REVISION NOTES
5.2.1 Understand how selective breeding can develop plants with desired characteristics
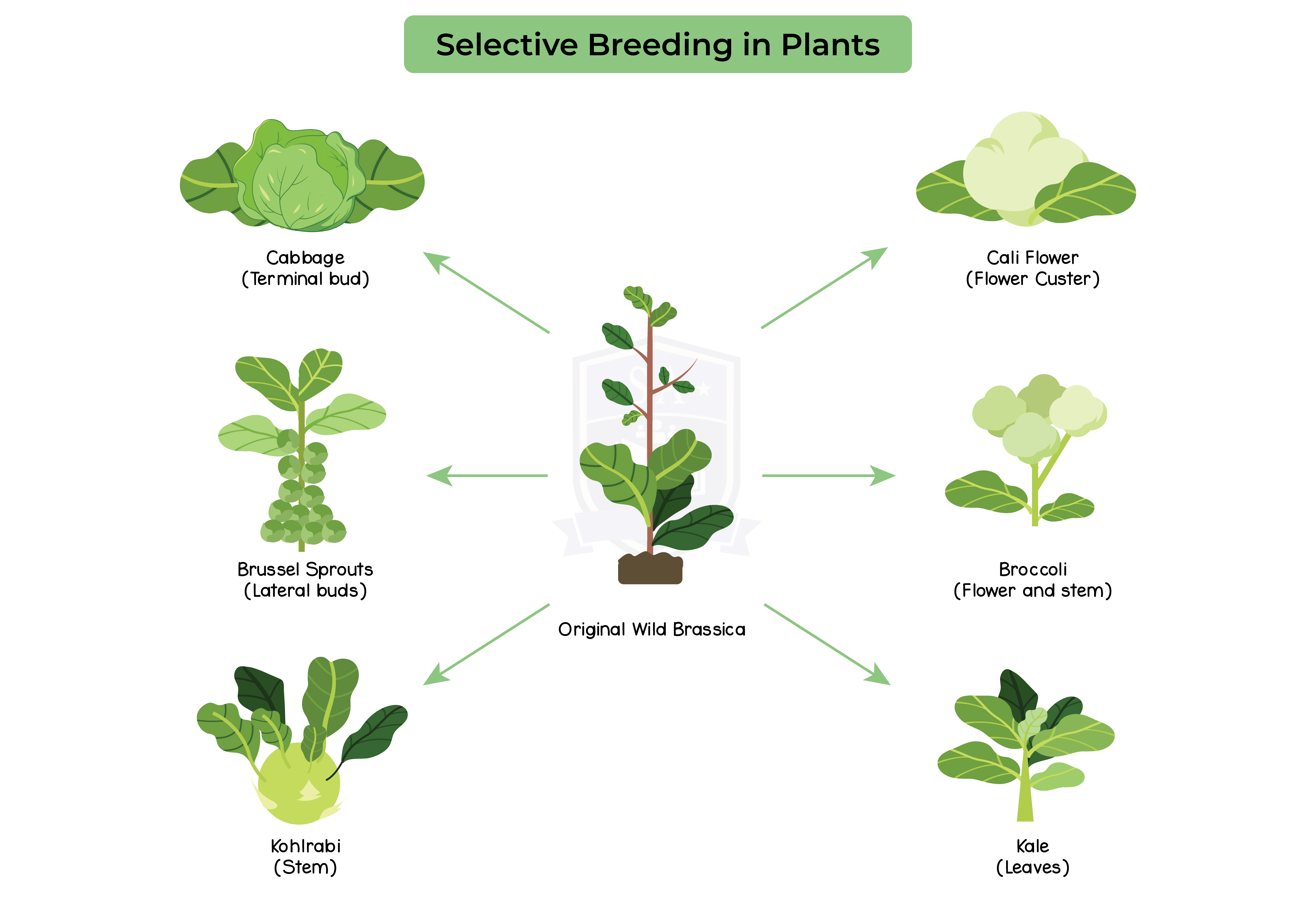
Selective breeding:
Selective breeding of plants:
5.2.2 Understand how selective breeding can develop animals with desired characteristics
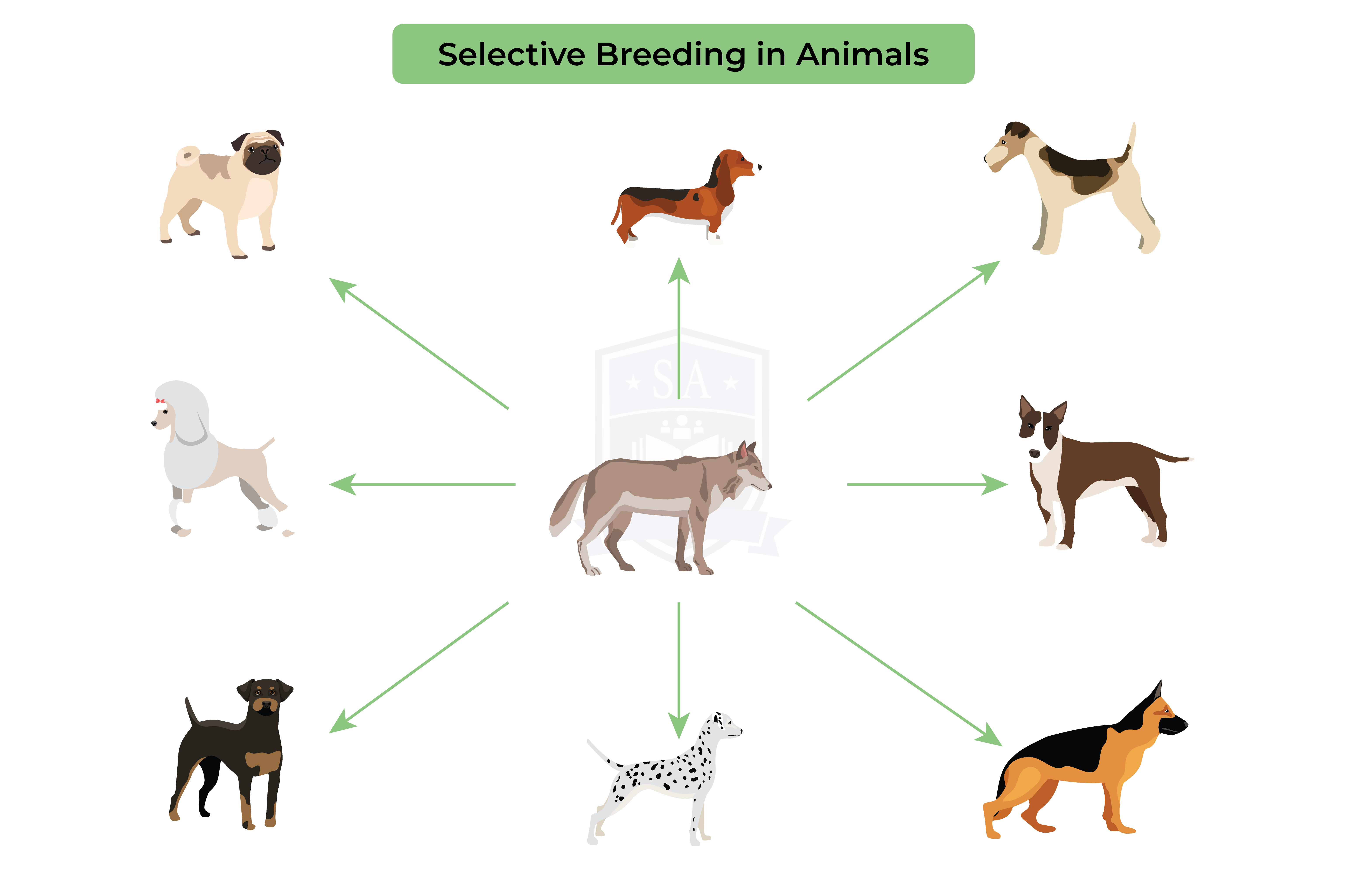
Selective breeding of animals:
Disadvantages of selective breeding:

© 2025 Studia Academy. All rights reserved.