REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Biology
a
1.2 Variety of Living Organisms
1.2.1 Describe the common features shown by eukaryotic organisms: plants, animals, fungi and protoctists
Eukaryotic organisms:
- Plant
- Animals
- Fungi
- Protoctists
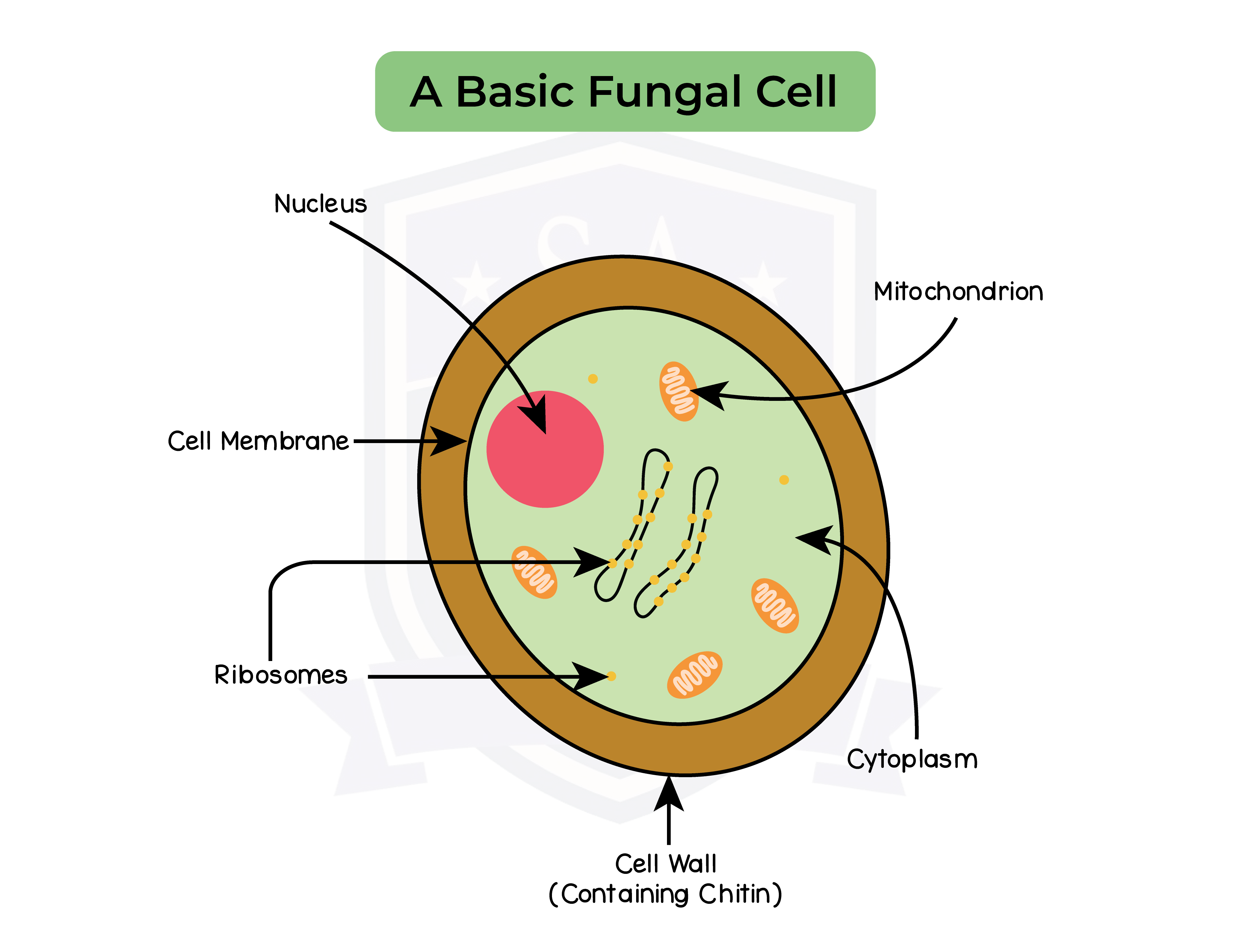
Common features by eukaryotic organisms:
- Multicellular or single-celled
- Cell contains membrane bound Nucleus
Common features of plants:
- chloroplasts allow plants to photosynthesize
- Chlorophyll pigments absorb light from the sun
Common features of fungi:
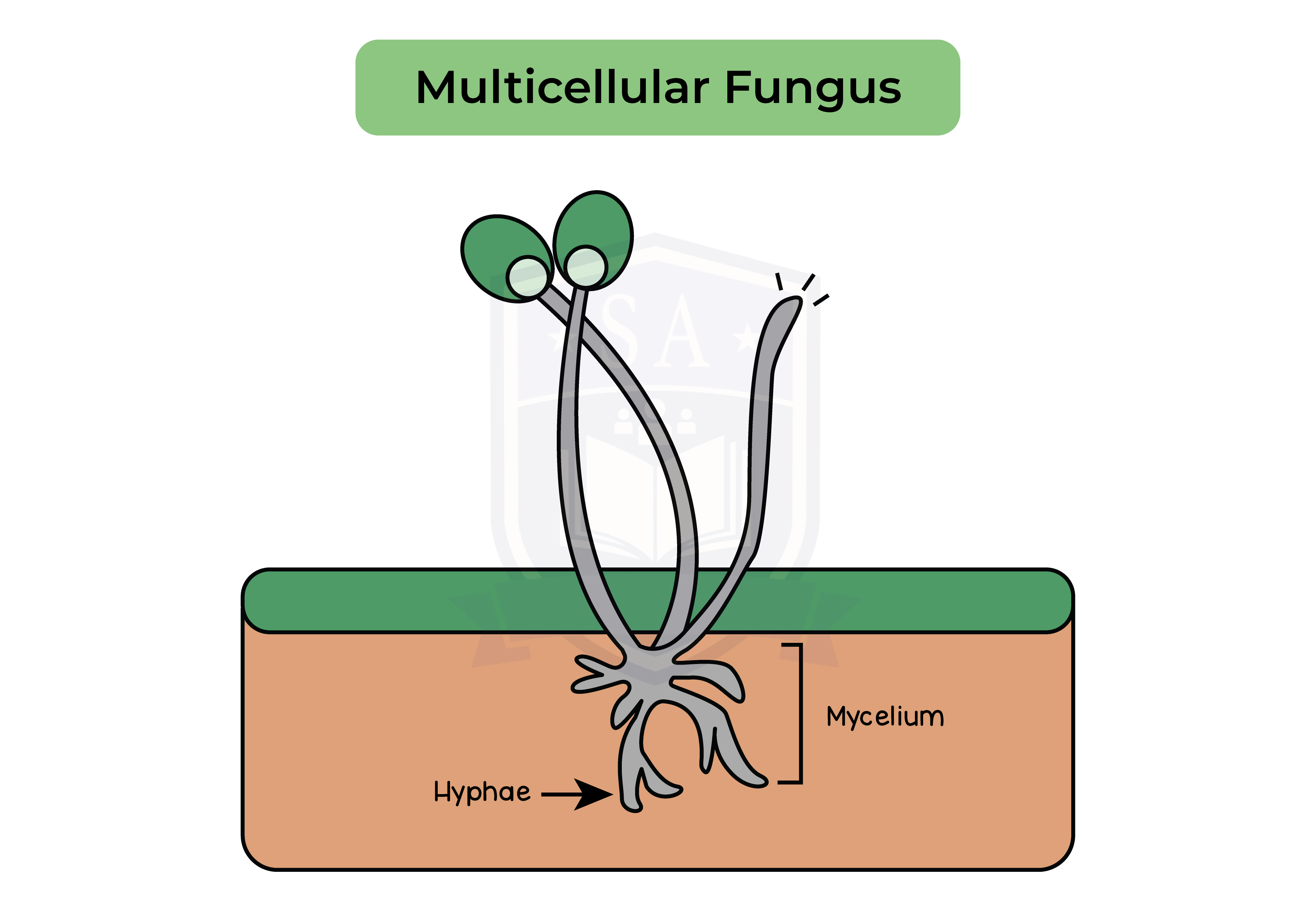
- Multicellular fungi (e.g. mushroom) contain thread-like filaments called hyphae that have many nuclei
- Hyphae are organized into a network of mycelium
- Parasitic fungi feed on living organisms
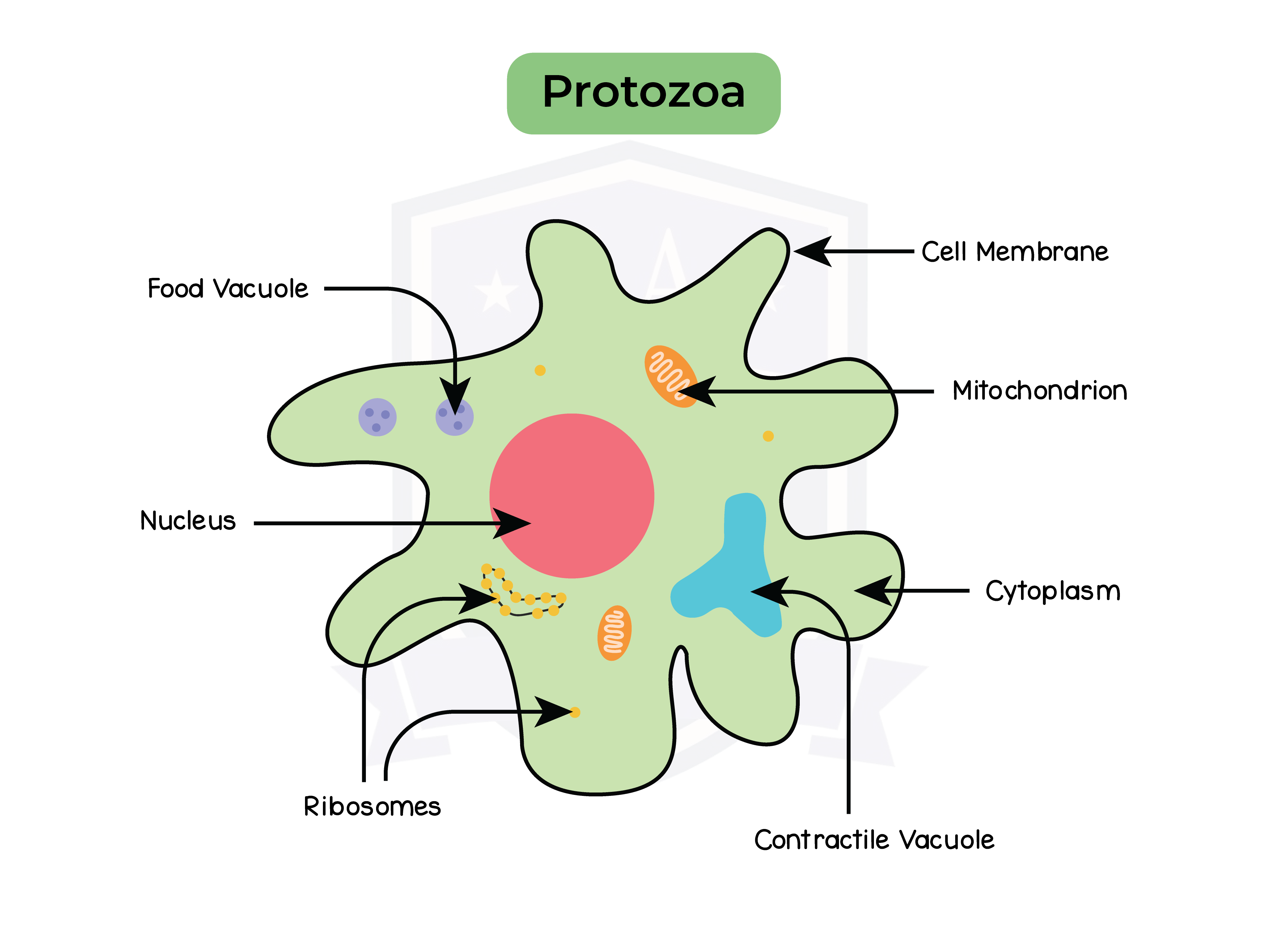
Common features of protoctists:
- can aggregate into colonies or filaments
- Protozoa which are cells that similar to animal cells (e.g. amoeba or plasmodium)
- Plasmodium is responsible for malaria
Algae which contain cells that are similar to plant cells (e.g.chlorella)
1.2.2 Describe the common features shown by prokaryotic organisms such as bacteria
Prokaryotic organisms:
- Bacteria
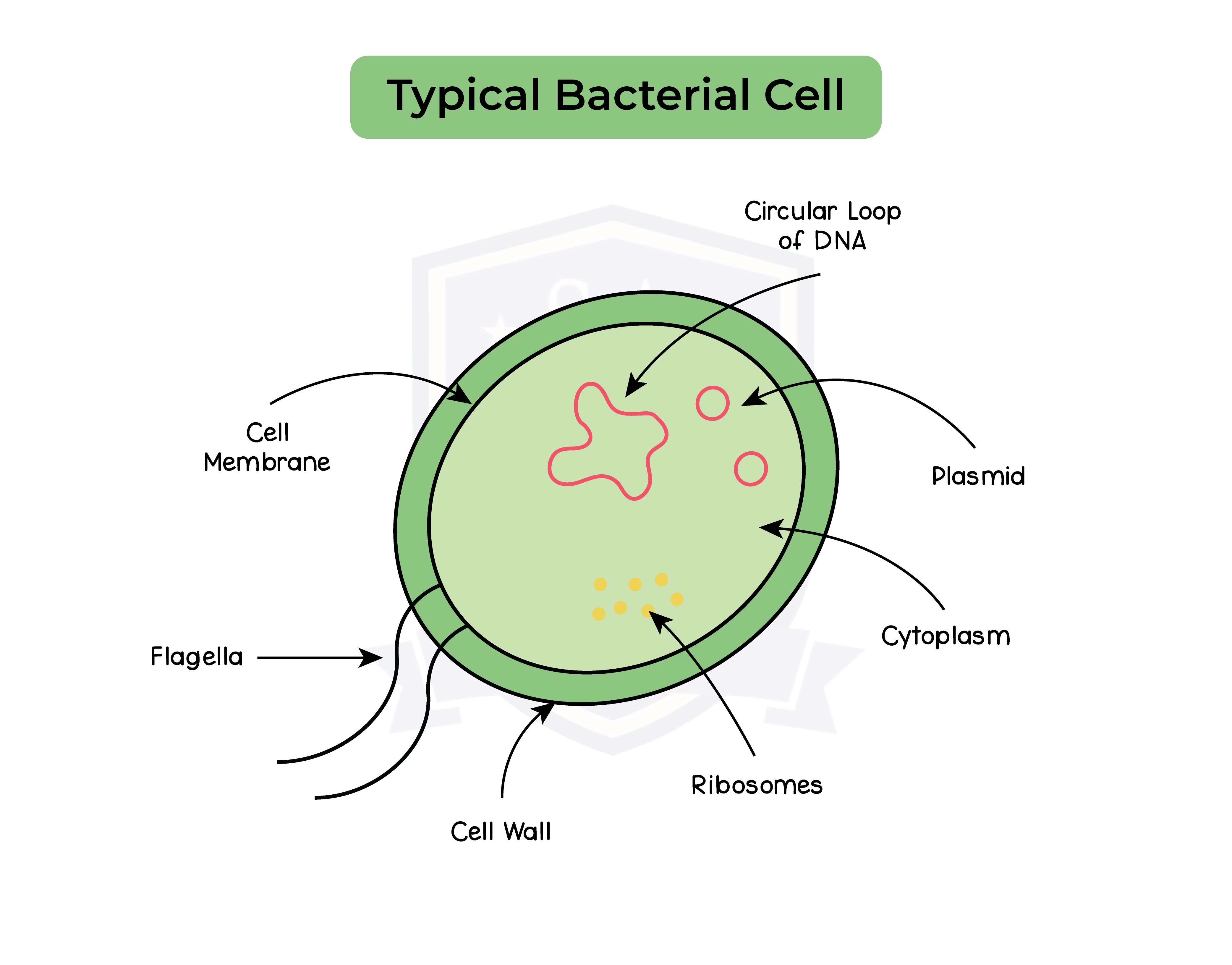
Common features of prokaryotic bacteria:
- Always single-celled
- No nucleus but contain circular chromosomes
- nuclear material found in the cytoplasm
- smaller than eukaryotic cells
- Lack any membrane bound organelles
- Contain cell wall made of peptidoglycan, cell membrane, cytoplasm and plasmids
- Plasmids are small circular rings of DNA carrying some bacterial genes
- Some have a capsule or slime layer outside the cell wall for protection
- Some contain flagella/ flagellum for movement
- Bacteria can feed by:
- Photosynthesis if they contain chlorophyll
- Most bacteria feed on living or dead organisms
- They are decomposers
- Bacteria can also come in different shapes:
- Rod shaped
Spherical shaped
1.2.3 Understand the term pathogen and know that pathogens may include fungi, bacteria, protoctists or viruses
What are pathogens:
- Any microorganism that causes diseases in other organisms
- Pathogenic organisms are:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
- Protoctists
- Viruses
- Not all species of each group are pathogens
- All viruses are pathogenic and can only exist in host cells of other living organisms
Viruses:
- Parasitic
- Not considered a living organism
- they can infect:
- Animals
- Plants
- Bacteria
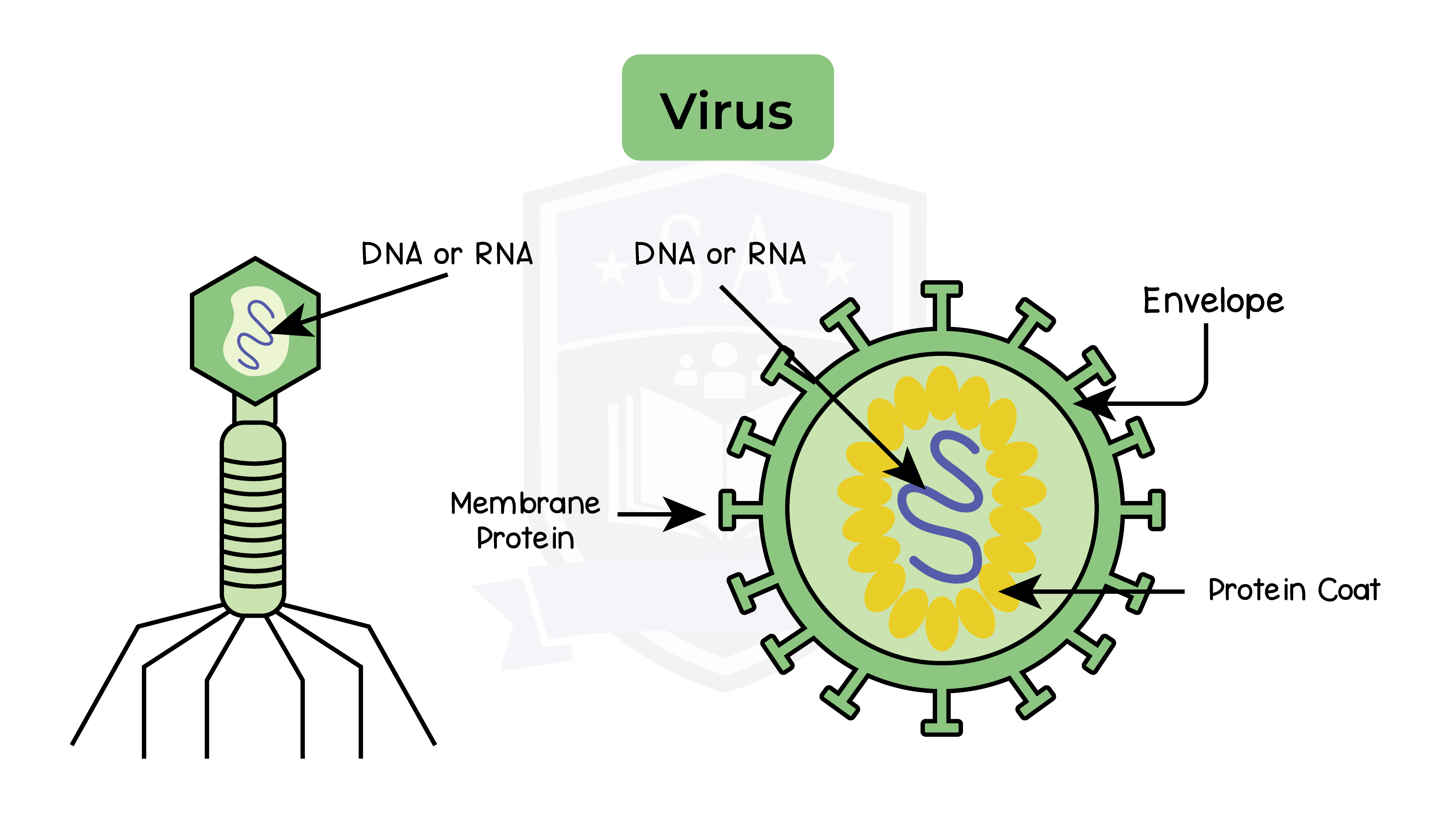
- Viruses have a wide range of shapes and sizes
- Virus characteristics:
- Smaller than bacteria
- Only reproduce inside host cells
- Take over host cell’s metabolic pathways to reproduce
- At a high volume of virus particles, the host cell dies and particles are released to infect other cells
- No cellular structure such as cytoplasm or nucleus
- Virus cells can contain the following:
- Core genetic material as DNA or RNA
- Protein coat
- Envelope stolen from the surface membrane of the host cell
Examples of viruses:
- Tobacco Mosaic Virus causing discolouration of leaves by preventing chloroplast formation
- HIV virus that causes AIDS
- Influenza virus that causes the flu
Bacteria:
- Reproduce through binary fission
- Damage cells by excreting toxins
- E.g. Salmonella that causes food poisoning
Fungi:
- Spread through spores
- Treated by fungicides
- E.g. Athlete’s foot
Protocists:
- Parasitic
- E.g. Malaria