REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Chemistry
2.1 Group 1 (Alkali Metals) – Lithium, Sodium and Potassium
2.1.1 Understand how the similarities in the reactions of these elements with water provide evidence for their recognition as a family of elements
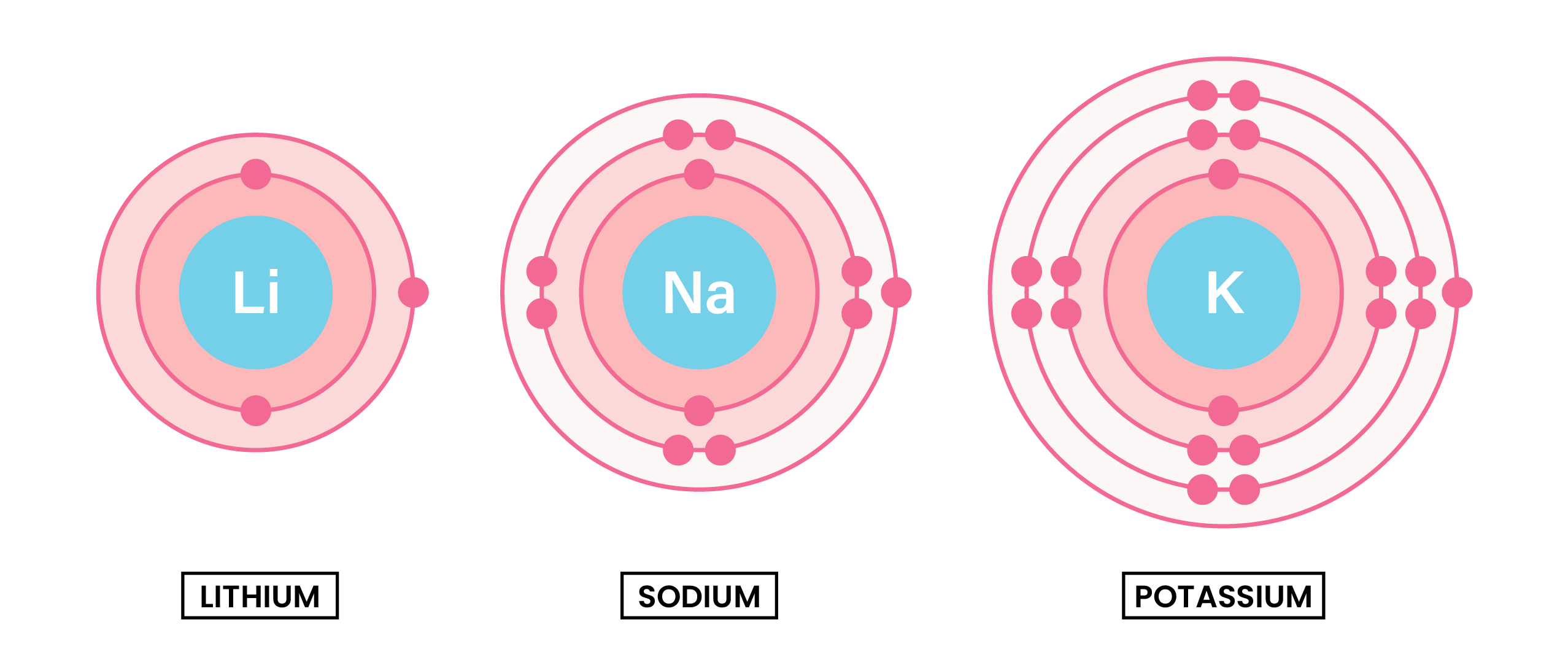
Group 1 metals (alkali metals) are found in the 1st group (column) of the periodic table. They form alkaline solutions when they react with water.
Because they have same number of electrons in the outer shell, they have similar chemical properties.
- Soft metals which can easily be cut with a knife
- Low densities
- Low melting point
- Very reactive
2.1.2 Understand how the differences between the reactions of these elements with air and water provide evidence for the trend in reactivity in Group 1
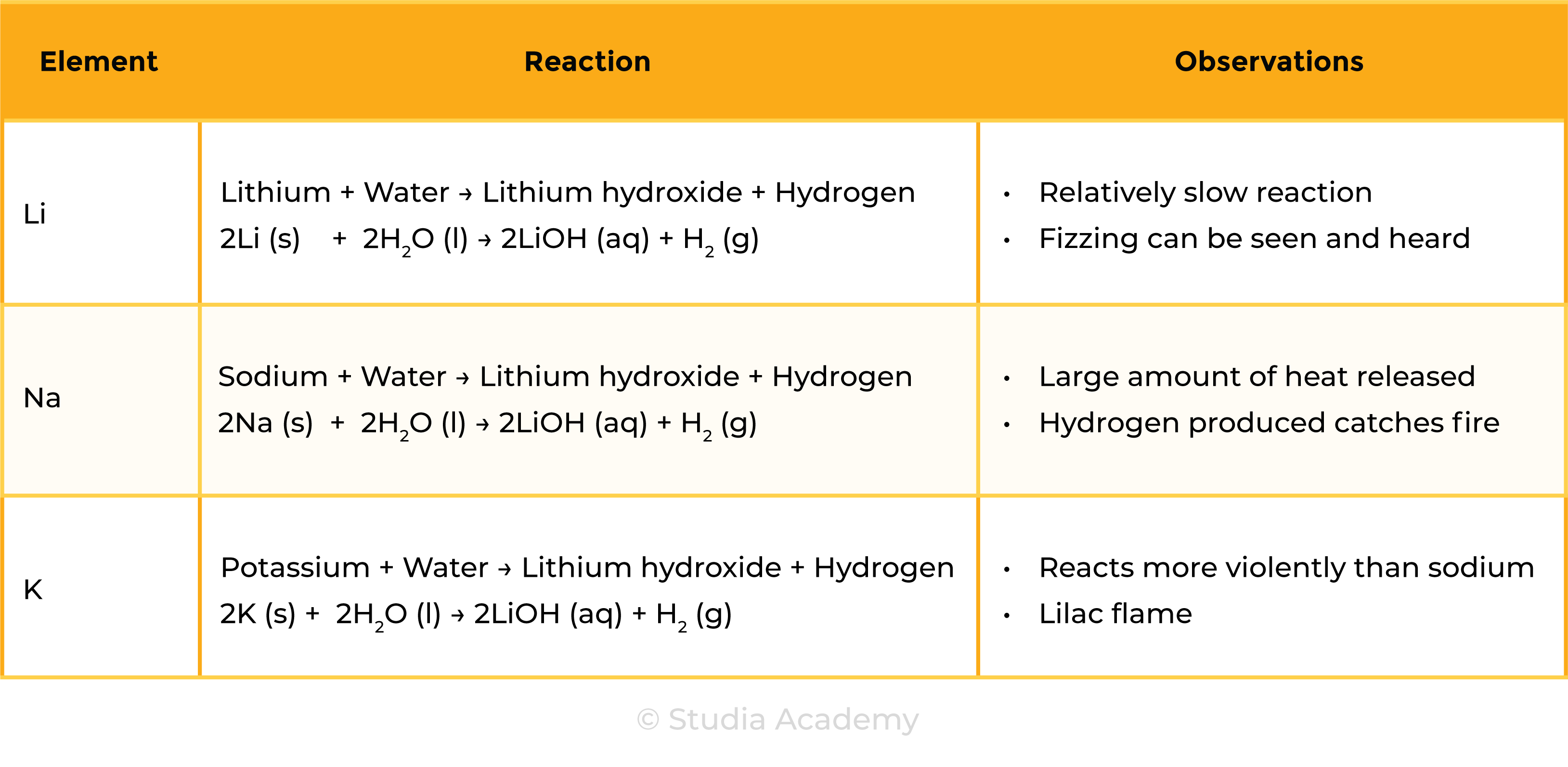
REACTION WITH WATER
- They form alkalis in water, this is why group 1 is called alkali metal
- Reaction of alkali metals with water is more vigorous down the group
Group 1 metal + Water → Metal hydroxide + Hydrogen
2M (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2MOH (aq) + H2 (g)
Observations during Group 1 Metal reaction with Water:
- Metal disappears or melts
- Metal turns into a round ball
- Metal floats on water surface
- Effervescence (bubbling)
- Flame produced (for more reactive Group 1 Metals, lower down the group)
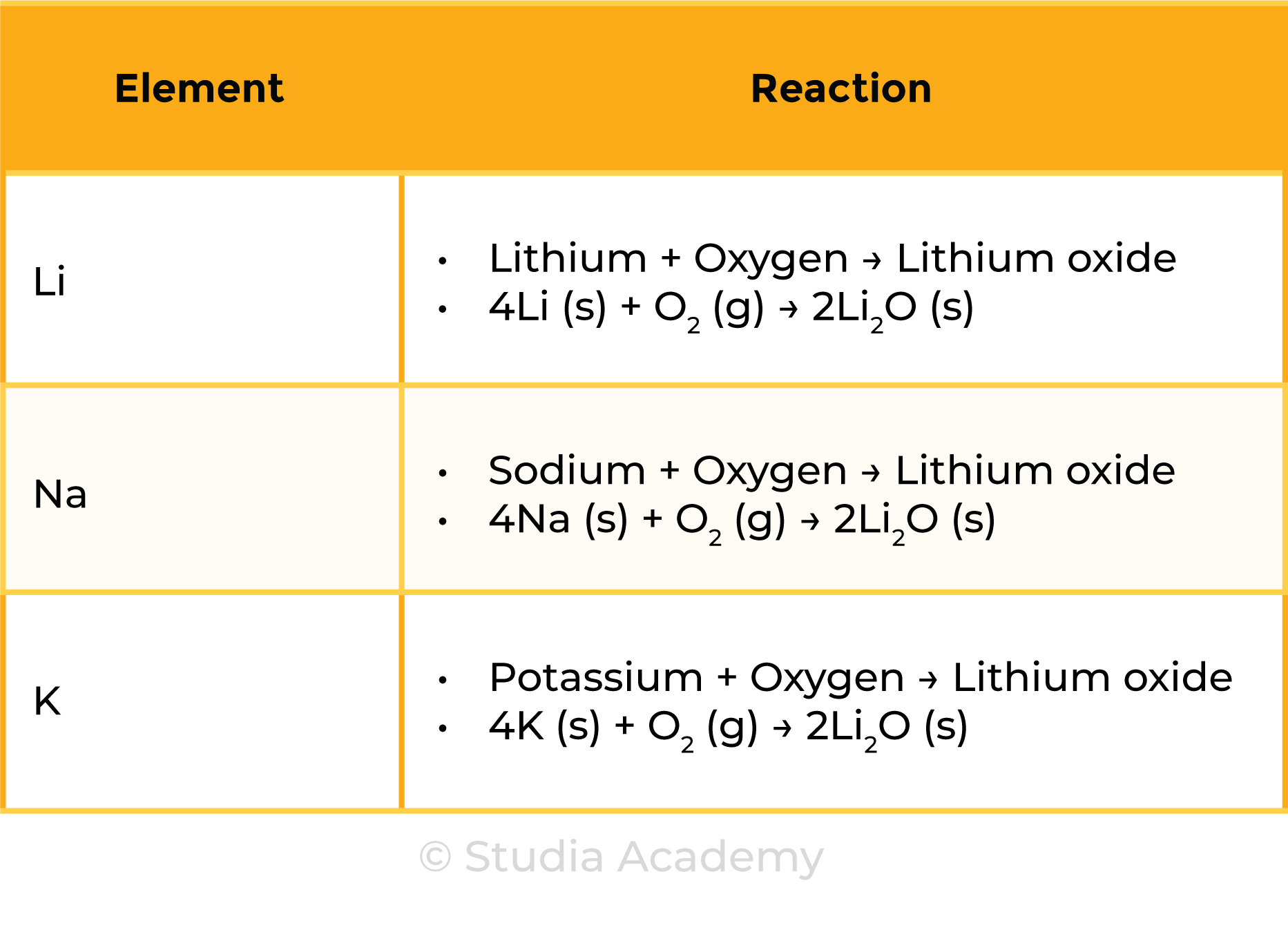
REACTION WITH OXYGEN
- Reaction of alkali metals with oxygen is more vigorous down the group
- Alkali metals react with oxygen in the air forming metal oxides
- The metal oxide produced covers the surface of the metal as a coating
2.1.3 Use knowledge of trends in Group 1 to predict the properties of other alkali metals
TRENDS IN CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKALI METALS
- Reaction with water and oxygen gets more vigorous down the group (from 2.1.2)
TRENDS IN PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKALI METALS
- Alkali metals get softer down the group
- Due to increasing atomic size and decreasing metallic bond down the group
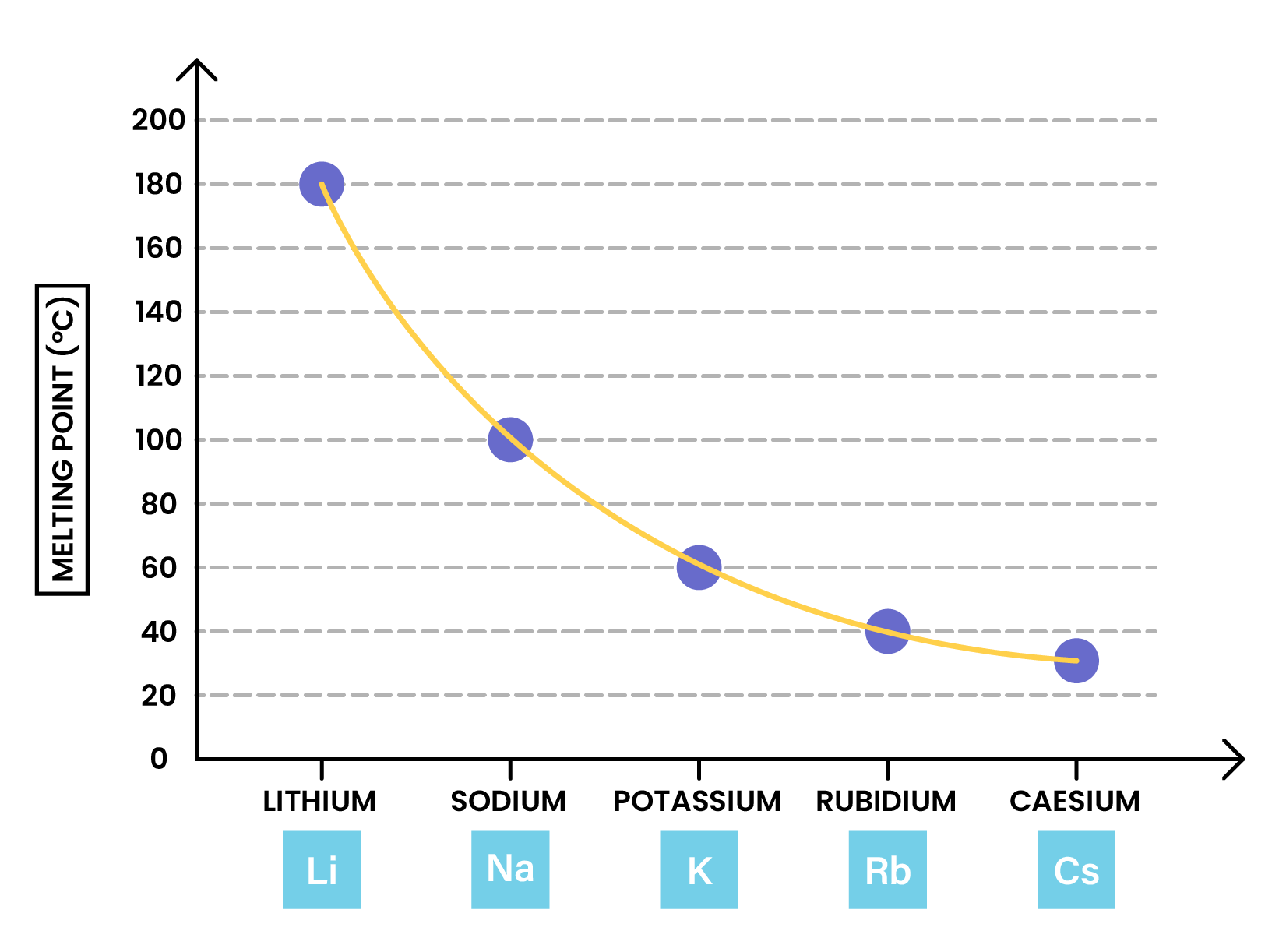
- Melting point >decreases down the group
- Due to decreasing attraction forces between the outer shell electrons and nuclei down the group
PREDICTING PROPERTIES IN GROUP 1
- As the reactivity of alkali metals increases down the group:
- Lithium is the least reactive
- Francium would be the most reactive
- According to the trend, rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs) and francium (Fr) react even more vigorously with water and oxygen compared to first three alkali metals
- We could also predict rubidium:
- Is a soft solid metal
- Is shiny when freshly cute
- Is more dense than potassium
- Has a lower melting point than potassium
2.1.4C Explain the trend in reactivity in Group 1 in terms of electronic configurations
The reactivity of group 1 increases down the group
EXPLANATION OF TREND IN REACTIVITY
- The number of electron shells increases down the group
- Outermost electrons gets further away from the nucleus down the group
- So there are weaker forces between the outermost electron and the nucleus
- Less energy is required to remove the electron
- Thus, it is easeire to lose the electron dowh the group
- Reactivity increases