REVISION NOTES
1.3.1 Simple algebraic division
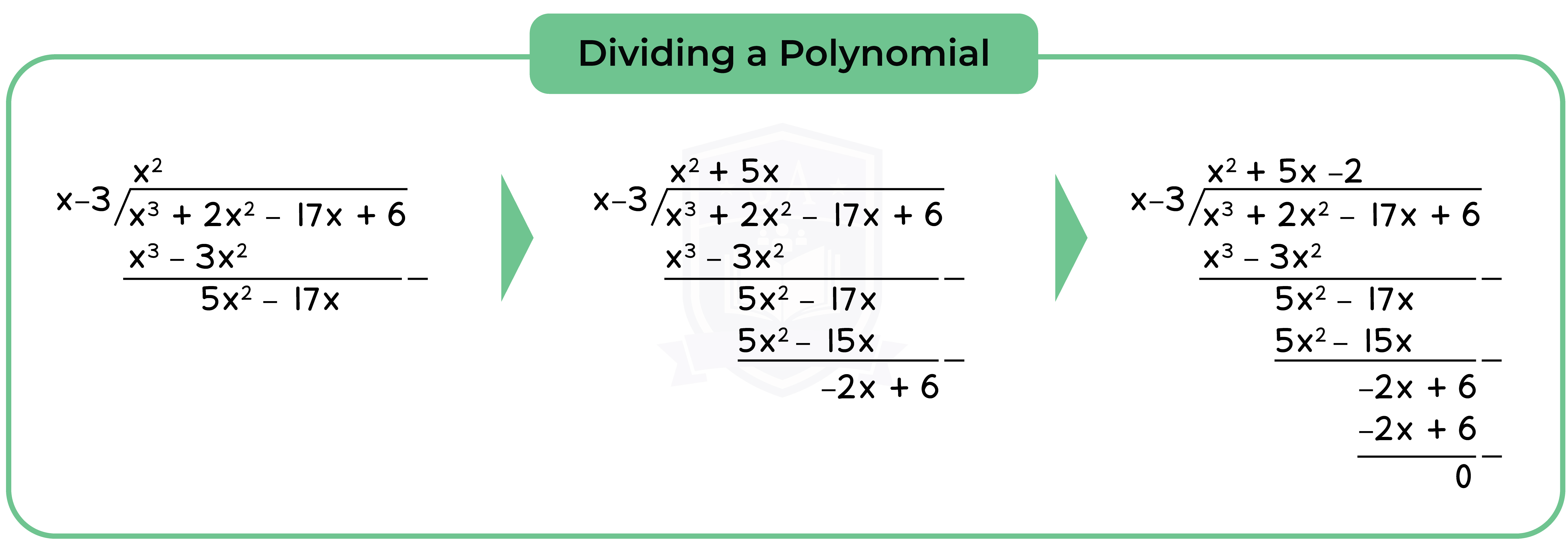
1.3.2 The factor and remainder theorems
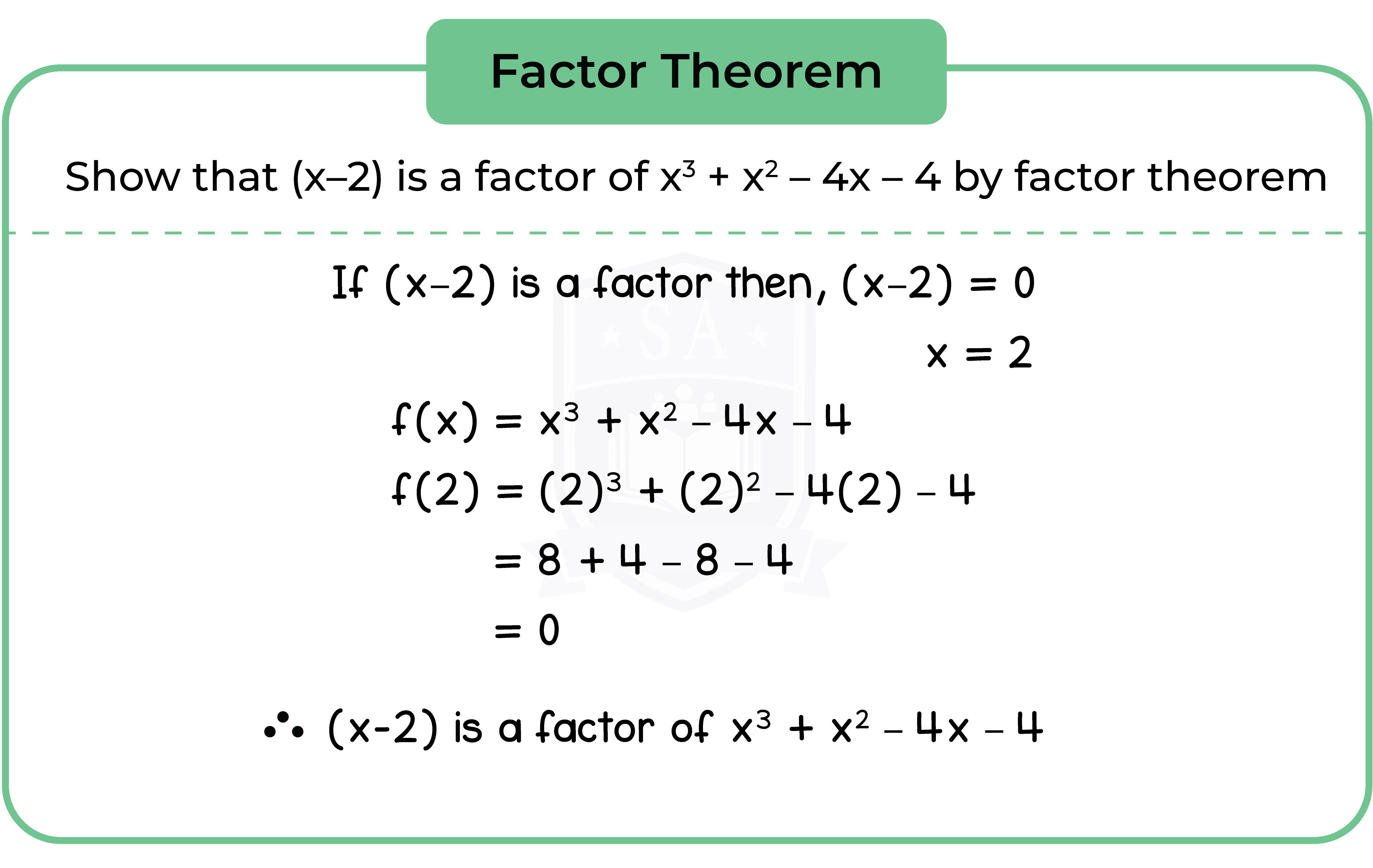
Part 1: Factor Theorem
If f(x) is a polynomial and f(p) = 0, the (x – p) is a factor of f(x).

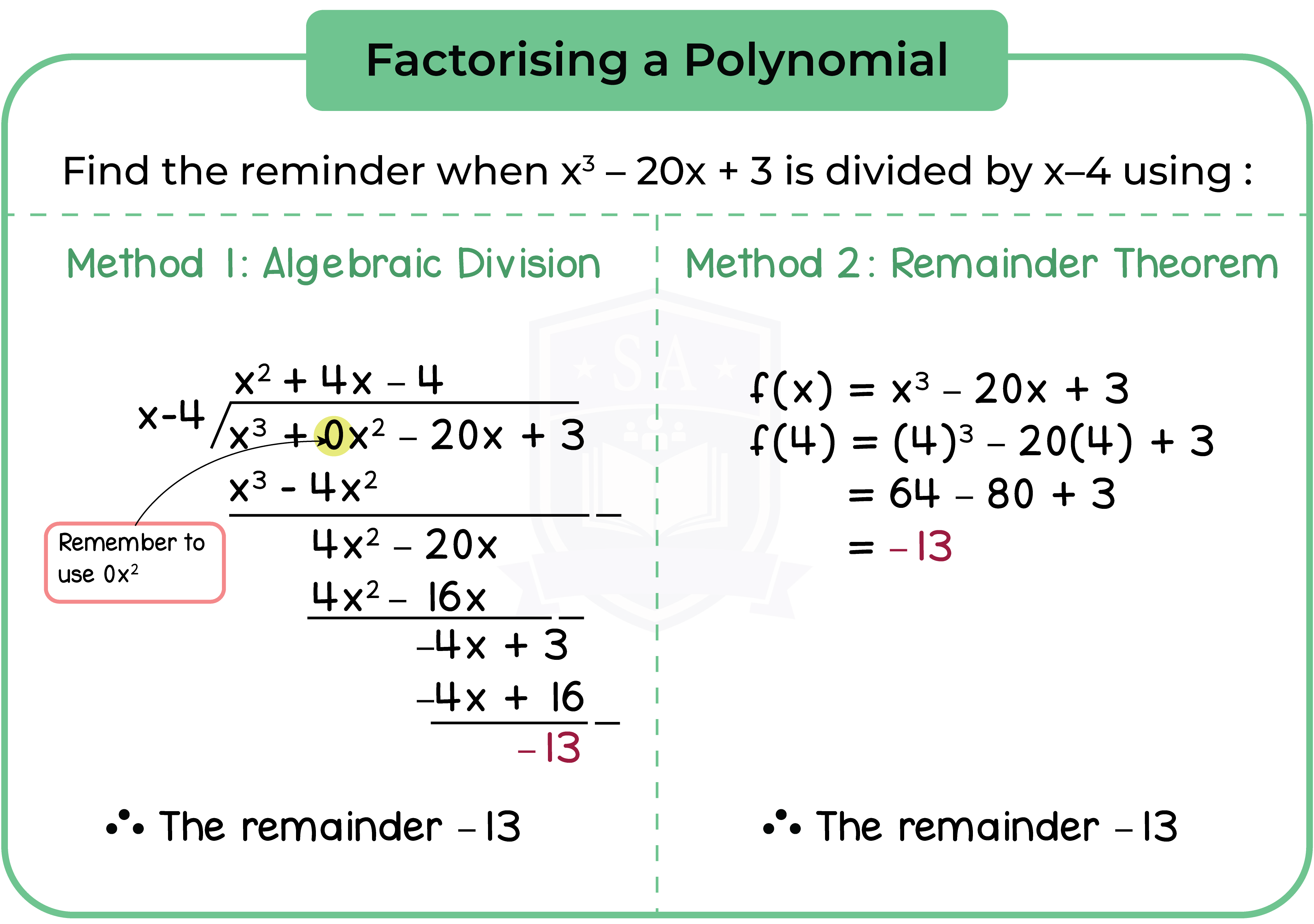
Part 2: Remainder Theorem
If a polynomial f(x) is divided by (ax – b), the remainder is f(b/a).
1.3.3 Simple inequalities, linear and quadratic

If two sides of an equation are not equal, use inequalities.
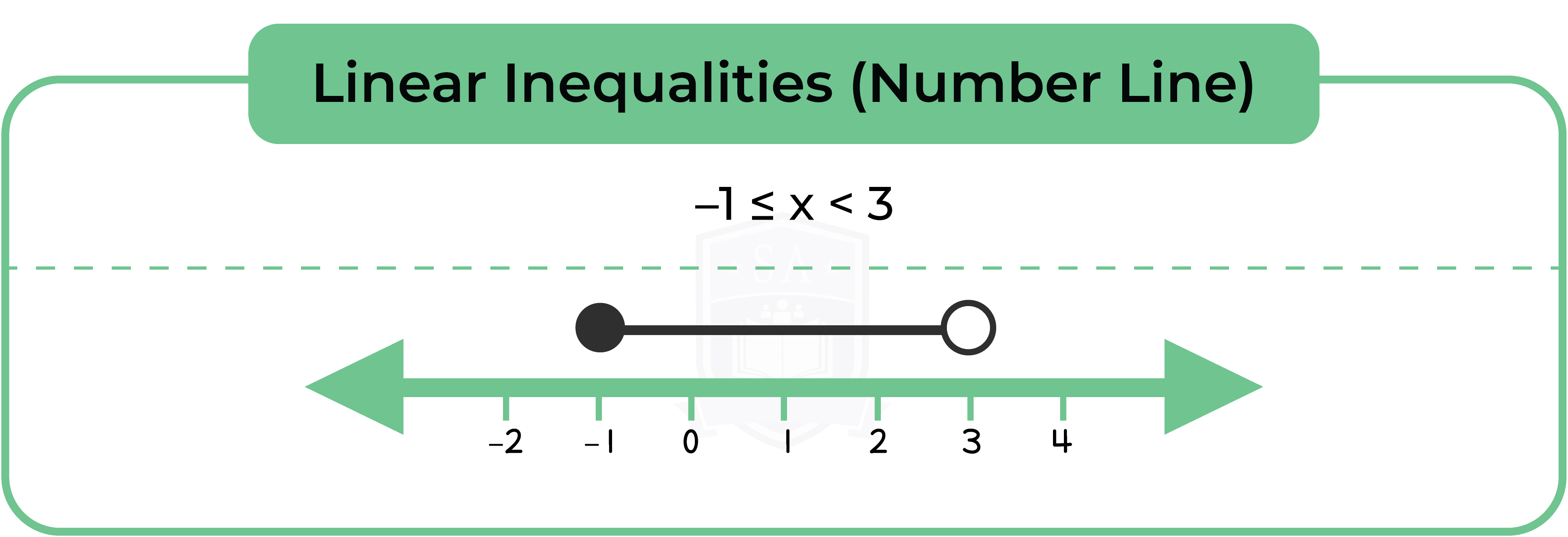
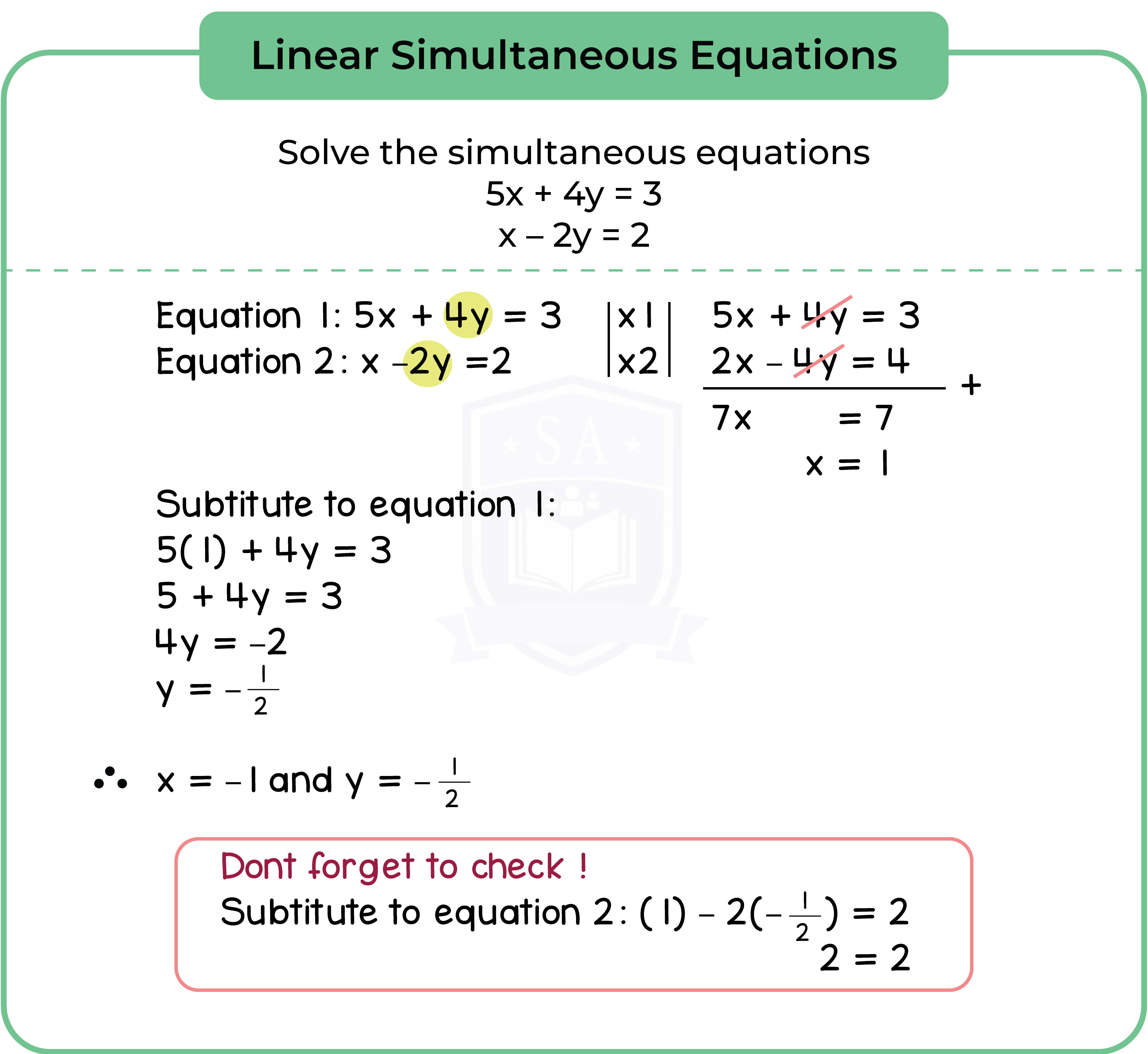
Type 1: Linear Inequalities
Solving linear inequalities is just like solving linear equations.

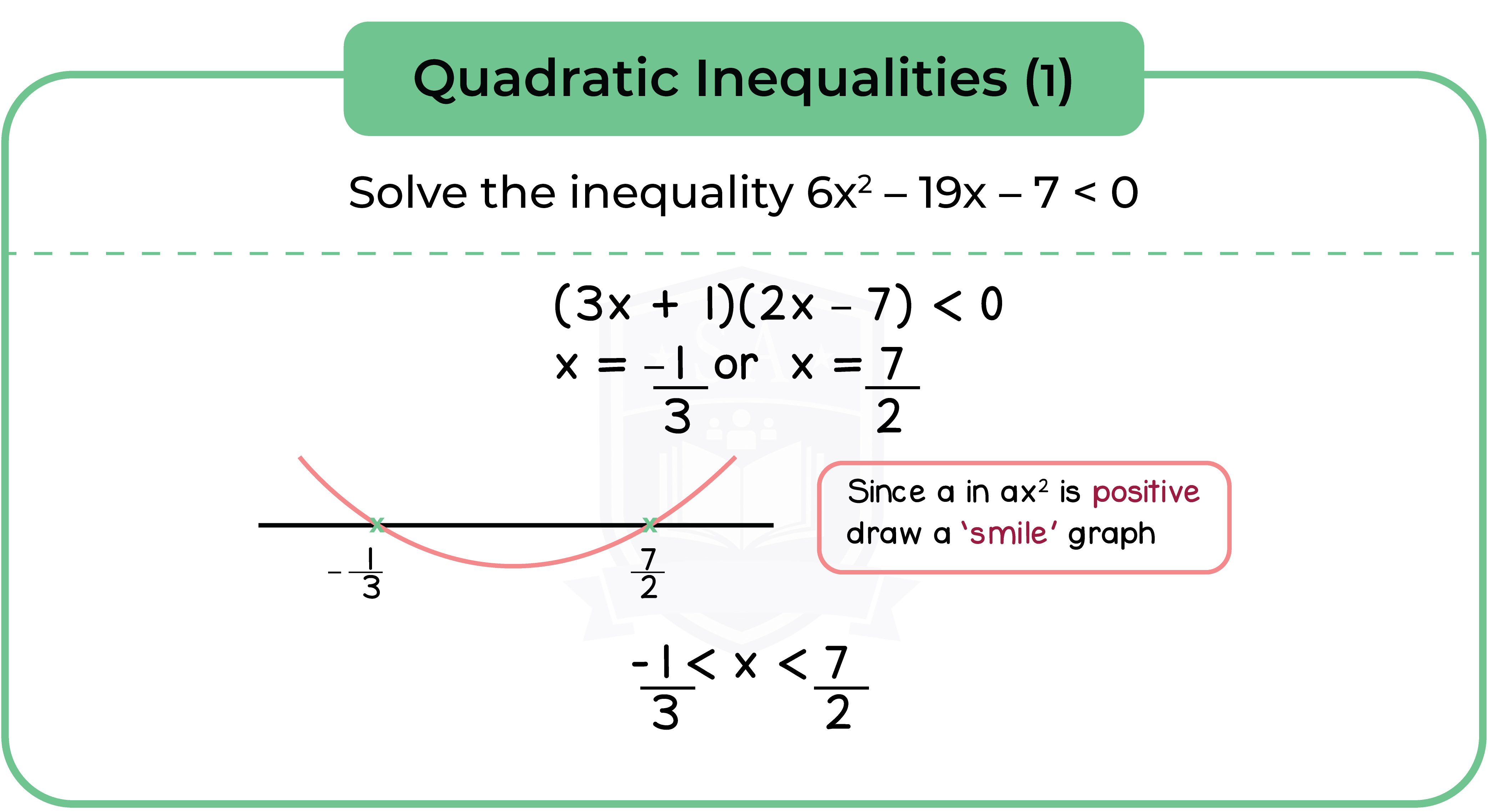
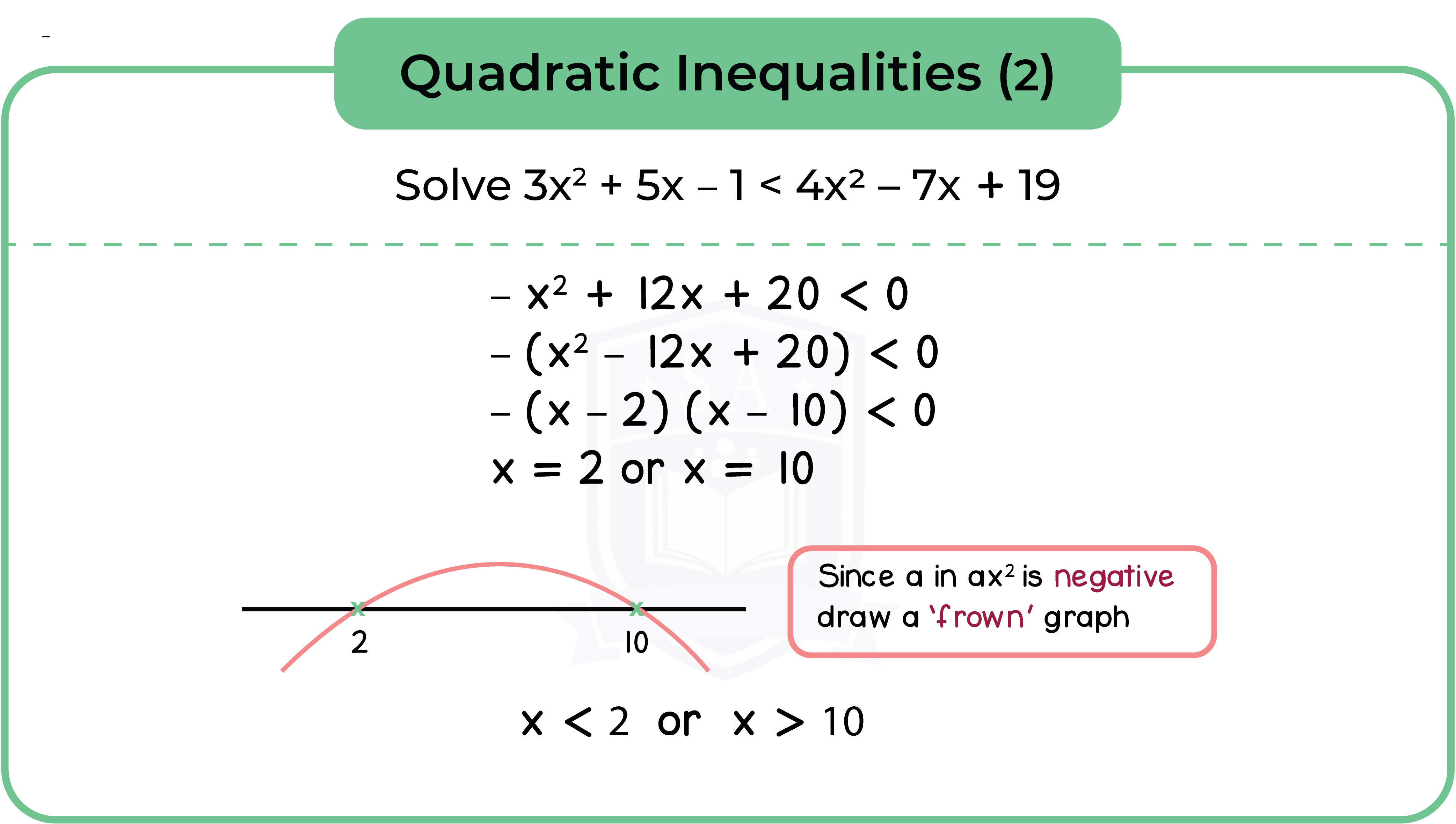
Type 2: Quadratic Inequalities
Step 1: Rearrange the quadratic equation into f(x) > 0 or f(x) < 0
Step 2: Factorise and solve the quadratic equation
Step 3: Sketch a quadratic graph using a number line
Step 4: Solve the quadratic inequalities
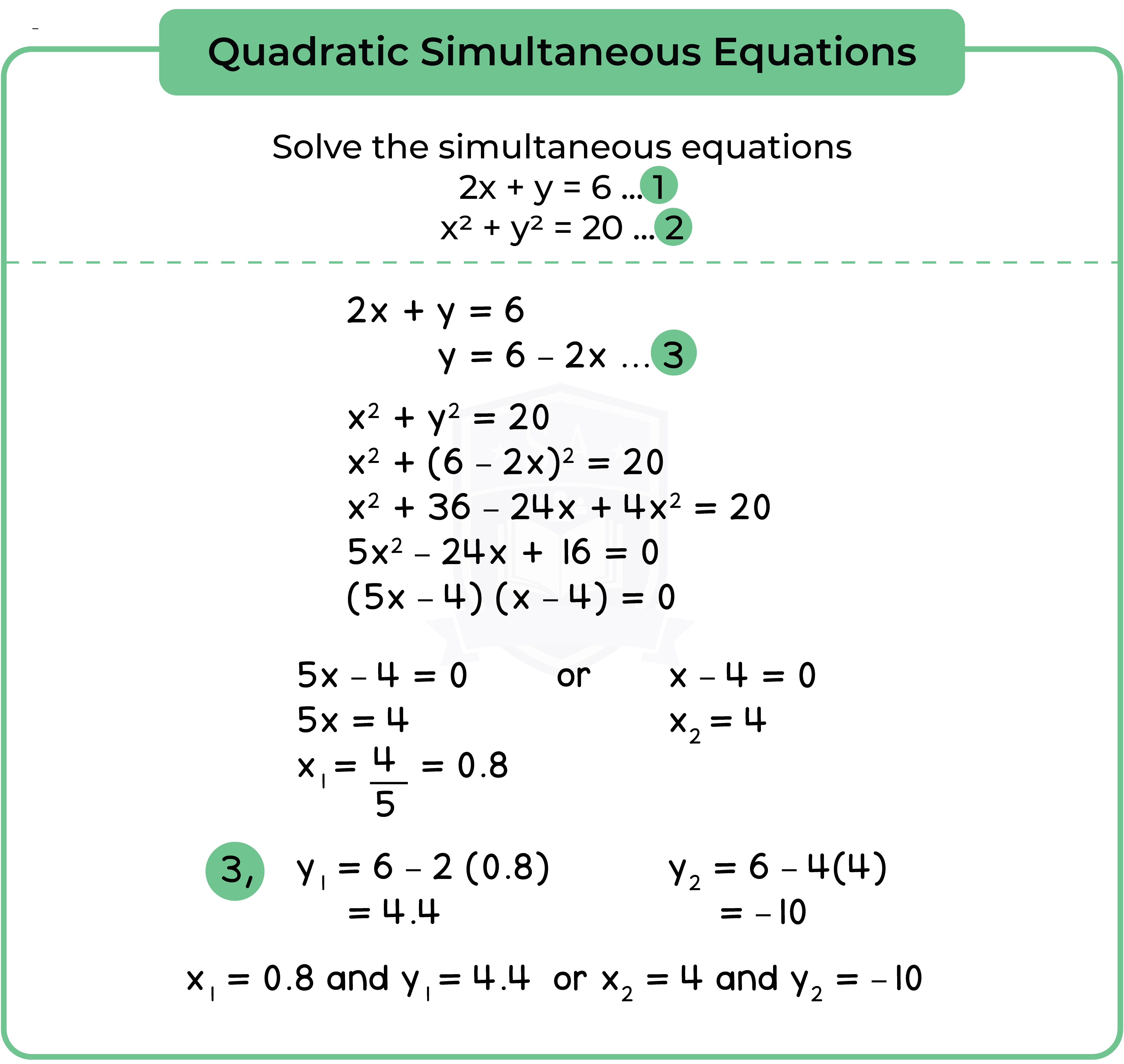
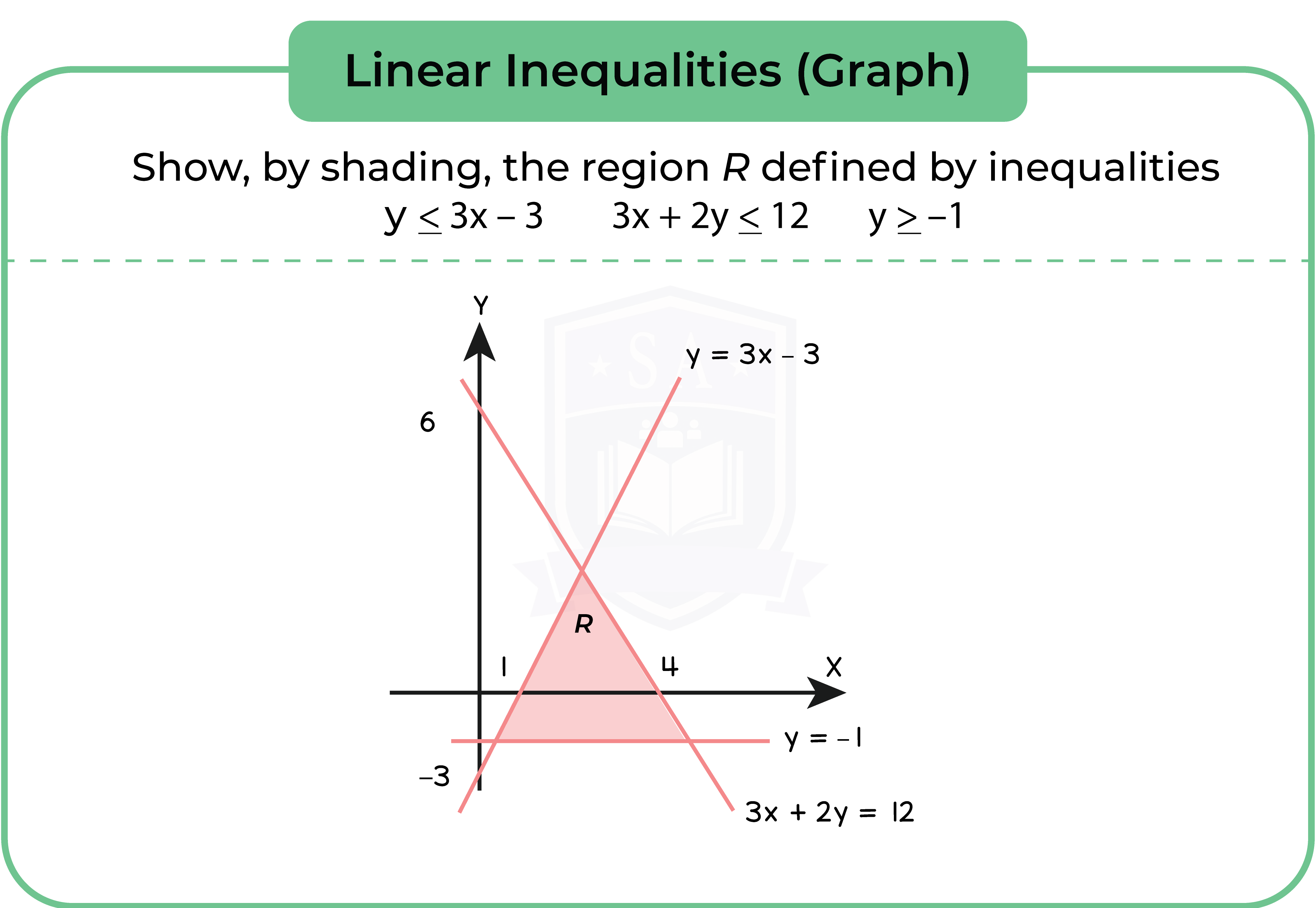
1.3.4 The graphical representation of linear inequalities in two variables
Type 1: Linear Inequalities (Graph)
Step 1: Draw the line for each equation
Step 2: Use a coordinate to determine whether the the region is true or not true
Step 3: Shade the region that is true
Step 4: Label the region R

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.