REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Physics
5.3 Ideal Gas Molecules
5.3.1 Explain how molecules in a gas have random motion and that they exert a force, and hence a pressure, on the walls of a container

5.3.2 Understand why there is an absolute zero of temperature, which is –273 °C
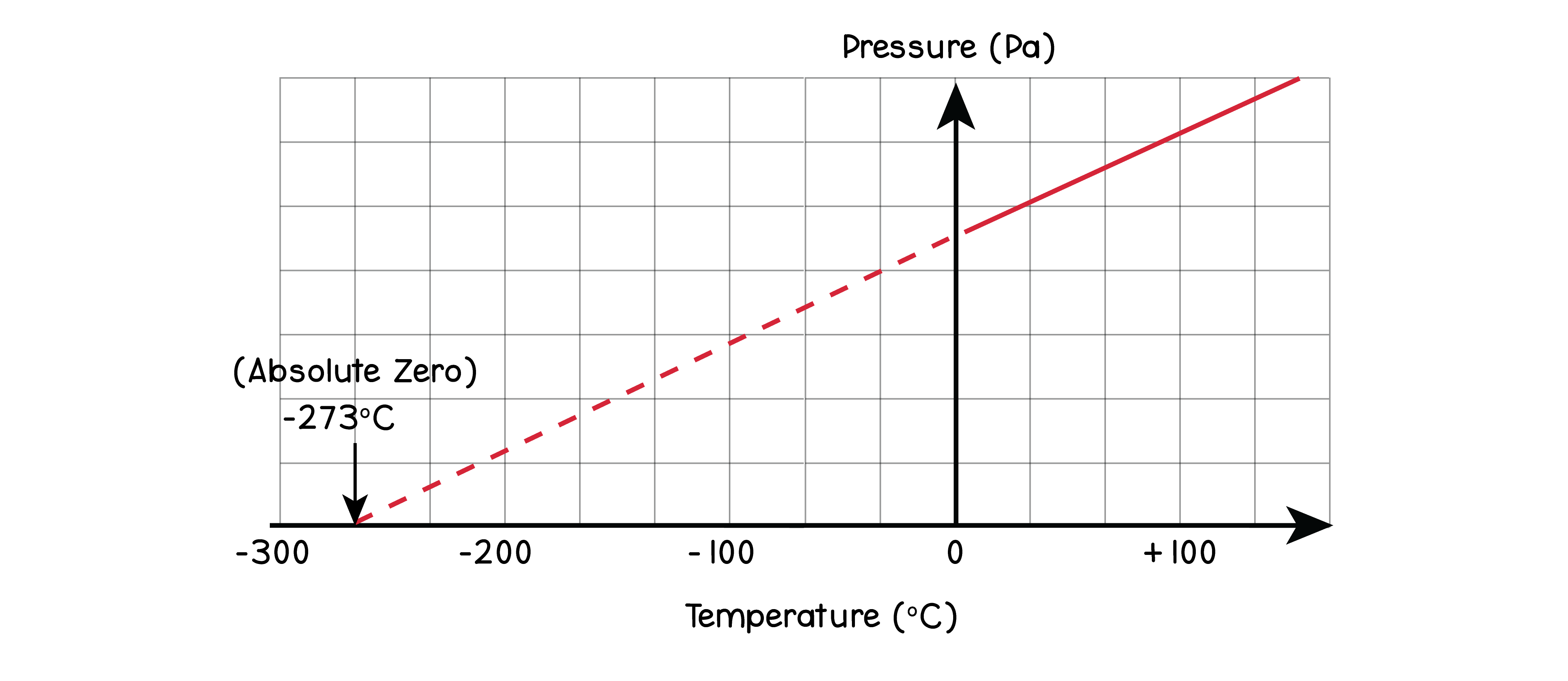
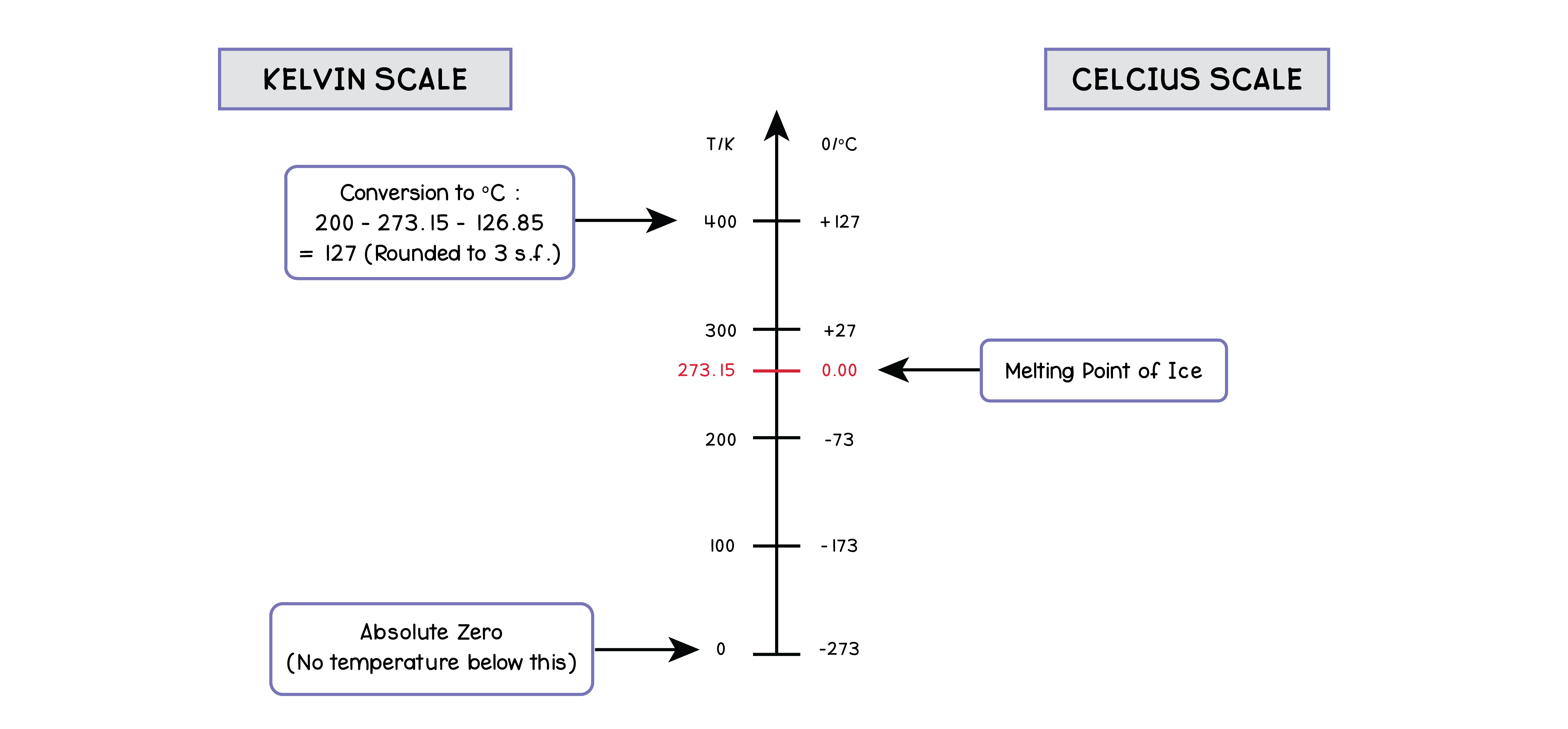
5.3.3 Describe the Kelvin scale of temperature and be able to convert between the Kelvin
and Celsius scales
5.3.4 Understand why an increase in temperature results in an increase in the average speed of gas molecules
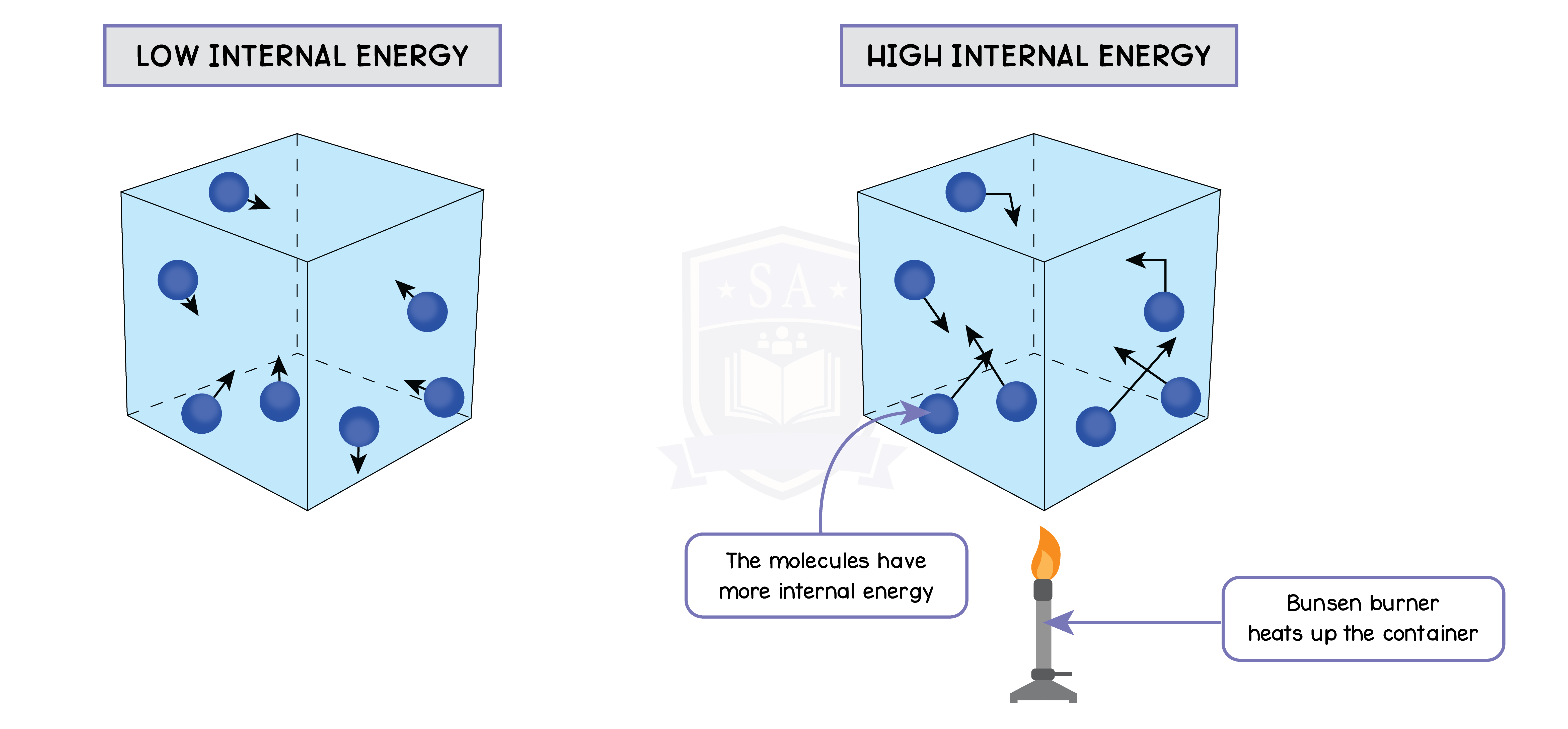
5.3.5 Know that the Kelvin temperature of a gas is proportional to the average kinetic energy of its molecules
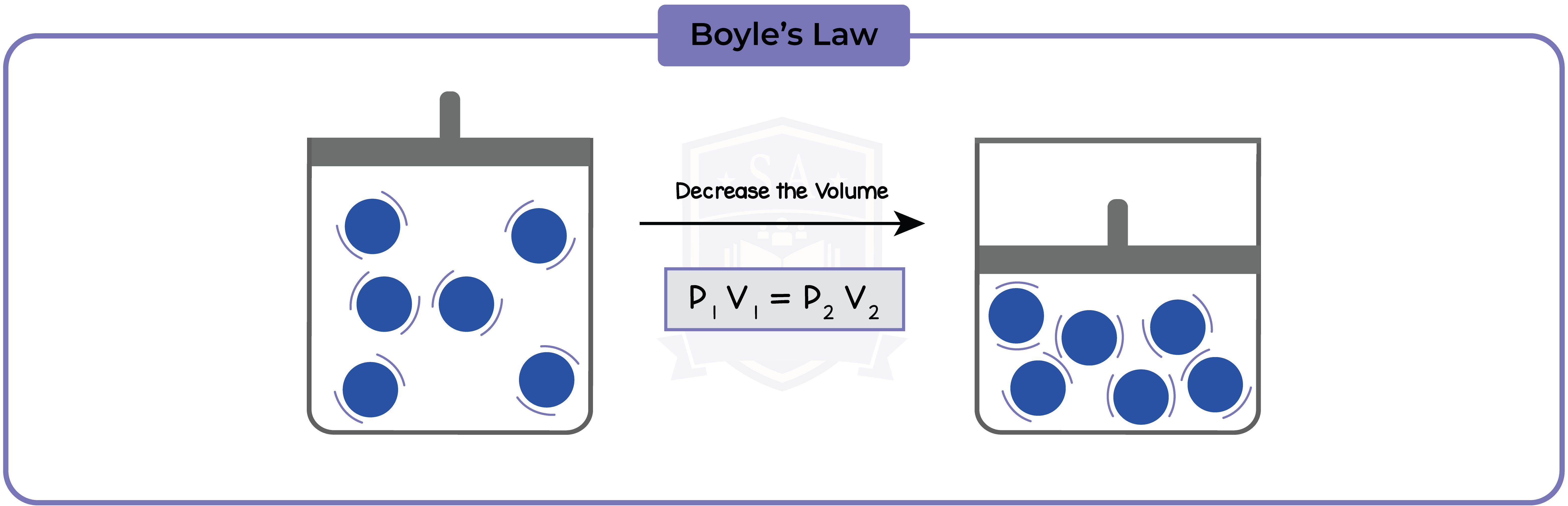
5.3.6 Explain, for a fixed amount of gas, the qualitative relationship between:
- pressure and volume at constant temperature
- pressure and Kelvin temperature at constant volume
5.3.7 Use the relationship between the pressure and Kelvin temperature of a fixed mass of gas at constant volume:
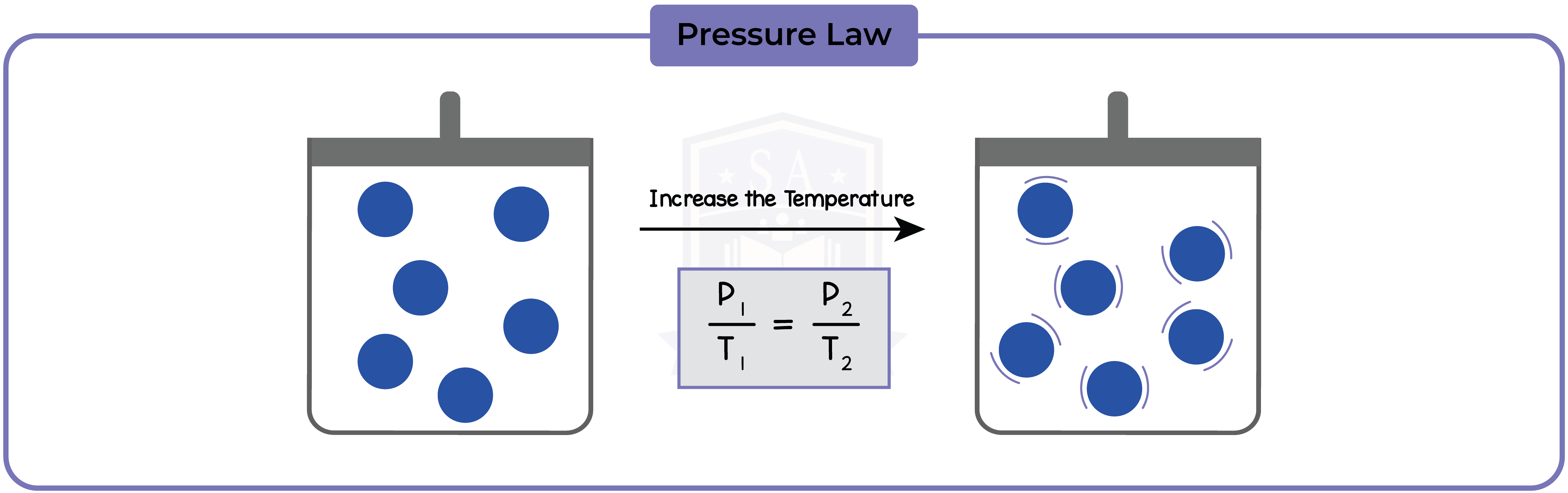
5.3.8 Use the relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature:
Initial pressure(Pa) x initial volume(m3) = Final pressure(Pa) x final volume(m3)
p1V1 = p2V2

