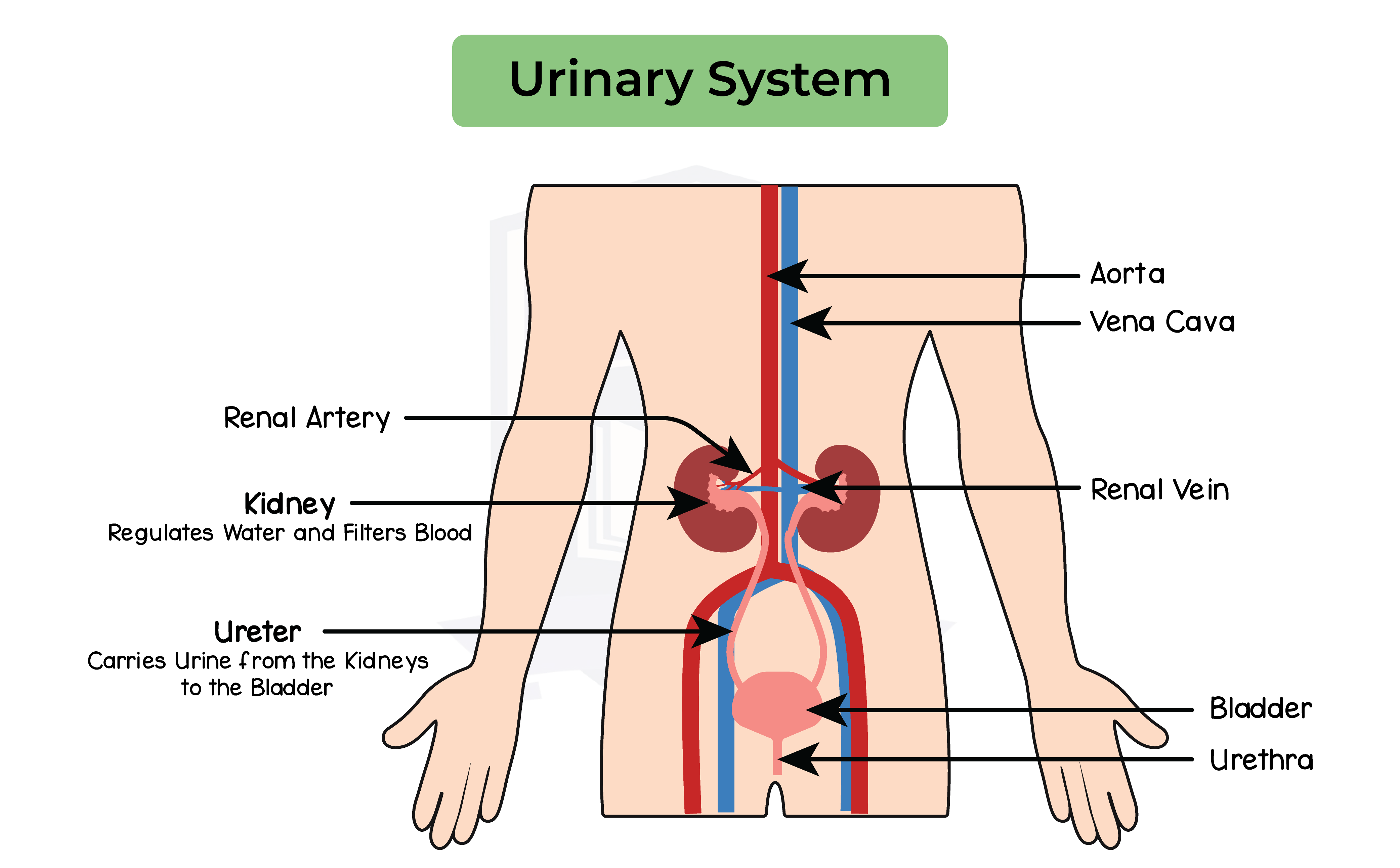
2.12.4B Describe the structure of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra
Urinary system:
Structure of urinary system:
Structure of kidney:
Urine is collected before being transported to the bladder by the ureter for storage
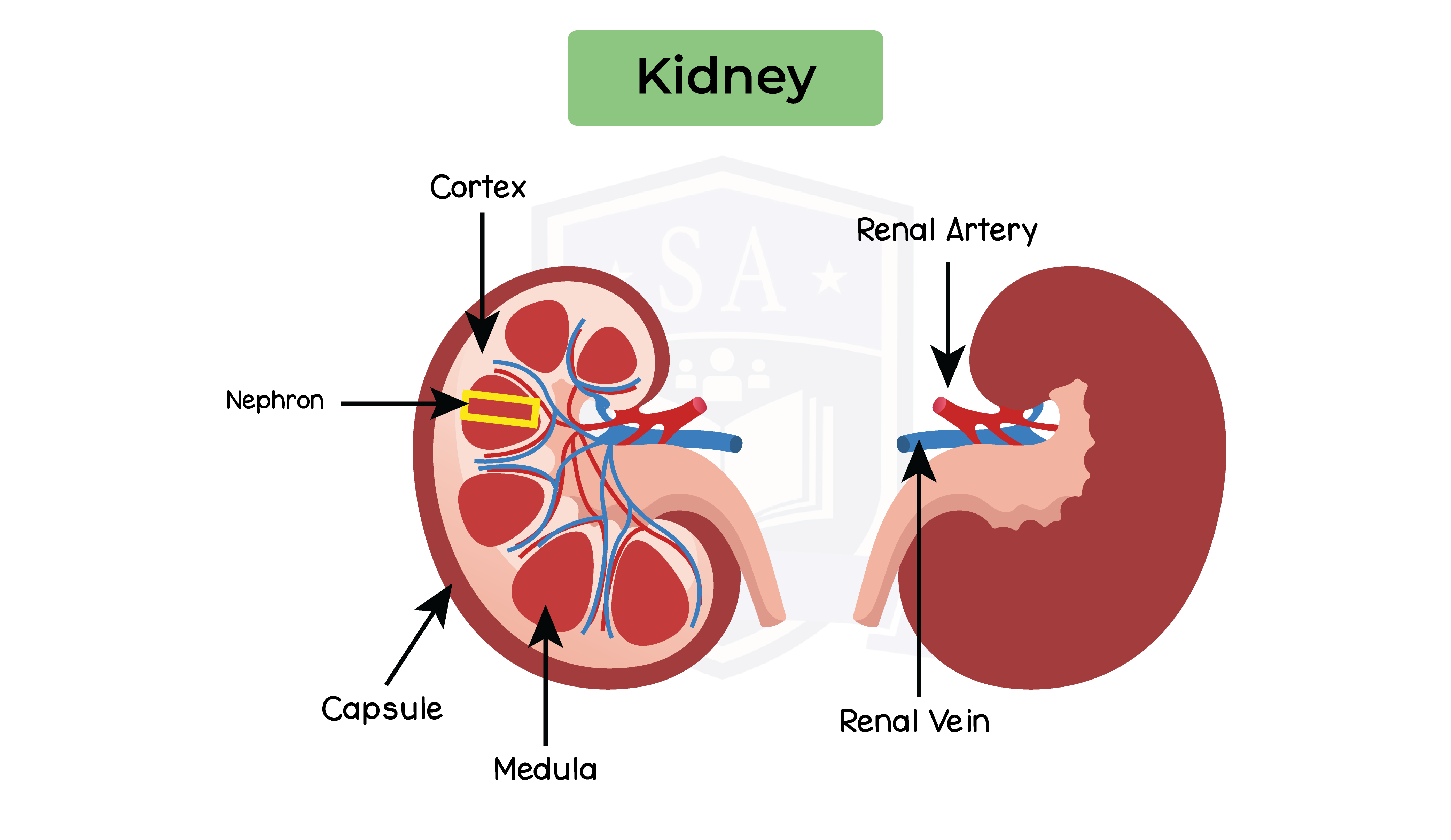
2.12.5B Describe the structure of a nephron, including:
Structure of nephron:
2.12.6B Describe ultrafiltration in the Bowman’s capsule and the composition of the glomerular filtrate
Ultrafiltration:
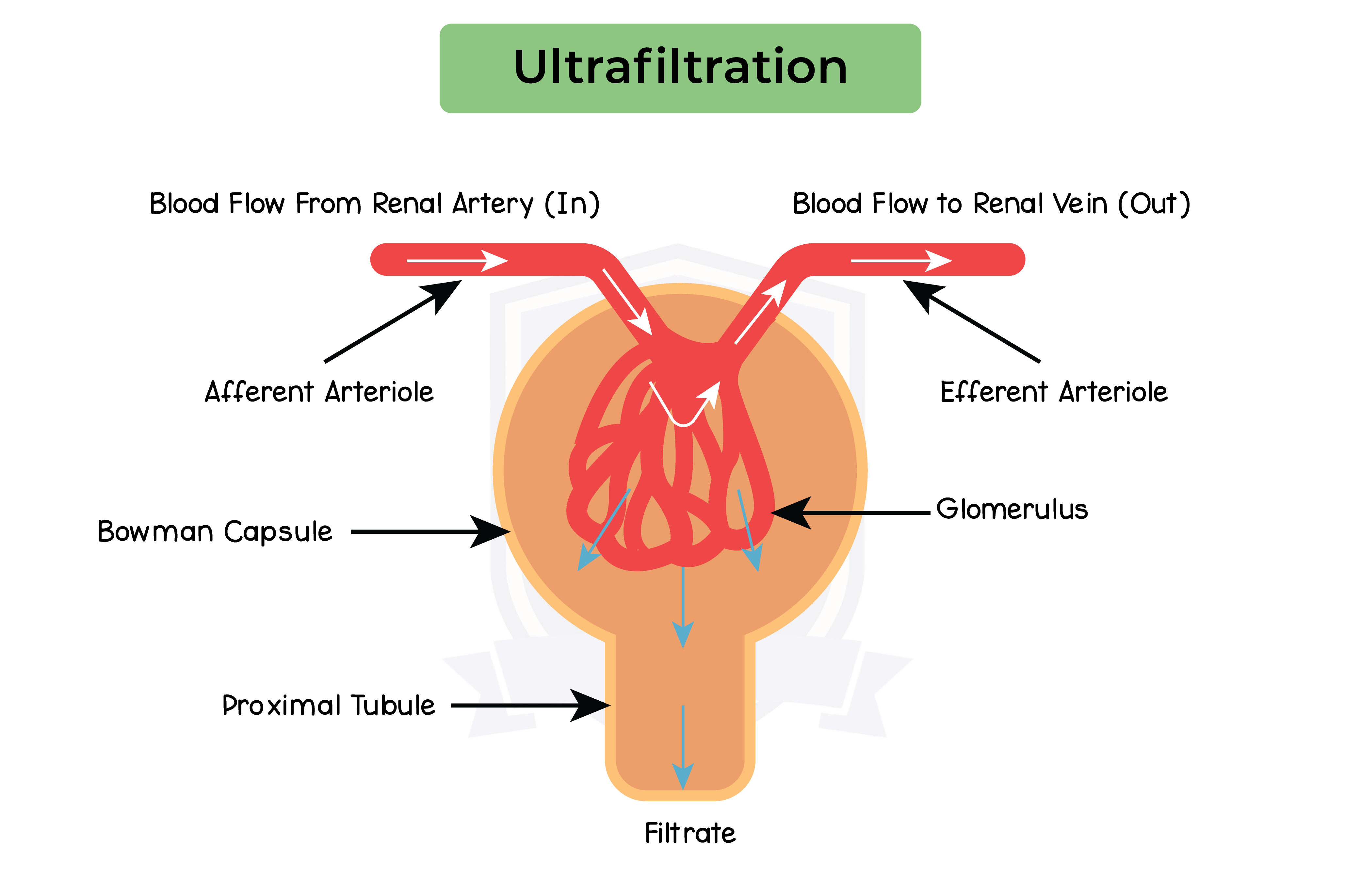
2.12.7B Understand how water is reabsorbed into the blood from the collecting duct
Water reabsorption:
2.12.8B Understand why selective reabsorption of glucose occurs at the proximal convoluted tubule
Glucose reabsorption:
2.12.9B Describe the role of ADH in regulating the water content of the blood
Role of ADH:
2.12.10B Understand that urine contains water, urea and ions
Urine content:
Changes in concentration of urine:
The more sweat lost in exercise, the more water is lost overall so more concentrated urine will be produced

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.