REVISION NOTES
1.1.1 Understand and use integers (positive, negative and zero)

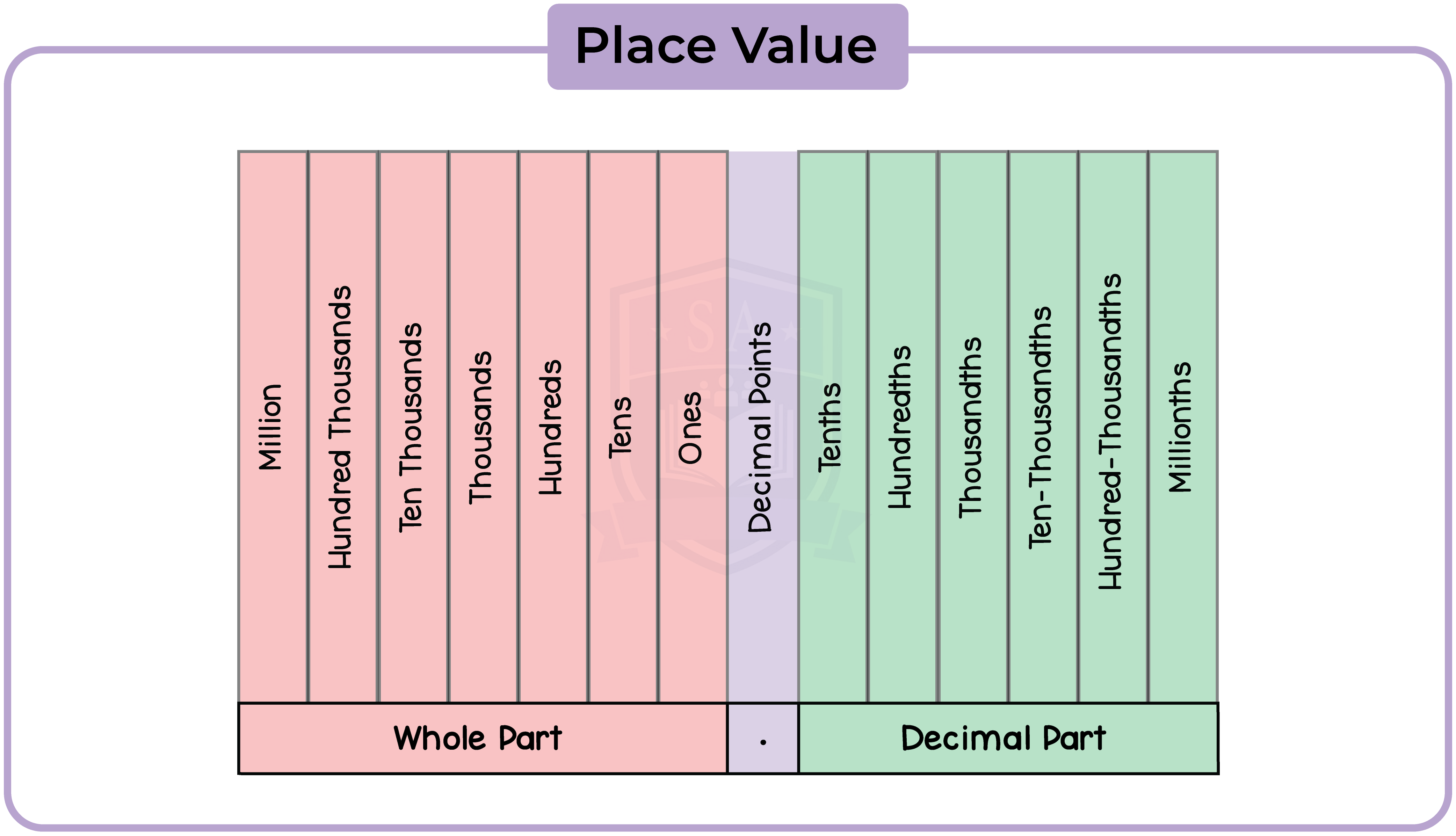
1.1.2 Understand place value
1.1.3 Use directed numbers in practical situations
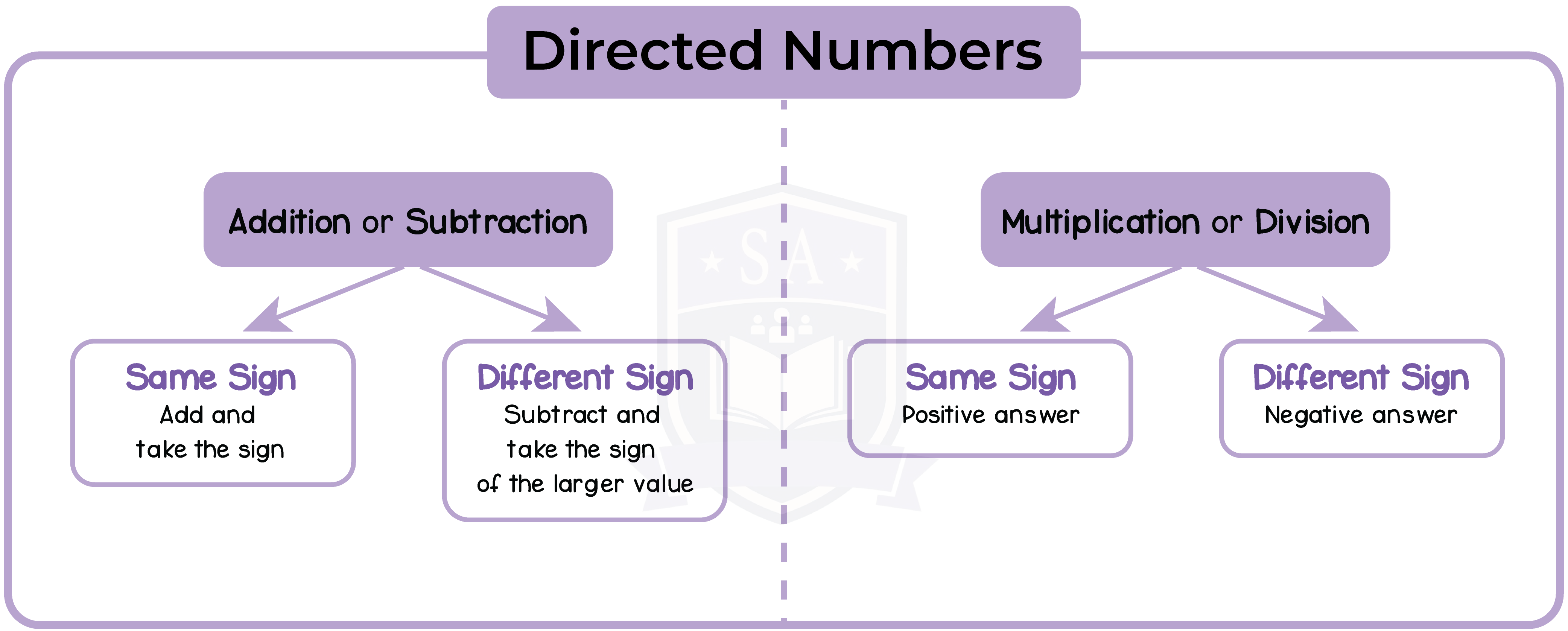
Directed Numbers
Positive Numbers | Negative Numbers |
‘Increase’ ‘Going up’ ‘Above’ | ‘Decrease’ ‘Going down’ ‘Below’ |
Example
1. Suppose 5 represents 5 floors above ground level. Use a directed number to represent 10 levels below ground level.
10 levels below ground level can be represented by –10
2. Suppose +3 km represents walking 3 km due east. Use a directed number to represent walking 7 km due west.
Walking 7km due west can be represented by –7
1.1.4 Order integers
Number Lines
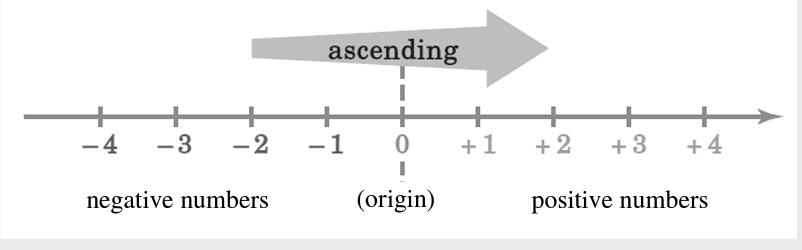
Example
–4 is on the left of –2, it means –4 is smaller than –2
1.1.5 Use the four rules of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
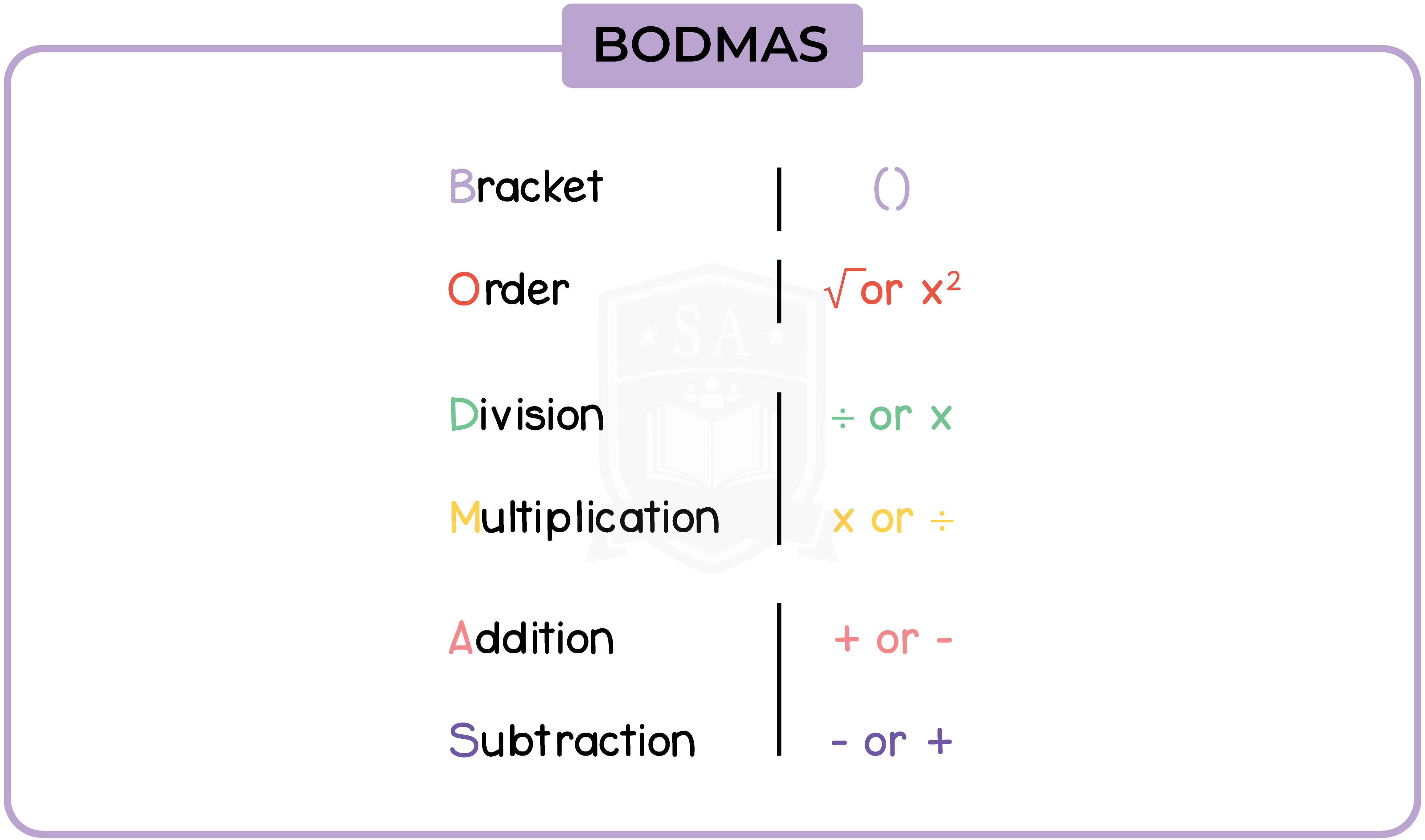
1.1.6 Use brackets and the hierarchy of operations
Bracket
Order
Division
Multiplication
Addition
Subtraction
1.1.7 Use the terms ‘odd’, ‘even’, ’prime numbers’, ‘factors’ and ‘multiples’
A prime number is a whole number with exactly two factors, namely 1 and iself.
The number 1 is not normally considered to be rime.
The prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, …
A factor of a number is a whole number that divides exactly into it, with no remainder.
Example: The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
A multiple of a number is the result of multiplying it by a whole number.
Example: The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, …
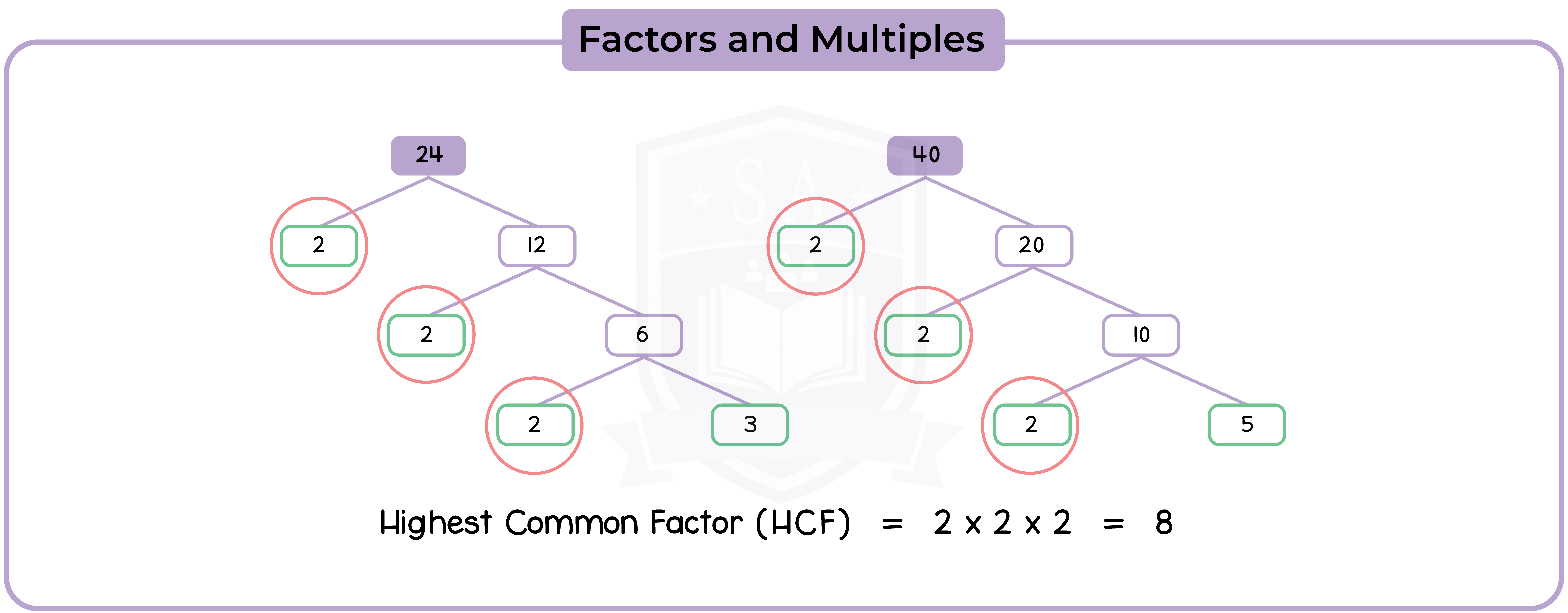
1.1.8 Identify prime factors, common factors and common multiples

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.