REVISION NOTES
2.1.1 Use the following units: ampere (A), coulomb (C), joule (J), ohm (Ω), second (s), volt (V) and watt (W)
| Measurement | Unit |
| Current | Amperes (A) |
| Charge | Coulombs (C) |
| Energy | Joules (J) |
| Resistance | Ohms (Ω) |
| Time | Seconds (s) |
| Voltage | Volts (V) |
| Power | Watts (W) |
2.1.2 Understand how the use of insulation, double insulation, earthing, fuses and circuit breakers protects the device or user in a range of domestic appliances
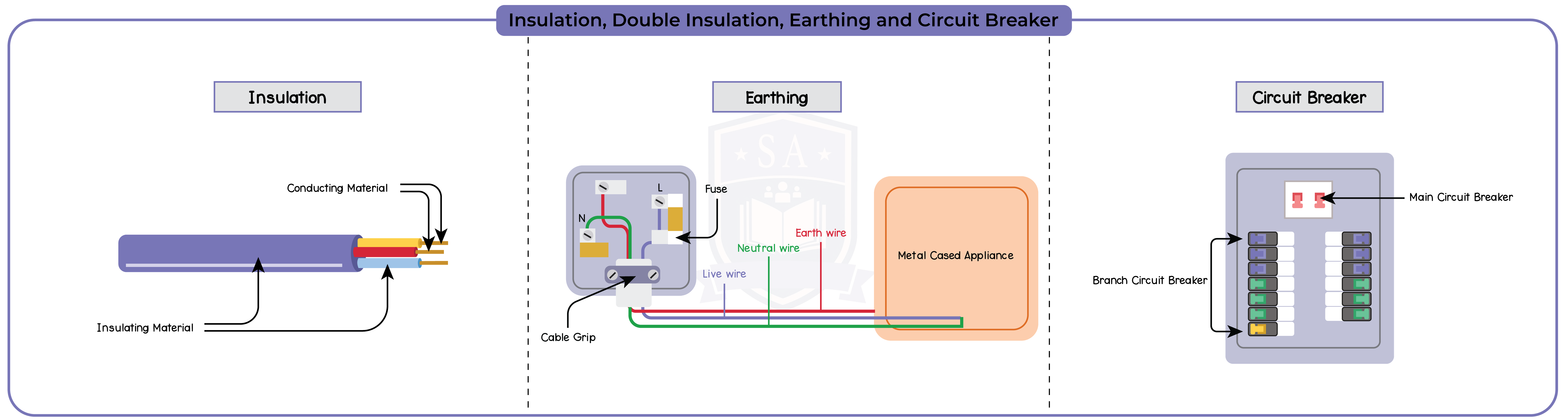
2.1.3 Understand why a current in a resistor results in the electrical transfer of energy and an increase in temperature, and how this can be used in a variety of domestic contexts
2.1.4 Know and use the relationship between power, current and voltage:
Power = Current × Voltage

and apply the relationship to the selection of appropriate fuses.
2.1.5 Use the relationship between energy transferred, current, voltage and time:
Energy Transferred = Current × Voltage × Time

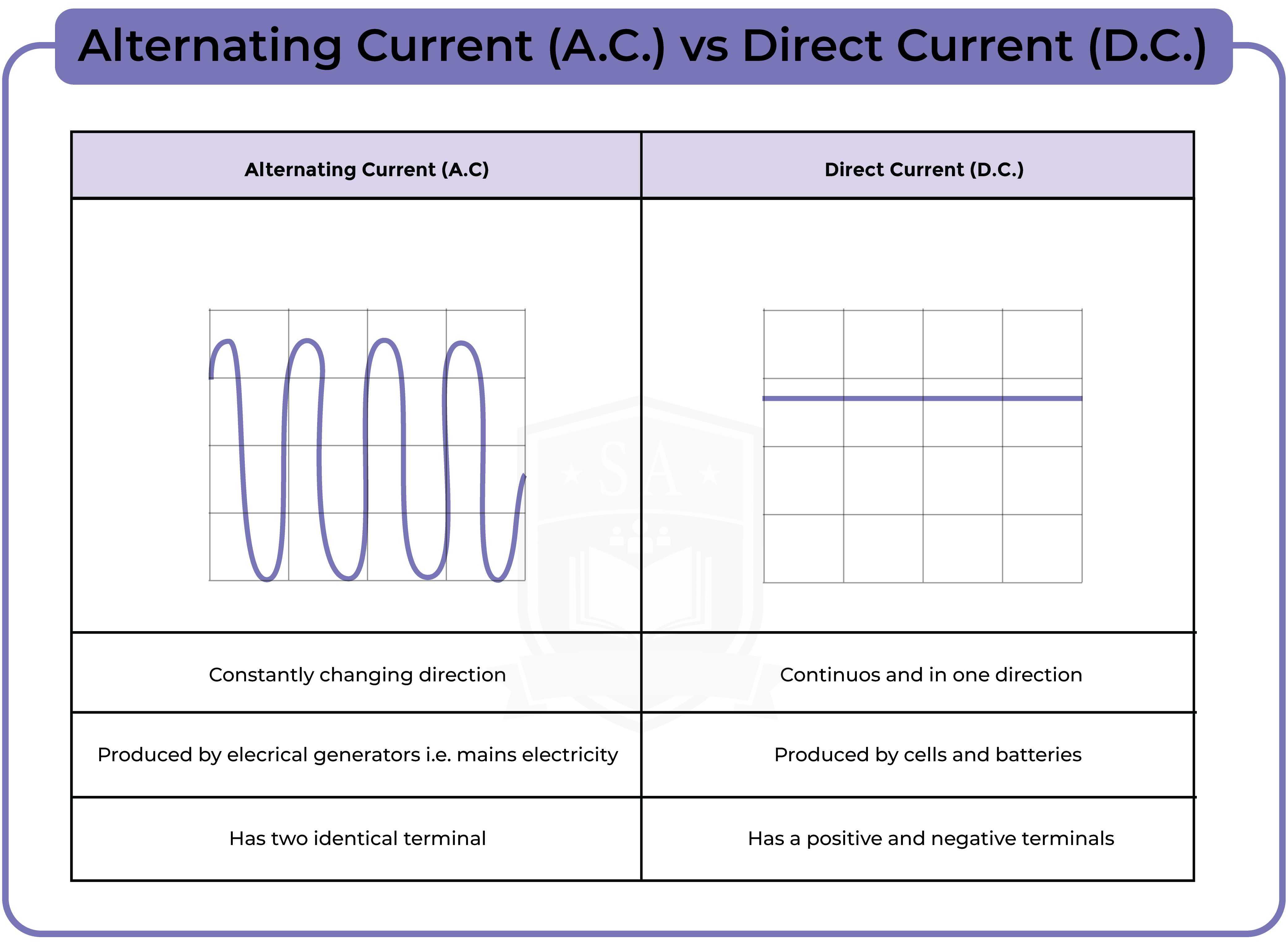
2.1.6 Know the difference between mains electricity being alternating current (a.c.) and direct current (d.c.) being supplied by a cell or battery

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.