REVISION NOTES
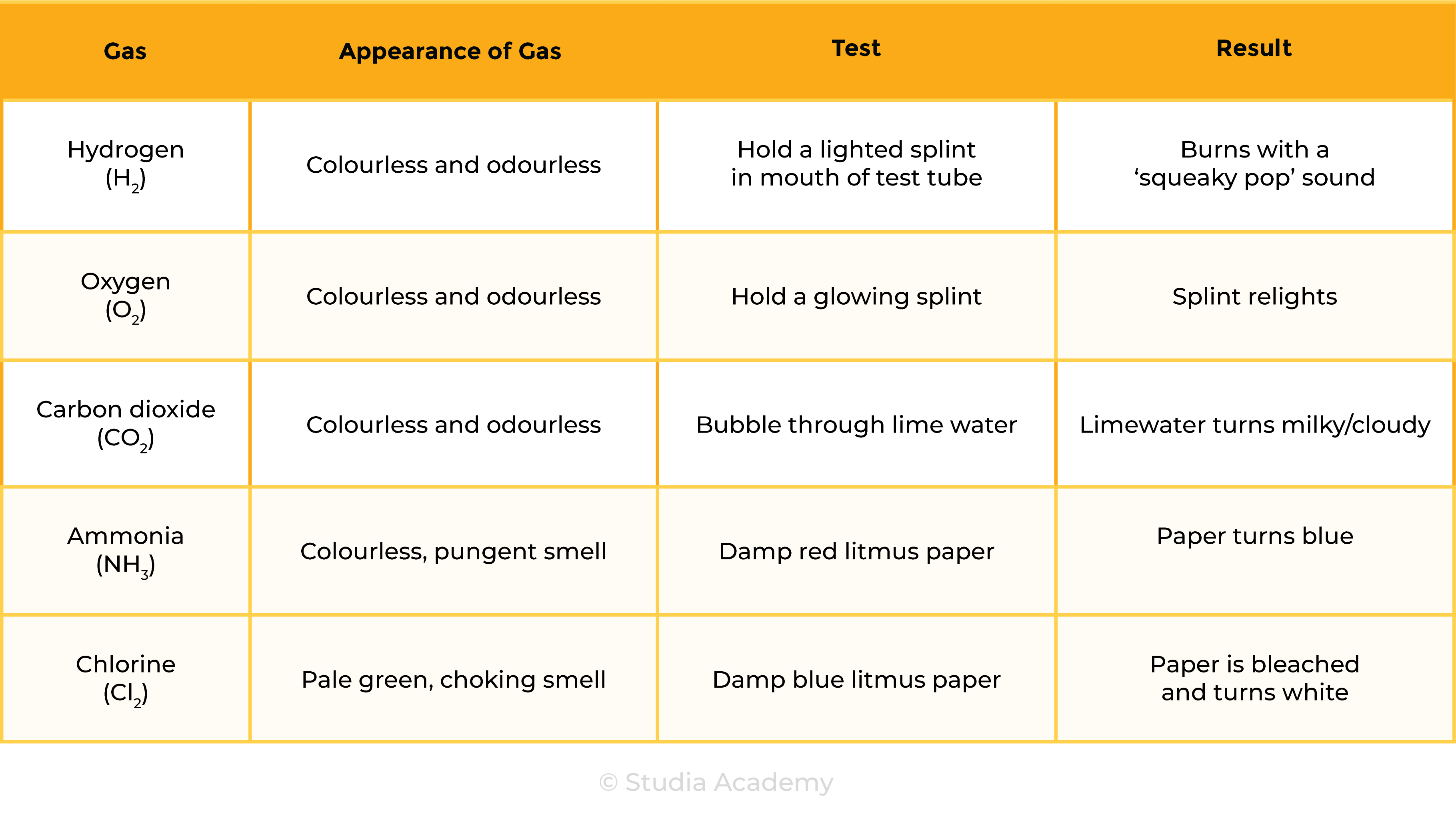
2.8.1 Describe tests for these gases:
Test of Gases
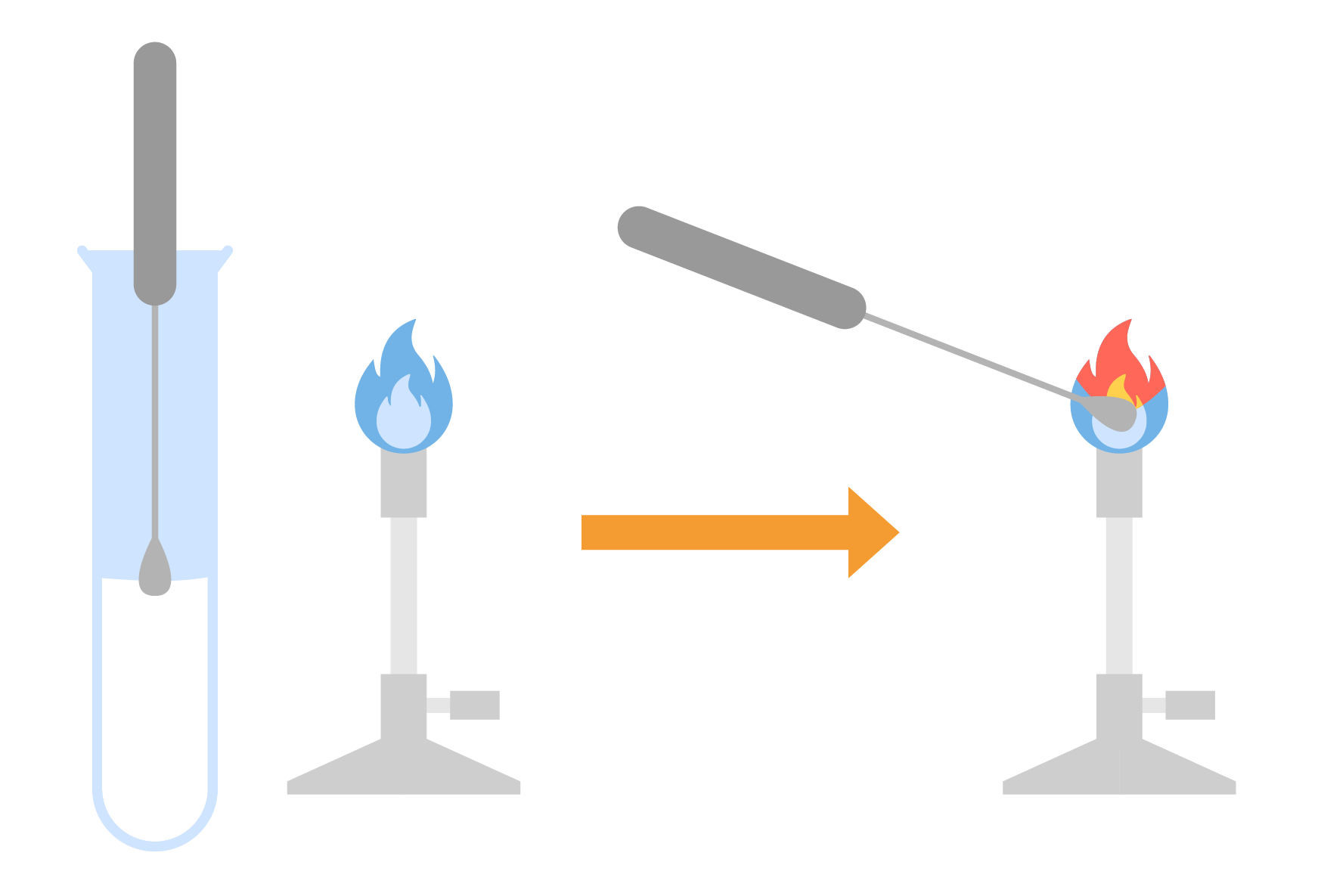
2.8.2 Describe how to carry out a flame test
FLAME TEST
Methods
2.8.3 Know the colours formed in flame tests for these cations:
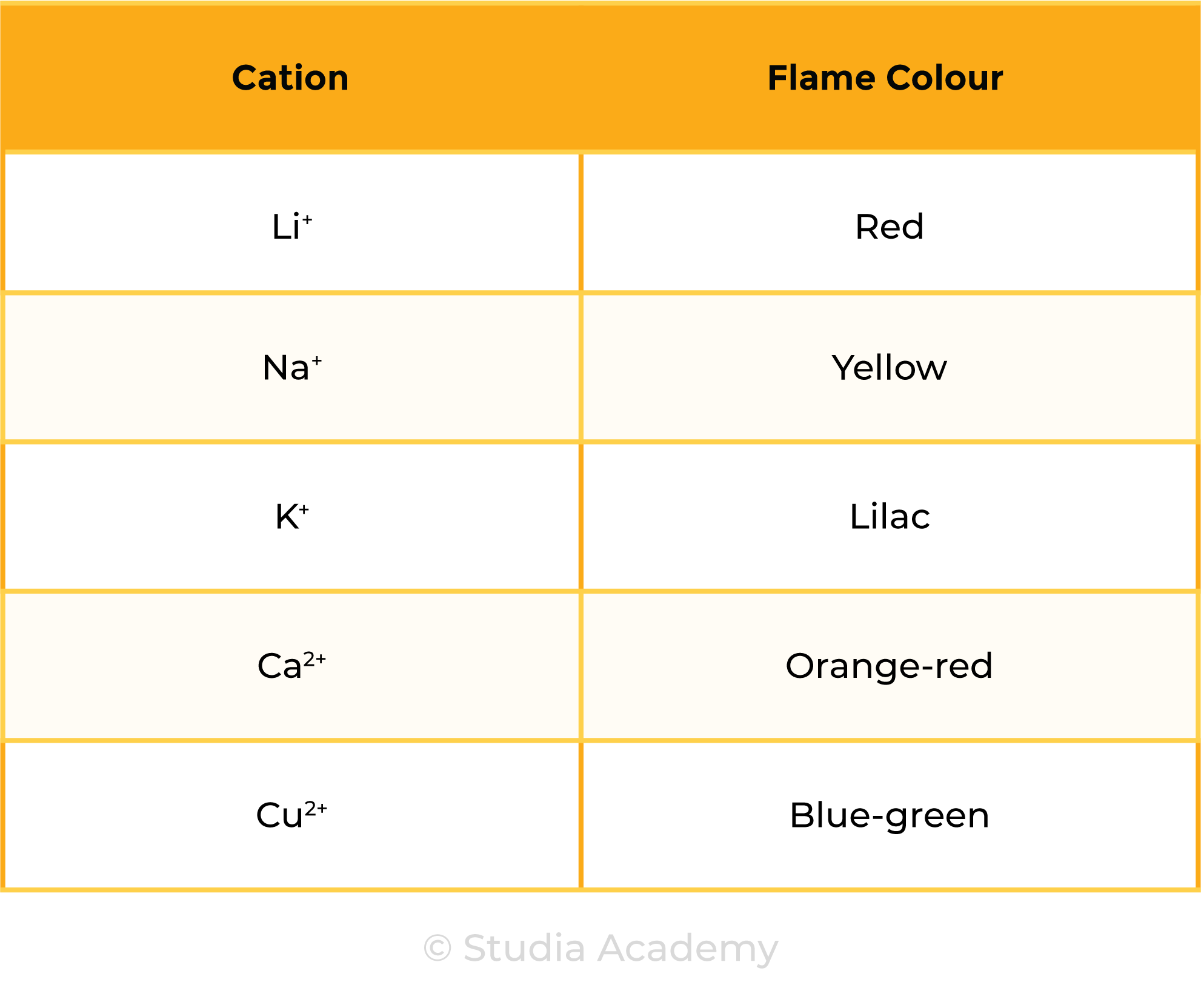
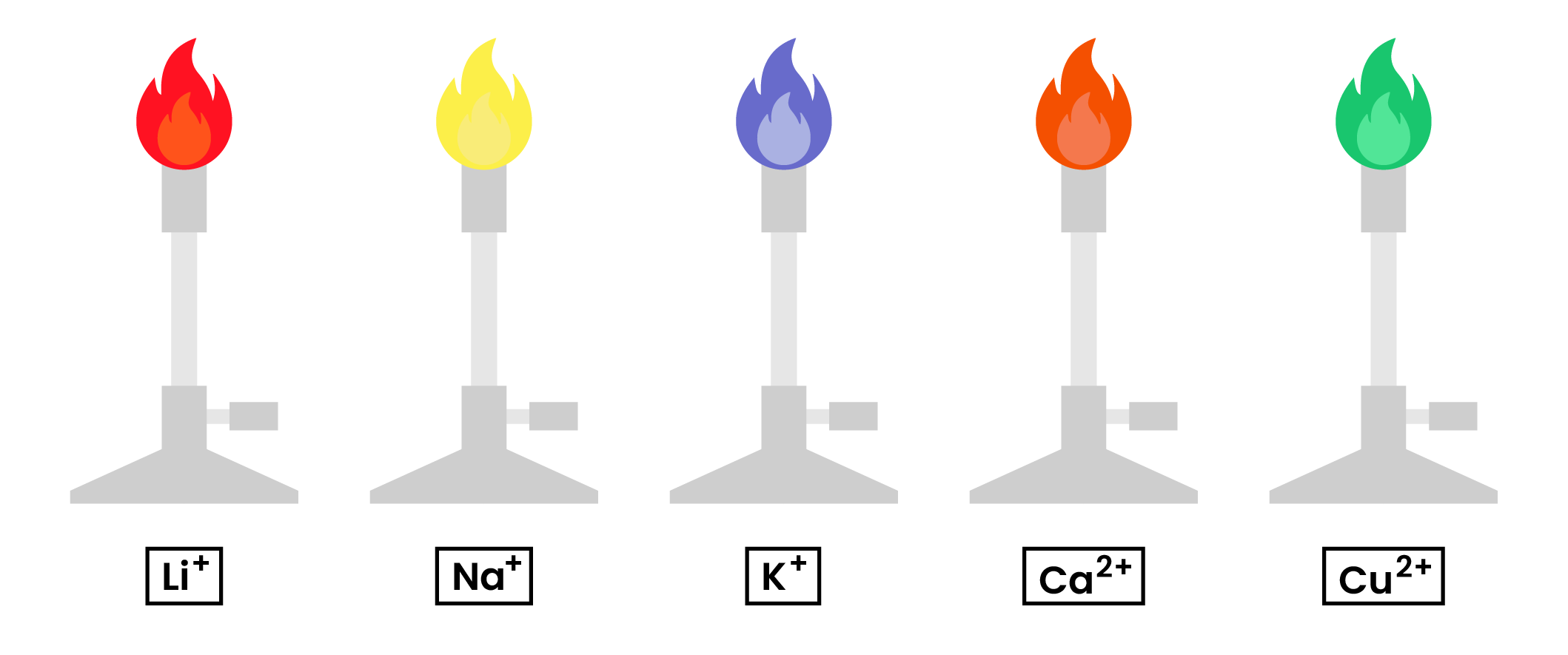
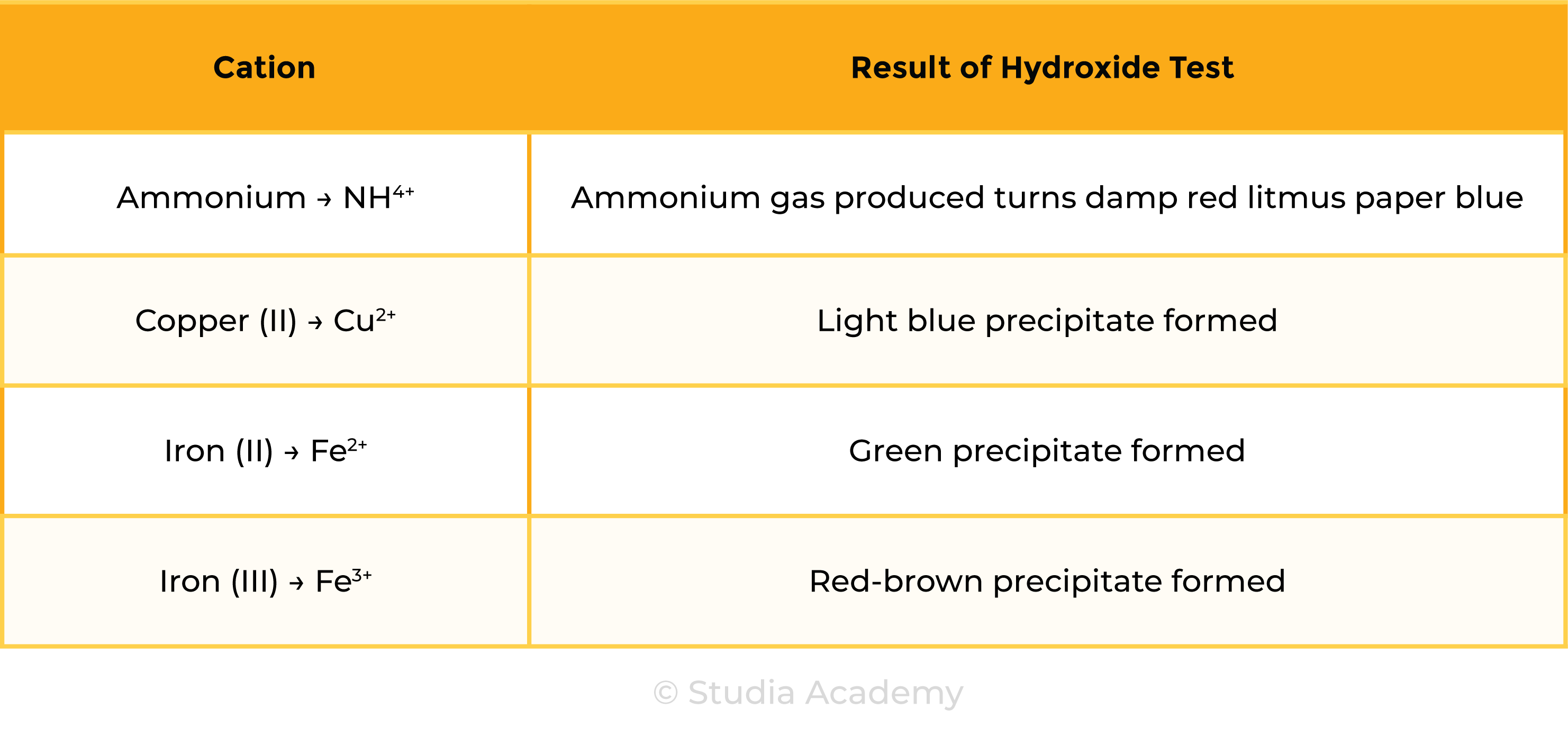
2.8.4 Describe tests for these cations:
Test for Cations
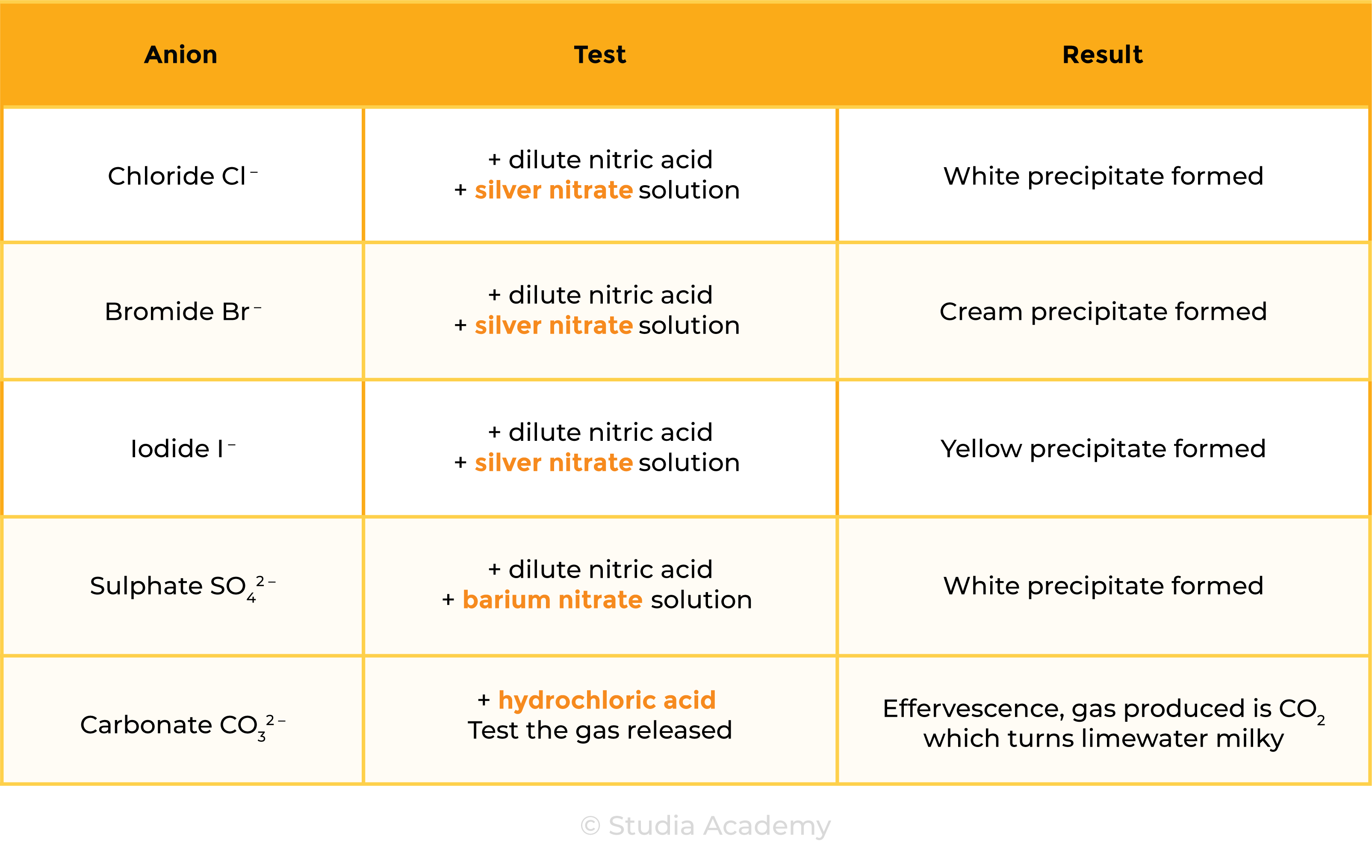
2.8.5 Describe tests for these anions:
Test for Anions
Nitric acid is added first to react with and remove any other ions (e.g. carbonate ions) that may be present that would give a confusing precipitate with silver nitrate. (E.g. If carbonate ions are present, a white precipitate of silver carbonate would be produced which gives a false result of chloride ions)
2.8.6 Describe a test for the presence of water using anhydrous copper(II) sulfate
TESTS FOR WATER (CHEMICAL)
2.8.7 Describe a physical test to show whether a sample of water is pure
TETS FOR WATER (PHYSISCAL)


© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.