REVISION NOTES
1.2.1 Understand how to classify a substance as an element, compound or mixture
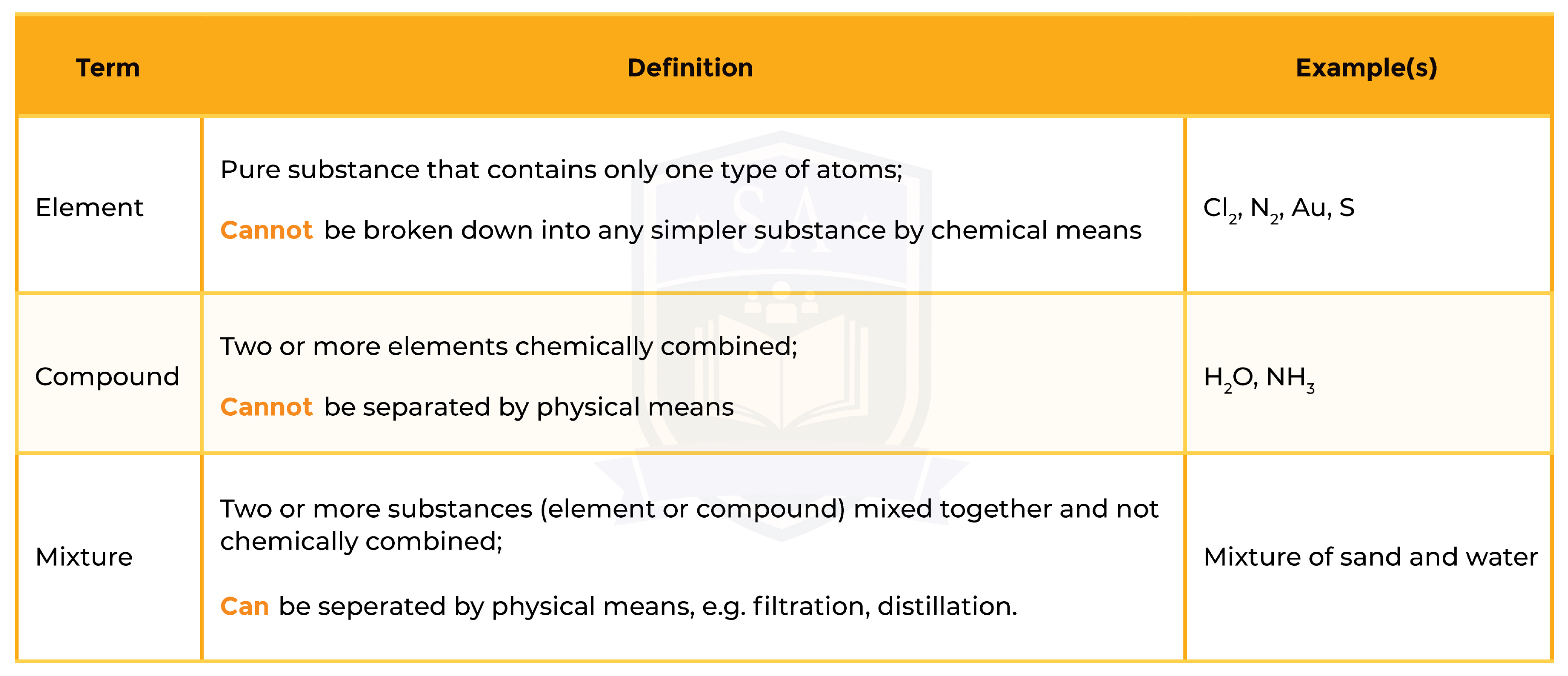
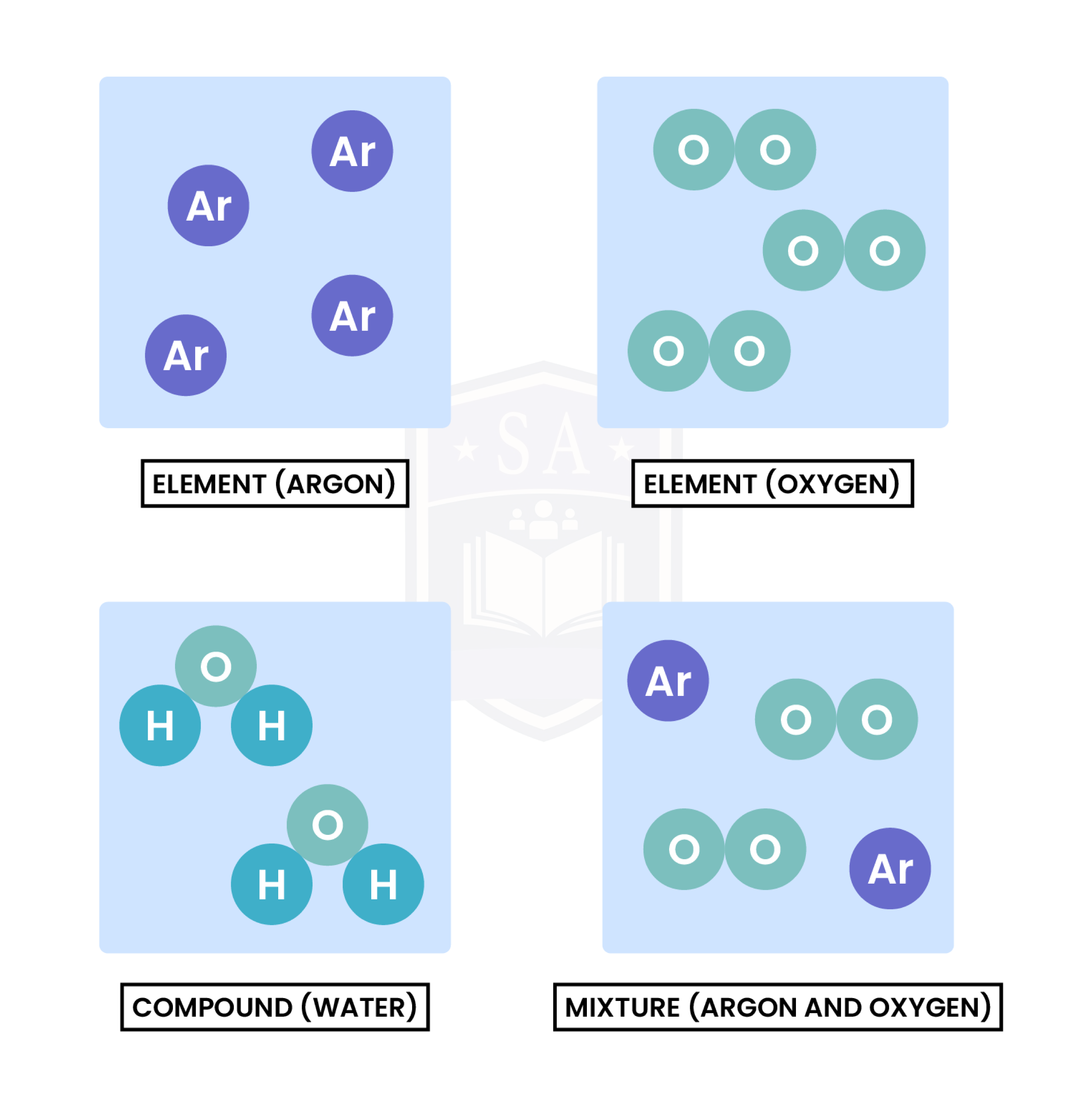
1.2.2 Understand that a pure substance has a fixed melting and boiling point, but that a mixture may melt or boil over a range of temperatures

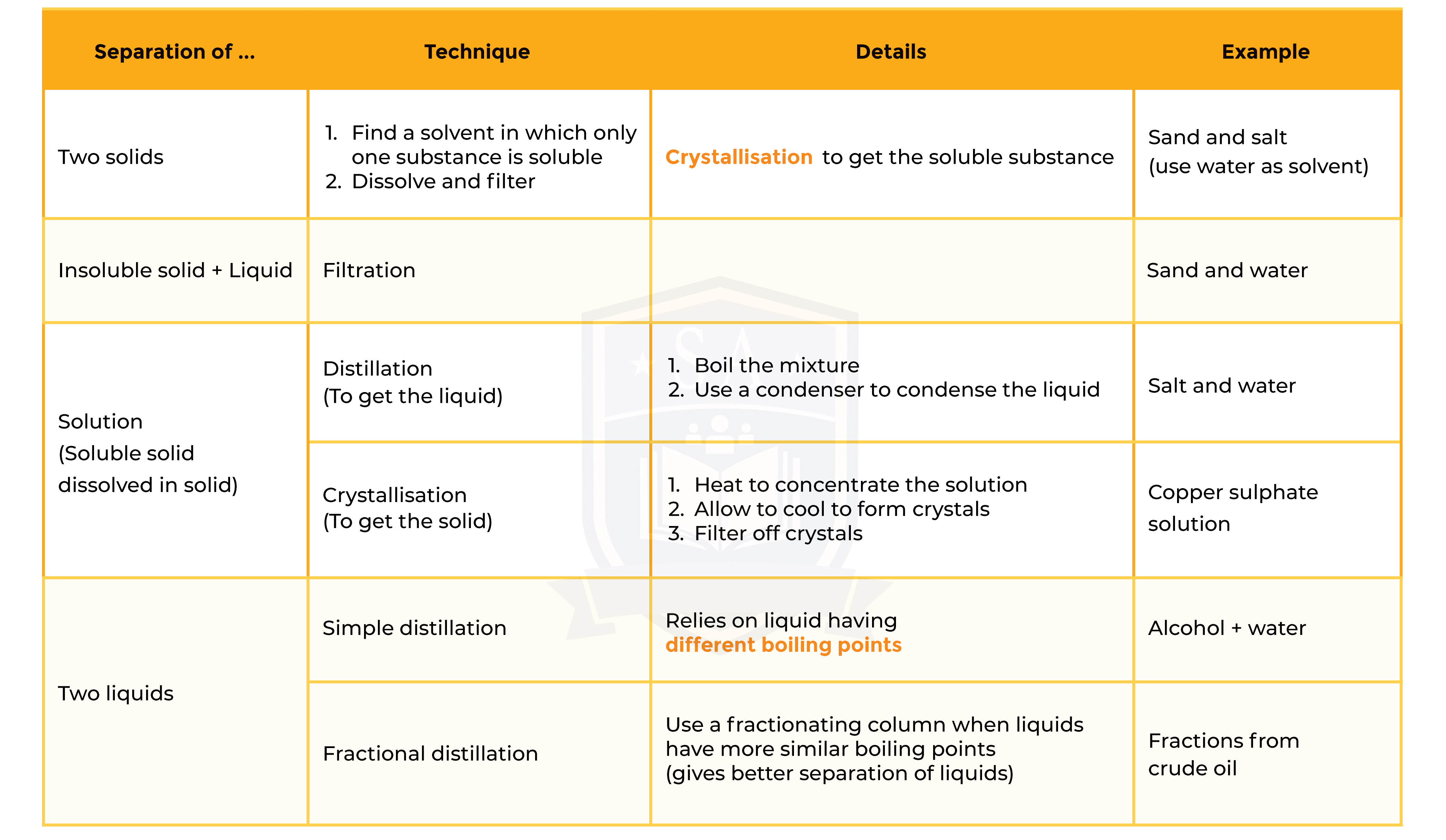
1.2.3 describe these experimental techniques for the separation of mixtures:
Summary of Separation Technique
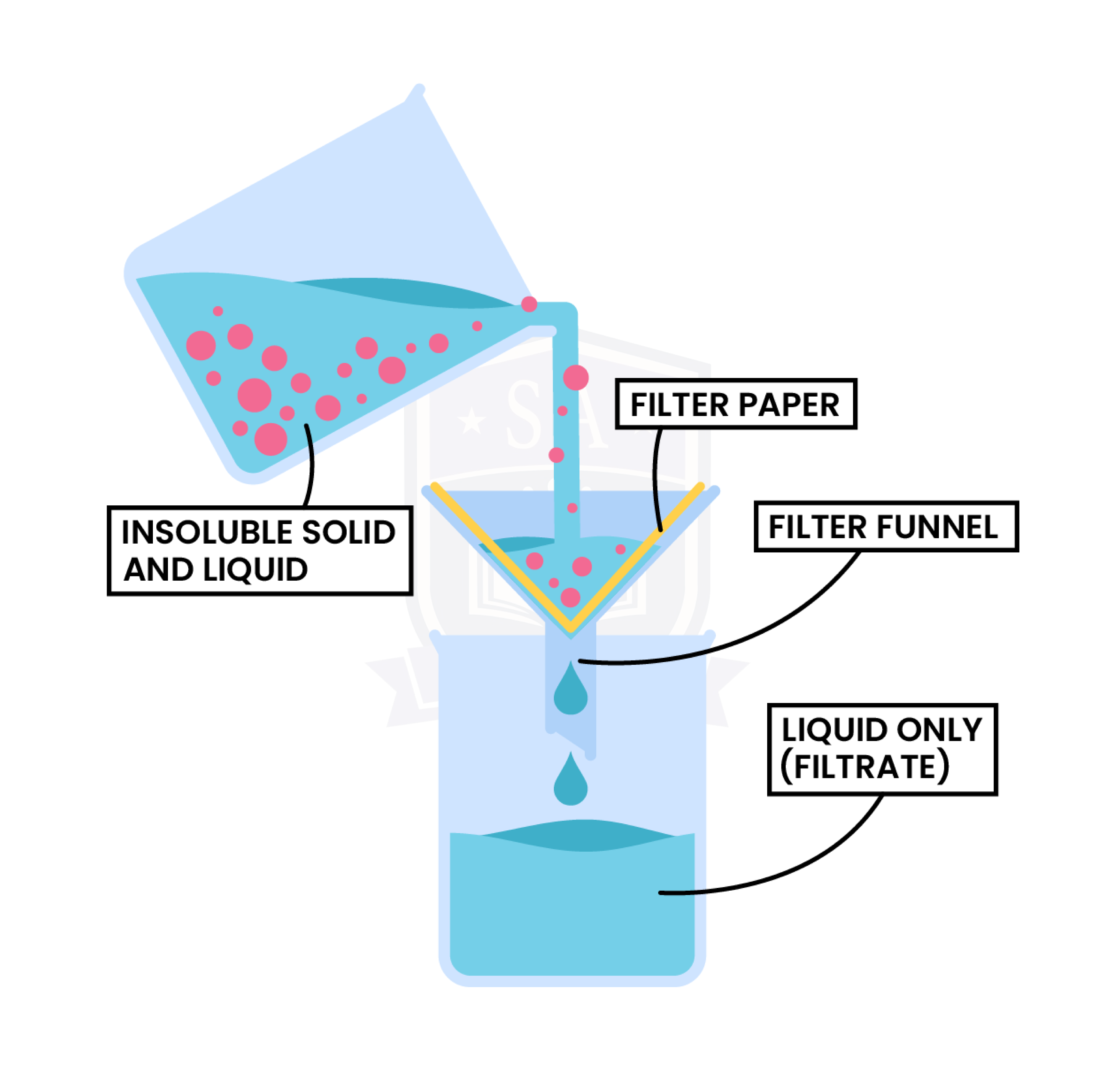
Filtration
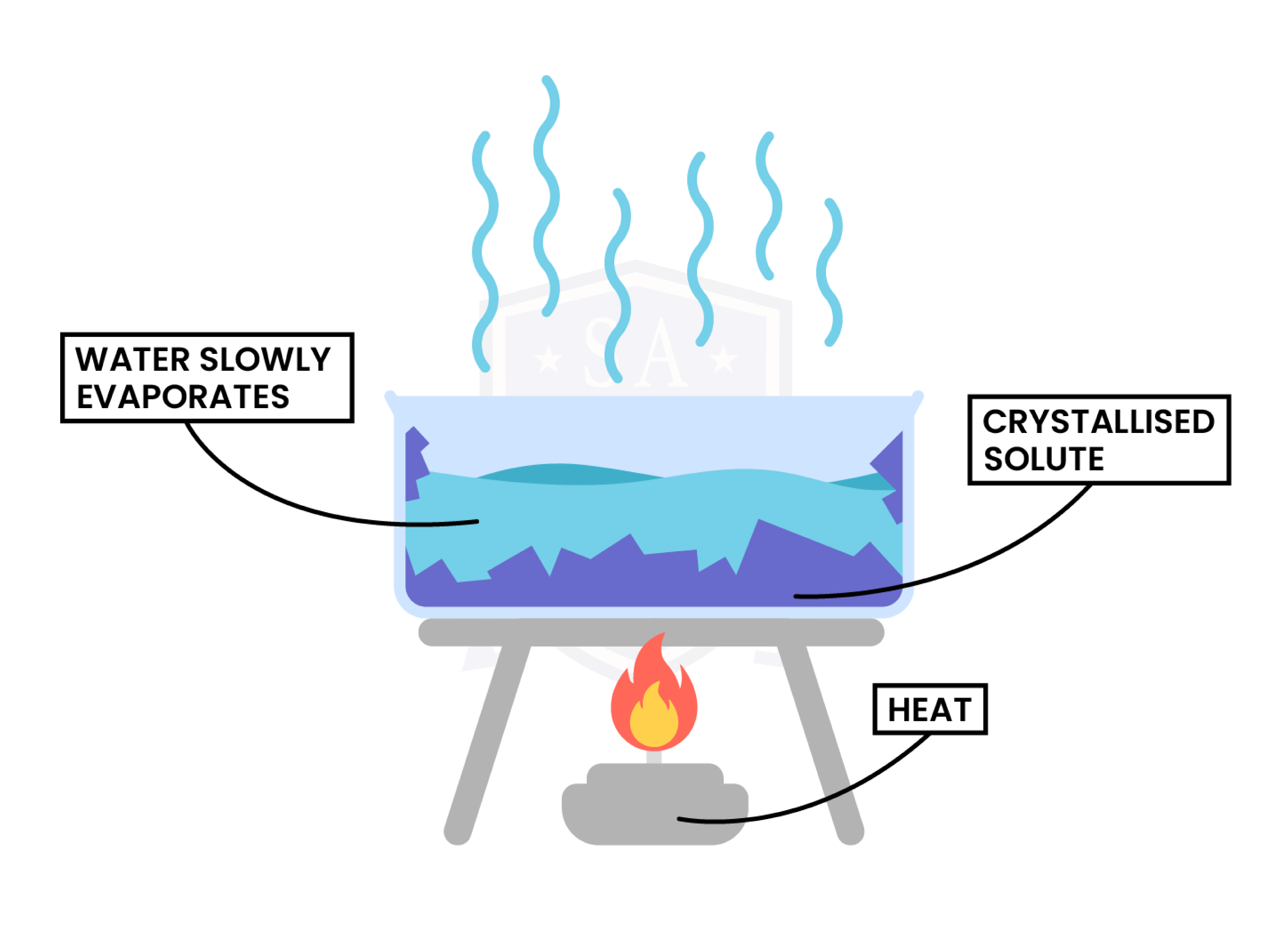
Crystallisation
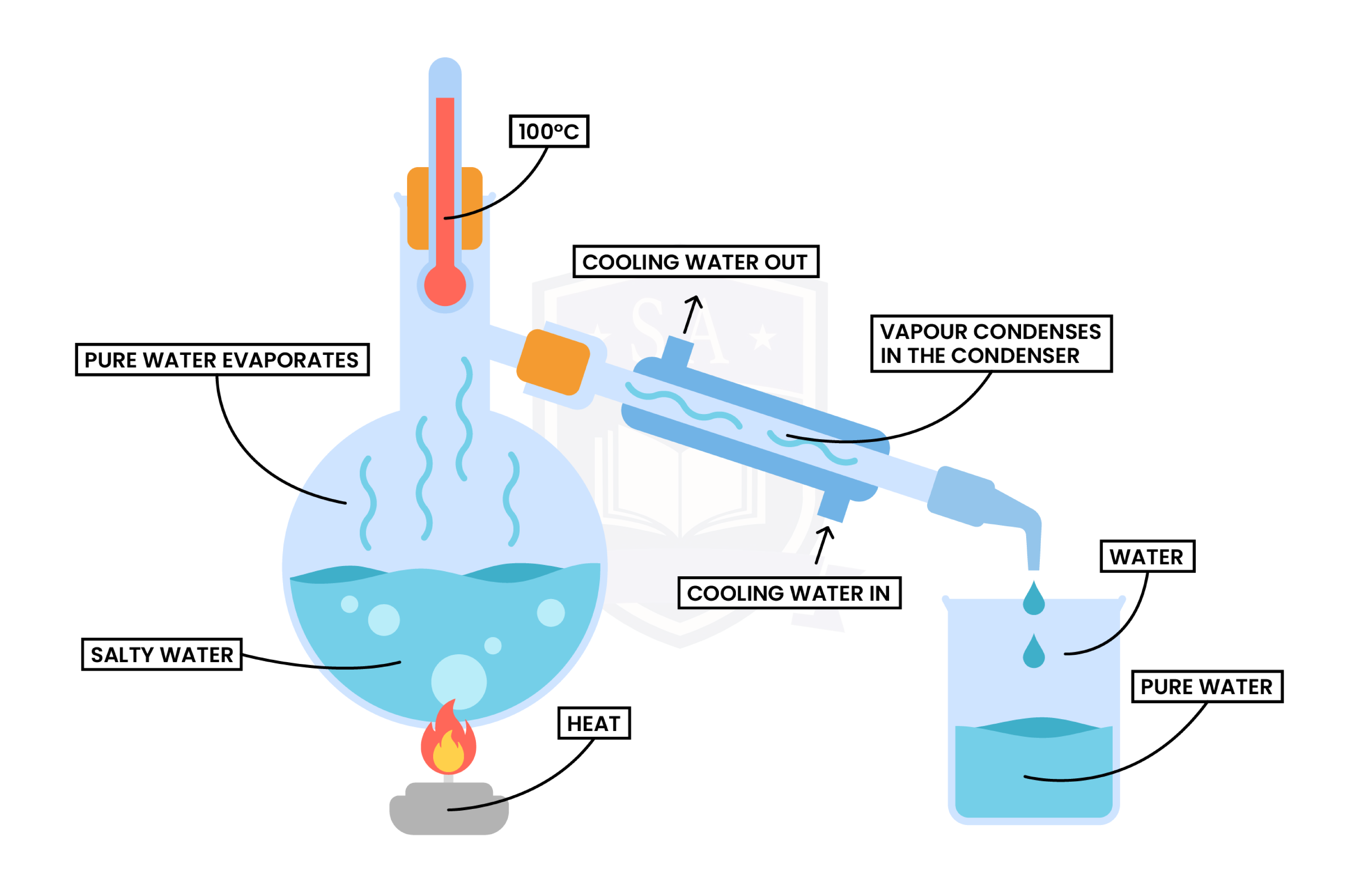
Simple Distillation
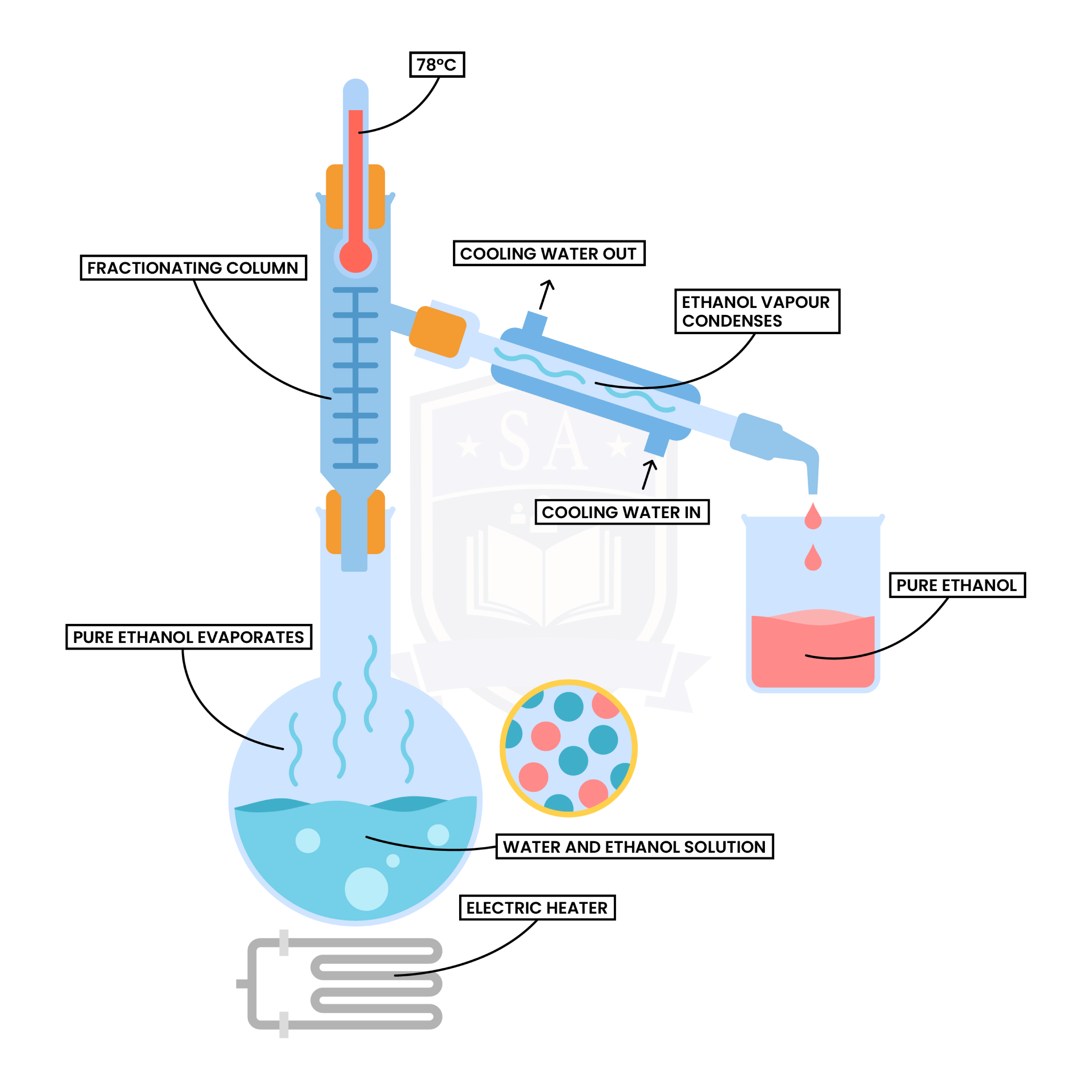
Fractional Distillation
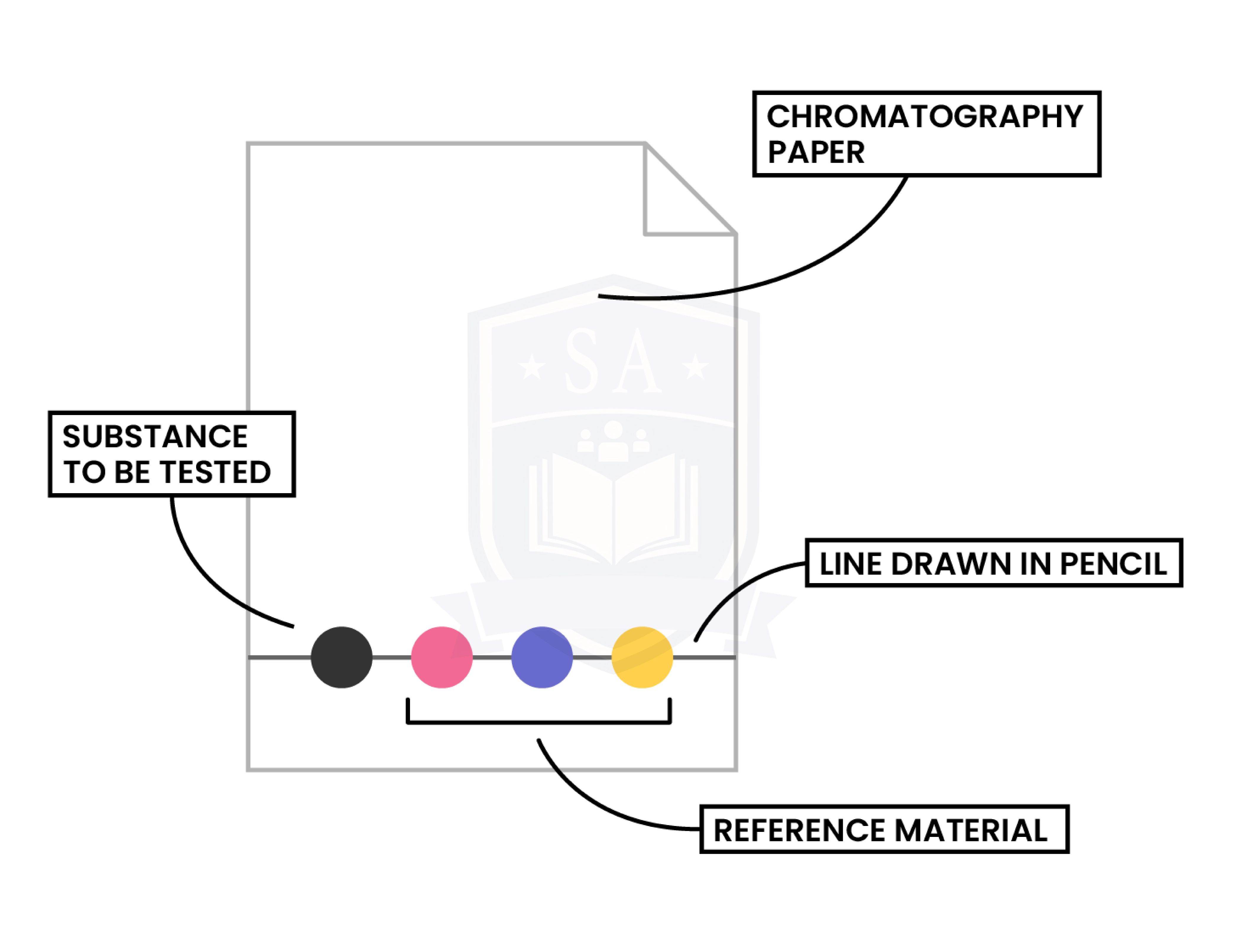
PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY
Step 1: A pencil line is drawn on chromatography paper
Step 2: Sample is spotted on the pencil line
Step 3: The paper is then lowered into the solvent container (make sure that the pencil line sits above the level of the solvent)
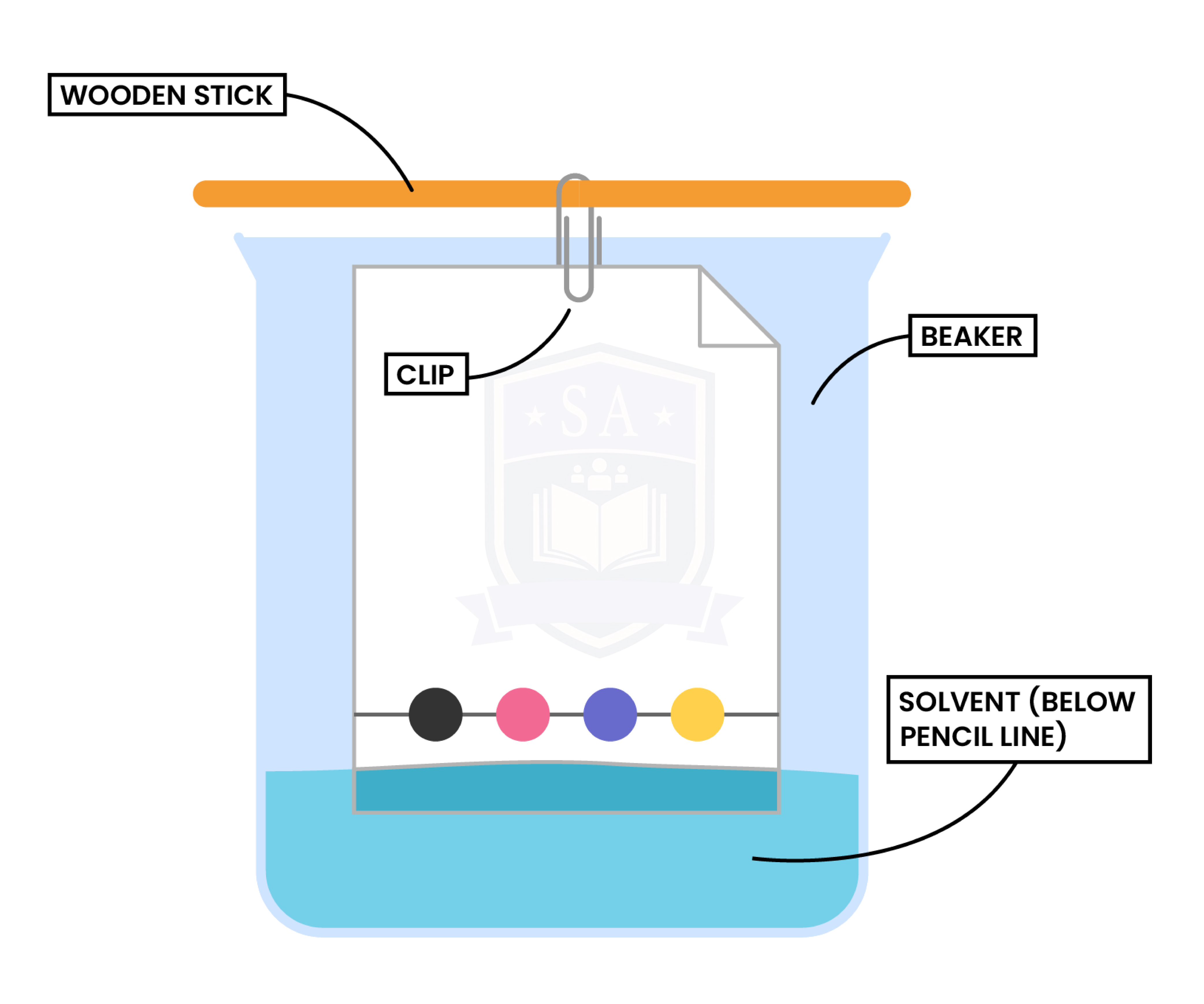
Step 4: The solvent travels up the paper, taking some of the coloured substances with it
Step 5: Different substances have different solubilities so will travel at different rates, causing the substances to spread apart
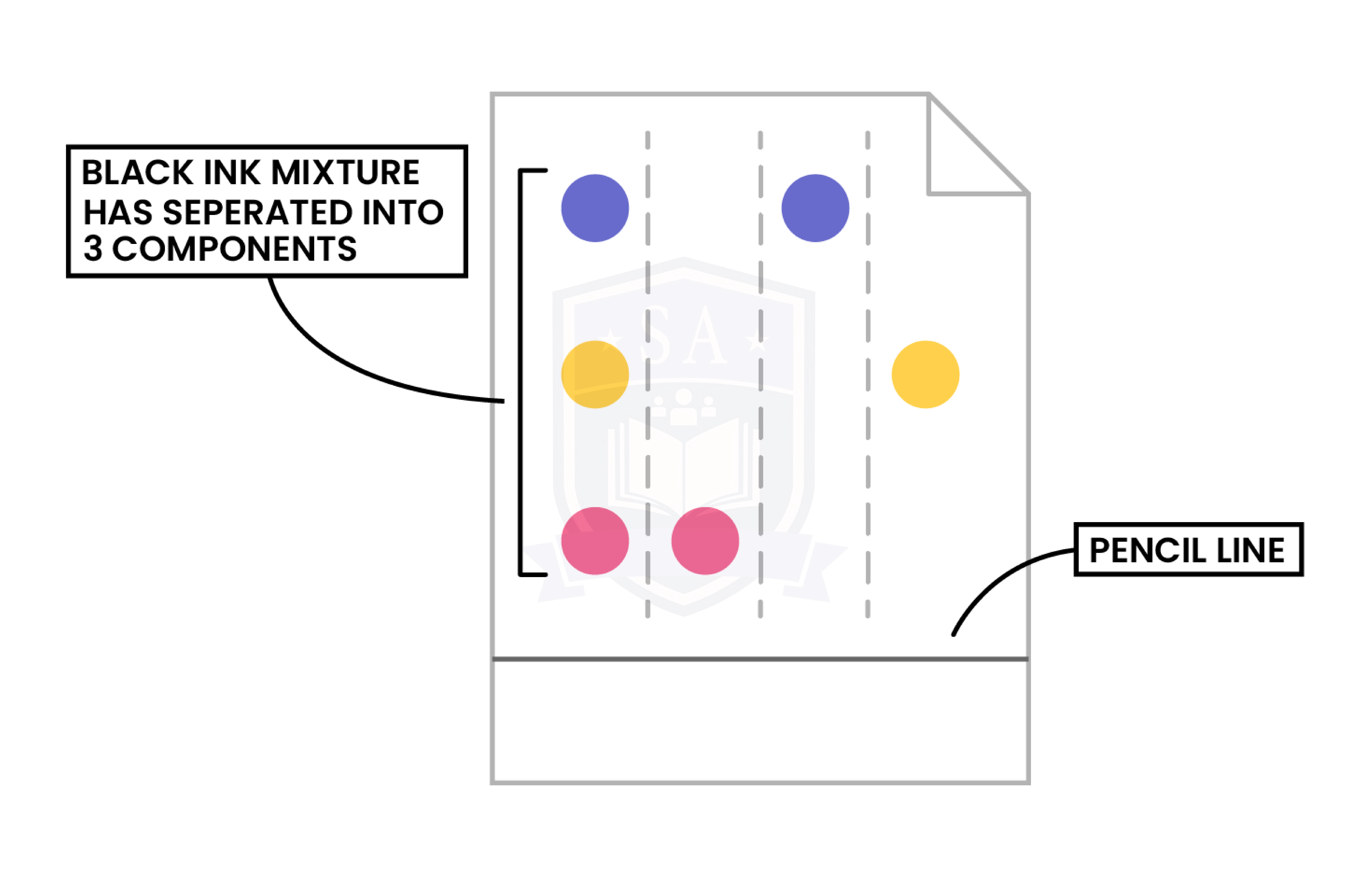
KEY POINTS
1.2.4 Understand how a chromatogram provides information about the composition of a mixture

1.2.5 understand how to use the calculation of Rf values to identify the components of a mixture
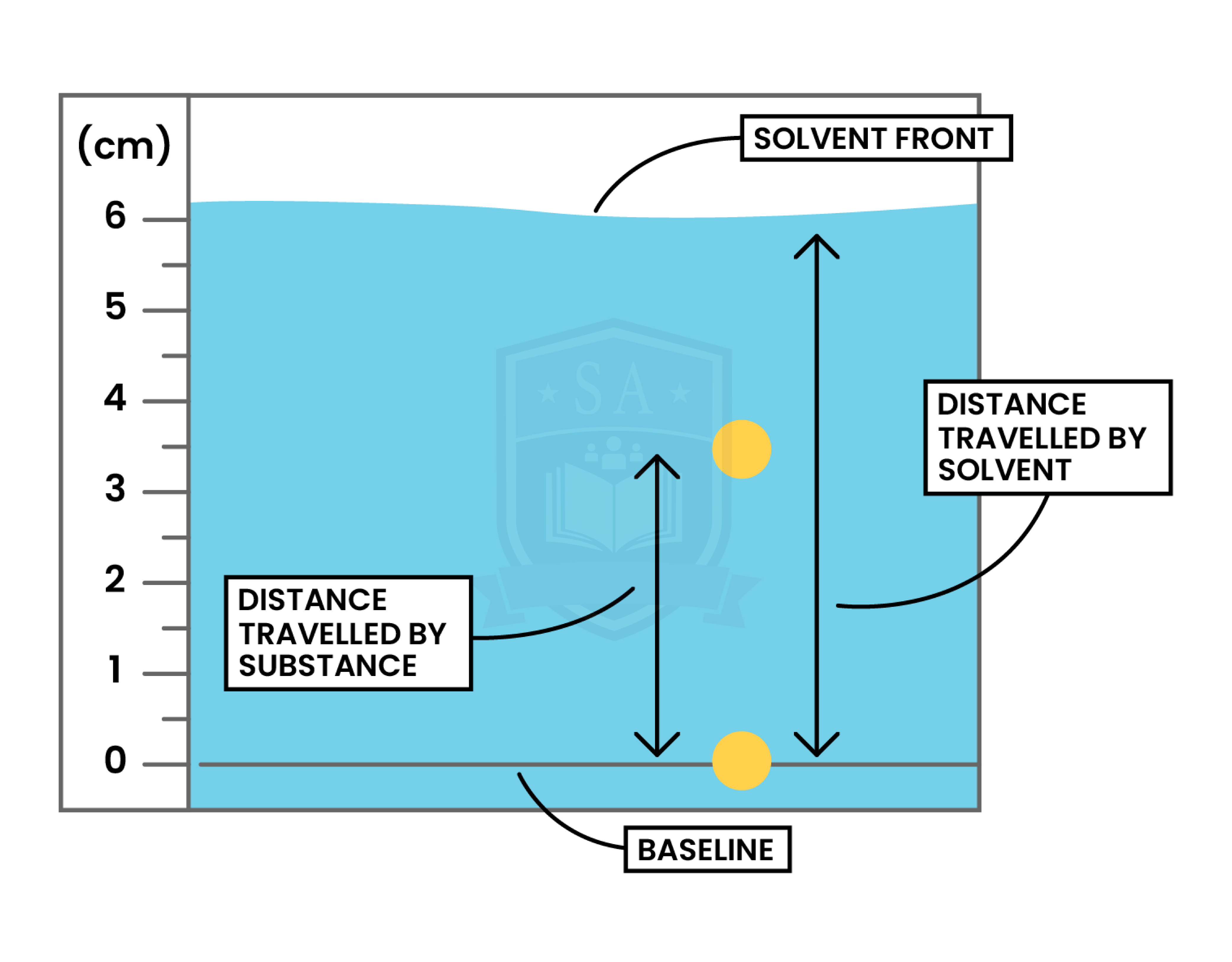
RETENTION FACTOR (Rf) VALUE
Calculation
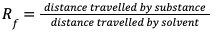
1.2.6 Practical: investigate paper chromatography using inks/food colourings
AIM
EQUIPMENT LIST
METHOD
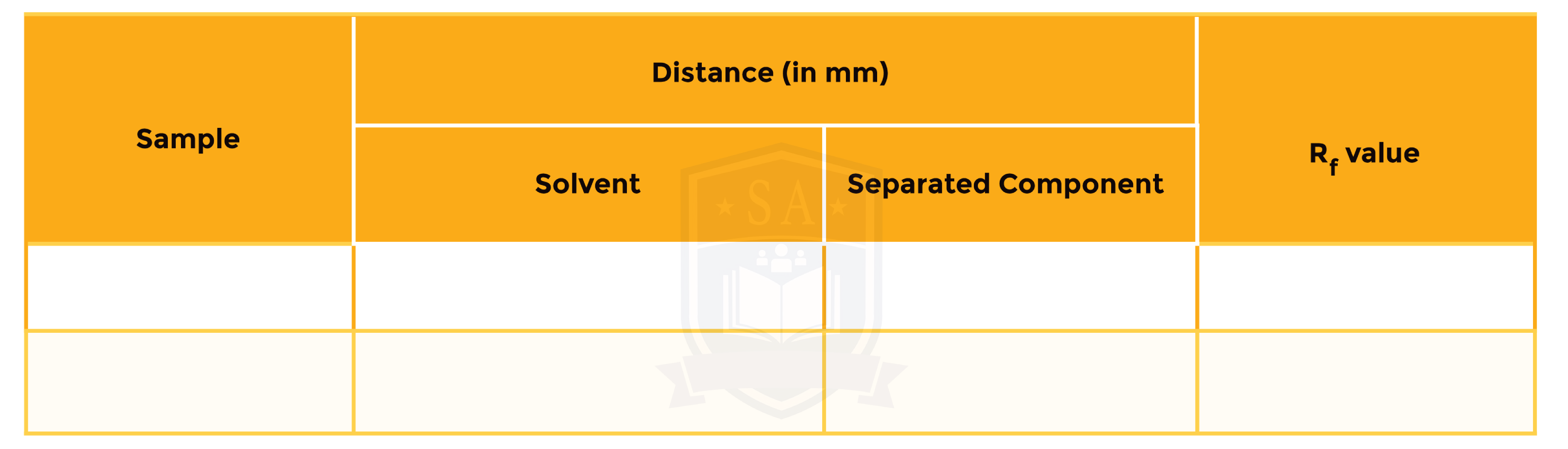
Result Table
RESULTS

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.