REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Mathematics A
1.3 Decimals
1.3.1 Use decimal notation
7×106
= 7,000,000
(the decimal point went to the right by 6 digits)
8×10-4
= 0.0004
(the decimal point went to the left by 4 digits)
1.3.2 Understand place value
What is place value?
- When a number is displayed with digits in words, each one of the digits has their own value which is dependant on where it is located within a number
- For example in the number 12345.
- 5 = ones
- 4 = tens
- 3 = hundreds
- 2 = thousands
- 1 = ten thousands
- So therefore this “12345” in words would be “twelve thousand three hundred forty five”
1.3.3 Order decimals
7 + 0.5 + 0.04 + 0.003+ 0.0002
= 7.5432
8.5 + 0.004+ 0.0005
= 8.5405
1.3.4 Convert a decimal to a fraction or a percentage
Equivalent fractions are used to compare the sizes of fractions written with a different denominator
- 0.25 = 25% or ¼
- 0.2 = 20% or ⅕
1.3.5 Express a given number as a fraction of another number
Terminating decimals stop after a finite number of decimal places.
Example: 0.315
Terminating decimals can be written as exact fractions with denominator 10, 100, 1000, etc. and then cancelled down when possible.
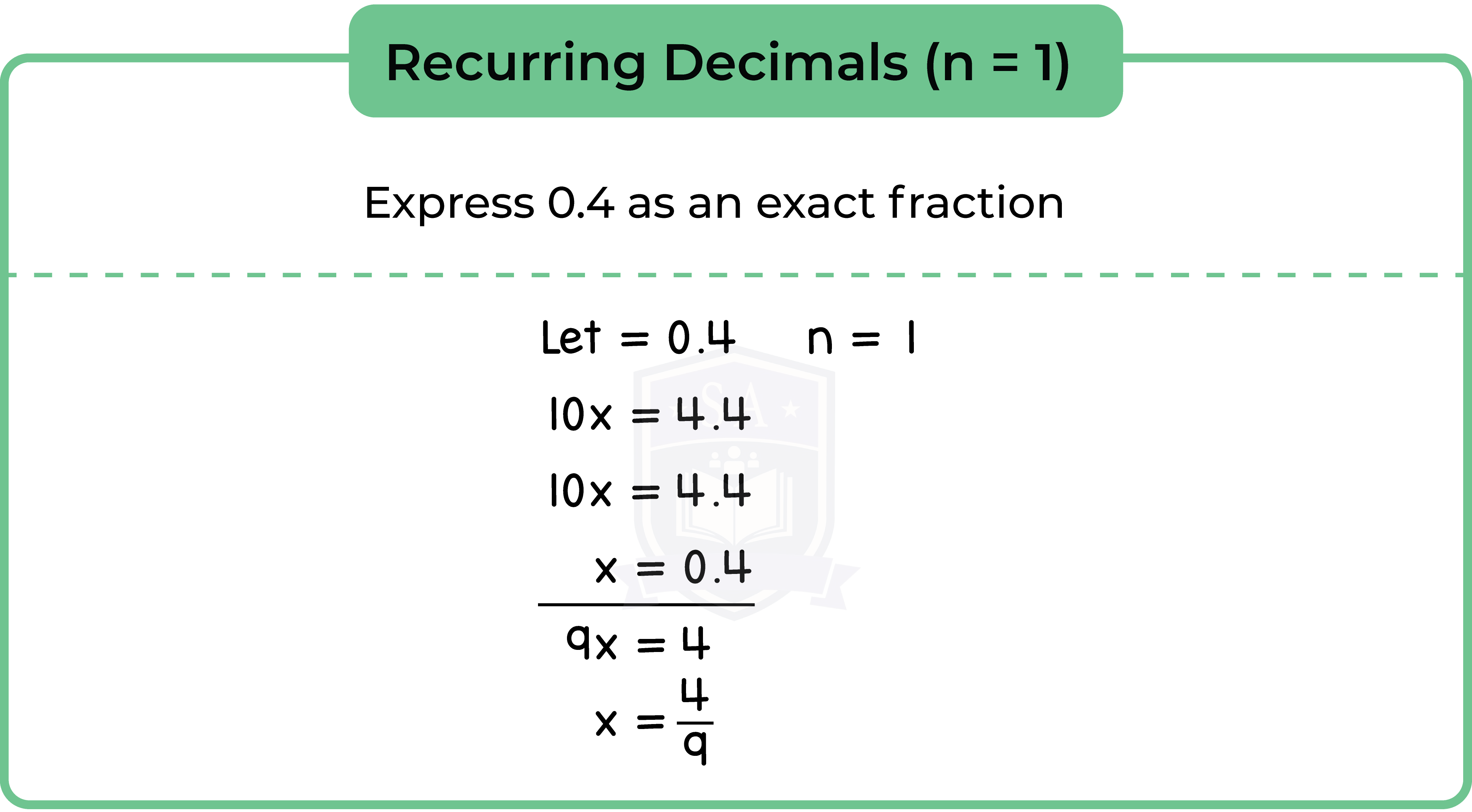
1.3.6 Convert recurring decimals into fractions (Higher Tier Only)
Recurring decimals do not stop after a finite number of decimal places, but they do settle into a patern of digits that repeats indefinitely.
Example: 0.315 315 315 315 315…
Recurring decimals can be written as exact fractions