REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics
a
1.6 The Binomial Series
1.6.1 Use of the binomial series (1 + x)n


Type 1: Binomial Expansion (n is a positive integer)

Type 2: Binomial Expansion (n is a negative integer)
When n is a negative integer, none of the (n – r) terms in the coefficient will be equal to zero, so the series will be infinite.

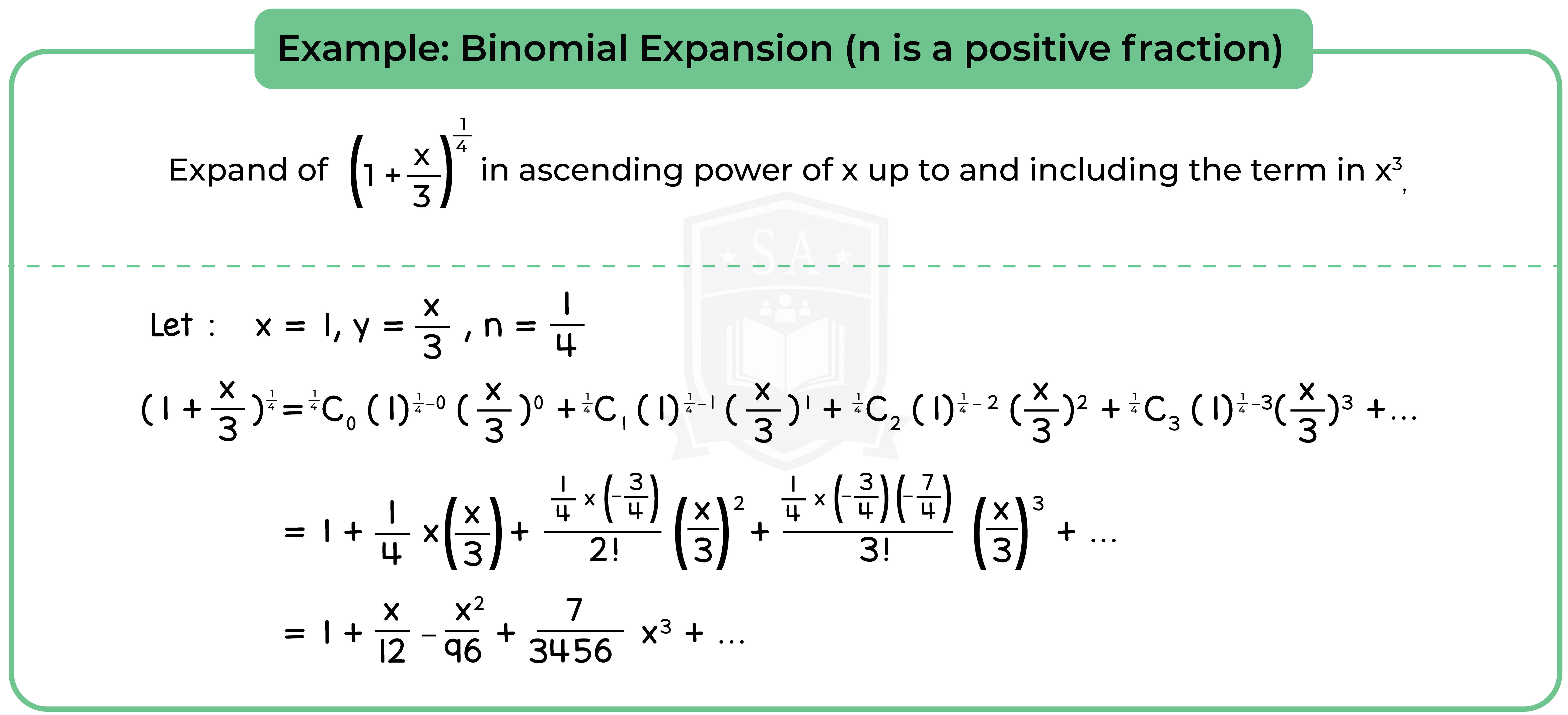
Type 3: Binomial Expansion (n is a positive fractions)
Type 3: Binomial Expansion (n is a negative fraction)


