REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Physics
2.2 Energy and Voltage in Circuits
2.2.1 Explain why a series or parallel circuit is more appropriate for particular applications, including domestic lighting
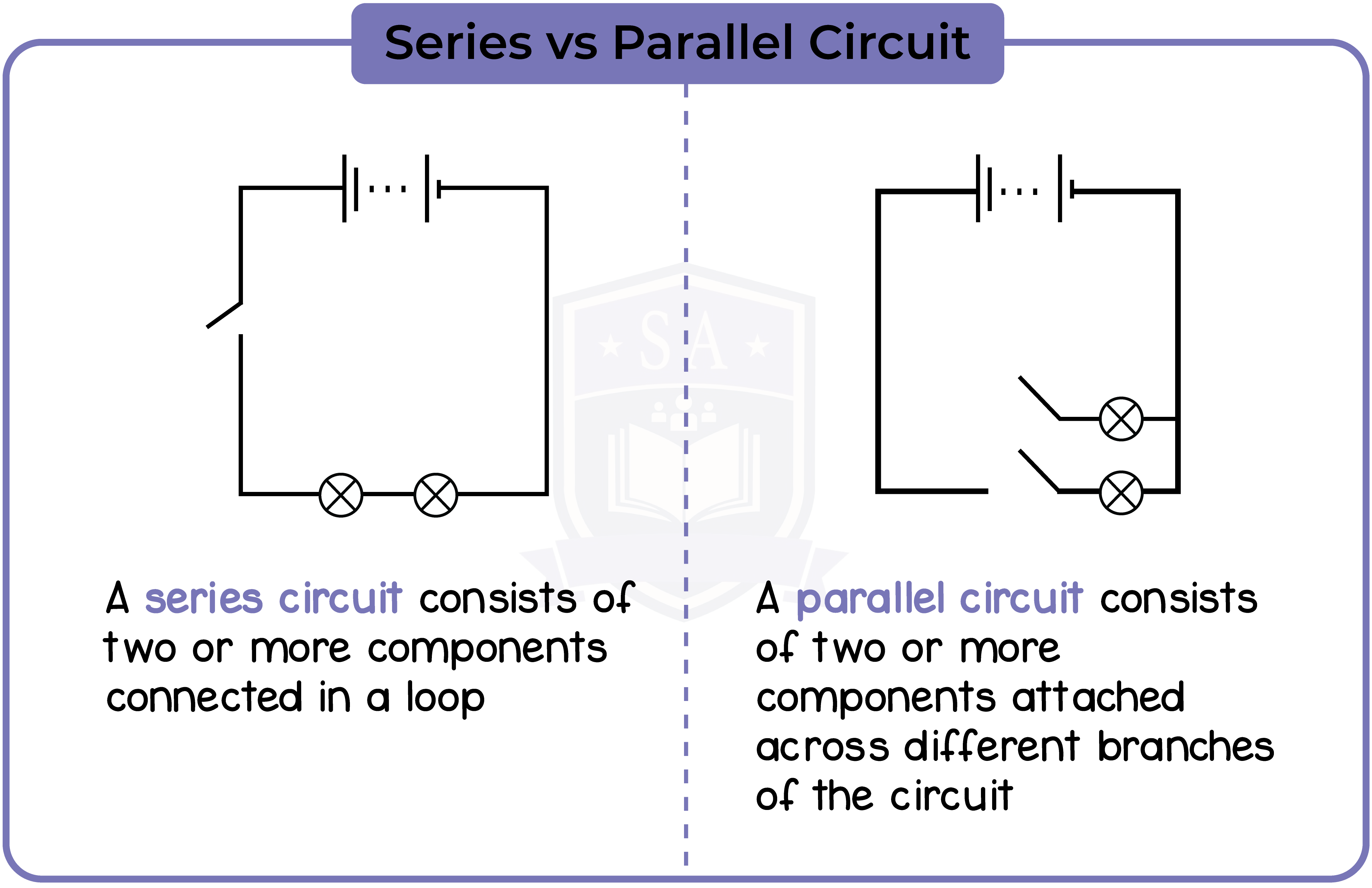
2.2.2 Understand how the current in a series circuit depends on the applied voltage and the number and nature of other components
2.2.3 Describe how current varies with voltage in wires, resistors, metal filament lamps and diodes, and how to investigate this experimentally

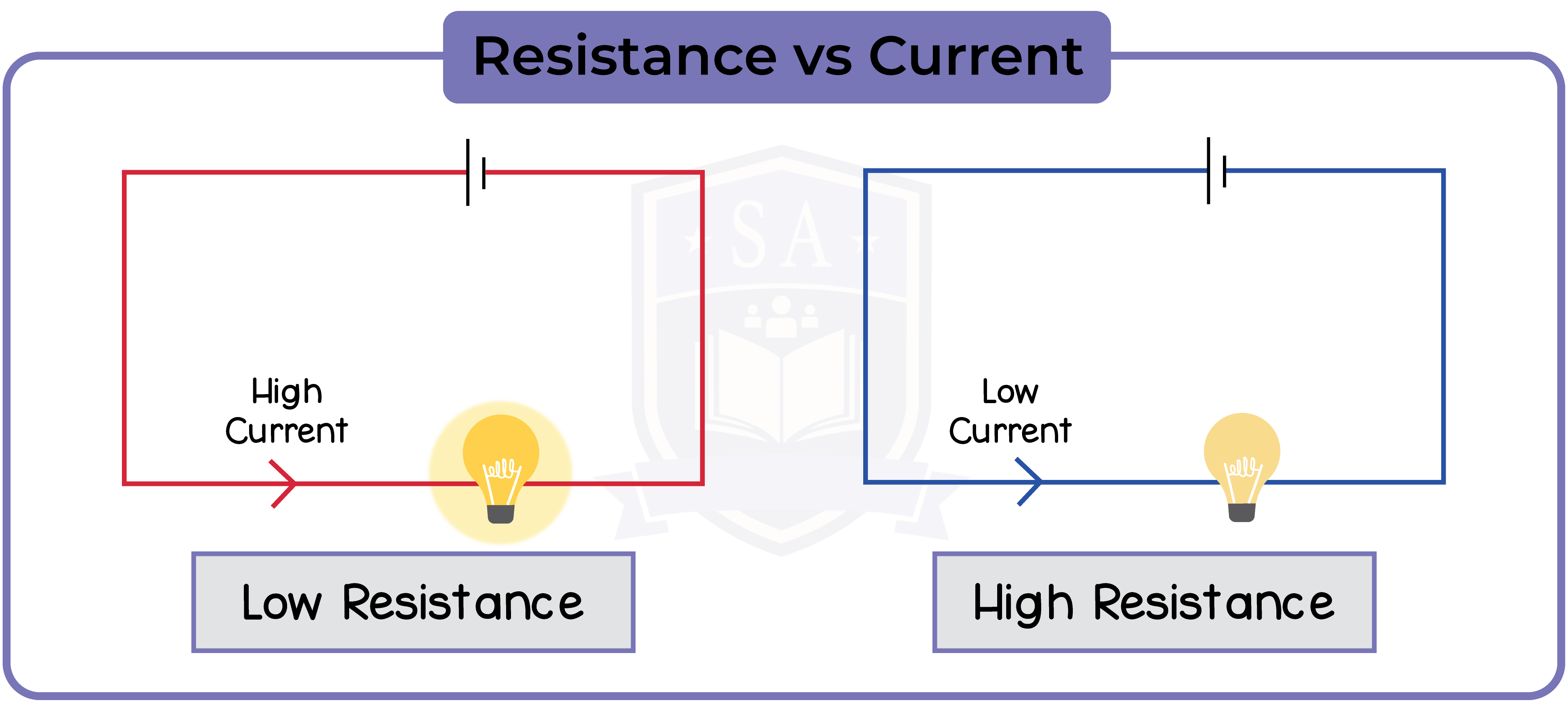
2.2.4 Describe the qualitative effect of changing resistance on the current in a circuit
- Increasing resistance will decrease current
- Decreasing resistance will increase current
- Due to the fact that current = voltage / resistance
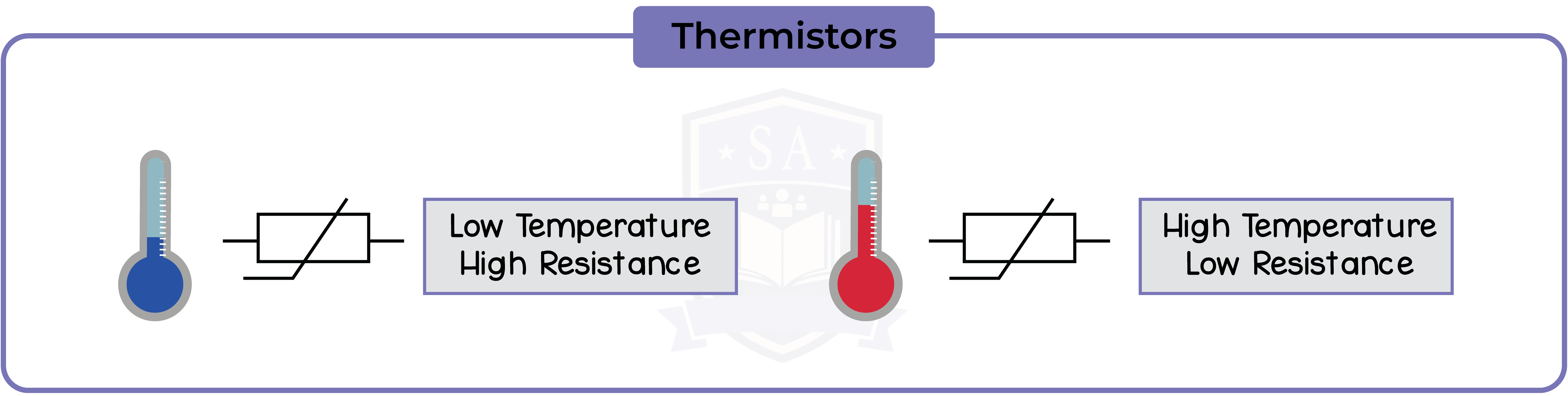
2.2.5 Describe the qualitative variation of resistance of light-dependent resistors (LDRs) with illumination and thermistors with temperature

2.2.6 Know that lamps and LEDs can be used to indicate the presence of a current in a circuit
2.2.7 Know and use the relationship between voltage, current and resistance:
voltage = current × resistance

2.2.8 Know that current is the rate of flow of charge
2.2.9 Know and use the relationship between charge, current and time:
charge = current × time

2.2.10 Know that electric current in solid metallic conductors is a flow of negatively charged electrons
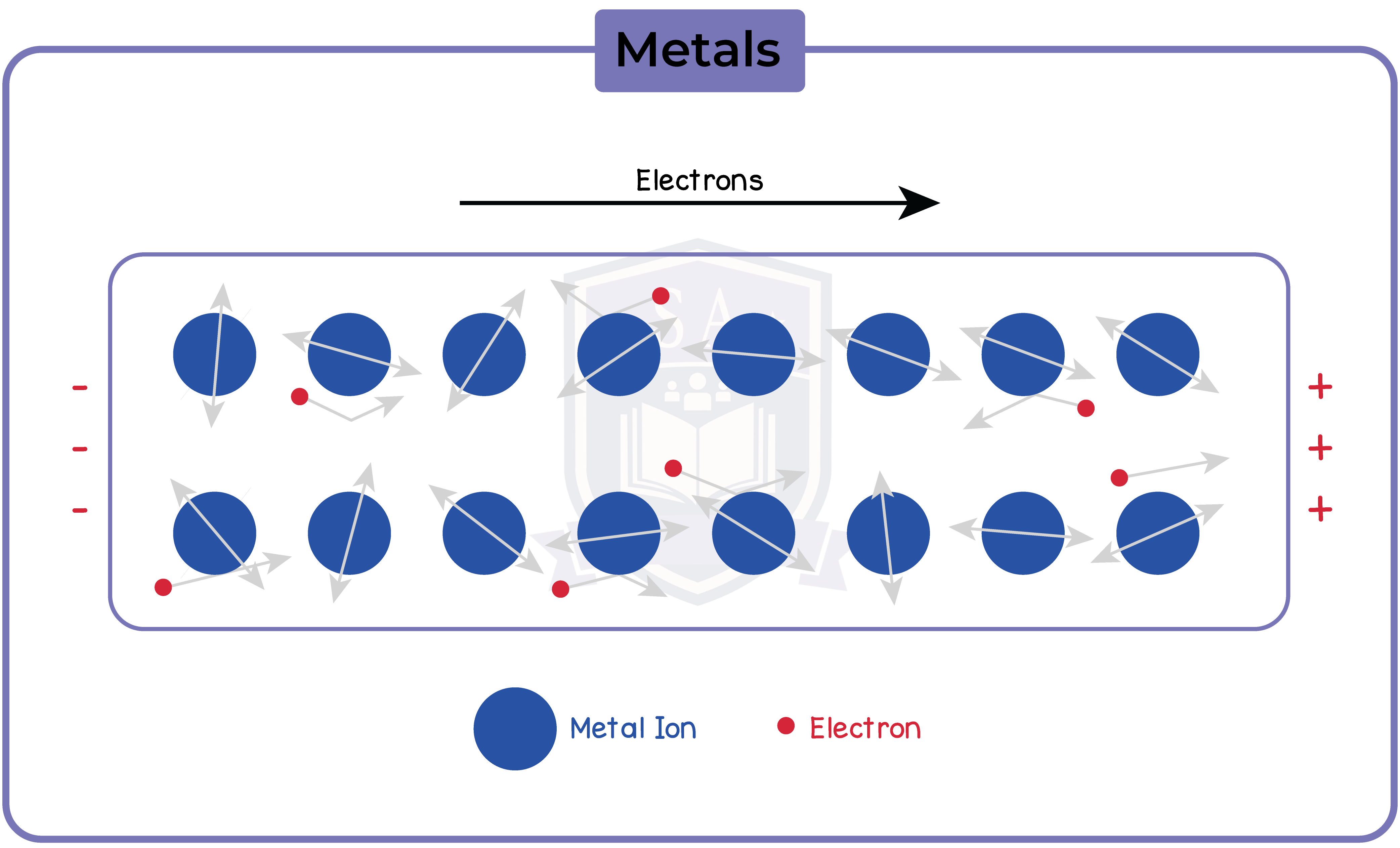
2.2.11 Understand why current is conserved at a junction in a circuit
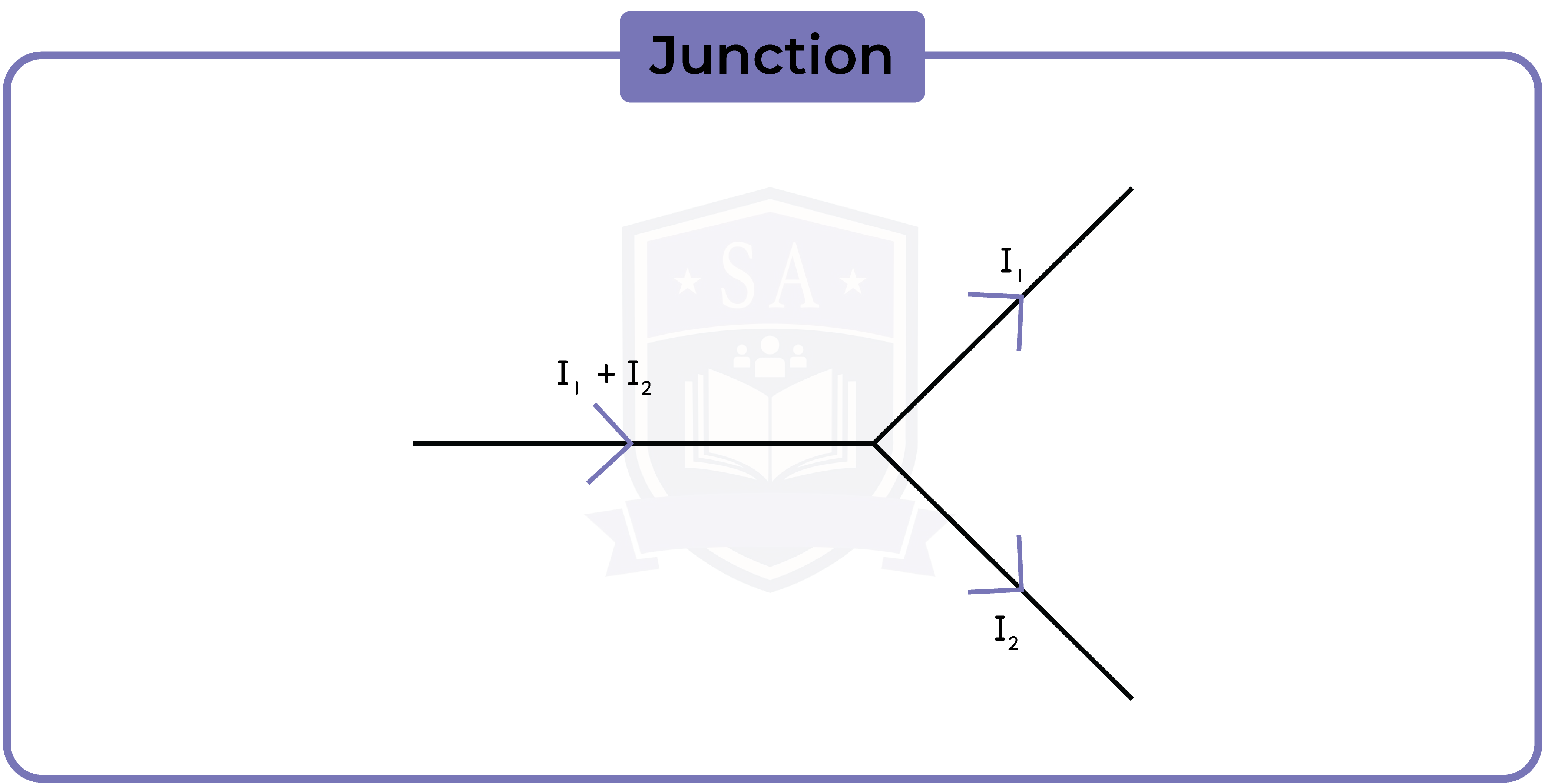
2.2.12 Know that the voltage across two components connected in parallel is the same
2.2.13 Calculate the currents, voltages and resistances of two resistive components connected in a series circuit
In a series circuit:
Current of entire circuit = current at first component = current at second component
Voltage of entire circuit = voltage at first component + voltage at second component
Resistance of entire circuit = resistance of first component + resistance of second component
Ctotal = C1 = C2
Vtotal = V1 + V2
Rtotal = R1 + R2
In a parallel circuit:
Current of entire circuit = current at first component + current at second component
Voltage of entire circuit = voltage at first component = voltage at second component
1/Resistance of entire circuit = 1/resistance of first component + 1/resistance of second component
Ctotal = C1 + C2
Vtotal = V1 = V2
1/Rtotal = 1/R1 + 1/R2
2.2.14 Know that:
- voltage is the energy transferred per unit charge passed
- the volt is a joule per coulomb
2.2.15 Know and use the relationship between energy transferred, charge and voltage:
energy transferred = charge × voltage


