REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Mathematics A
1.4 Powers and Roots
Powers tell you how many times a number is to be multiplied by itself.
Powers are also called indices.
1.4.1 Identify square numbers and cube numbers
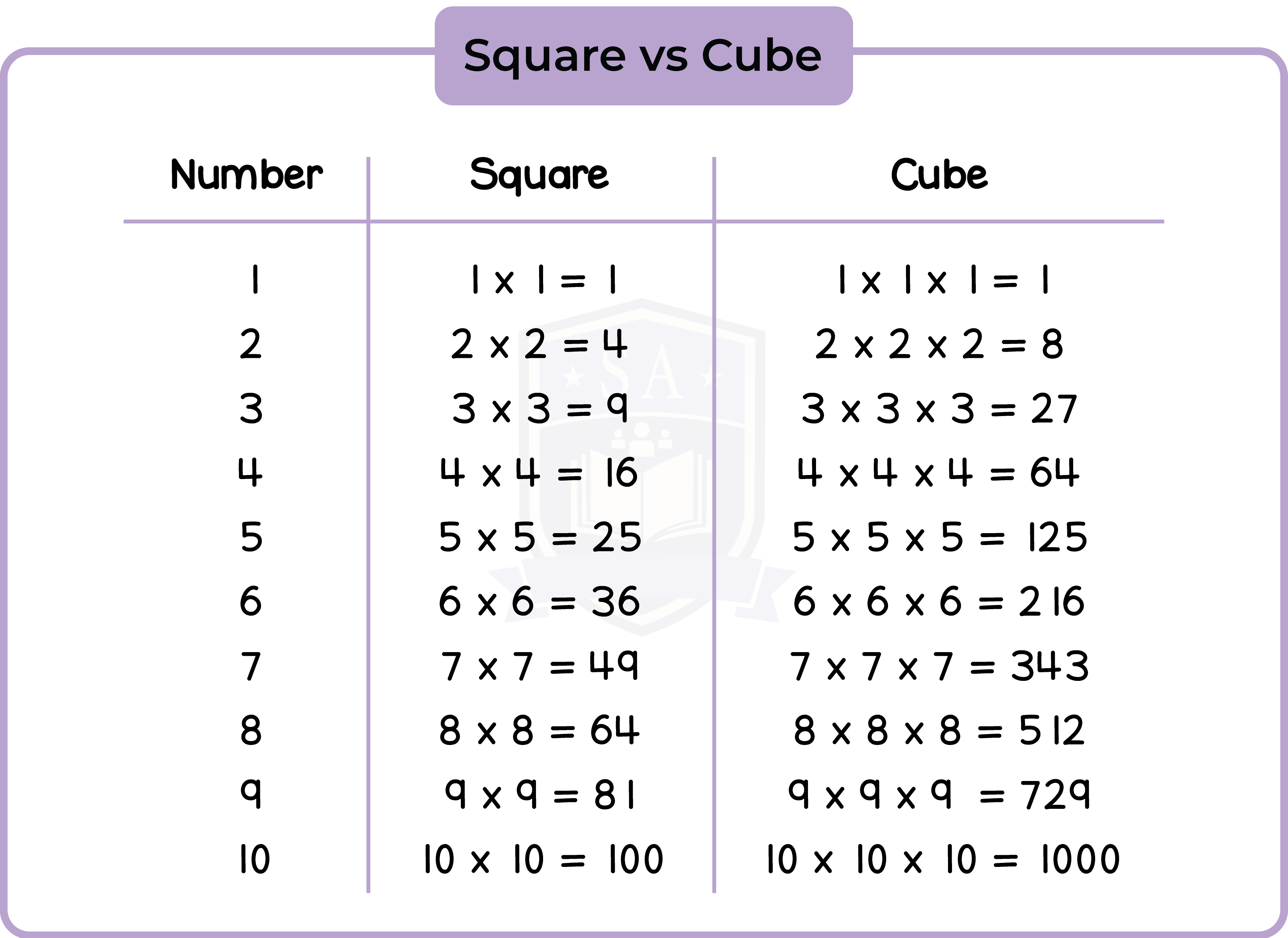
A square number is a number that is multiplied by itself.
A cube number is a number that is multiplied by istelf and then by itself again.
1.4.2 Calculate squares, square roots, cubes and cube roots
The reverse of raising to a power is taking a root.
2² = 4
√4 = 2
∛27 = 3
1.4.3 Use index notation and index laws for multiplication and division of positive and negative integer powers including zero
- The powers of a number is the definition of a number getting multiplied by itself again and again
- 21 means 2
- 22 means 2 × 2
- 25 means 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2
- Keep in mind that any number except 0 to the power of 0 is always equal to 1
1.4.4 Express integers as a product of powers of prime factors
- The root of a number is the opposite of a power of a number
- A square root of 16 is a number that when squared equals 16
1.4.5 Find highest common factors (HCF) and lowest common multiples (LCM)
Type 1: Highest Common Factor (HCF)
What is HCF?
It is the highest common factor that 2 numbers share, for example 88 and 121 share the HCF of 11.
Step 1: Find the factor of A
Step 2: Find the factor of B
Step 3: Find the highest common factor
Type 2: Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)
What is LCM?
It is the lowest common multiple of 2 numbers.
Step 1: Find the multiple of A
Step 2: Find the multiple of B
Step 3: Find the lowest common multiple
1.4.6 Understand the meaning of surds (Higher Tier Only)
A surd is the square root of a number that is not a square number, for example √8 is not a square number so therefore it has to be broken down into 4 and 2. In which 4 is a square number, therefore √8 becomes 2√2
1.4.7 Manipulate surds, including rationalising a denominator (Higher Tier Only)
1.4.8 Use index laws to simplify and evaluate numerical expressions involving integer, fractional and negative powers (Higher Tier Only)

