REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Mathematics A
5.2 Transformation Geometry
5.2.1 Understand that rotations are specified by a centre and an angle
A rotation is specified by centre of rotation, angle of rotation, and direction (clockwise or anticlockwise)
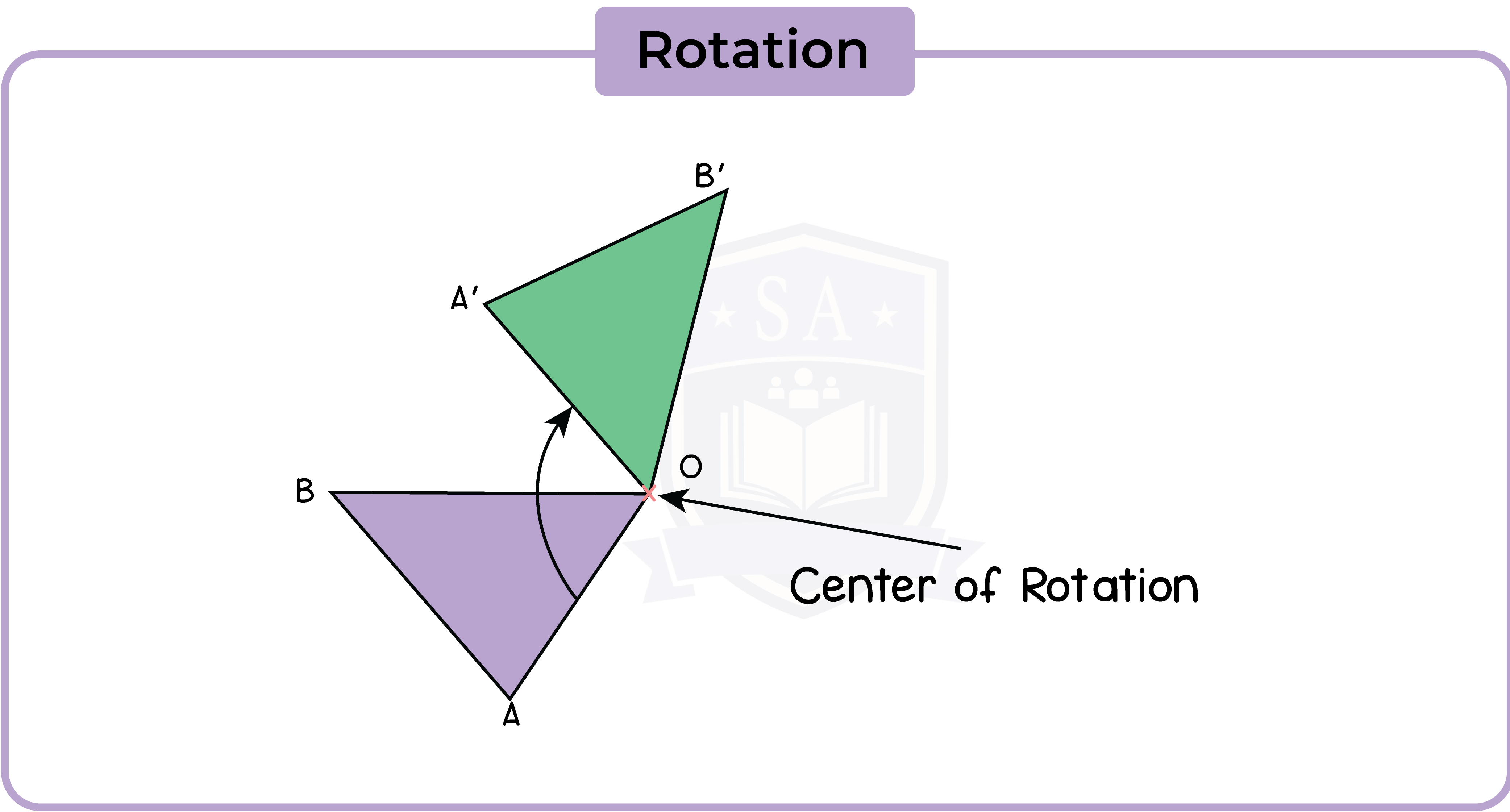
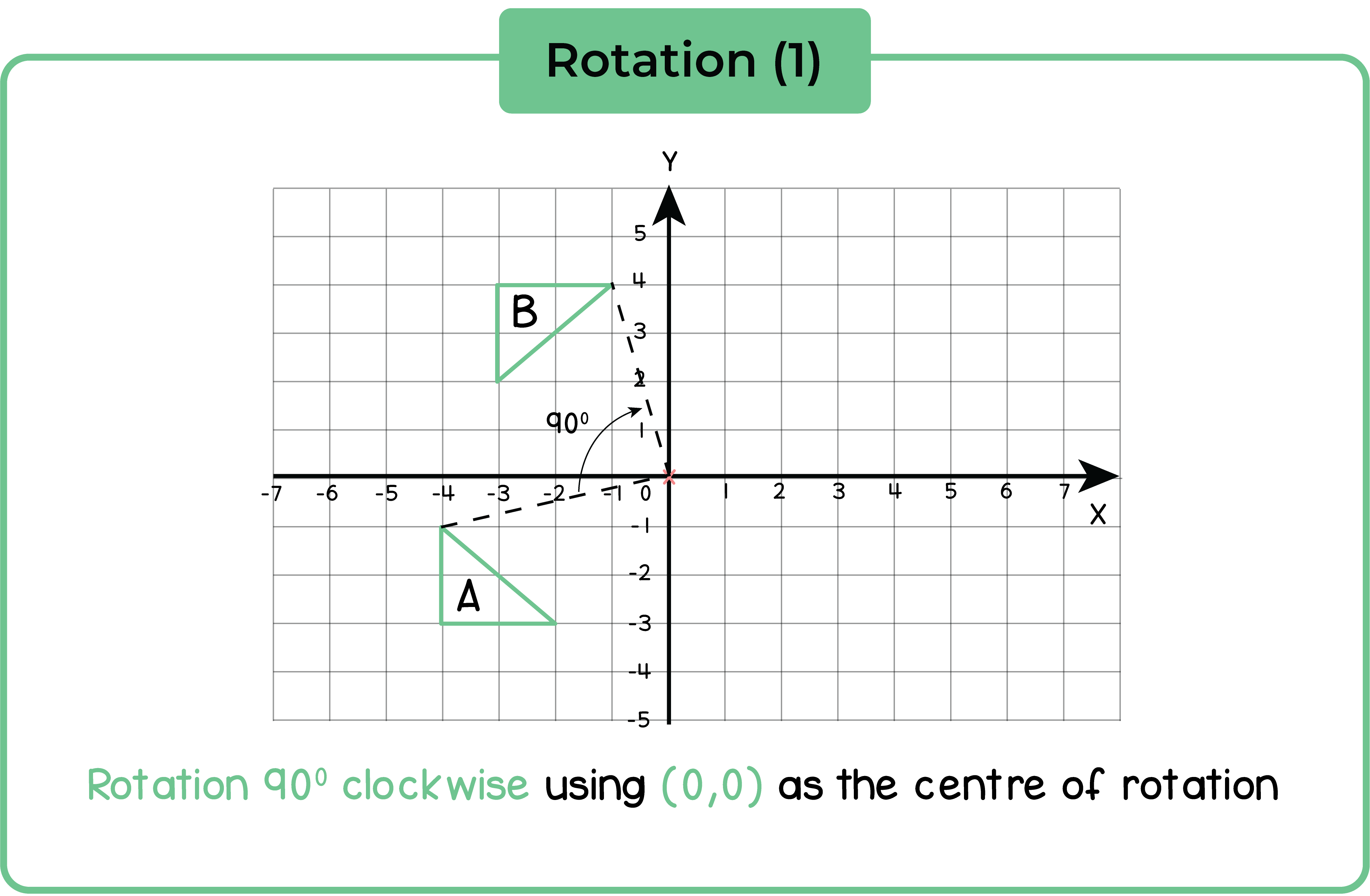
5.2.2 Rotate a shape about a point through a given angle
An imaginary point acts as a pivot for the rotation. This is call the centre of rotation.
5.2.3 Recognise that an anti-clockwise rotation is a positive angle of rotation and a clockwise rotation is a negative angle of rotation
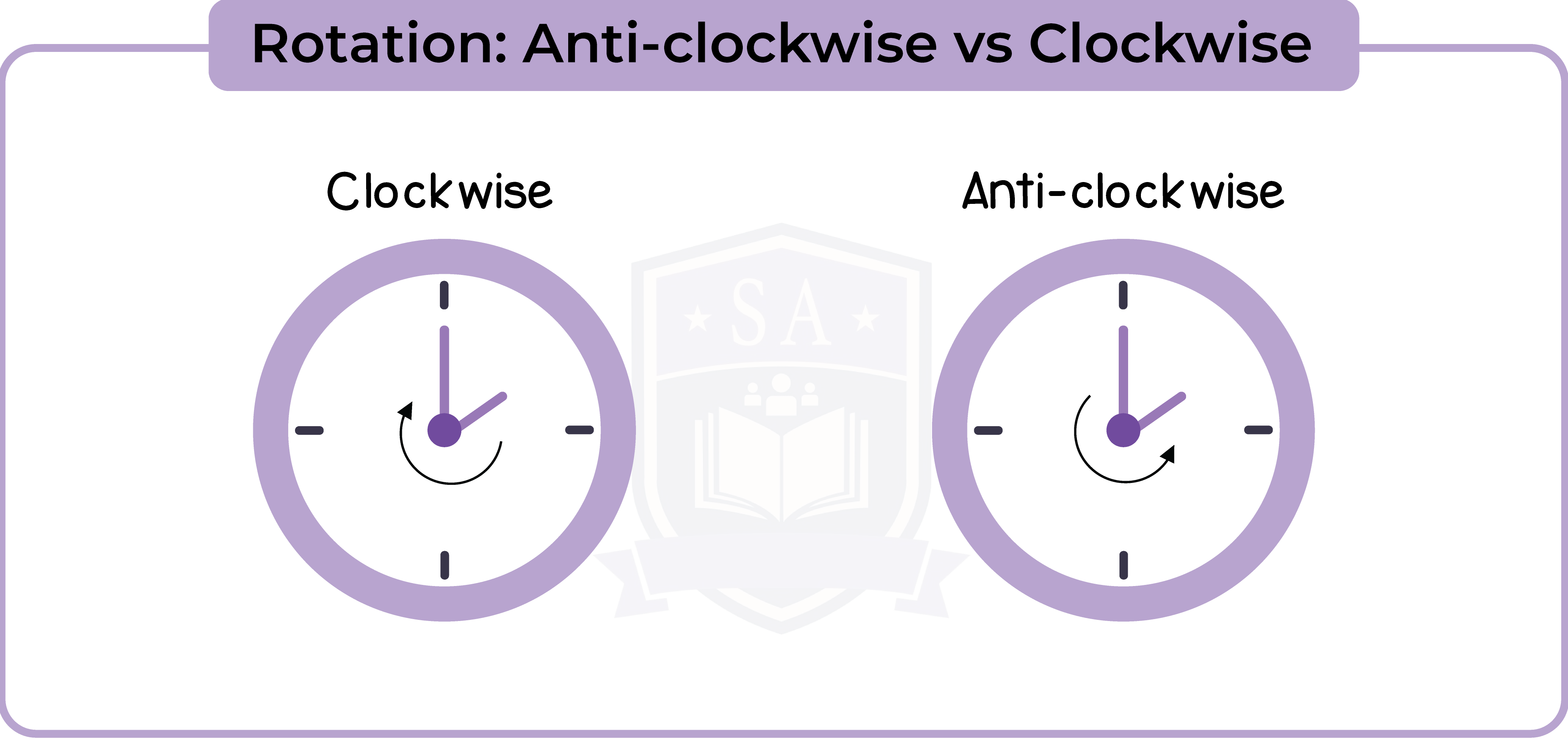
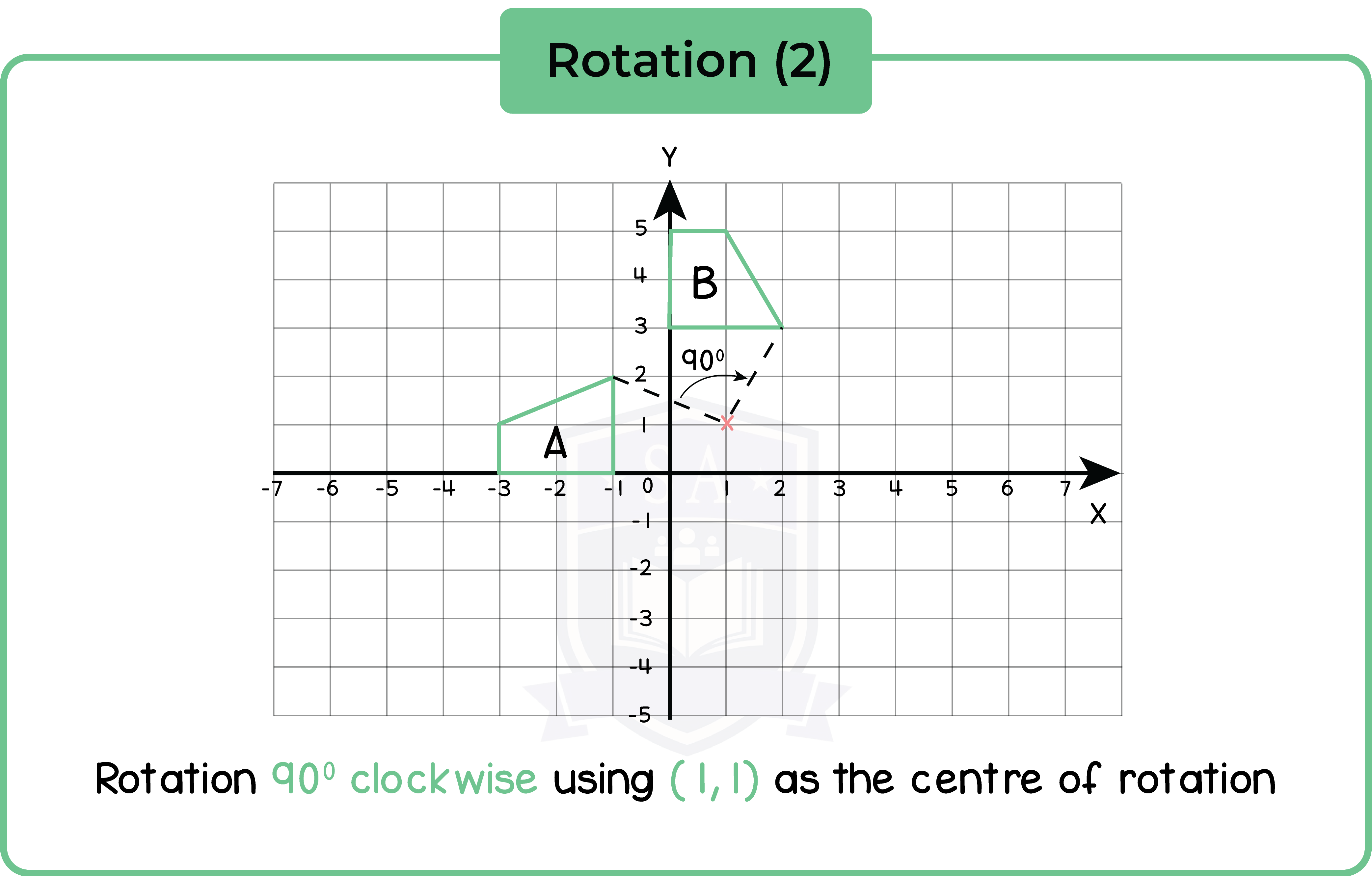
Positive and negative angles may be used instead of ‘clockwise’ and ‘anticlockwise’ to specify the direction of rotation.
Example: Rotate through -270o means rotate -270o clockwise.
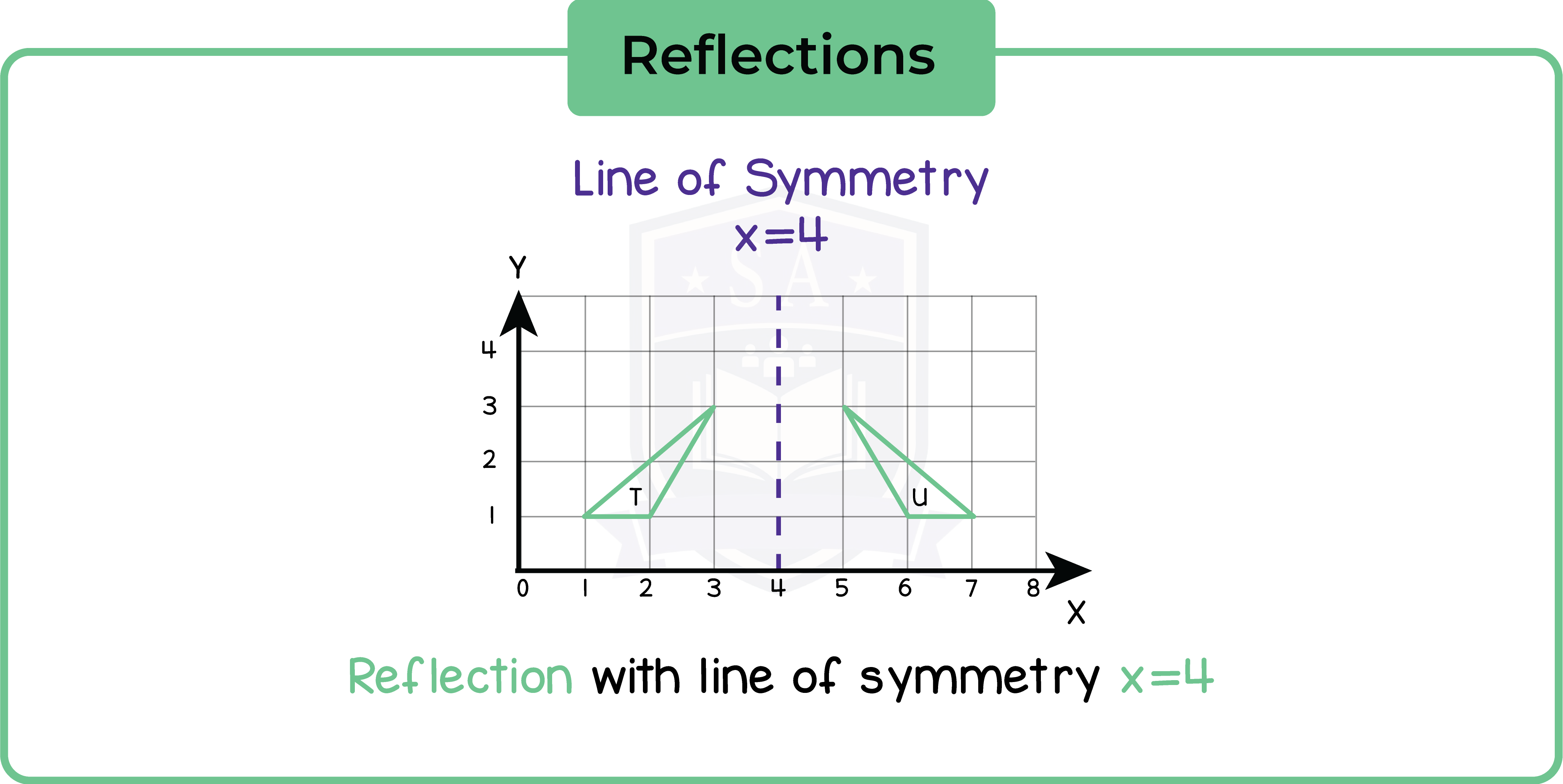
5.2.4 Understand that reflections are specified by a mirror line
A reflection is specified by a mirror line.
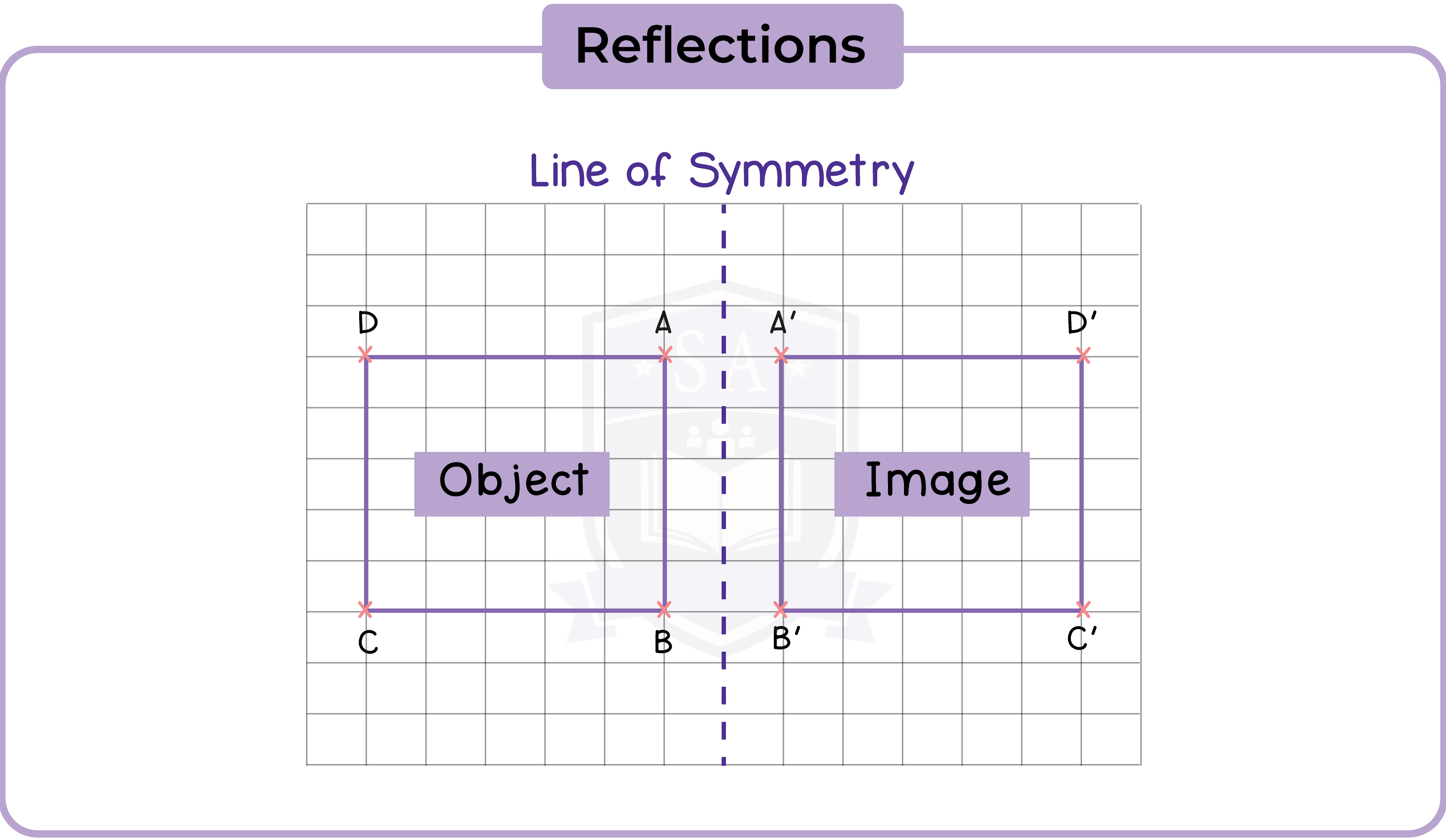
5.2.5 Construct a mirror line given an object and reflect a shape given a mirror line
5.2.6 Understand that translations are specified by a distance and direction
A translation simply slides an object left/right and/or up/down.
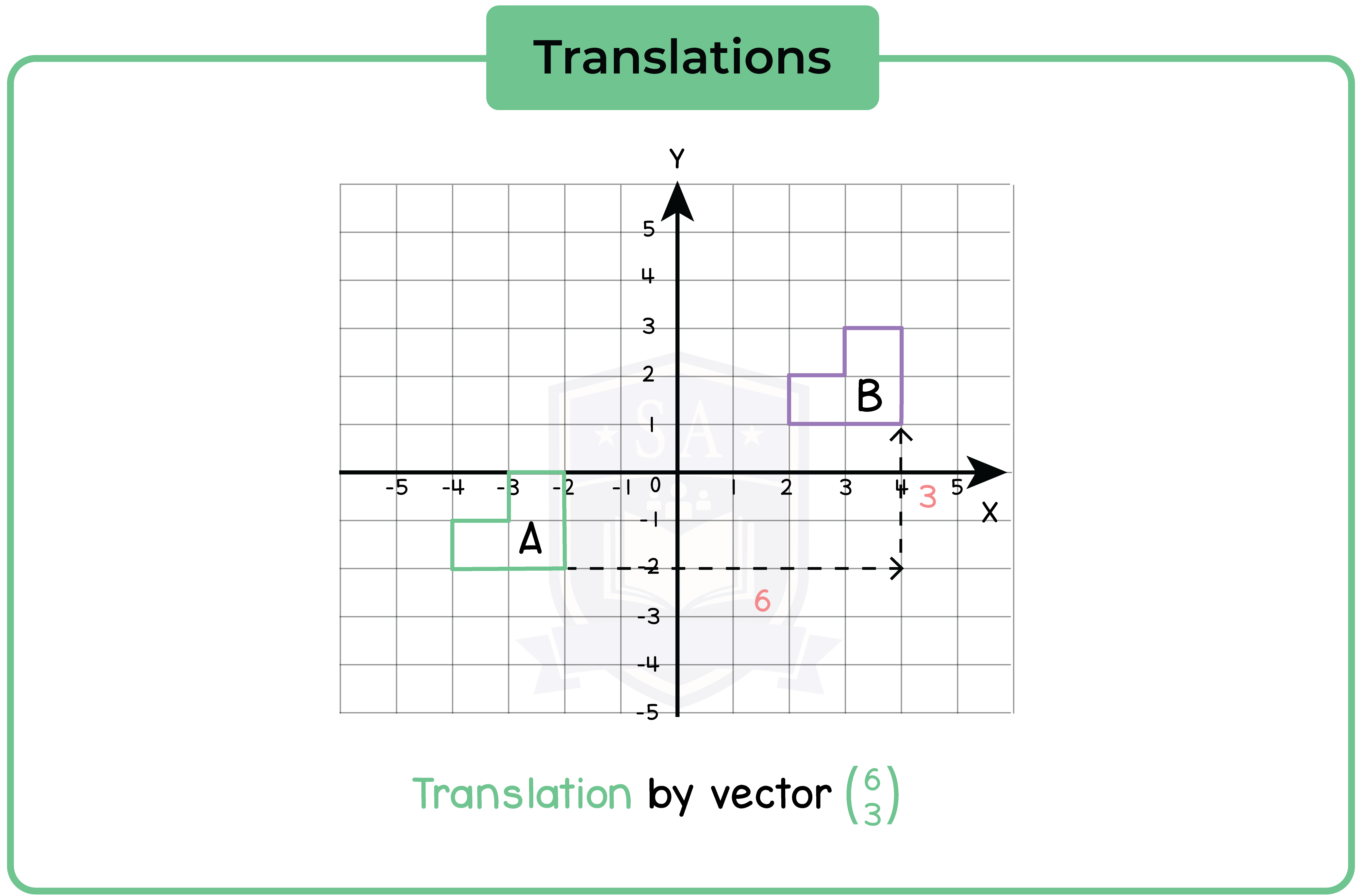
5.2.7 Translate a shape
5.2.8 Understand and use column vectors in translations
A translation can be expressed in a vector form.
5.2.9 Understand that rotations, reflections and translations preserve length and angle so that a transformed shape under any of these transformations remains congruent to the original shape
Two shapes are congruent if they are exactly the same shape and size.
Reflections, rotations and translations all preserve congruence.
5.2.10 Understand that enlargements are specified by a centre and a scale factor
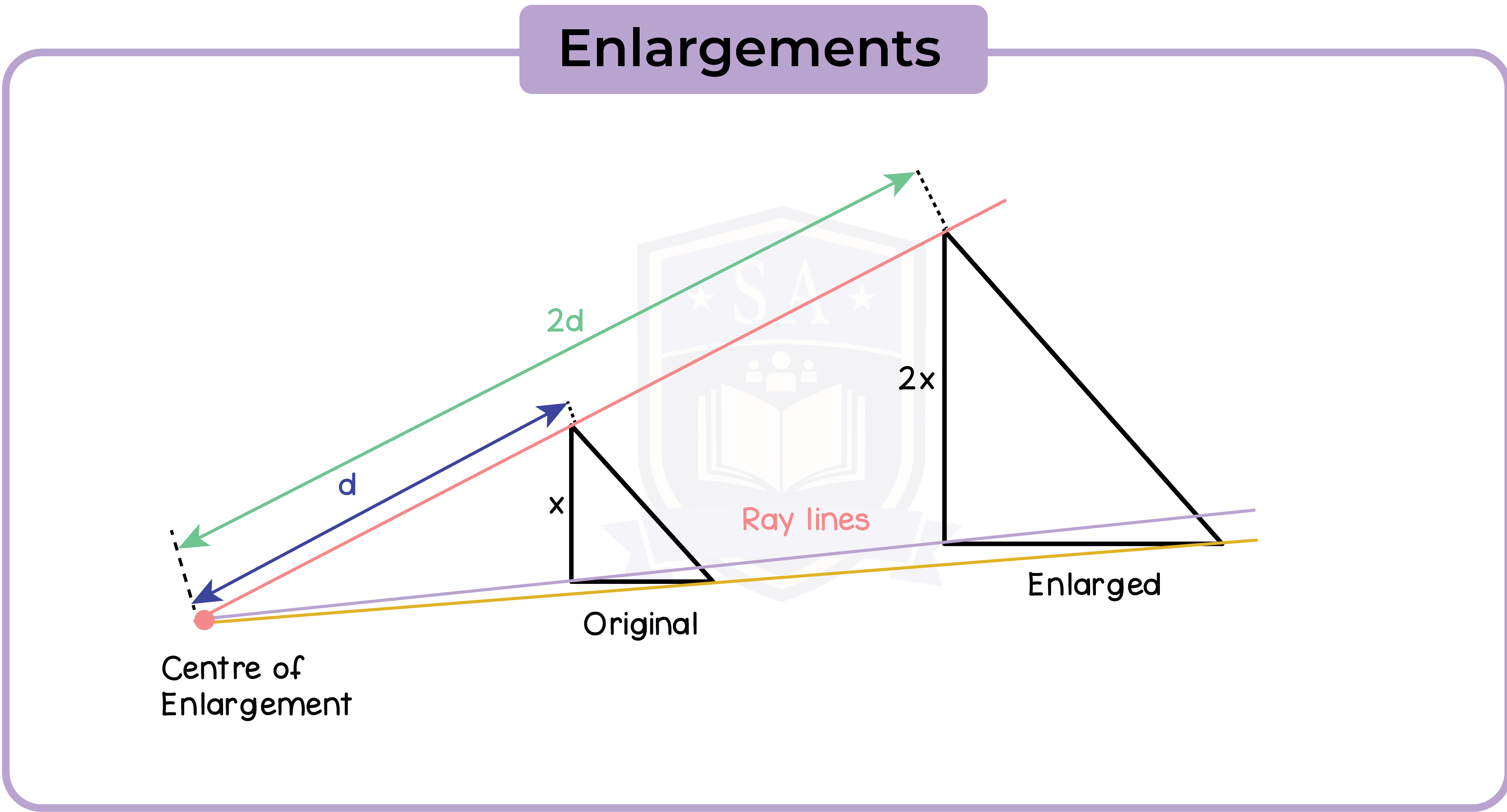
An enlargement is specified by centre of enlargement and a scale factor.
- Scale factors larger than 1 makes the image larger
- Scale factors between 0 and 1 makes the image smaller
5.2.11 Understand that enlargements preserve angles and not lengths
Enlargement do not preserve congruence.
The object and its image will have similar shape.
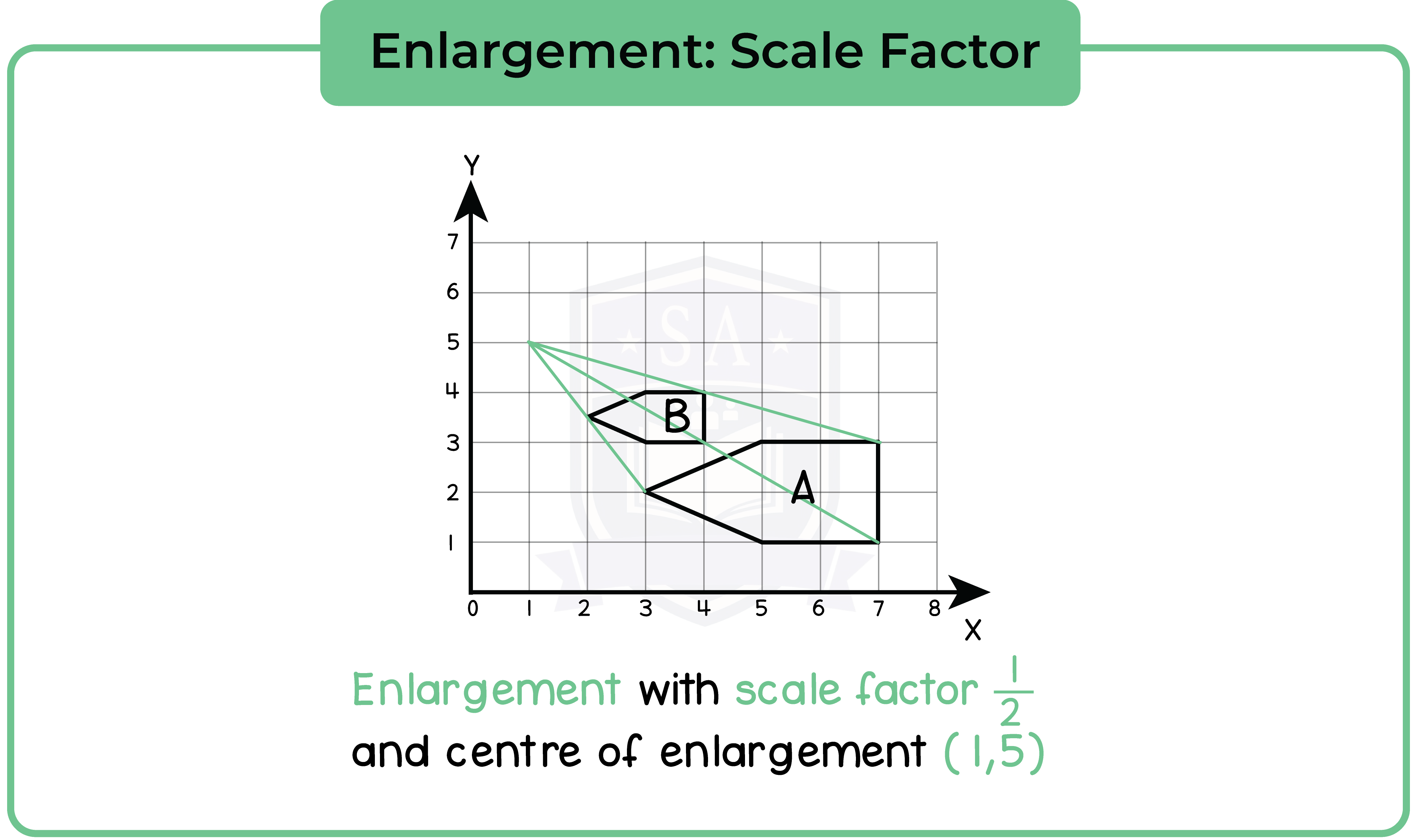
5.2.12 Enlarge a shape given the scale factor
Type 1: Length
When solid objects are enlarged by a scale factor, their length increases by the same ratio.

Type 2: Area
When solid objects are enlarged by a scale factor, their area increases by the square of the ratio.
Type 3: Volume or Weight
When solid objects are enlarged by a scale factor, their volume increases by the cube of the ratio.
5.2.13 Identify and give complete descriptions of transformations

