REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry
a
4.7 Esters
4.7.1C Know that esters contain the functional group -COO-
The functional group of esters is
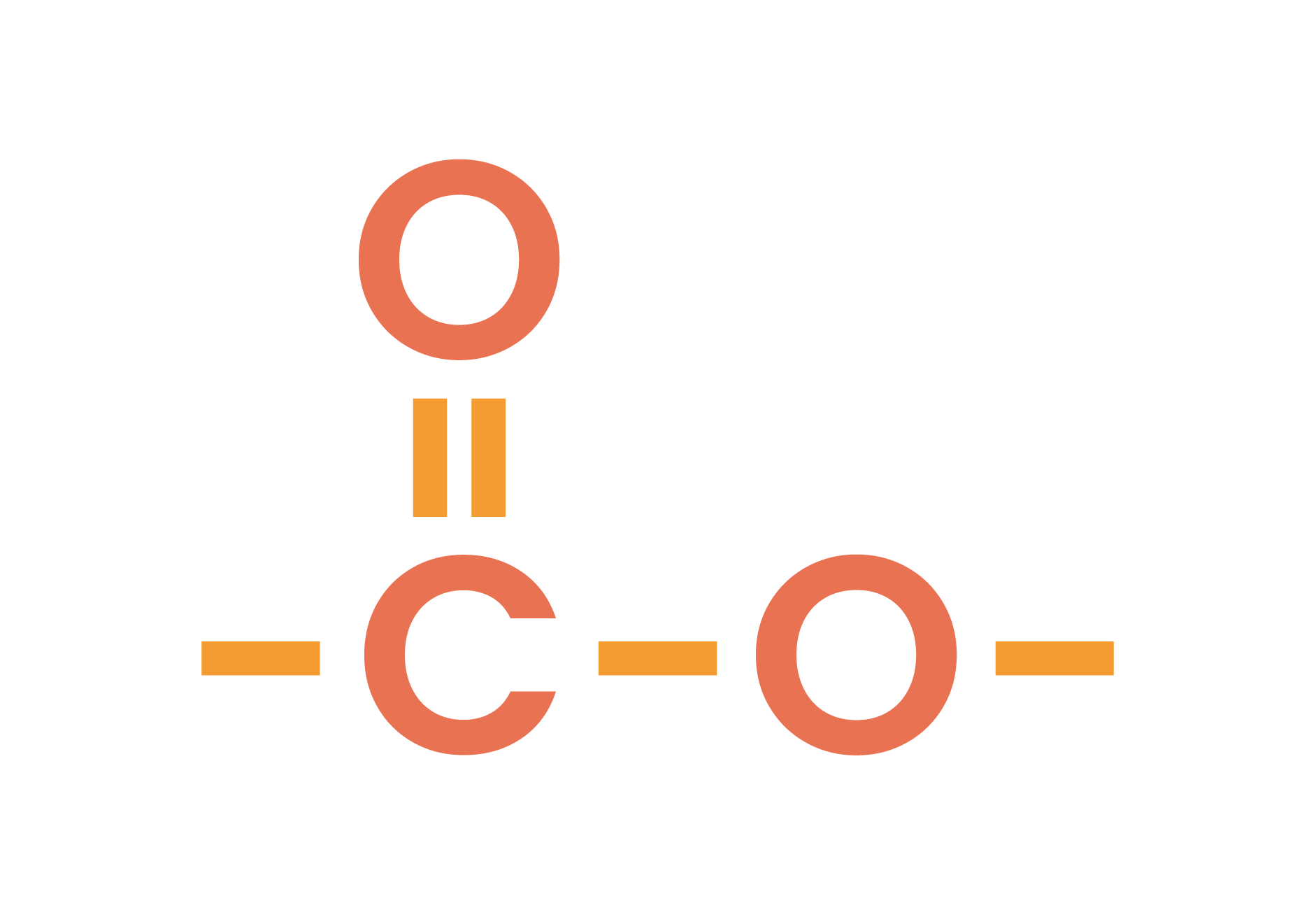
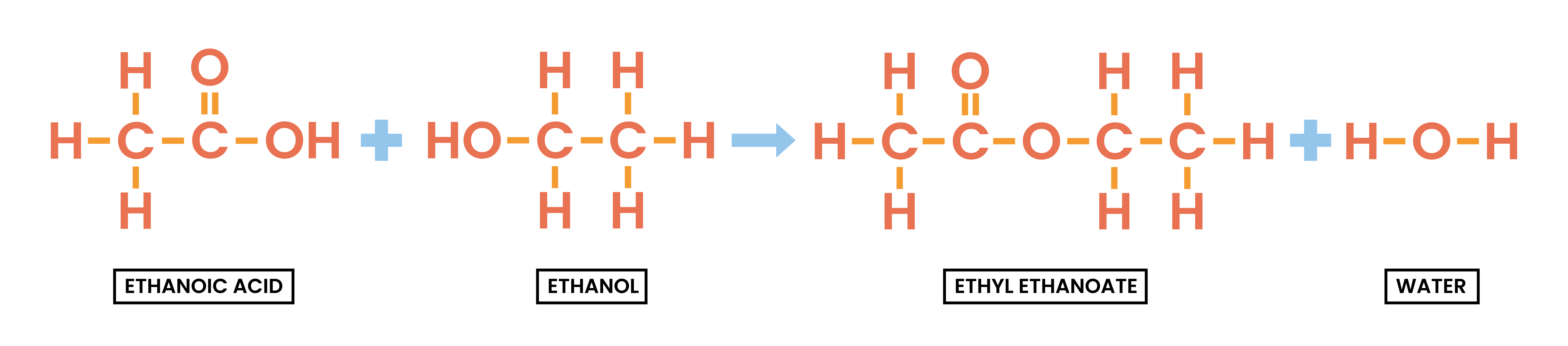
4.7.2C Know that ethyl ethanoate is the ester produced when ethanol and ethanoic acid react in the presence of an acid catalyst
ethanol + ethanoic acid → ethyl ethanoate (ester) + H2O
- In the presence of an acid catalyst
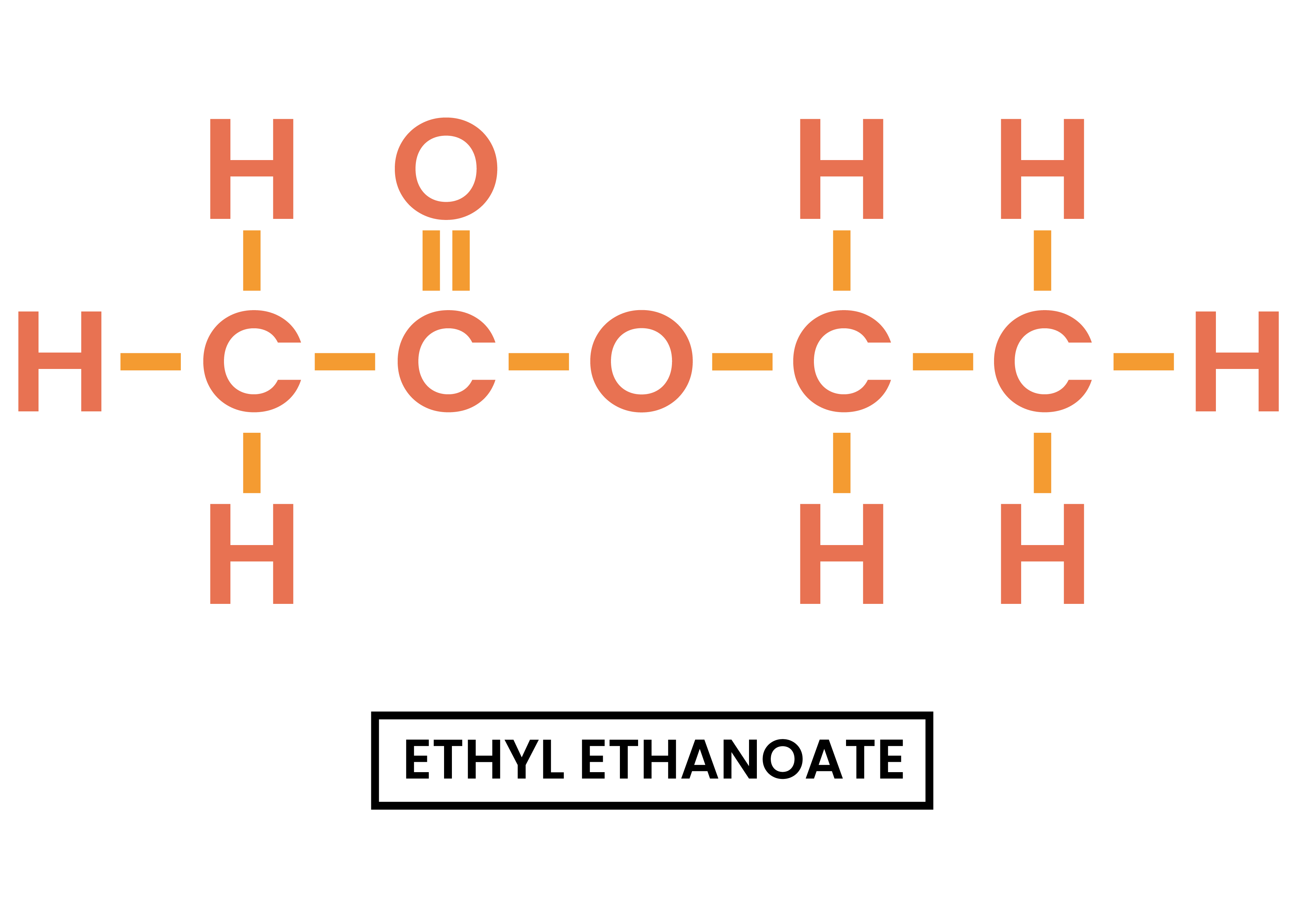
4.7.3C Understand how to write the structural and displayed formulae of ethyl ethanoate
ETHYL ETHANOATE
- Structural formula: CH3COOCH2CH3
- Displayed formula:
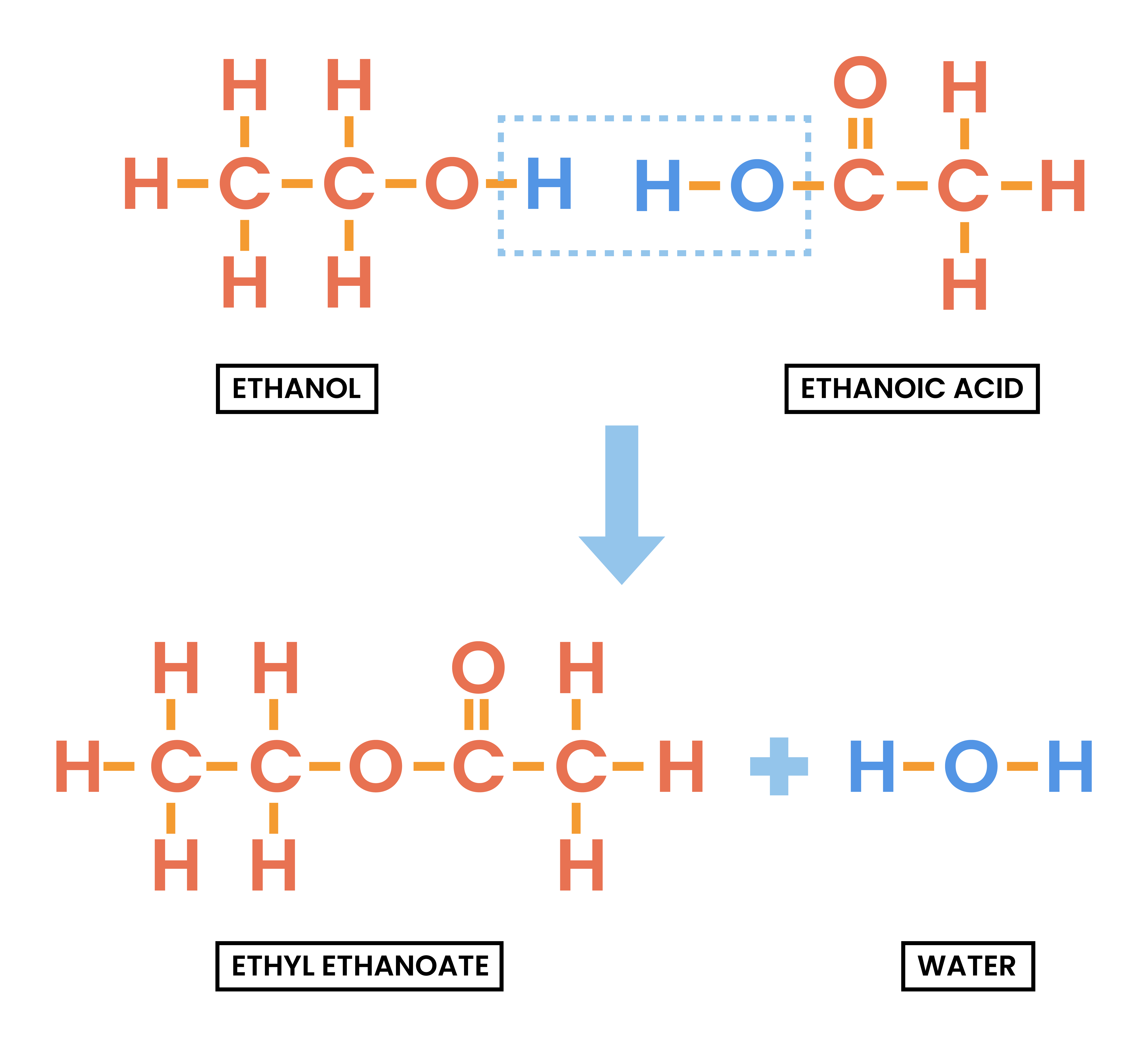
4.7.4C Understand how to write the structural and displayed formulae of an ester, given the name or formula of the alcohol and carboxylic acid from which it is formed and vice versa
Esterification
alcohol + carboxylic acid → ester + H2O
- During esterification:
- H is lost from the alcohol
- OH is lost from the carboxylic acid
- The parts are combined to form ester
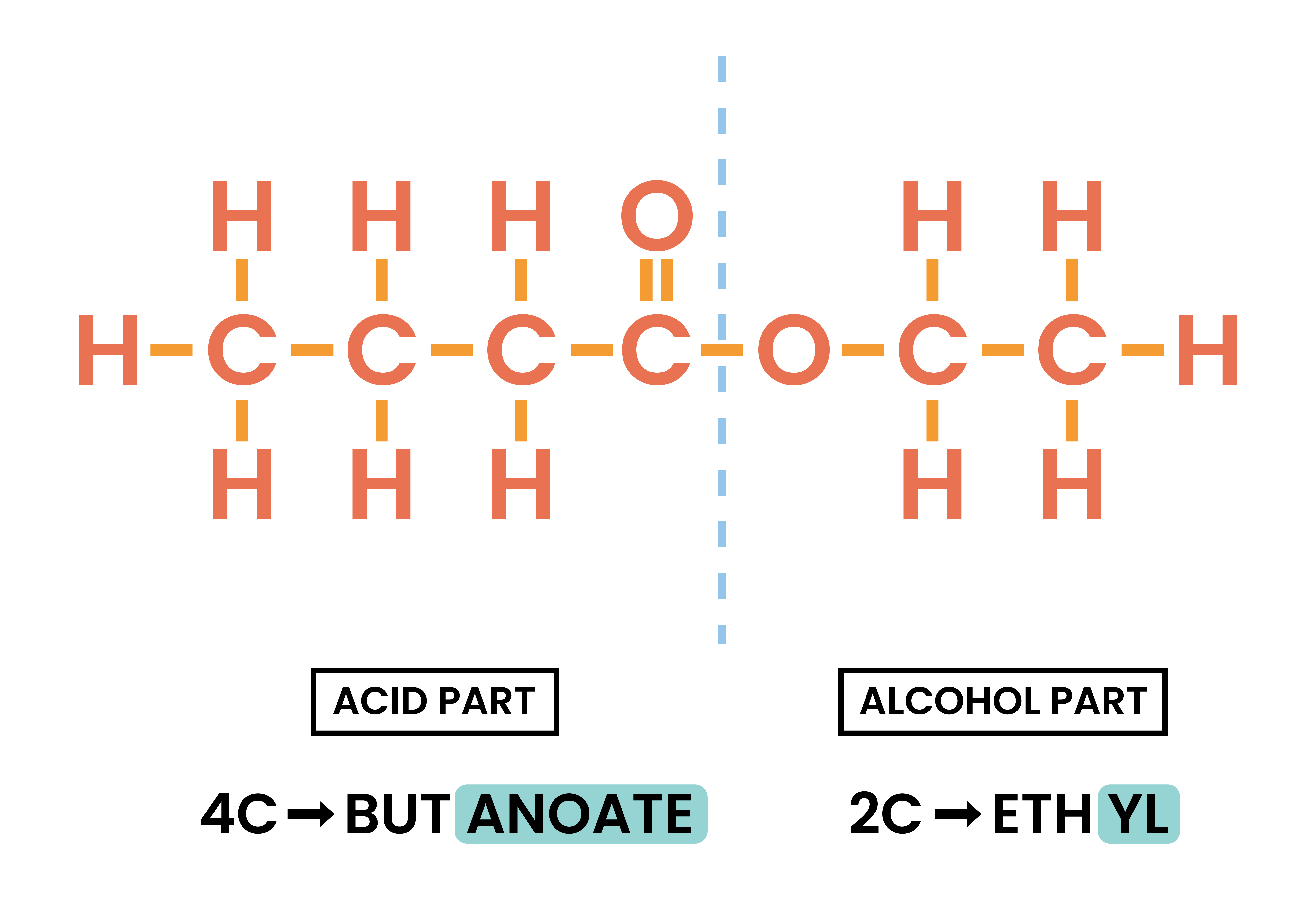
- Identify the acid and alcohol part:
- Split the compound between two oxygens
- Acid: the half with C=O
- Alcohol: the half with O
- Naming of ester:
- Count the number of carbons in both acid and alcohol part
- Alcohol part: -yl
- Carboxylic acid: -oate
4.7.5C Know that esters are volatile compounds with distinctive smells and are used as food flavourings and in perfumes
USES OF ESTERS
- Esters are volatile compounds with distinctive smells
- Ester are often used as food flavourings and in perfumes
4.7.6C Practical: prepare a sample of an ester such as ethyl ethanoate
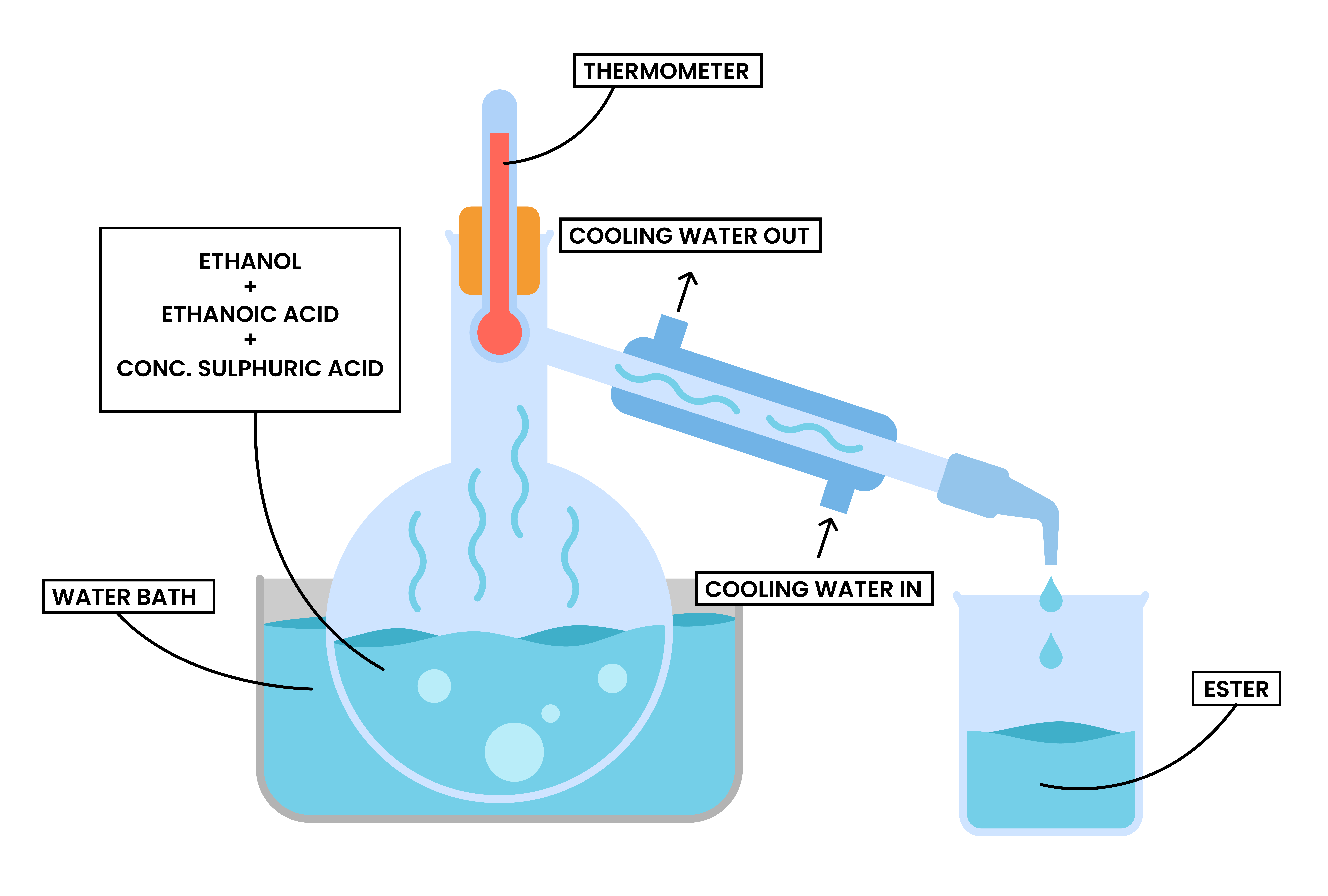
METHODS
- Mix ethanol, ethanoic acid and concentrated sulphuric acid in a round-bottom flask
- Gently heat the mixture using a water bath or electric heater
- Bunsen burner cannot be used because ethanol is flammable
- Ester formed is then distilled and collected to another beaker
- Esters have lower boiling points, so they will evaporate first
- Esters are removed from the mixture to prevent reverse reactions from occurring

