REVISION NOTES
1.6.1 Understand that ‘percentage’ means ‘number of parts per 100’
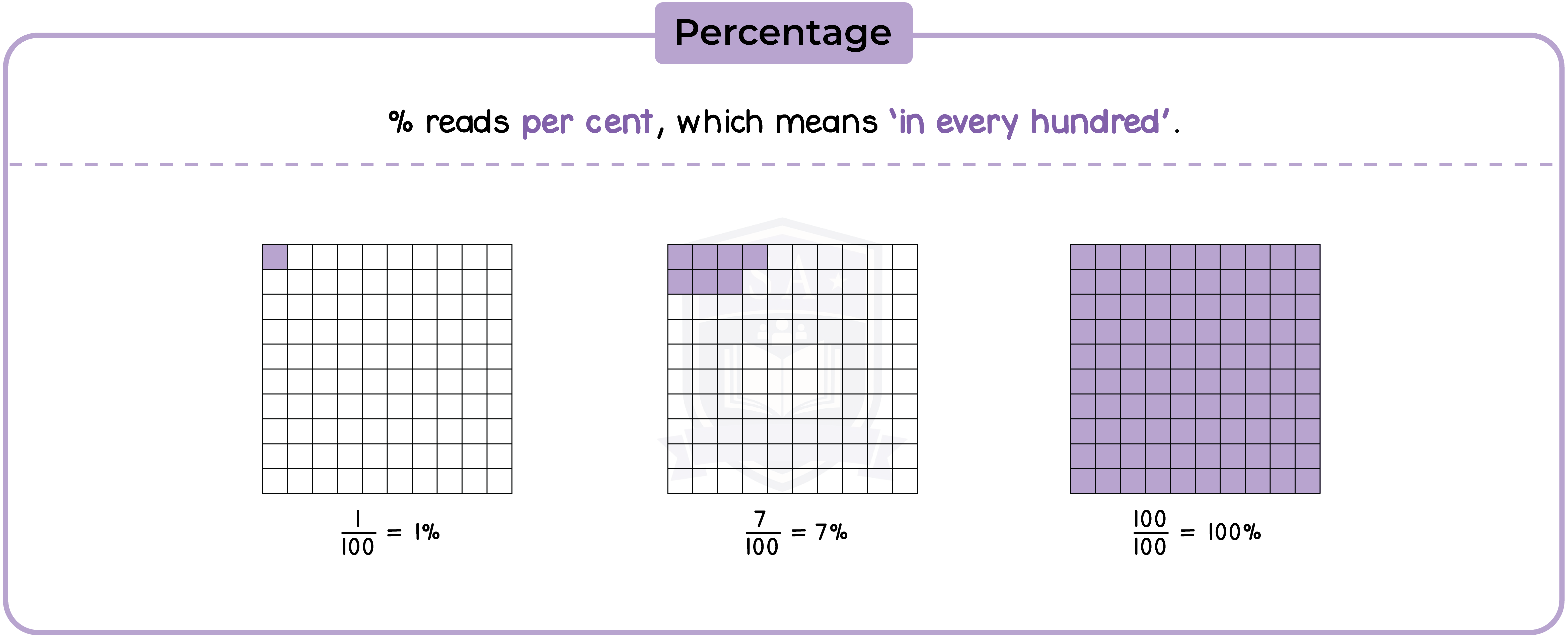
1.6.2 Express a given number as a percentage of another number
1.6.3 Express a percentage as a fraction and as a decimal
To convert a percentage into a fraction, simply write the given percentage over a denominator of 100, then cancel down if appropriate.

1.6.4 Understand the multiplicative nature of percentages as operators
1.6.5 Solve simple percentage problems, including percentage increase and decrease

Percentage increase or decrease may be calculated very efficiently using a multiplying factor. This may either be greater than 1 (increase) or less than 1 (decrease).
Example 1:
3% increase = 1 + 0.03 = 1.03
Example 2:
3% decrease = 1 – 0.03 = 0.97
1.6.6 Use reverse percentages
To reverse the calculation, simply divide by the multiplying factors.
1.6.7 Use compound interest and depreciation

1.6.8 Use repeated percentage change (Higher Tier Only)
1.6.9 Solve compound interest problems (Higher Tier Only)

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.