REVISION NOTES
1.3.1 Know what is meant by the terms atom and molecule


1.3.2 Know the structure of an atom in terms of the positions, relative masses and relative charges of subatomic particles
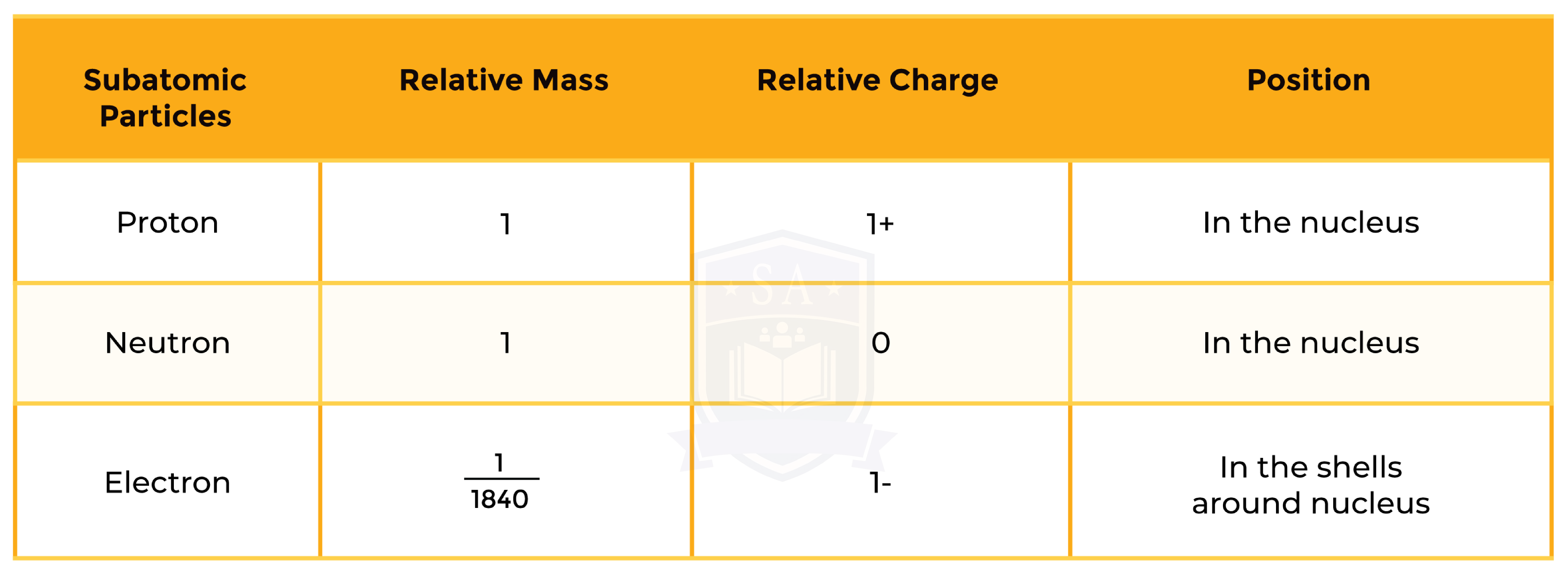
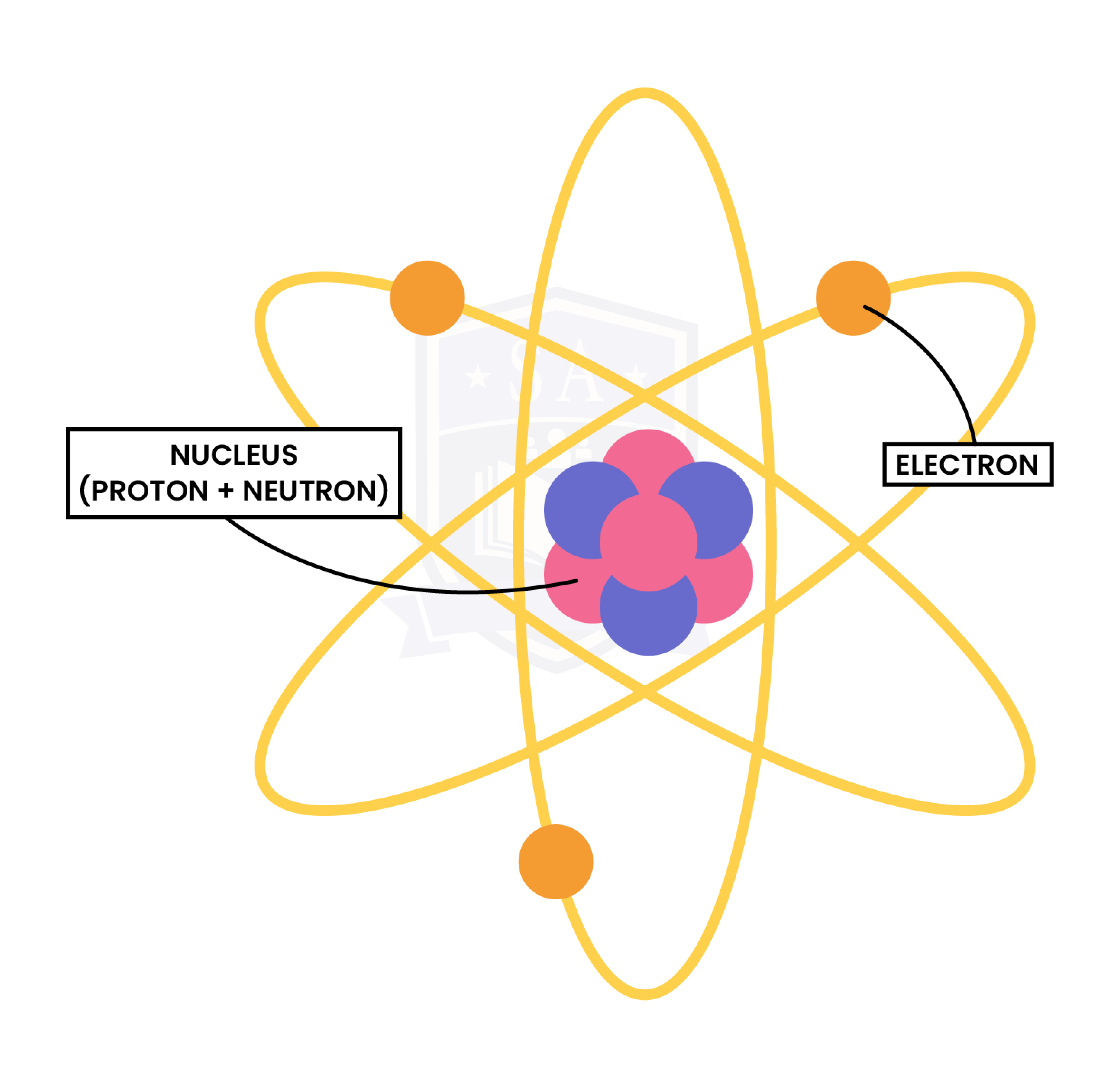
1.3.3 Know what is meant by the terms atomic number, mass number, isotopes and relative atomic mass (Ar)
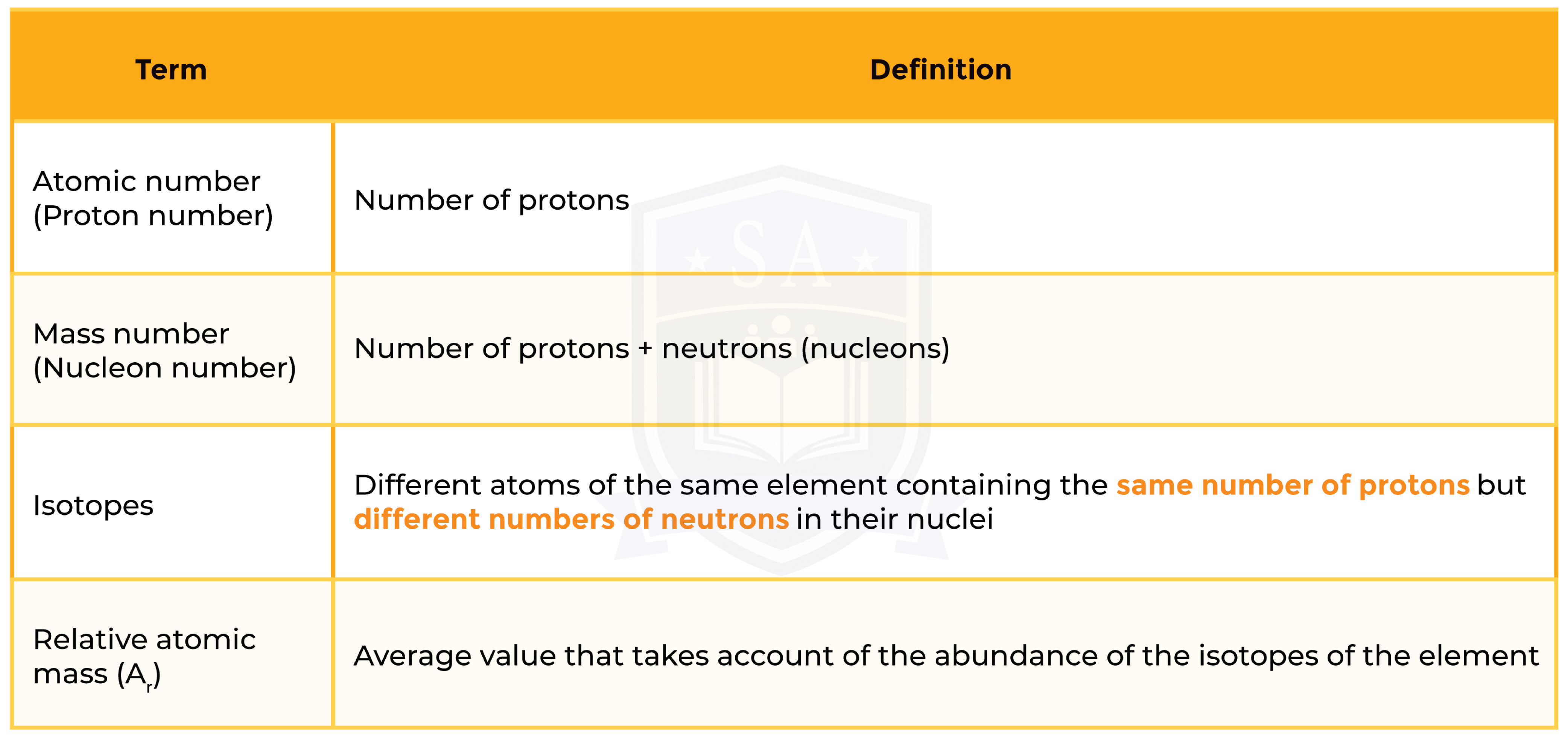
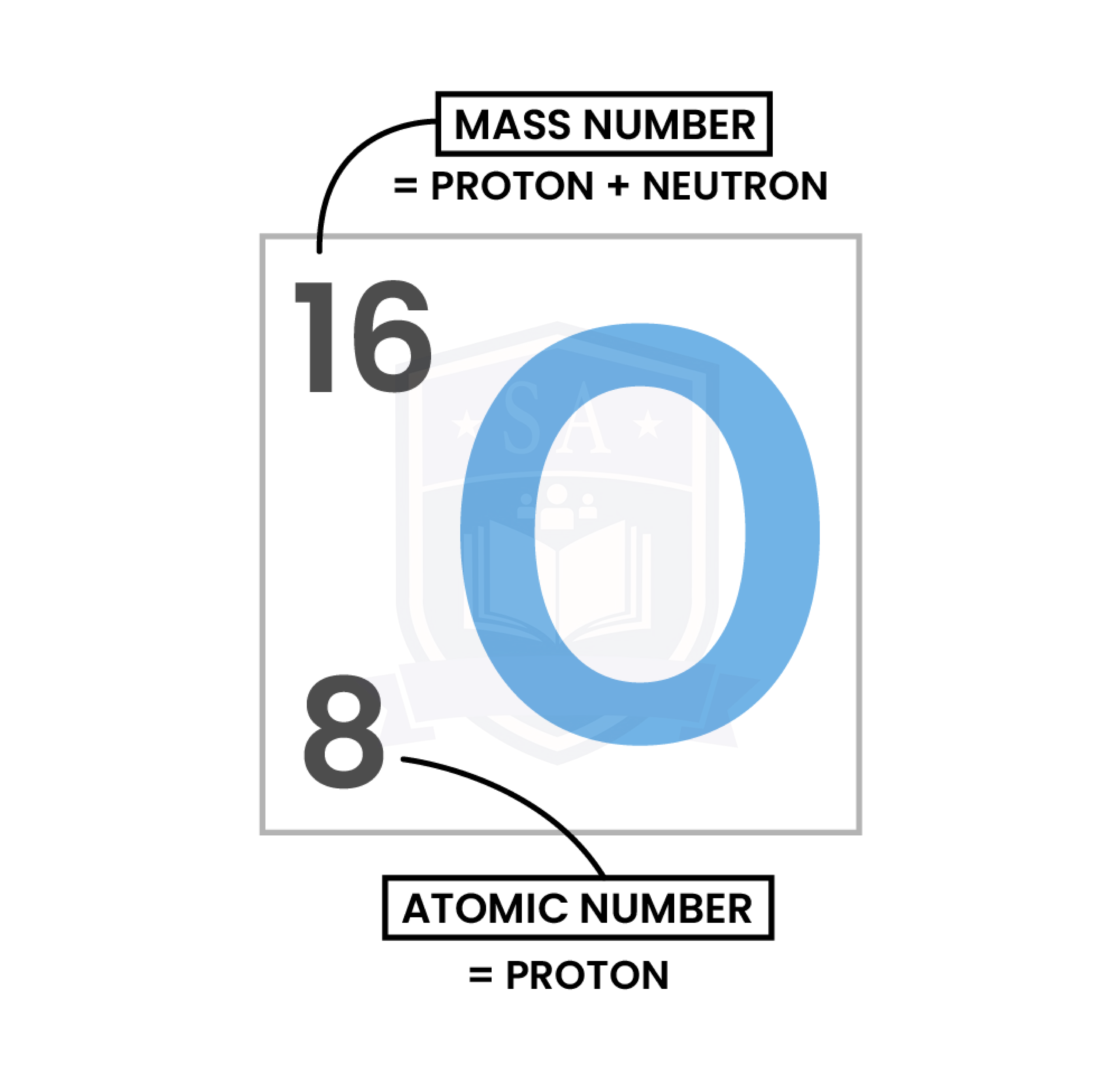
ISOTOPES
1.3.4 Be able to calculate the relative atomic mass of an element (Ar) from isotopic abundances
ISOTOPIC ABUNDANCE
The relative atomic mass of each element is calculated from the mass number and relative abundances of all the isotopes of a particular element
EXAMPLE
A sample of chlorine gas is a mixture of 2 isotopes, chlorine-35 and chlorine-37. These isotopes occur in specific proportions in the sample i.e. 75% chlorine-35 and 25% chlorine-37. Calculate the relative atomic mass of chlorine in the sample.
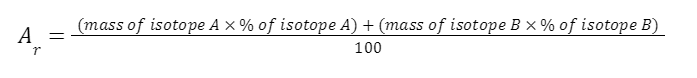
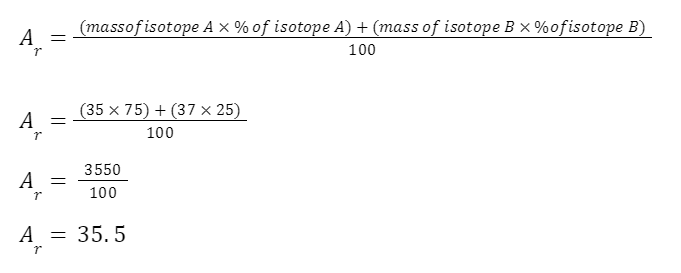

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.