REVISION NOTES
1.9.1C Understand why covalent compounds do not conduct electricity
Electricity is a flow of charged particles (e.g. ions, electrons)
Covalent compounds do not conduct electricity because the electrons are fixed in the covalent bonds
1.9.2C Understand why ionic compounds conduct electricity only when molten or in aqueous solution
Ions are fixed when ionic compounds are solid, meaning they can’t move so can’t conduct electricity.
However, when the compounds are molten or in aqueous solution, the ions (that are electrically charged) are able to move and carry charge.
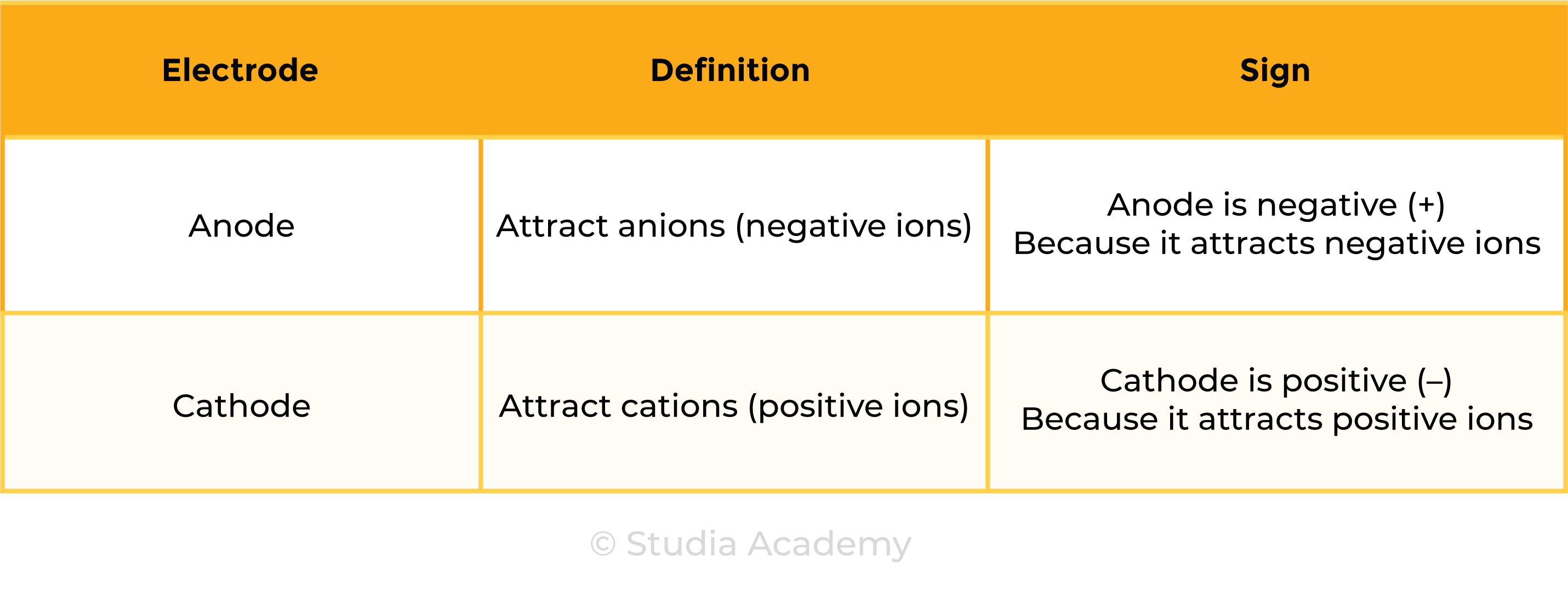
1.9.3C Know that anion and cation are terms used to refer to negative and positive ions respectively
Cations: positively charged ions (+) due to loss of electrons
Anions: negatively charged ions (-) due to gain of electrons
1.9.4C Describe experiments to investigate electrolysis, using inert electrodes, of molten compounds (including lead(II) bromide) and aqueous solutions (including sodium chloride, dilute sulfuric acid and copper(II) sulfate) and to predict the products
ELECTROLYSIS
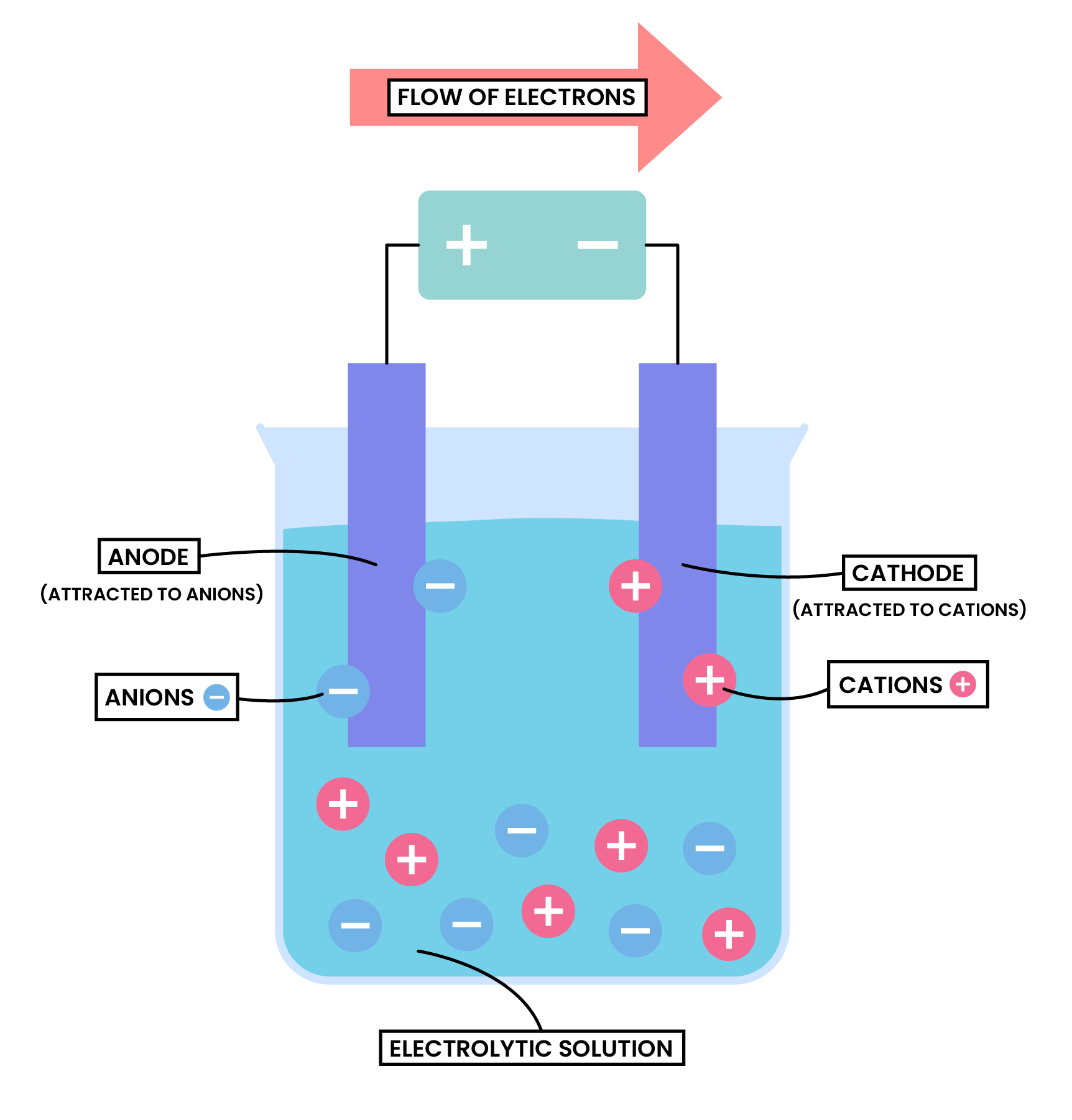
Procedure
Power supply
PRODUCTS OF ELECTROLYSIS
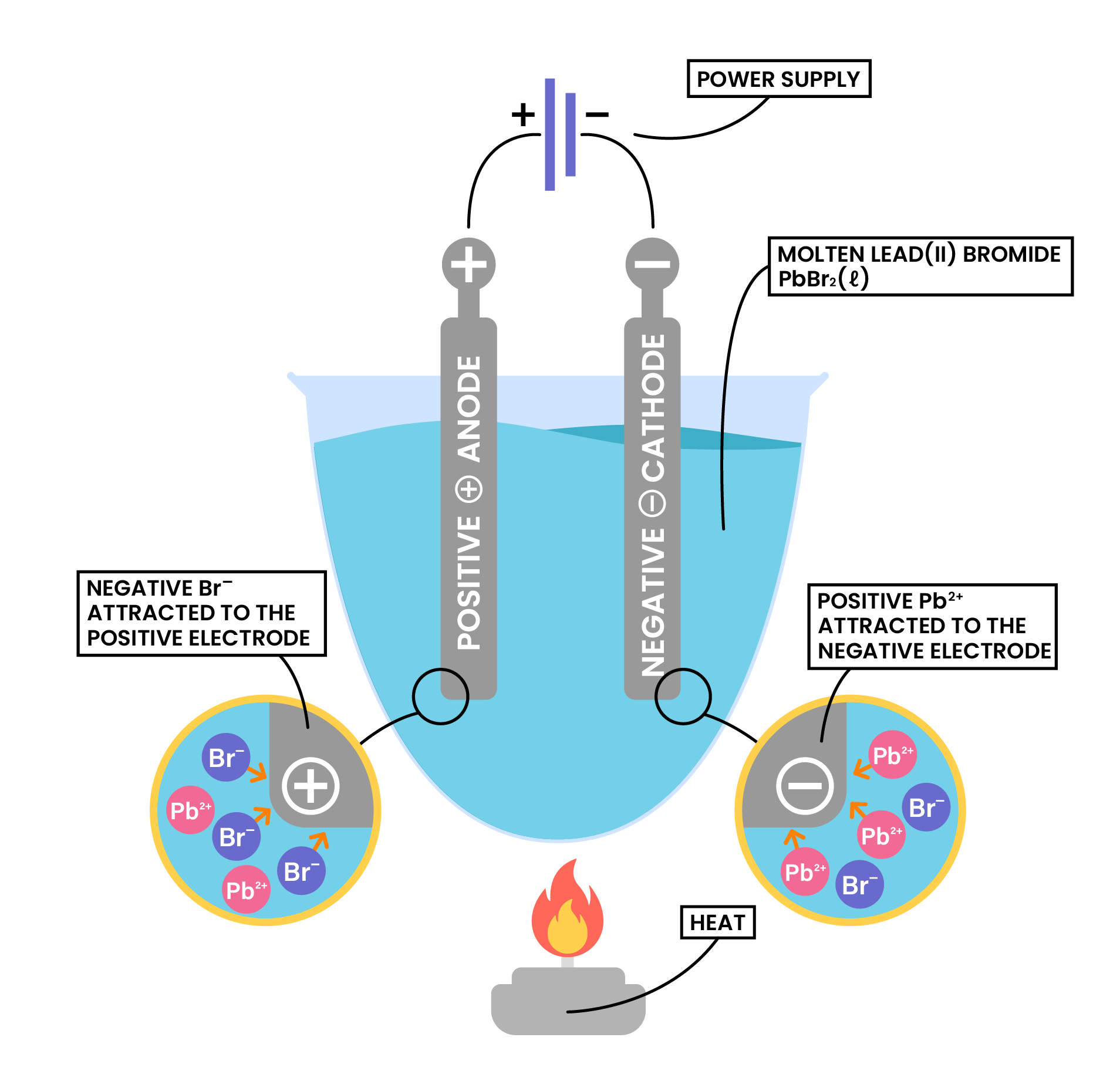
Example 1: Molten ionic compound, for example, NaCl (l)
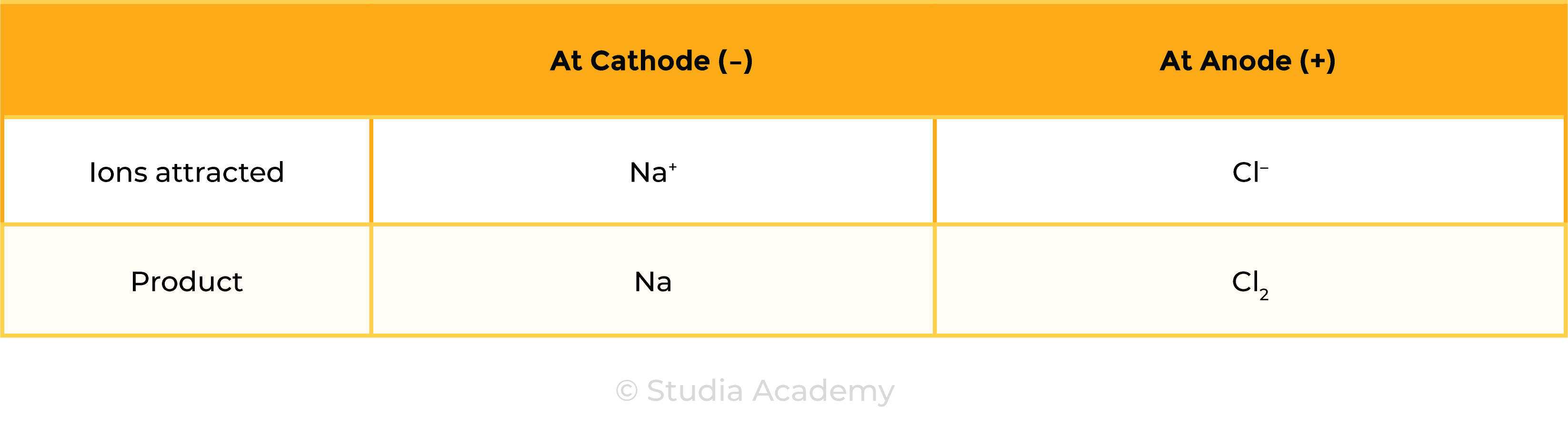
Example 2: Aqueous ionic compound, for example, NaCl (aq)
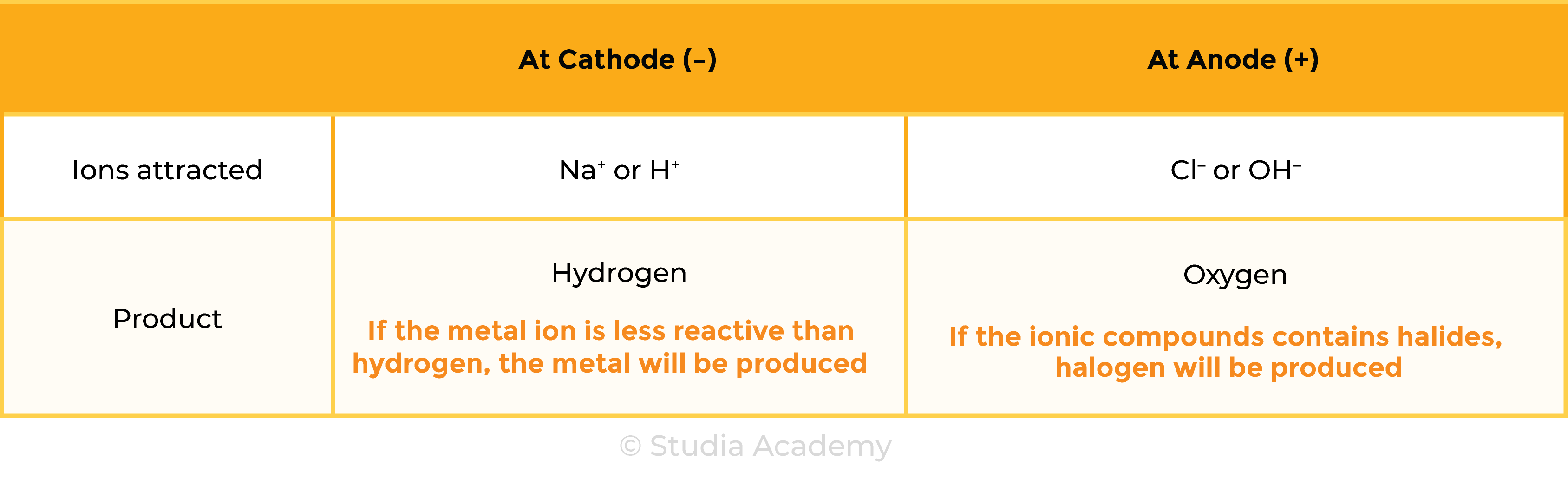
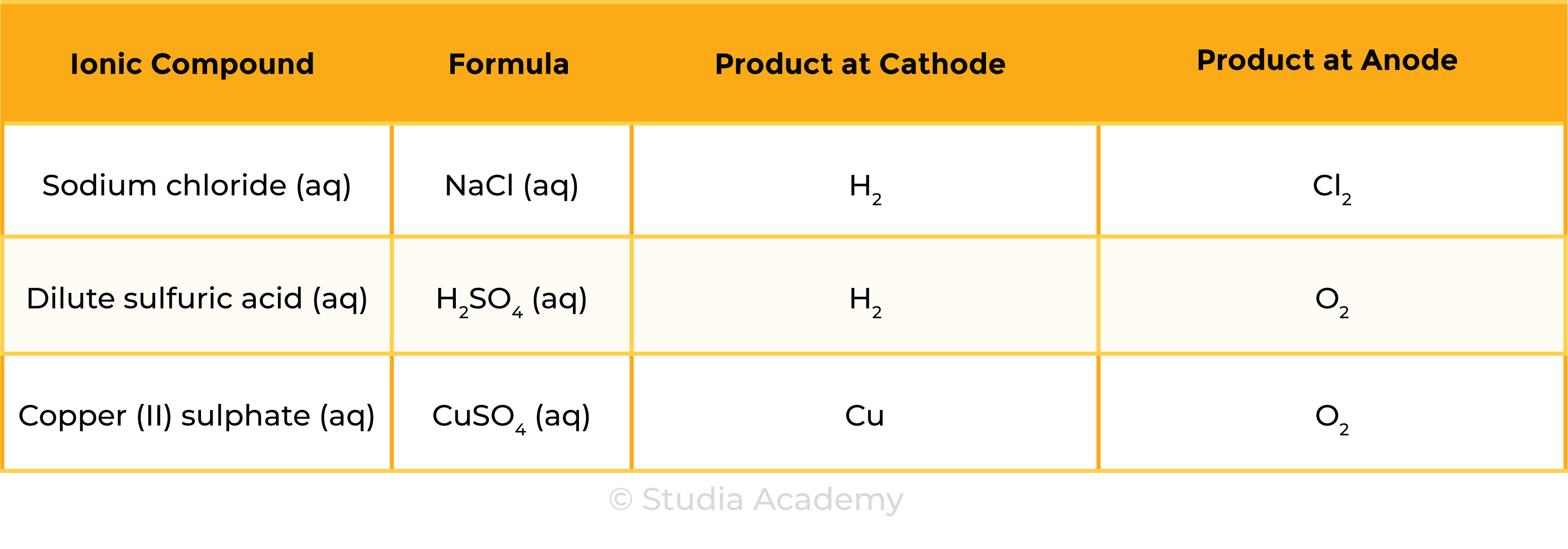
Summary Table
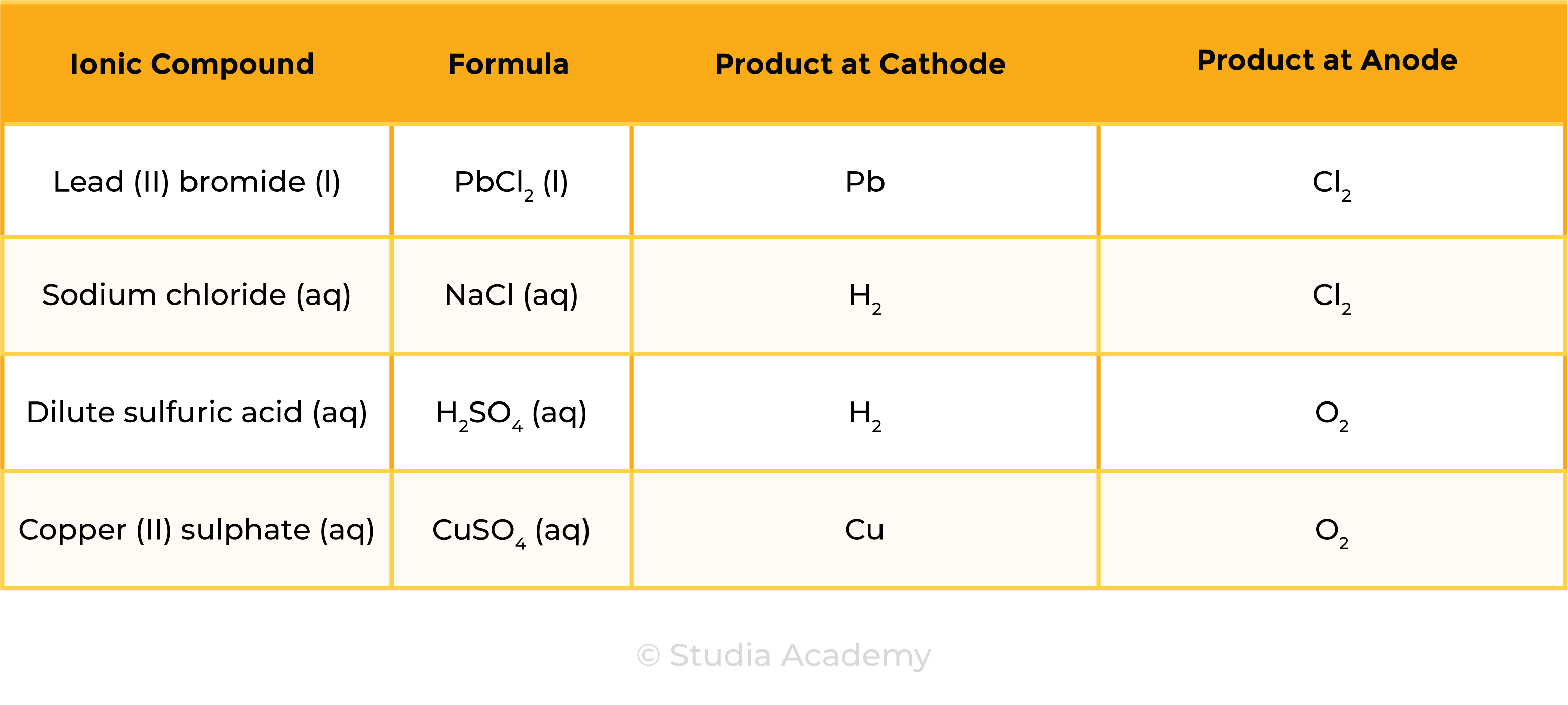
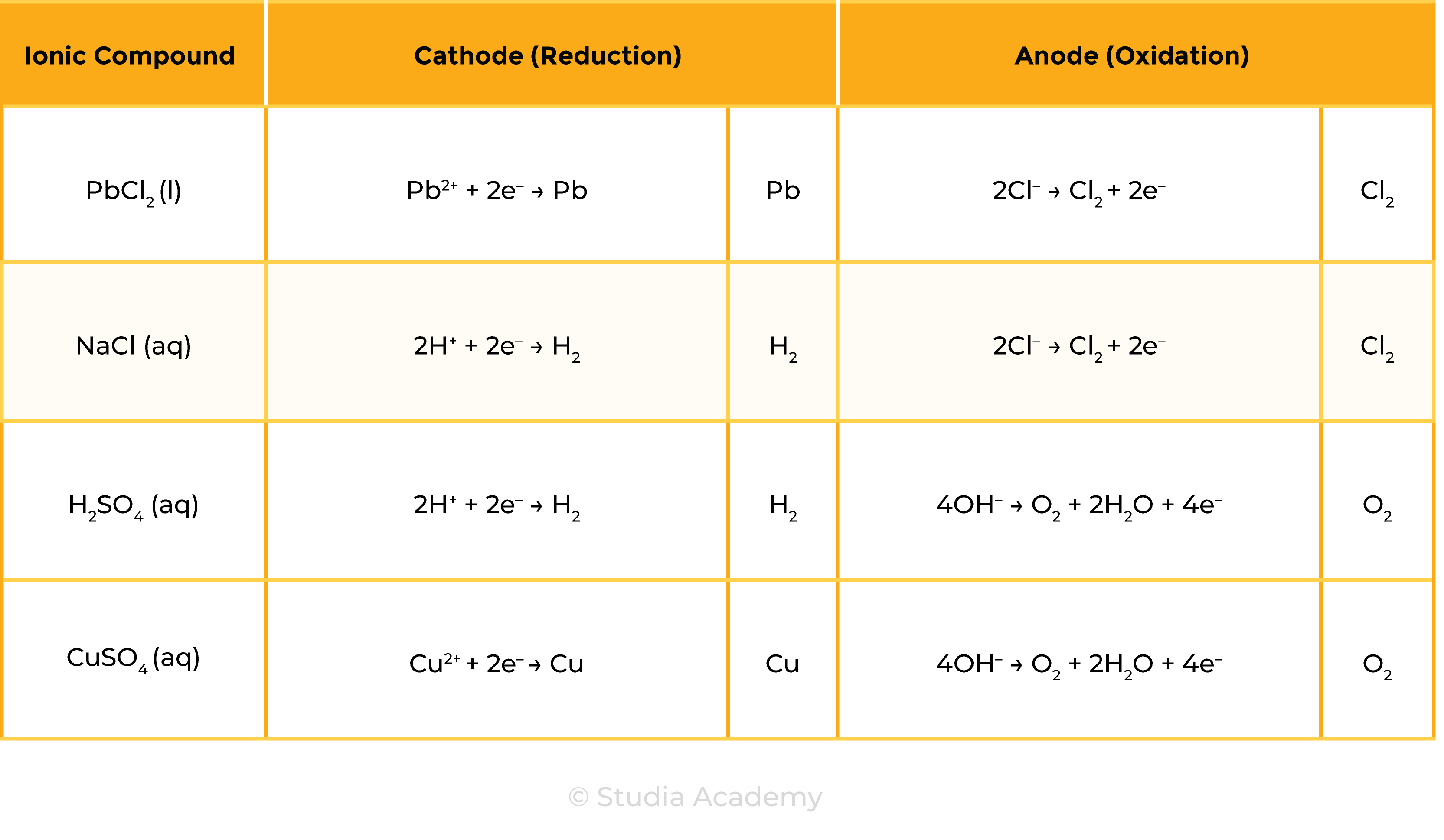
1.9.5C Write ionic half-equations representing the reactions at the electrodes during electrolysis and understand why these reactions are classified as oxidation or reduction
Oxidation: loss of electron(s)
Reduction: gain of electron(s)
Key points
1.9.6C Practical: investigate the electrolysis of aqueous solutions
AIM
To electrolyse aqueous solutions of sodium chloride, sulfuric acid and copper(II) sulphate, and to collect and identify the products at each electrode
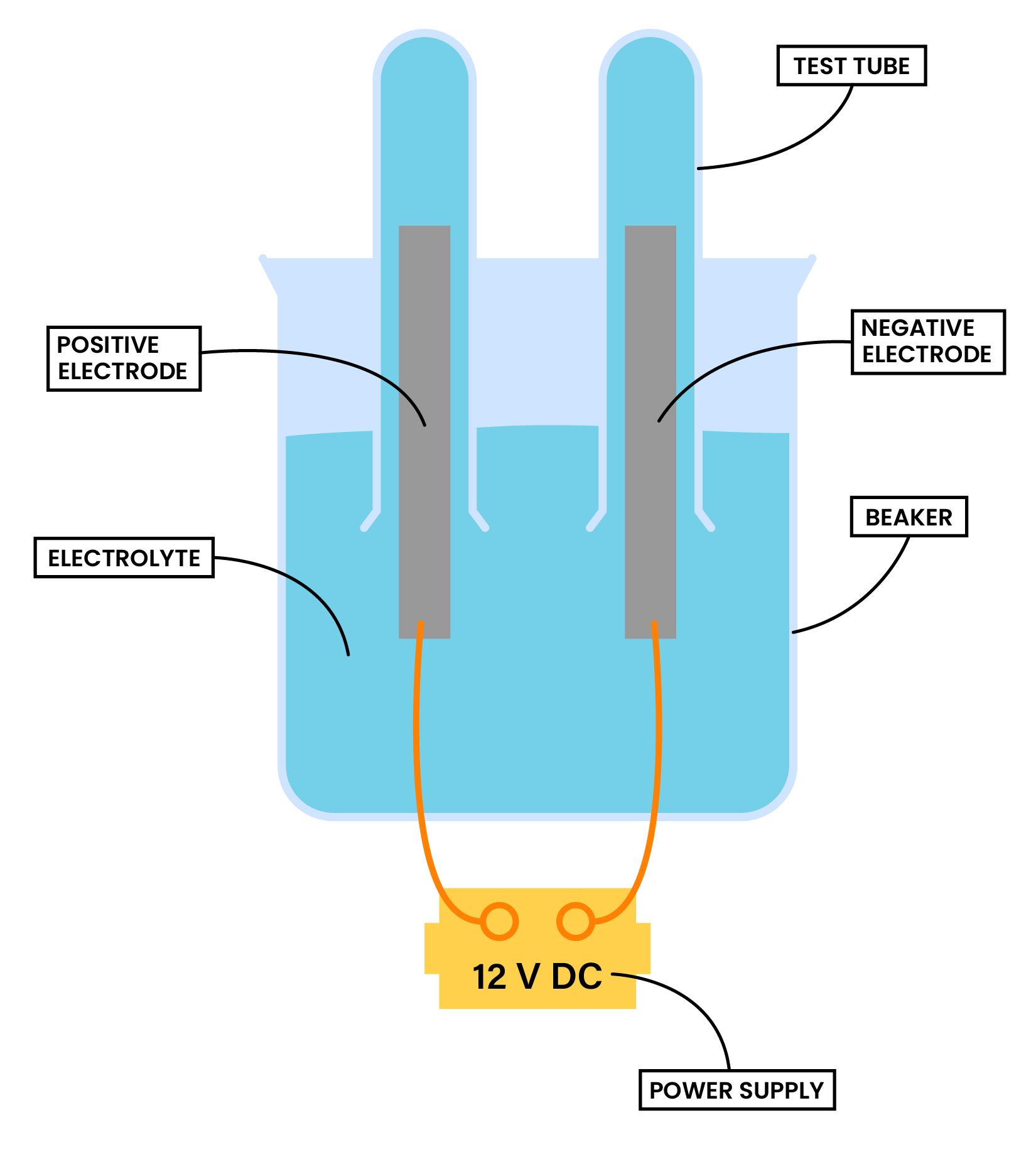
METHOD
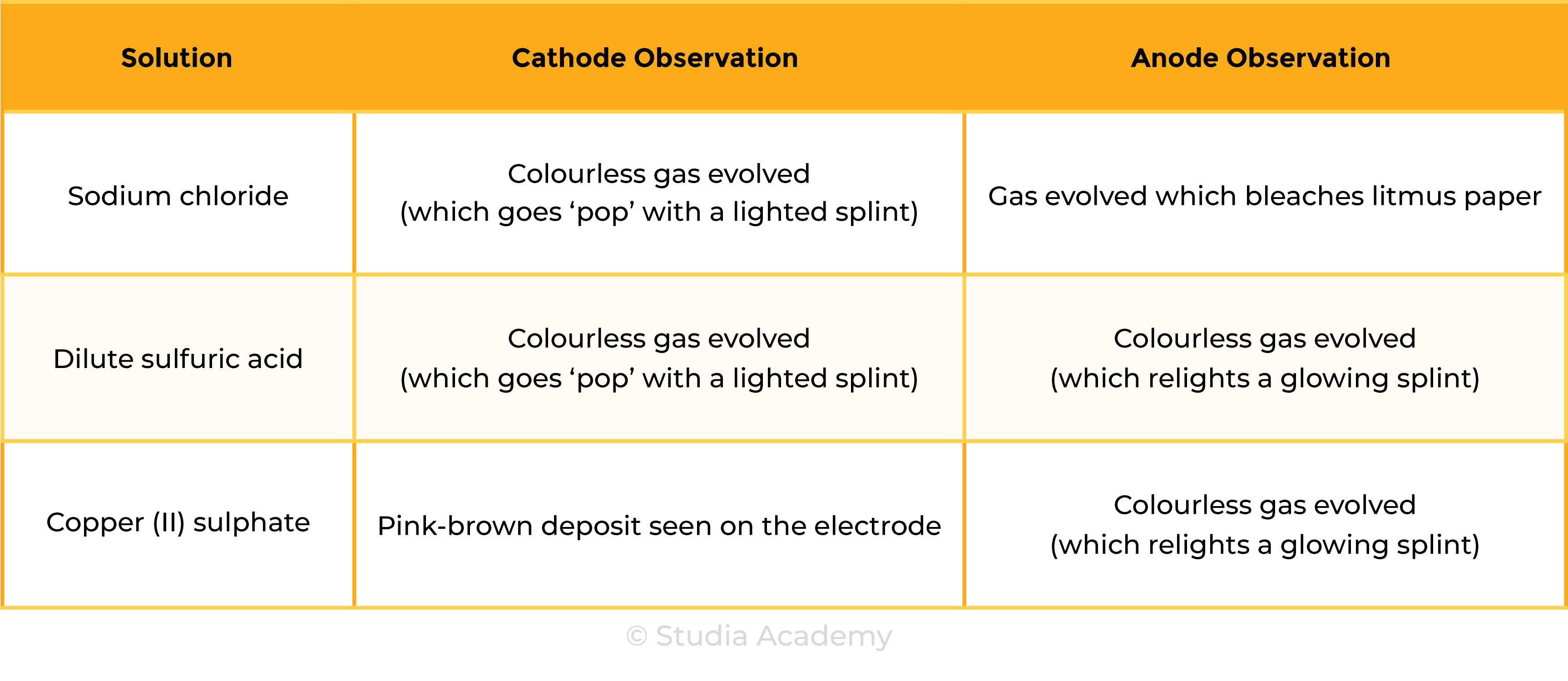
Tests for Products

Results

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.