REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry
4.4 Alkenes
4.4.1 Know that alkenes contain the functional group >C=C<
Unlike alkanes, alkenes contain the functional group C=C
4.4.2 Know the general formula for alkenes
General formula for alkenes
CnH2n
EXAMPLE
Ethene is a type of alkene with the formula C2H4
4.4.3 Explain why alkenes are classified as unsaturated hydrocarbons
ALKENES
- Alkenes contain one or more C=C bonds
- It means that alkenes can still break the double bond and attach to more atoms
- So it is classified as unsaturated hydrocarbons
4.4.4 Understand how to draw the structural and displayed formulae for alkenes with up to four carbon atoms in the molecule, and name the unbranched-chain isomers
knowledge of cis/trans or E/Z notation is not required
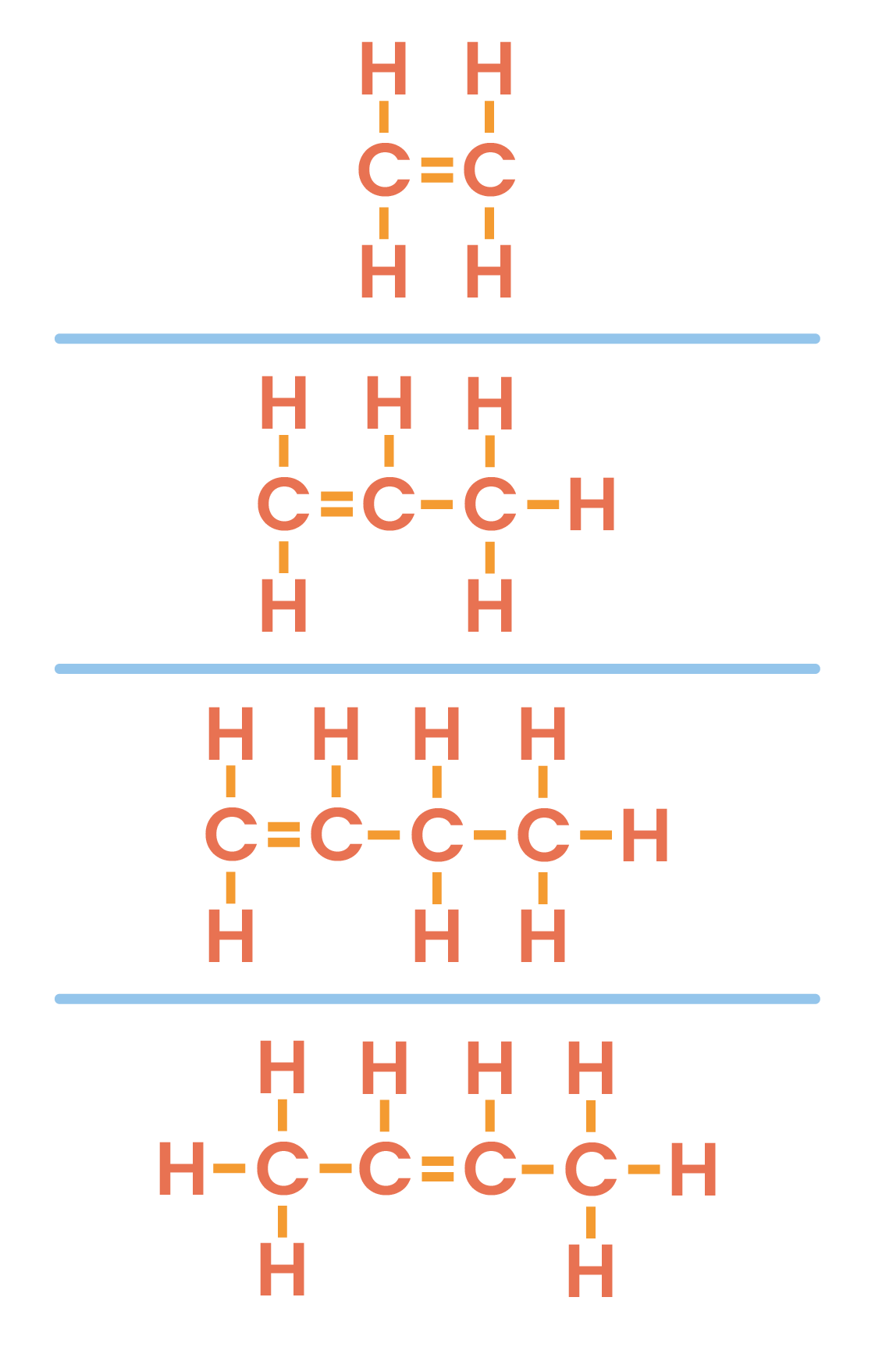
The numbers in but-1-ene, but-2-ene refer to the carbon atom the C=C is in
Numbers are not needed in naming ethene and propene, as the C=C is in the first position when counting from the nearest direction
Methene does not exist as a C=C cannot exist with only 1 carbon
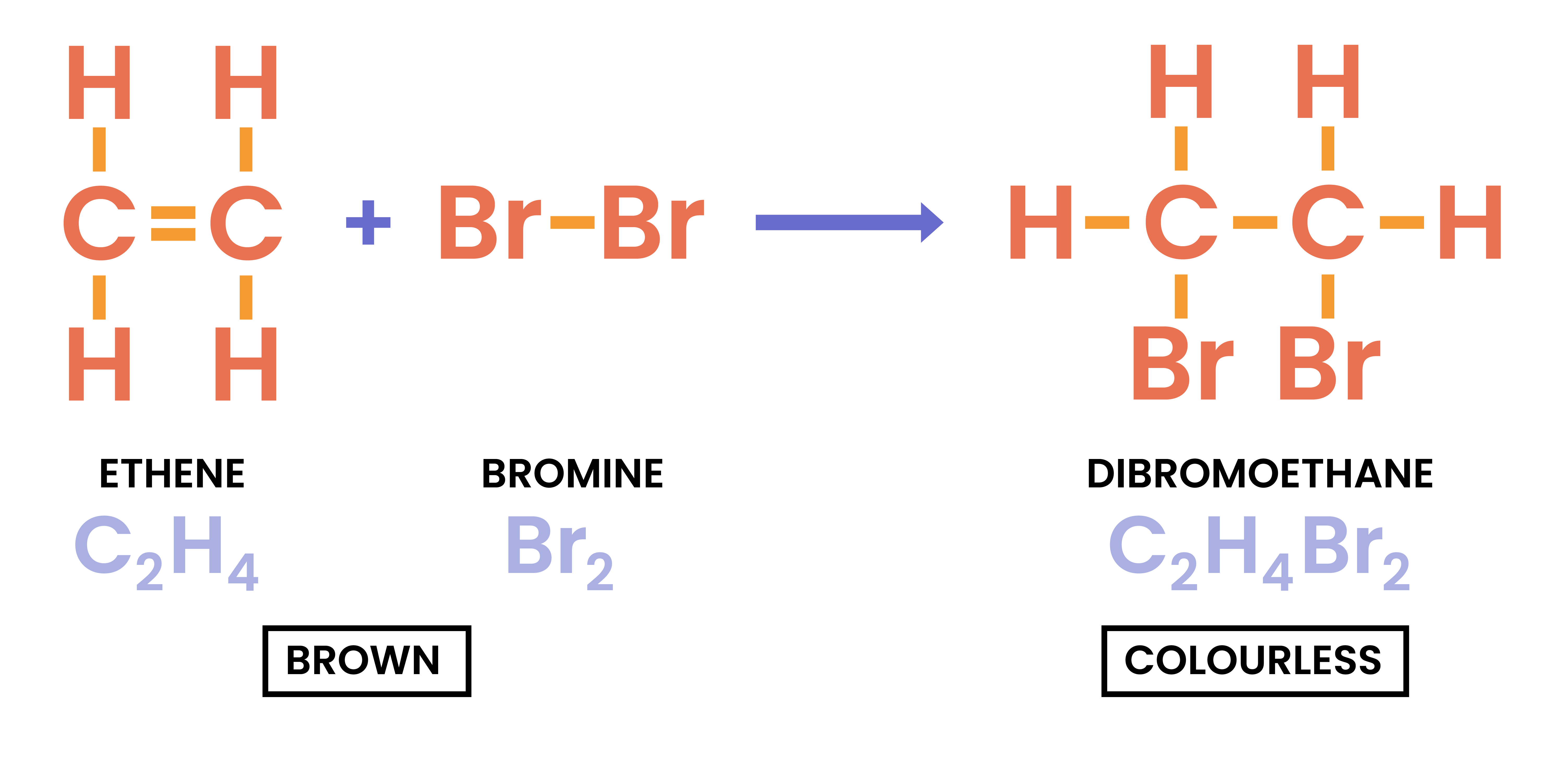
4.4.5 Describe the reactions of alkenes with bromine to produce dibromoalkanes
Reaction of Alkenes with Halogens
alkene + bromine → dibromoalkane
- As alkenes are unsaturated, they undergo addition reaction
- C=C double bond is removed
- Each carbon attaches to one bromine atom
- Br2 is a diatomic molecule:
- Br2 is brown in colour
- After reaction, Br2 is reacted
- Thus the reaction changes colour from brown to colourless
ethene + bromine → 1,2-dibromoethane
CH2CH2 + Br2 → CH2BrCH2Br
The numbers represent the carbon atom that the bromine atoms are attached to.
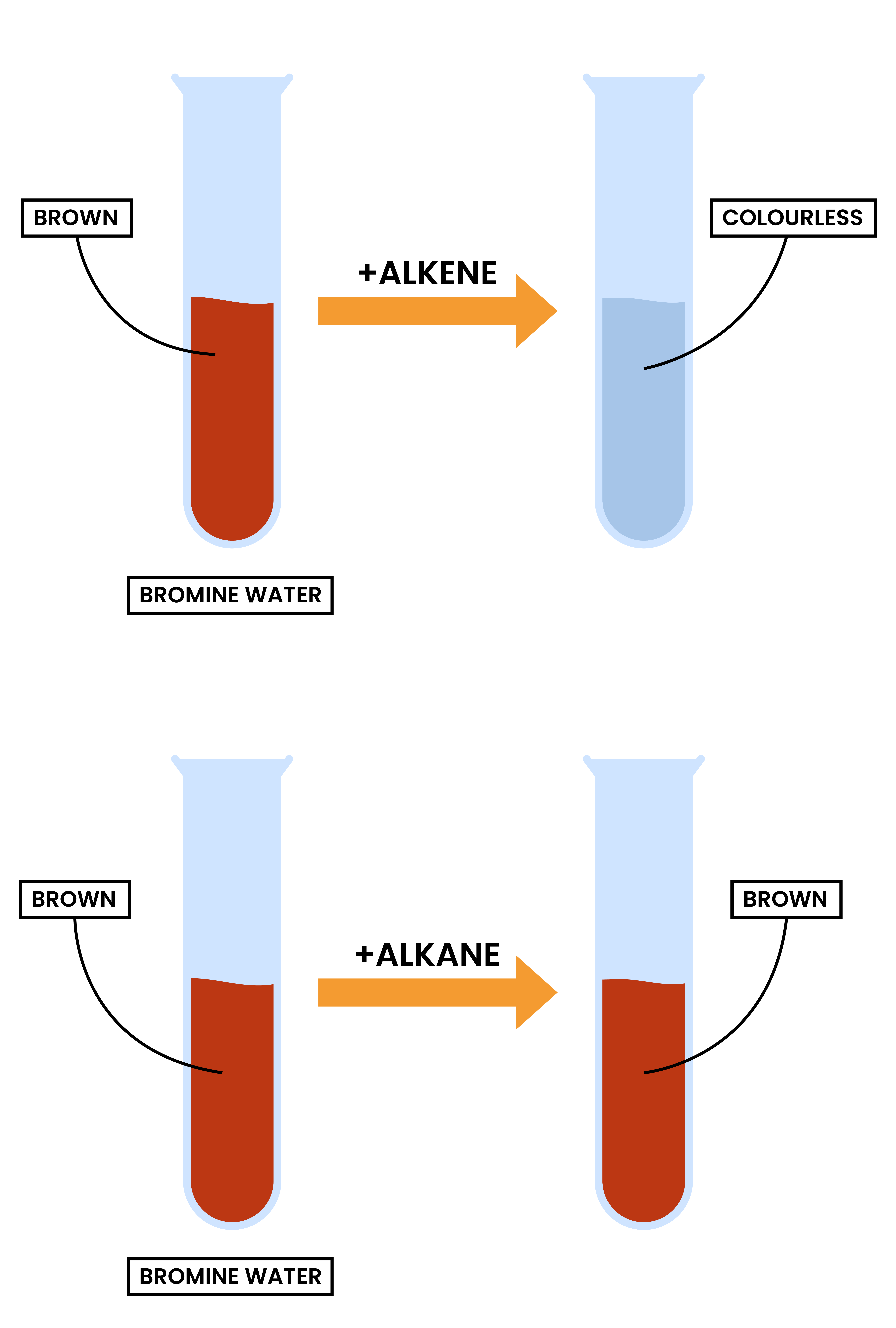
4.4.6 describe how bromine water can be used to distinguish between an alkane and an alkene
Bromine Water Test
- Alkanes react with bromine water ONLY when there is UV (light)
- Alkenes react with bromine water even without light
- Therefore, to distinguish between an alkane and alkene, add bromine water to the sample in a dark room
- If decolourisation happens, it means there is reaction happening, which implies it is an alkene