REVISION NOTES
2.11.1 Understand why simple, unicellular organisms can rely on diffusion for movement of substances in and out of the cell
Unicellular organisms:
2.11.2 Understand the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms
Multicellular organisms:
2.11.3 Describe the role of phloem in transporting sucrose and amino acids between the leaves and other parts of the plant
Phloem function:
Phloem structure:
2.11.4 Describe the role of xylem in transporting water and mineral ions from the roots to other parts of the plant
Xylem function and structure:
2.11.5B understand how water is absorbed by root hair cells
Absorption of water by root hair cells:
DIAGRAM of word equation:
Root hair cell → root cortex cells → xylem → leaf mesophyll cell
Root hair cells adaptations for absorption:
2.11.6B Understand that transpiration is the evaporation of water from the surface of a plant
Transpiration:
Effect of transpiration:
2.11.7B Understand how the rate of transpiration is affected by changes in
Effect of humidity:
Effect of wind speed:
Effect of temperature:
Effect of light:
2.11.8B Practical: investigate the role of environmental factors in determining the rate of transpiration from a leafy shoot
Effect of light intensity practical:
Method:
Results:
2.11.9 Describe the composition of the blood: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma
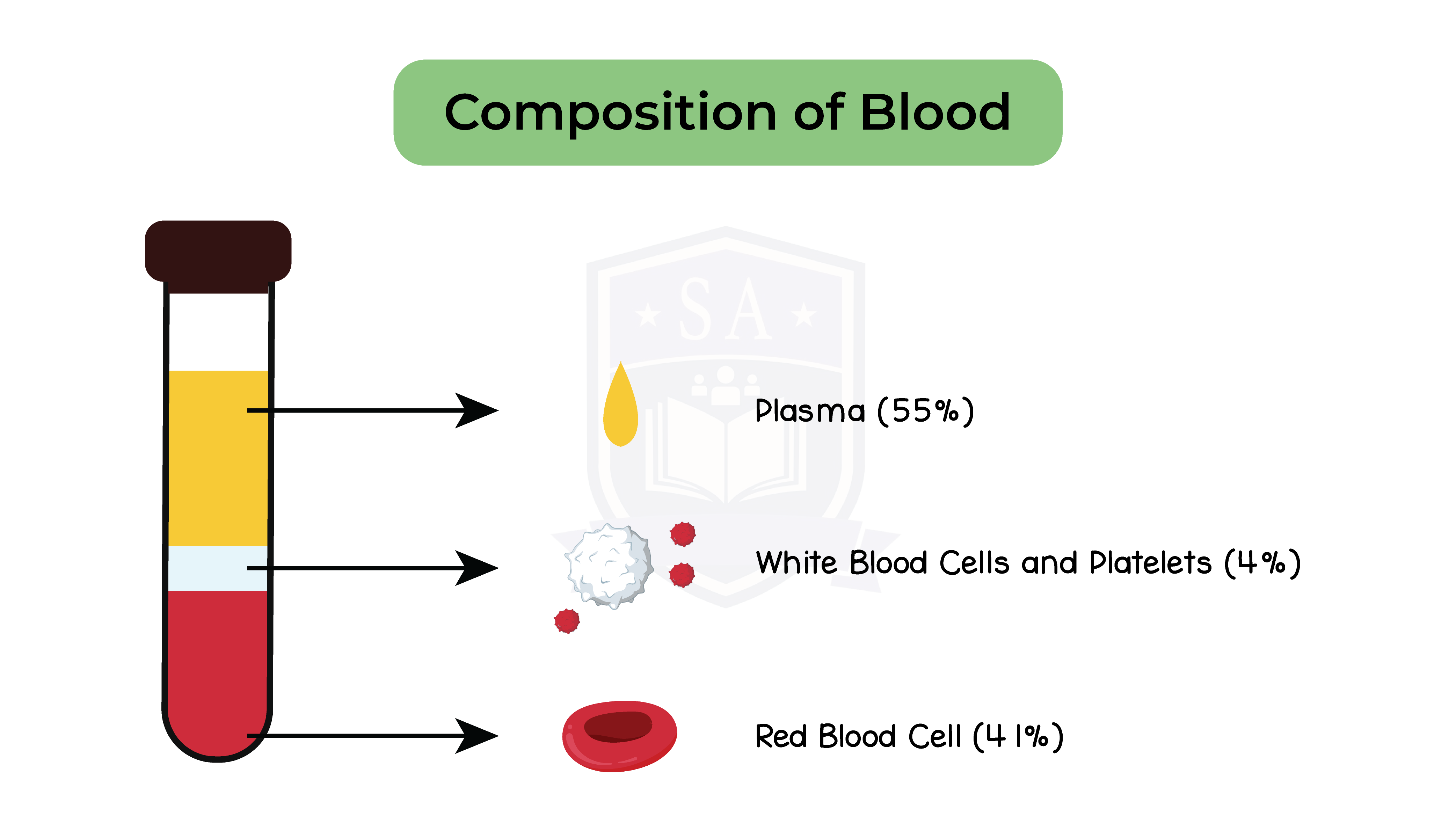
2.11.10 Understand the role of plasma in the transport of carbon dioxide, digested food, urea, hormones and heat energy
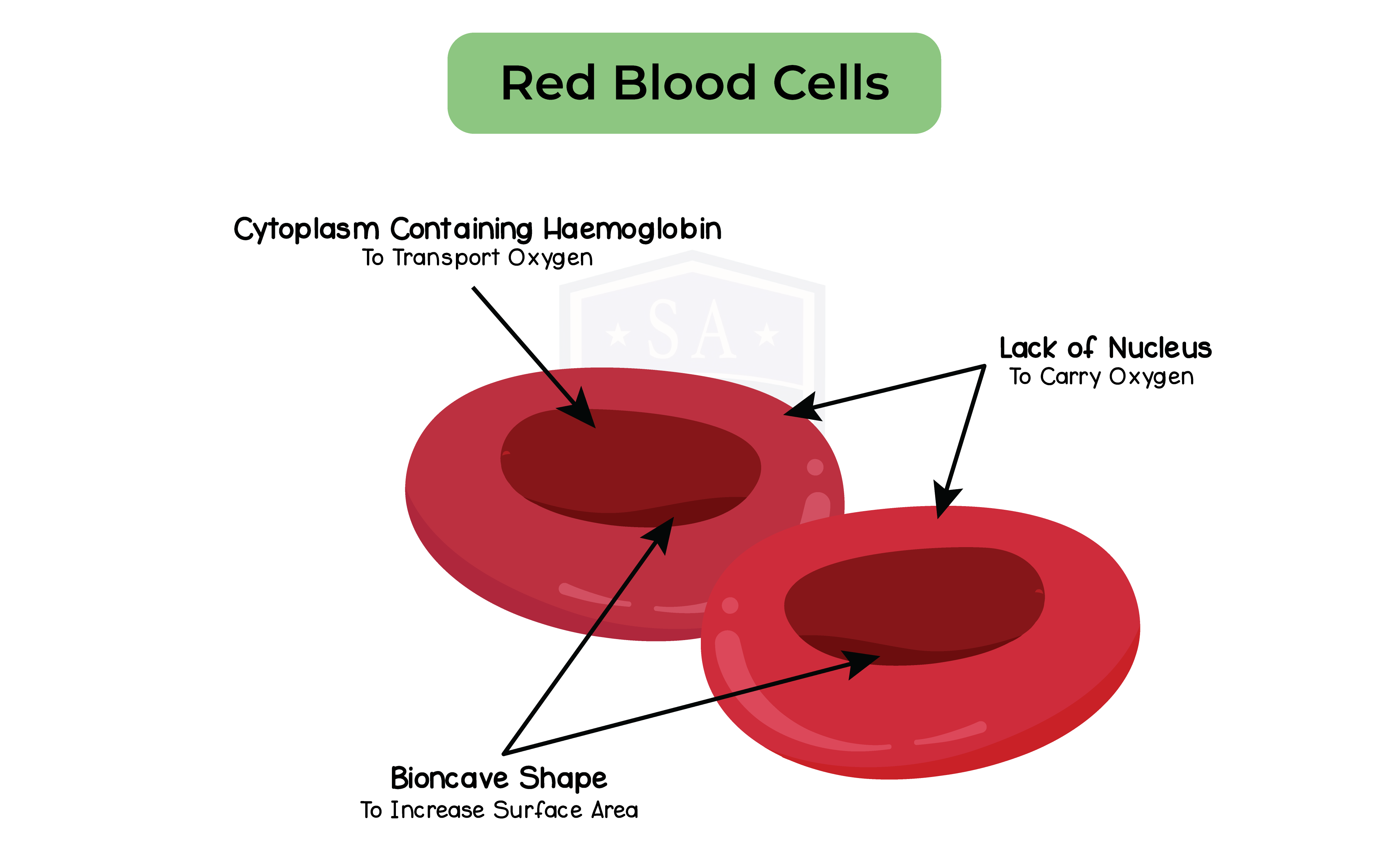
2.11.11 Understand how adaptations of red blood cells make them suitable for the transport of oxygen, including shape, the absence of a nucleus and the presence of haemoglobin
Adaptations of red blood cells
2.11.12 Understand how the immune system responds to disease using white blood cells, illustrated by phagocytes ingesting pathogens and lymphocytes releasing antibodies specific to the pathogen
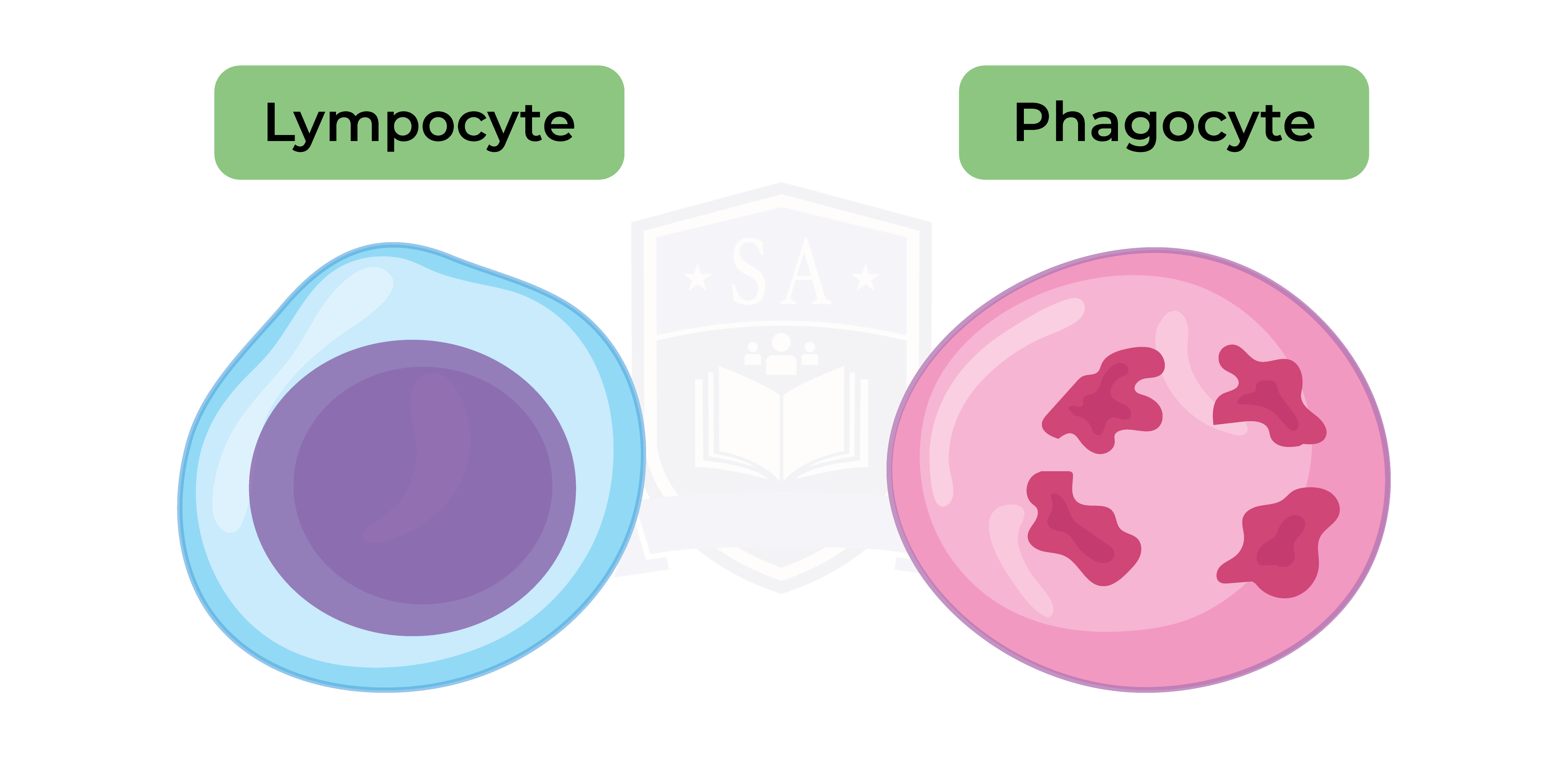
White blood cells
Phagocytes
Phagocytes can be recognised by their multi-lobed nucleus and their granular cytoplasm.
Lymphocytes
Agglutination
Response to infection
2.11.13B Understand how vaccination results in the manufacture of memory cells, which enable future antibody production to the pathogen to occur sooner, faster and in greater quantity
Vaccines:
How vaccines work:
Future infection by the same pathogen will trigger a response that is much faster and much larger compared to the initial response
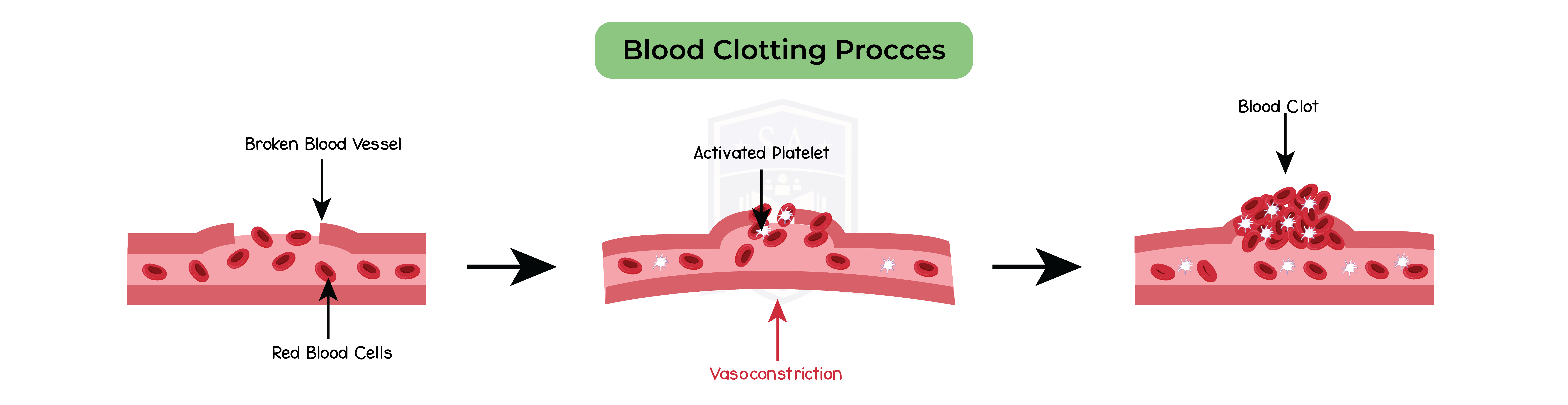
2.11.14B Understand how platelets are involved in blood clotting, which prevents blood loss and the entry of micro-organisms
Platelets:
How it works:
Importance of blood clotting:
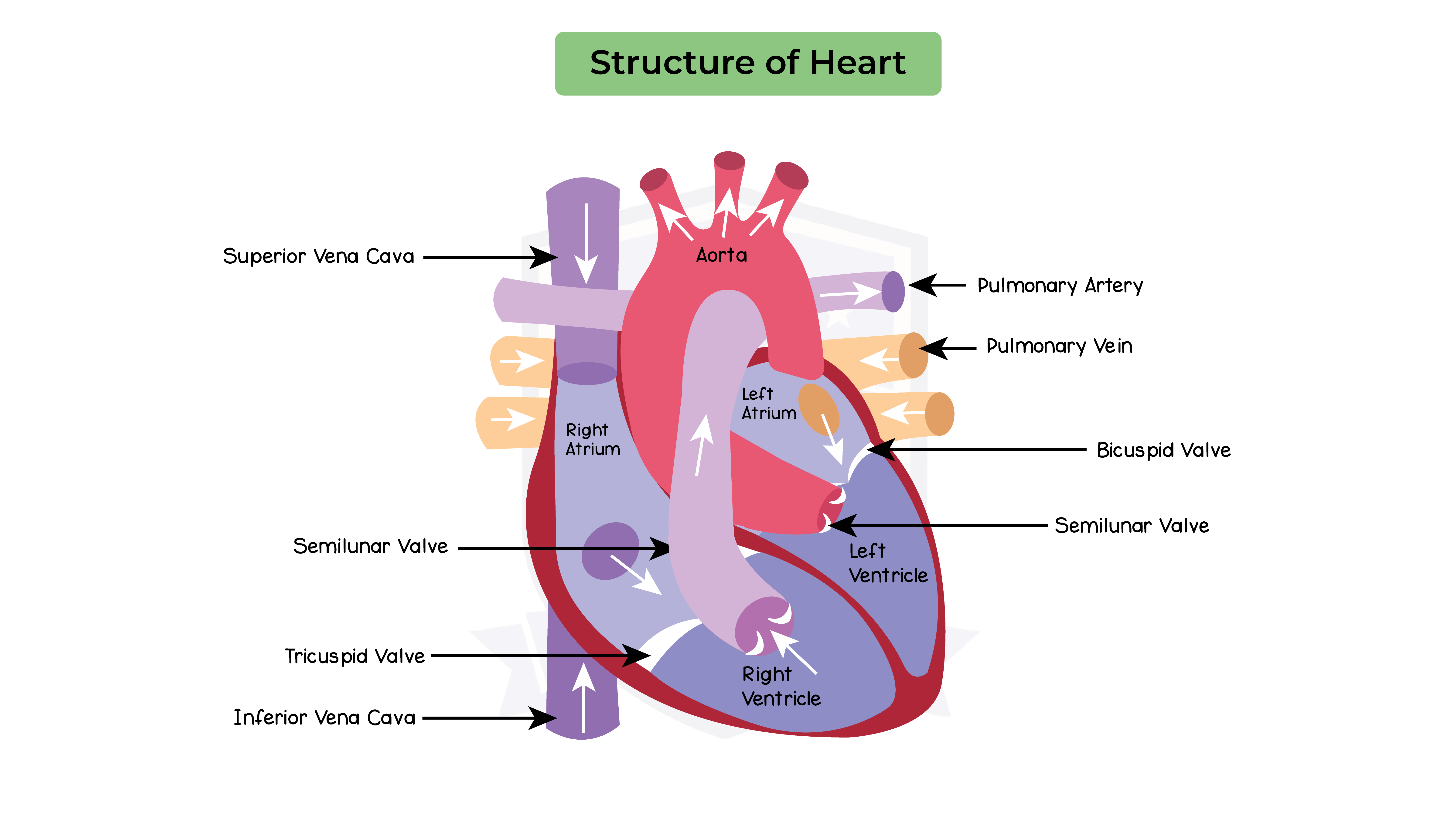
2.11.15 Describe the structure of the heart and how it functions
Structure of the heart:
Pathway of blood through the heart:
2.11.16 Explain how the heart rate changes during exercise and under the influence of adrenaline
Heart rate:
Heart rate during
Heart rate after exercise:
2.11.17 Understand how factors may increase the risk of developing coronary heart disease
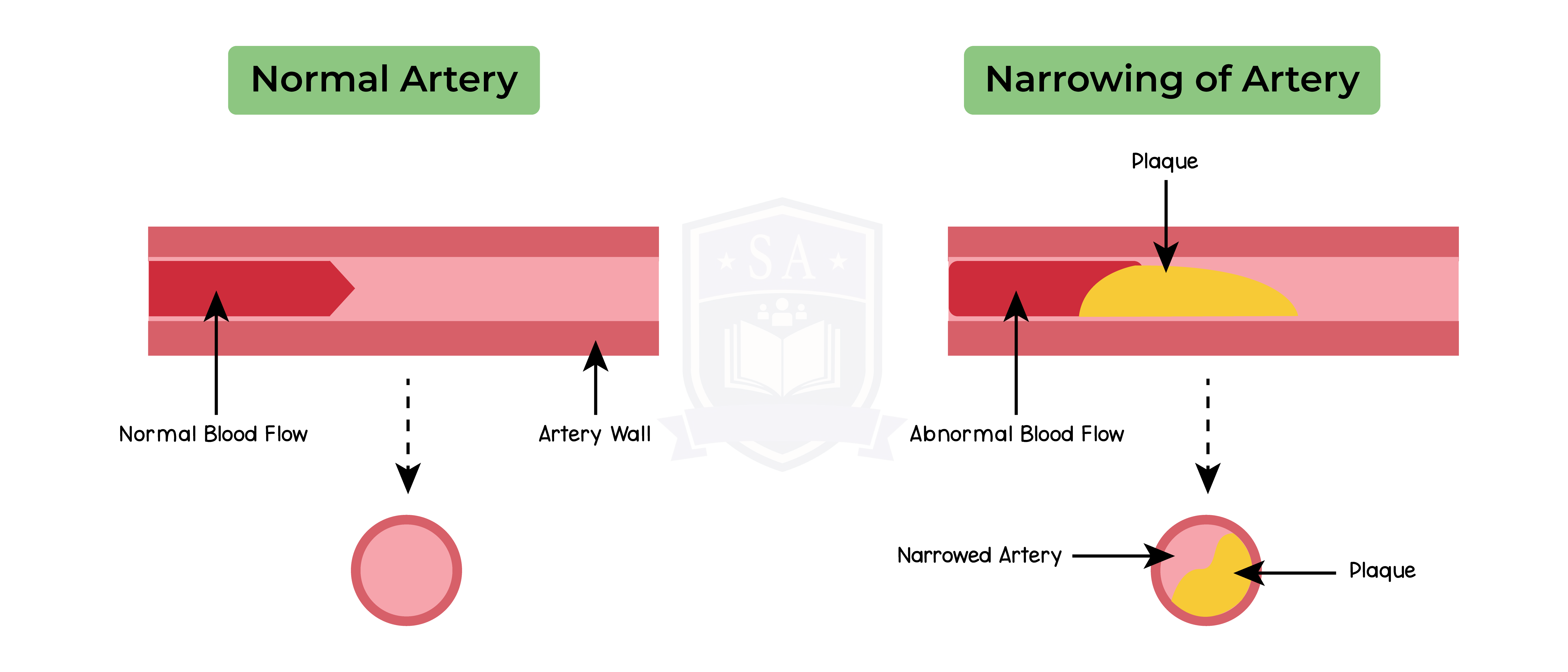
2.11.18 Understand how the structure of arteries, veins and capillaries relate to their function

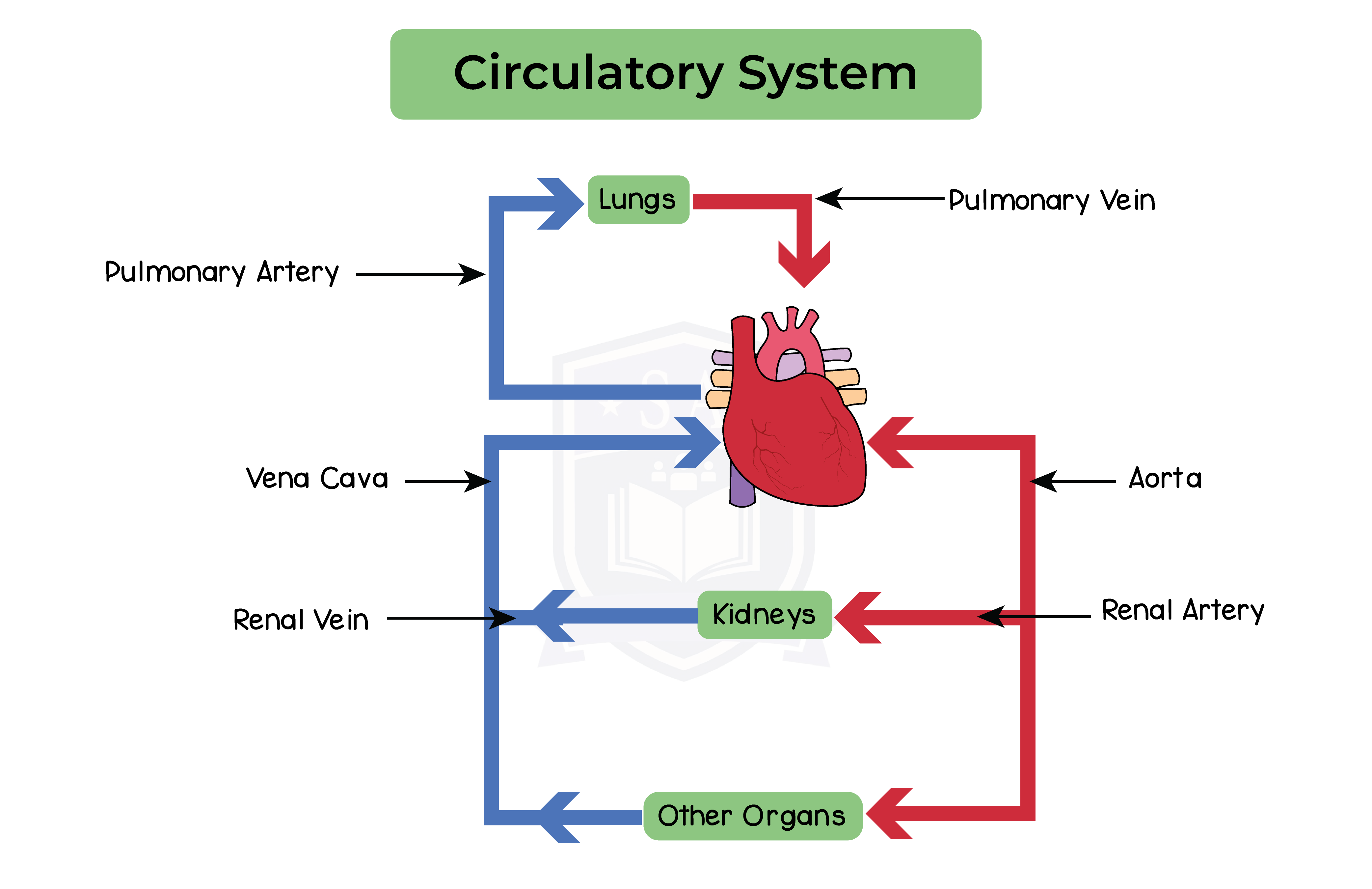
2.11.19 Understand the general structure of the circulation system, including the blood vessels to and from the heart and lungs, liver and kidneys
Always remember:

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.