REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Further Pure Mathematics
1.2 The Quadratic Function
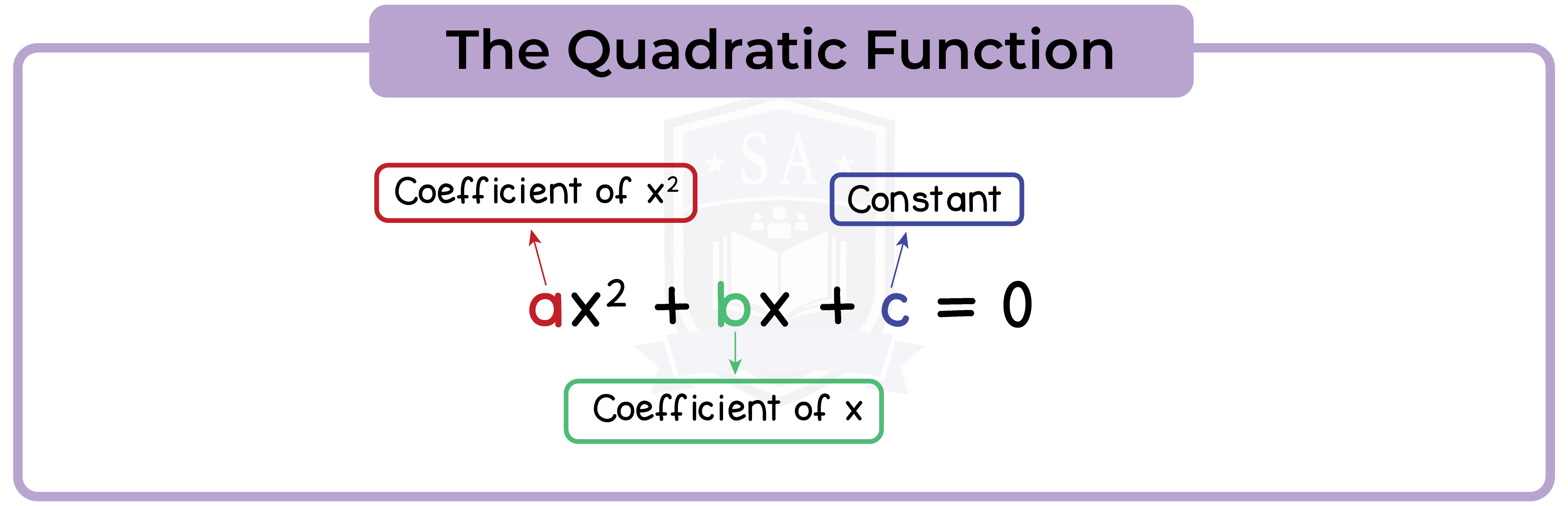
A quadratic function has the form ax2 + bx + c where a, b and c are constants and a is not 0.
1.2.1 The manipulation of quadratic expressions
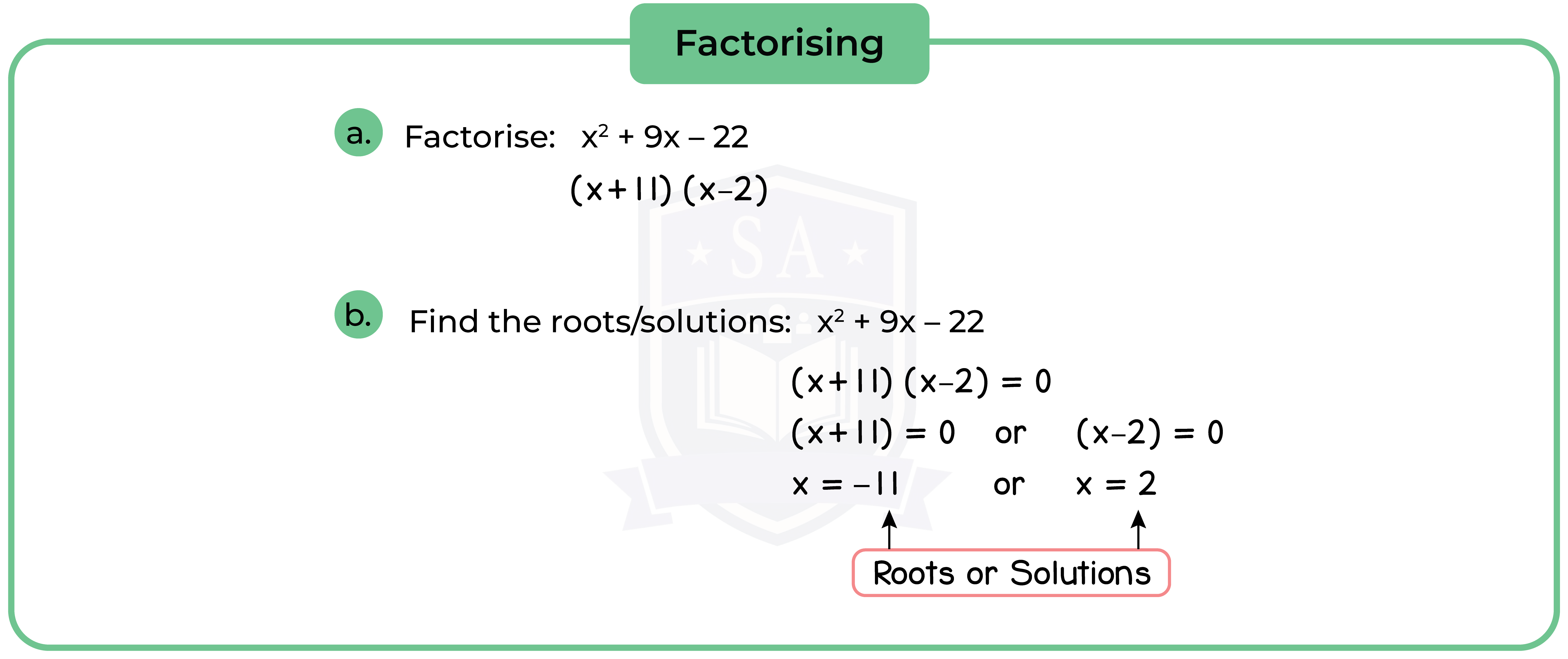
Type 1: Factorisation
Factorisation involves writing the quadratic expression of x2+ bx + c in the form (x + p)(x + q).
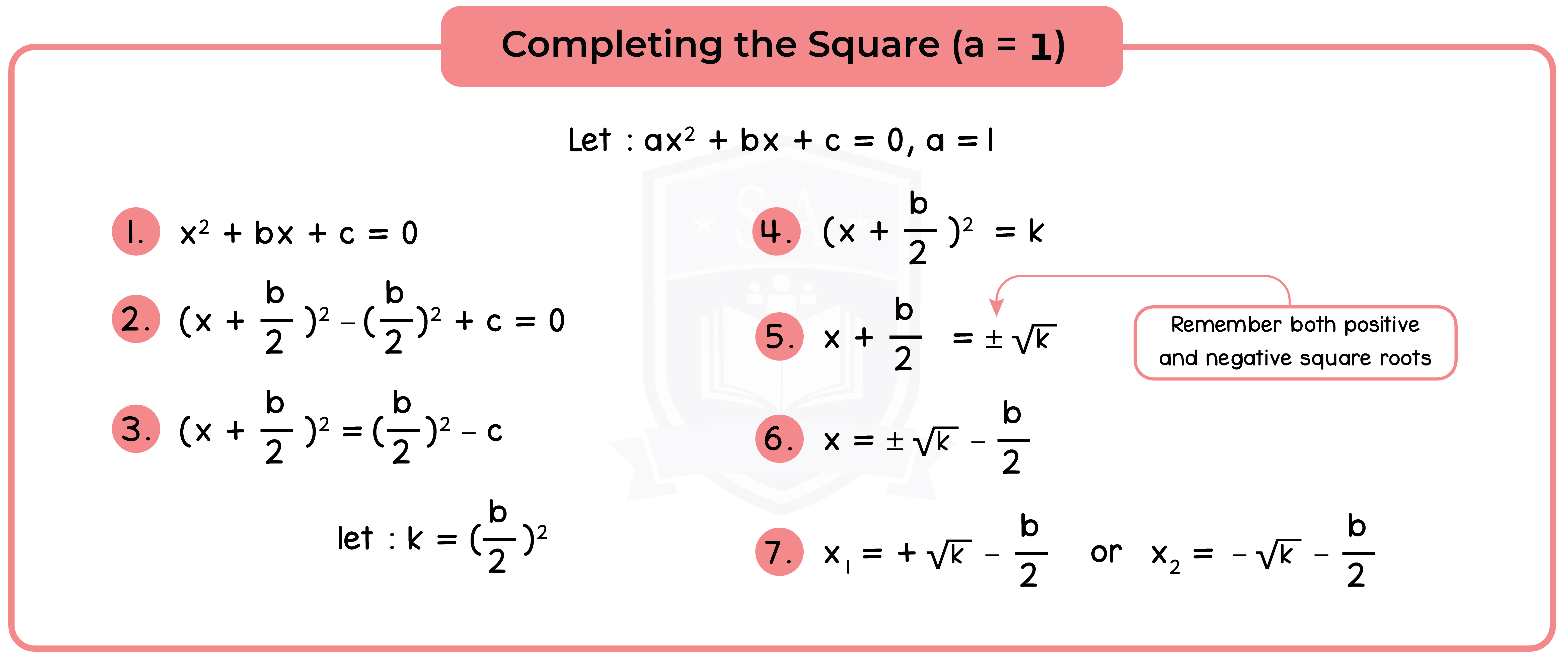
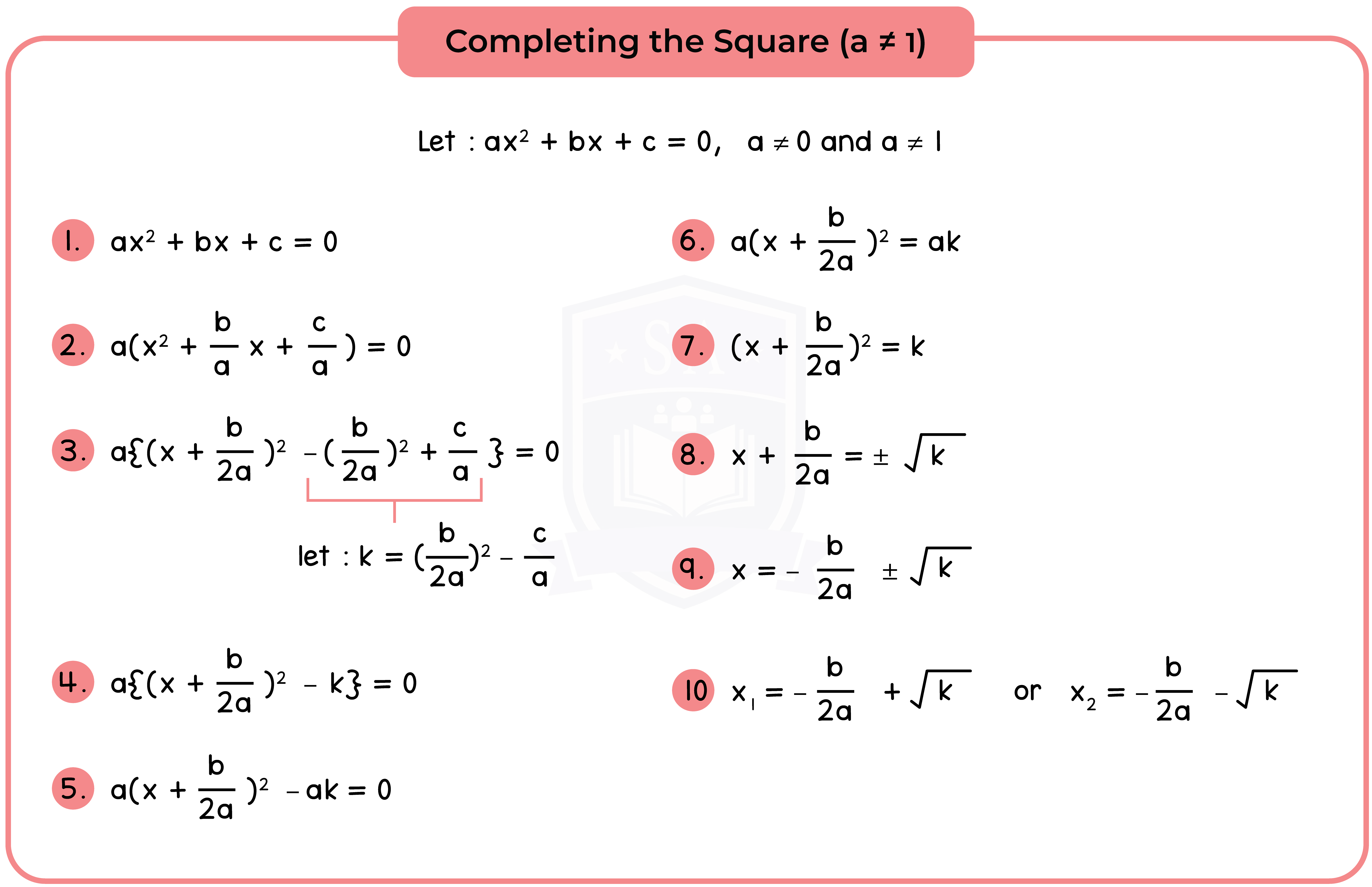
Type 2: Completing the Square
Completing the Square involves writing the expression x2 + bx + c in the form (x + p)2 + q.


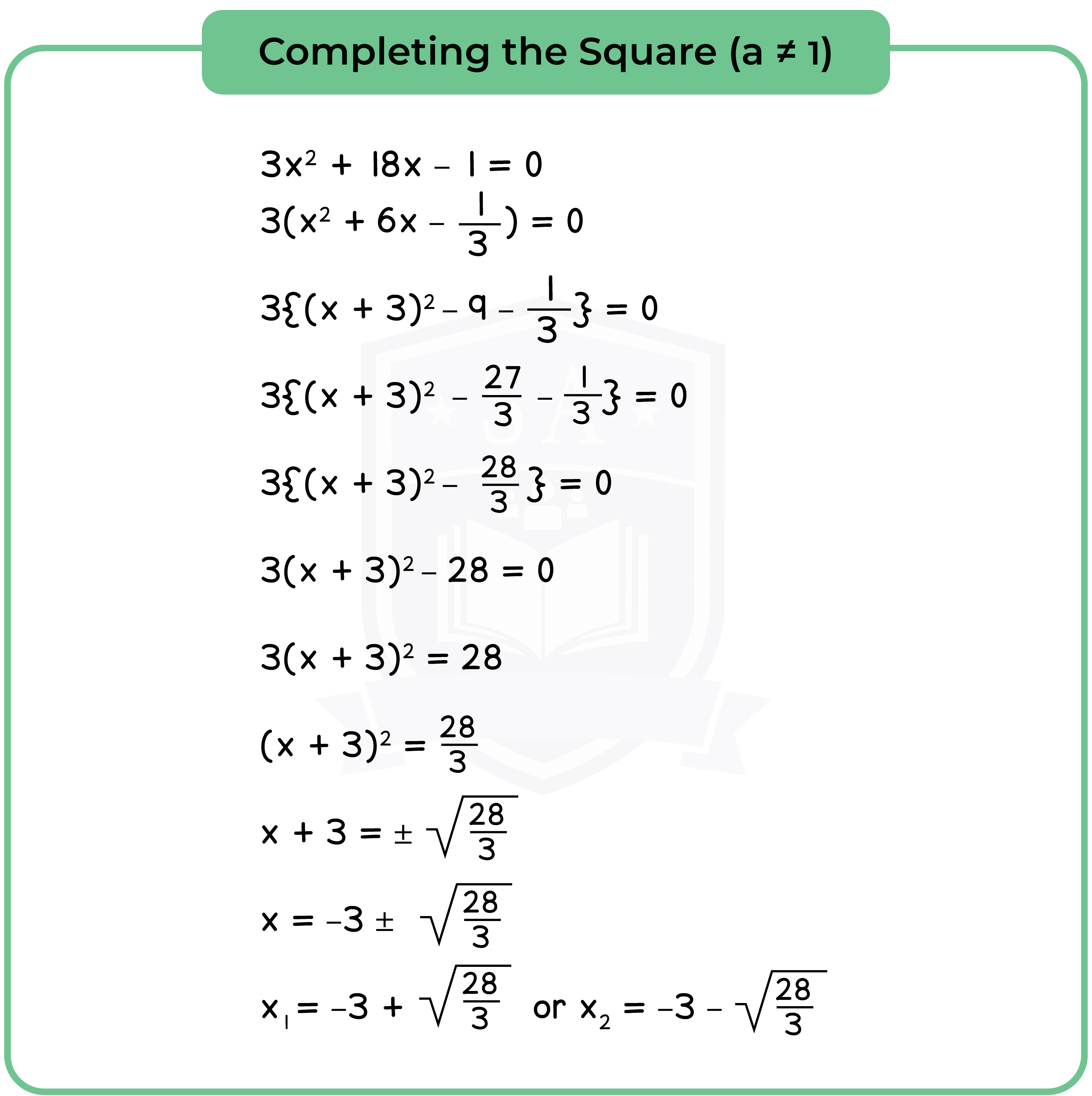
1.2.2 The roots of a quadratic equation
Method 1: Solve by Factorisation
Step 1: Factorise the quadratic equation [See 1.2.1].
Step 2: Equate to 0 (Null Factor Law).
Step 3: Find the roots or solution.
Method 2: Solve by Completing the Square
Step 1: Complete the Square [See 1.2.1].
Step 2: Equate to 0 (Null Factor Law).
Step 3: Find the roots or solution.
Method 3: Quadratic Formula
Step 1: Determine a, b and c.
Step 2: Substitute to quadratic formula to find the roots/solution.



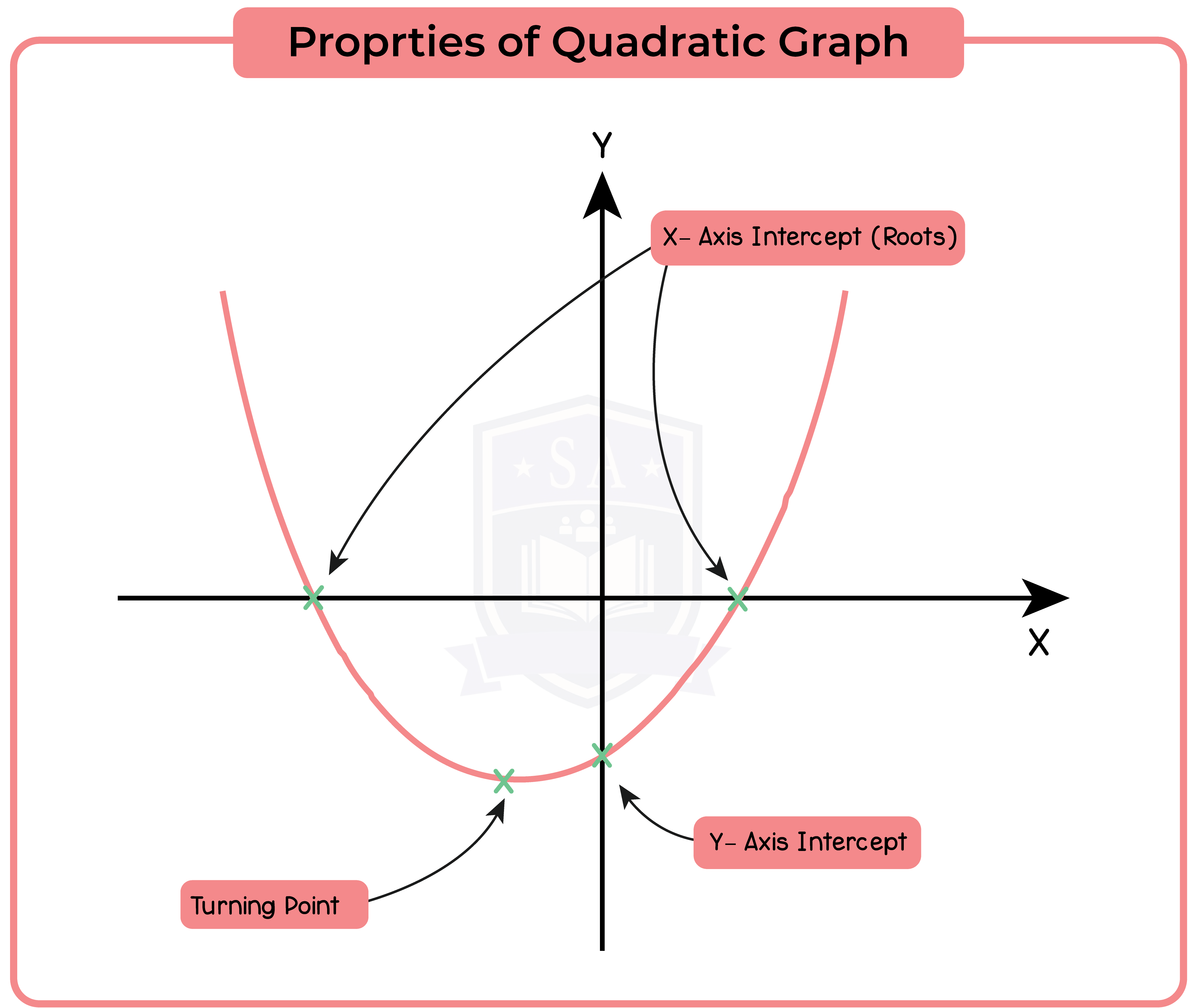
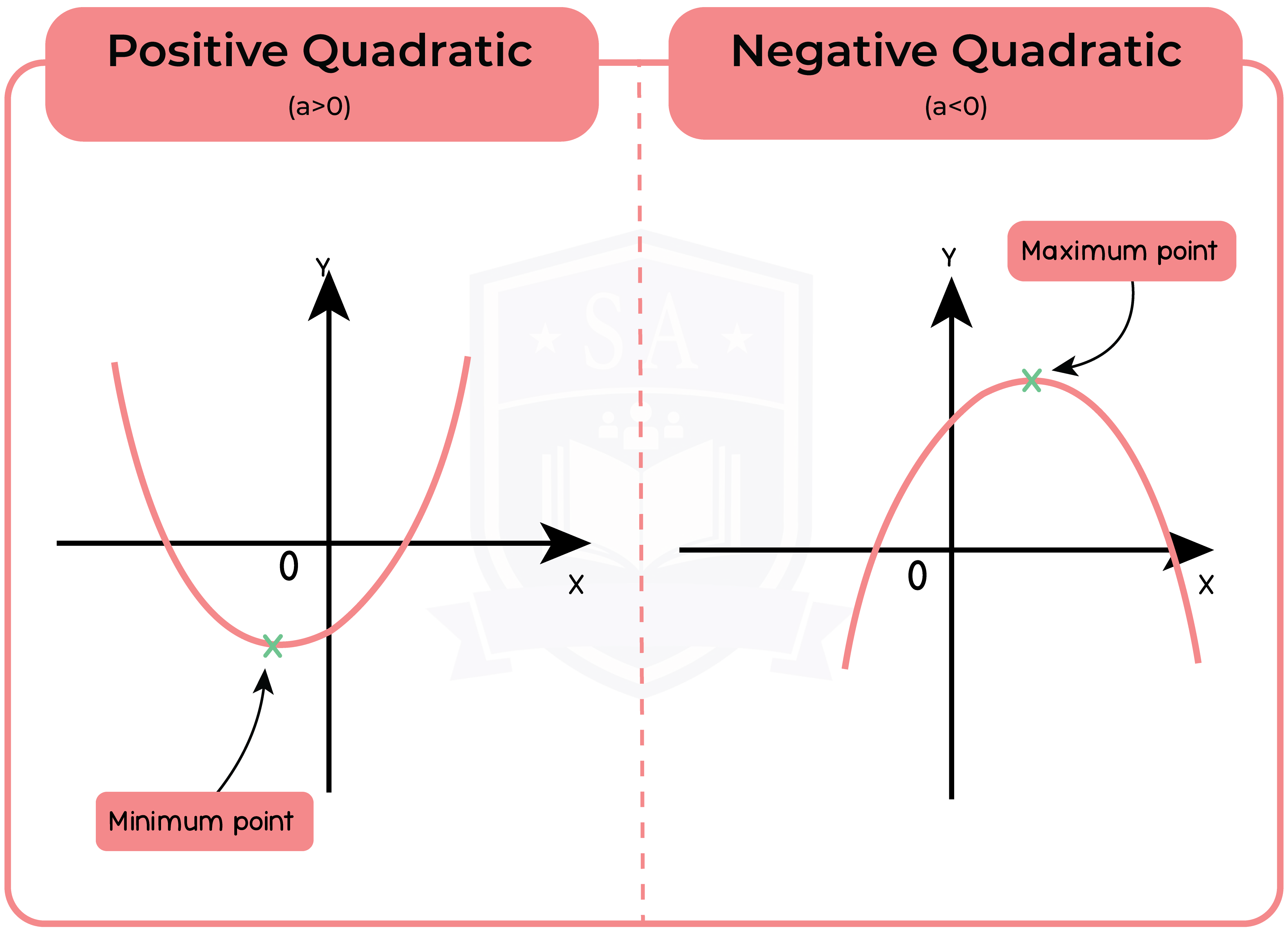
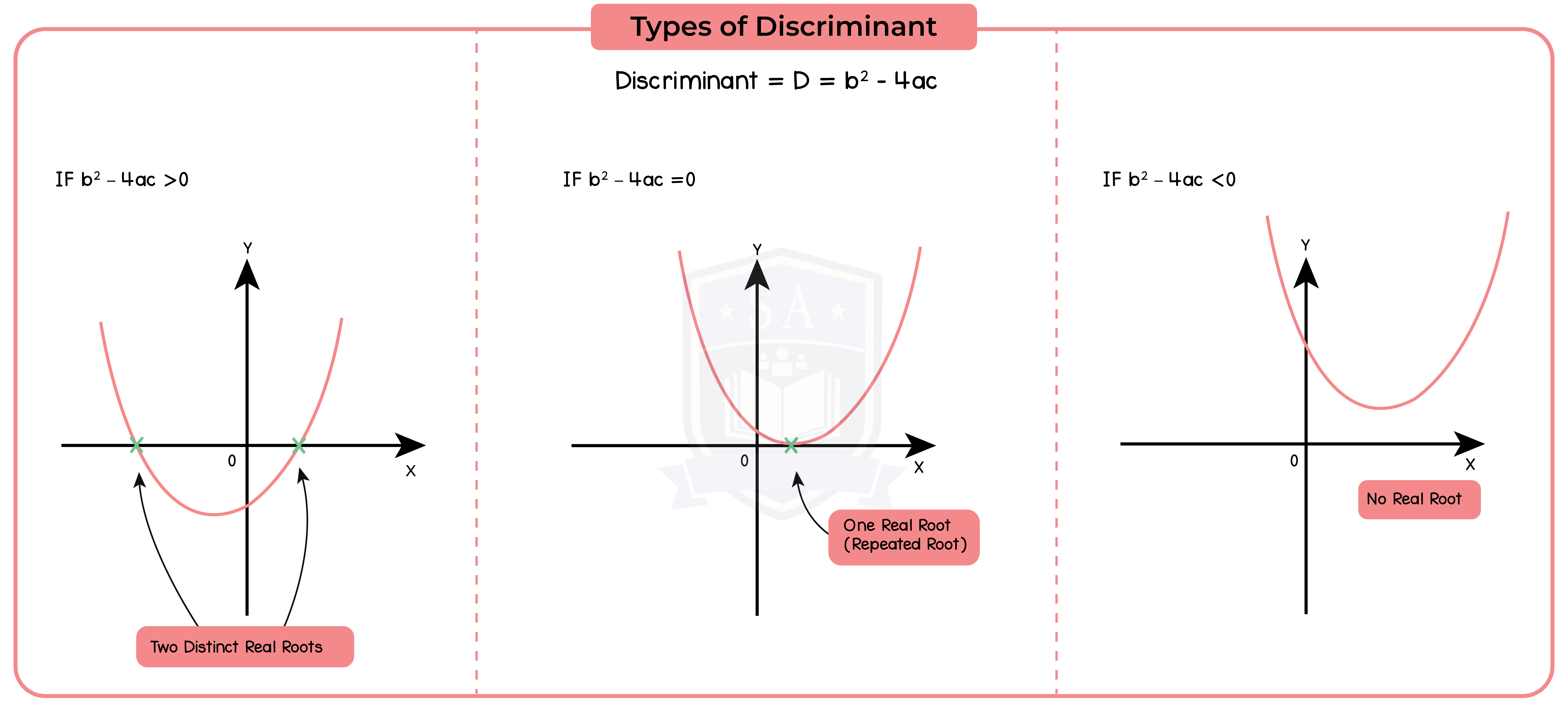
The part of the quadratic formula b2 – 4ac is called the discriminant.
The discriminant can be used to identify whether the roots are real or unreal.
1.2.3 Simple examples involving functions of the roots of a quadratic equation
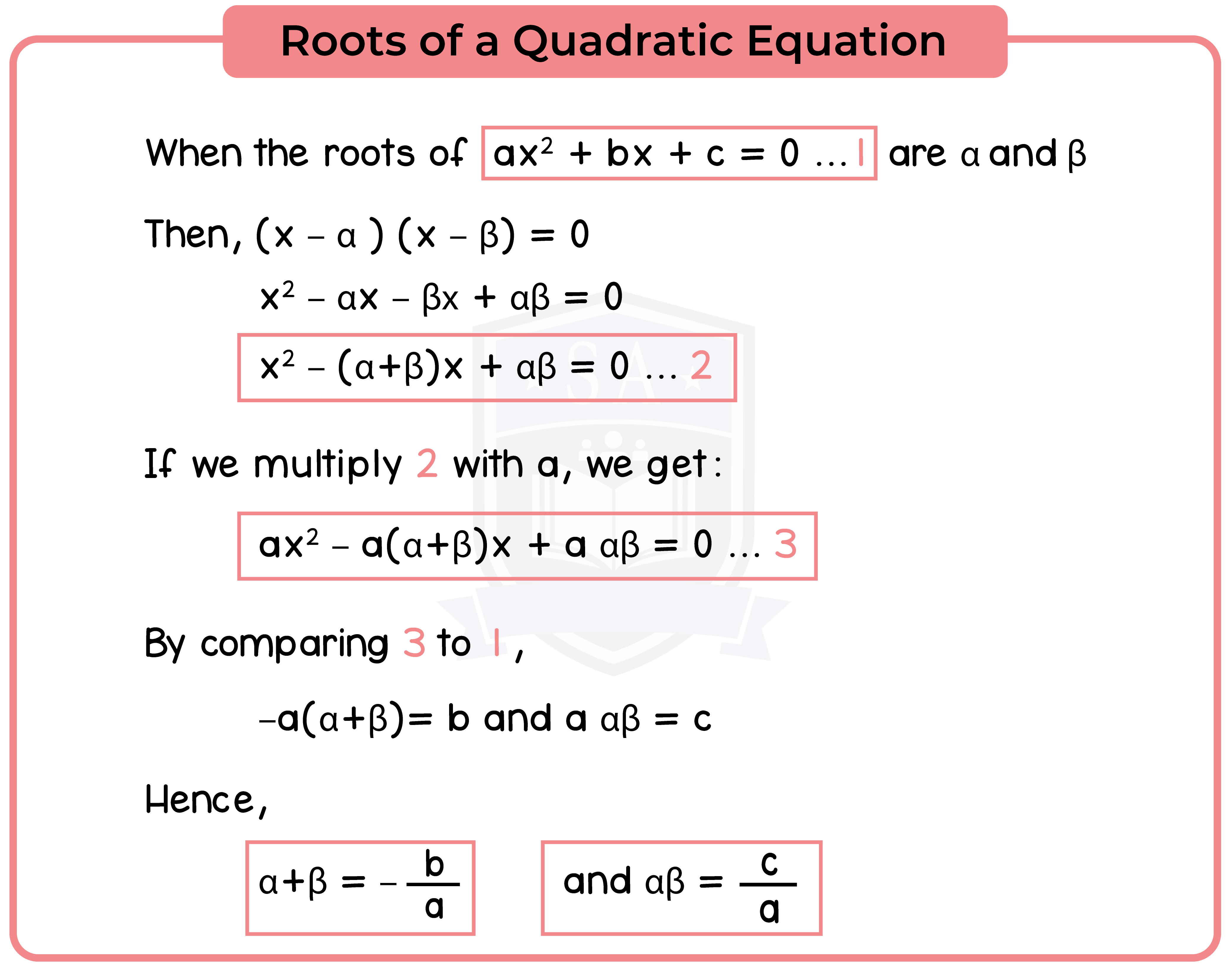
Important notes:
(a+b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab → a2 + b2 = (a+b)2 – 2ab
(a+b)3 = a3 + b3 + 3ab(a+b) → a3 + b3 = (a+b)3 – 3ab(a+b)

