REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Biology
2.8 Gas Exchange (in Plants)
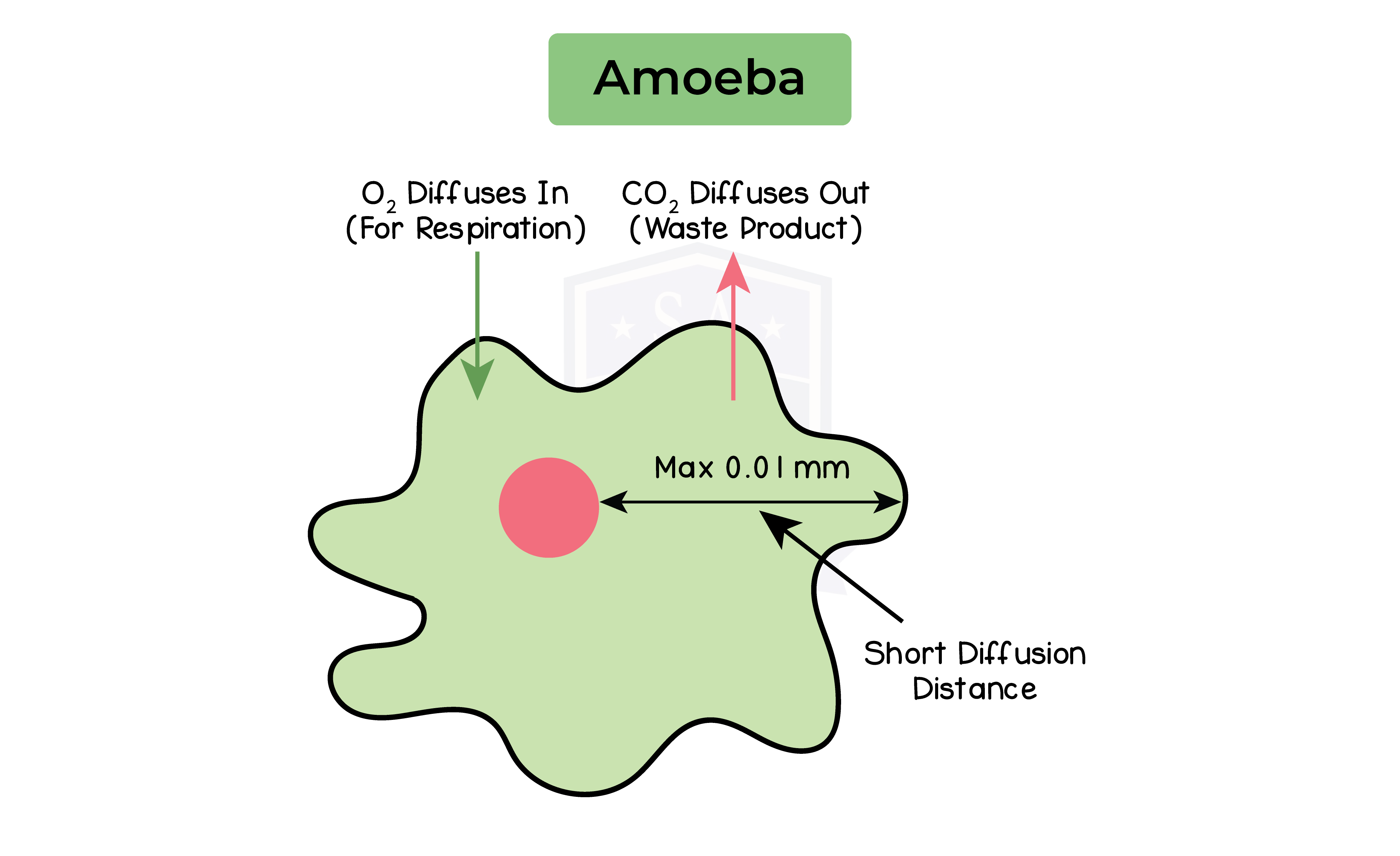
2.8.1B Understand the role of diffusion in gas exchange
Diffusion:
- Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
- Affected by partially permeable cell membrane
- Restricts the movement of molecules down the concentration gradient
- Restriction is based on molecular size
- Smaller molecules like water can diffuse
- Larger molecules like salts cannot
- Passive process
- Gas exchange occurs through diffusion
- Organ systems providing gas exchange surfaces
- Maximise diffusion
- Increase surface area
- Decrease diffusion distance
2.8.2 Understand gas exchange (of carbon dioxide and oxygen) in relation to respiration and photosynthesis
Respiration and photosynthesis rely on gas exchange
Gas exchange for respiration:
- Uptake of oxygen
- Release of carbon dioxide
- Gases diffuse from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
- Oxygen diffuses outside the leaf to inside the leaf
- Carbon dioxide diffuses from inside the leaf to outside the leaf
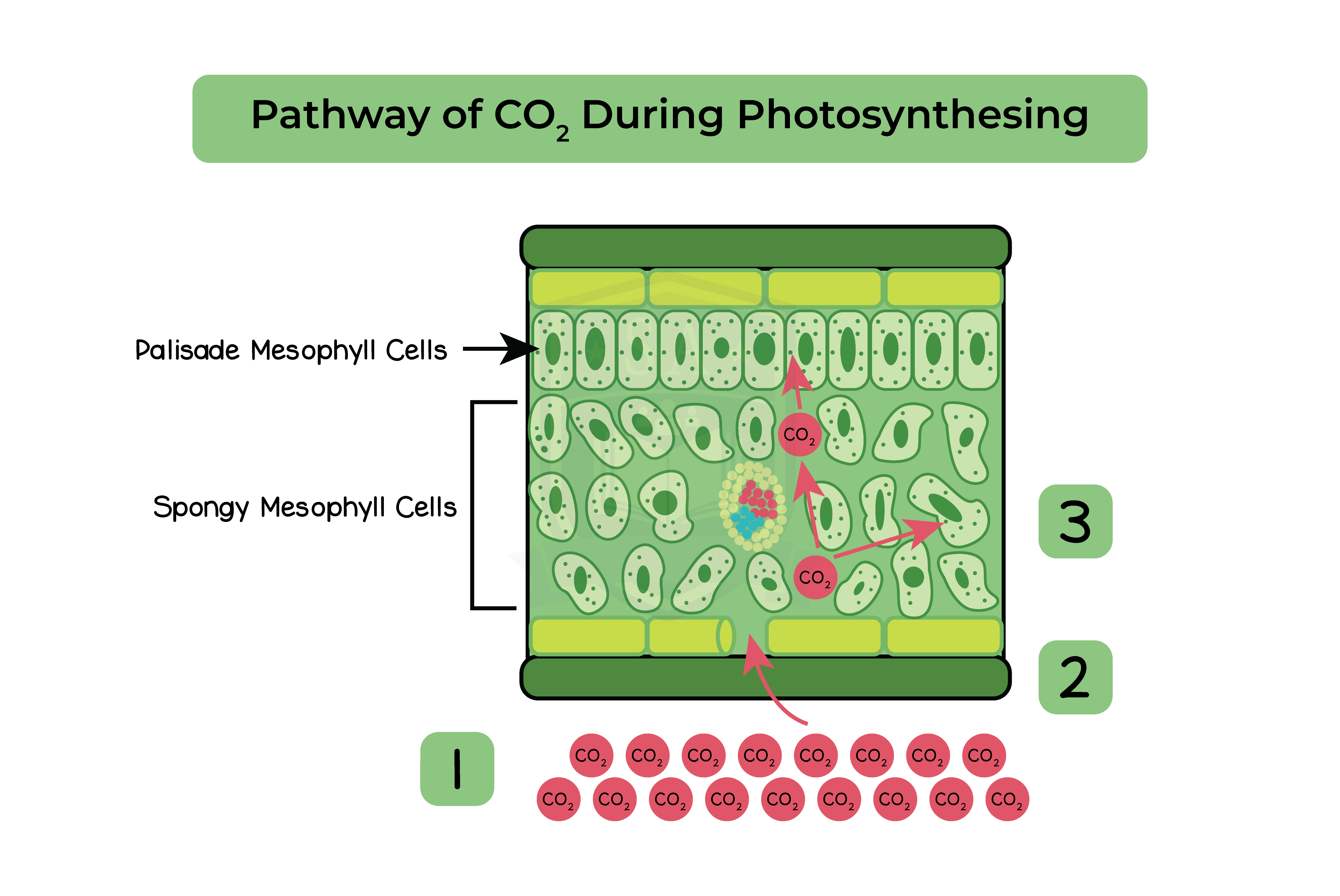
Gas exchange in photosynthesis:
- Uptake of carbon dioxide
- Release of oxygen
- Carbon dioxide diffuses from outside the leaf to inside the leaf
- Carbon dioxide is constantly used in photosynthesis
- Concentration inside photosynthesizing cells is always low
- Oxygen diffuses from inside the leaf to outside the leaf
2.8.3B Understand how the structure of the leaf is adapted for gas exchange
- Thin leaves and cell walls decrease diffusion distance
- Flat leaves increasing SA:V ratio
- Stomata that allow gases to move through air spaces
- Maintain a steep concentration gradient
- Air spaces allow gases to move around mesophyll cells
- Stomata in lower epidermis open under sunlight
- Increase movement of gases in and out of the leaf
- Moist air dissolving gases for easier movement through cells
2.8.4B Describe the role of stomata in gas exchange
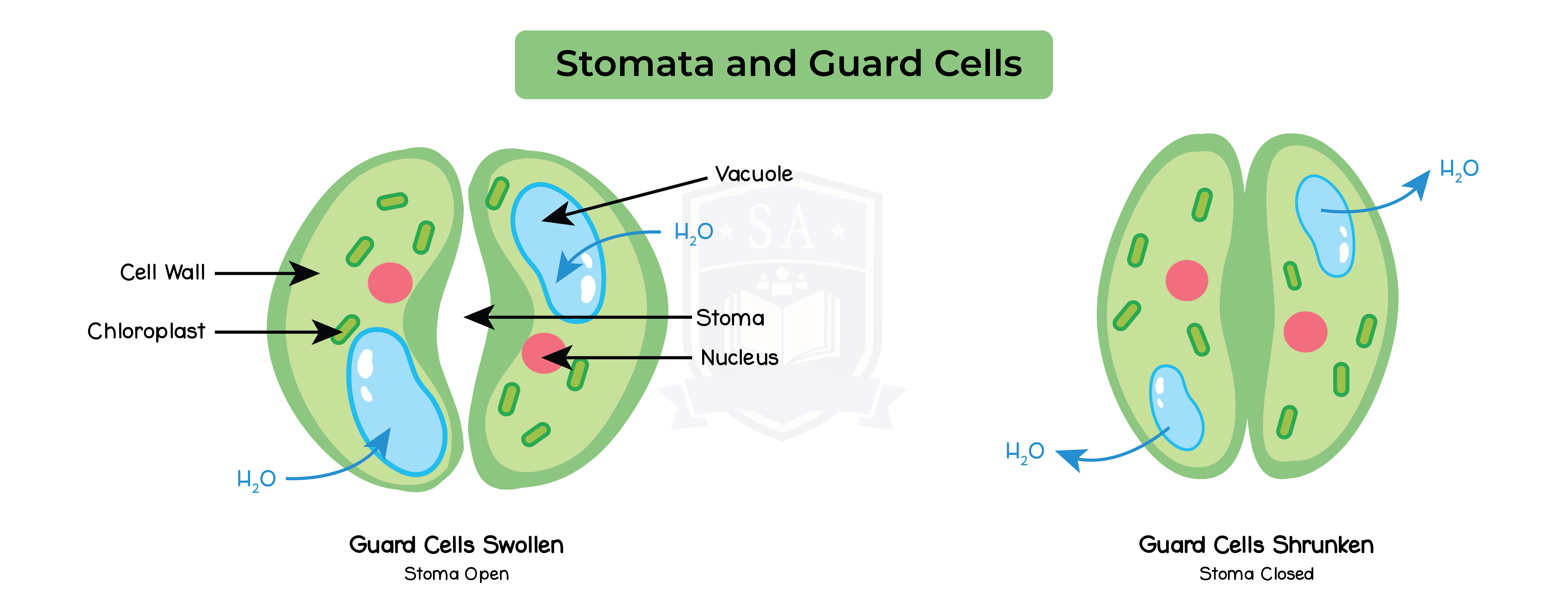
Stomata:
- Space in between two guard cells
- Located on the lower epidermis of the leaf
- Swelling and shrinking of guard cells control the opening and closing of the stomatal pore
- Controls gas exchange
Stomata in gas exchange:
- Opens when water diffuses into guard cells by osmosis
- Makes them turgid
- Allows gases to diffuse through stomatal pore
- Stomata opens in sufficient supply of water and sunlight
- Closes when guard cells lose water through osmosis
- They shrink and become flaccid
- Prevents diffusion through stomatal pore
- Stomata tends to be close when supply of water and sunlight is low
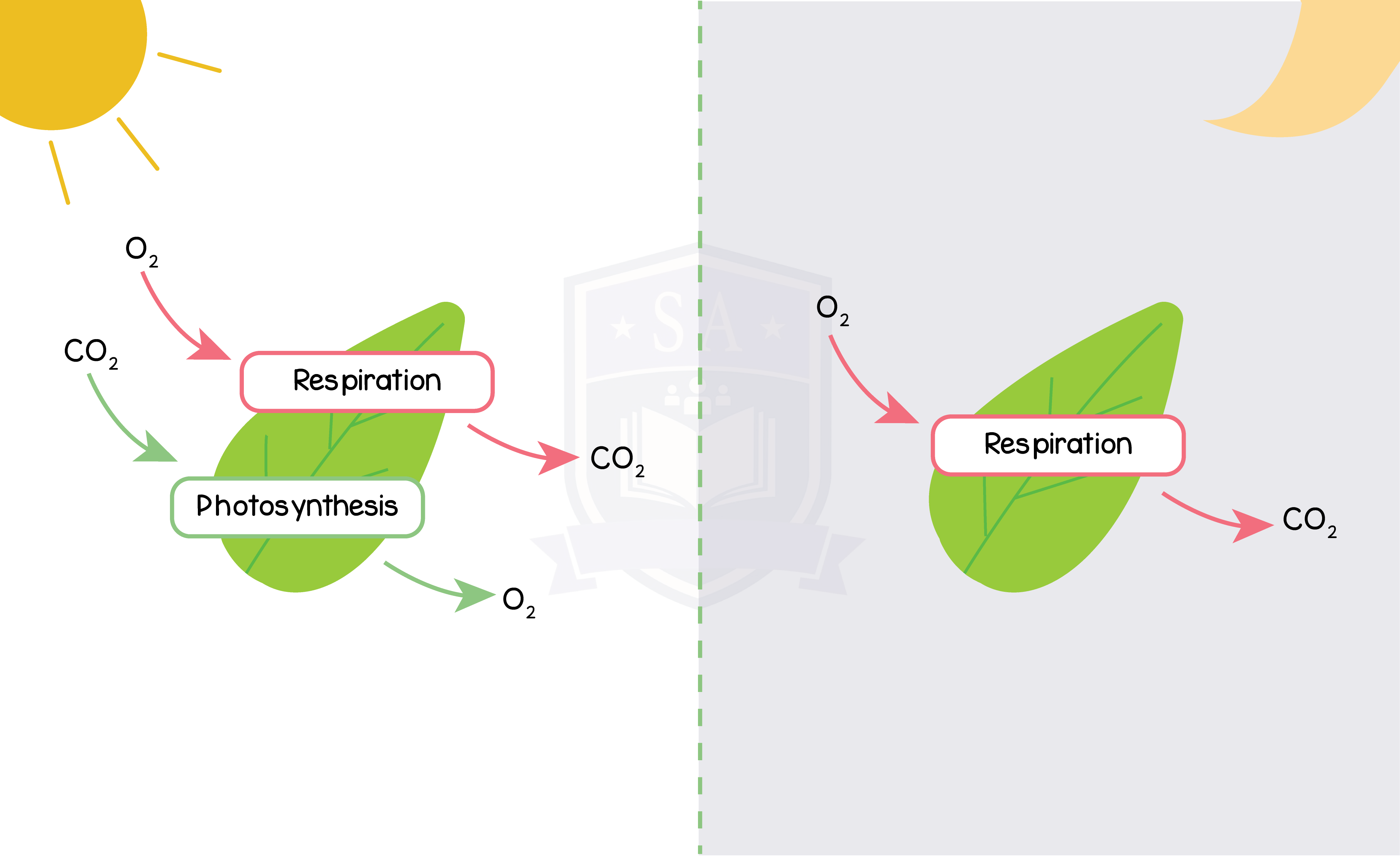
2.8.5B Understand how respiration continues during the day and night, but that the net exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen depends on the intensity of light
Daytime:
- Plants only photosynthesize during the day in the presence of light
- Continually respire during day and night
- Rate of photosynthesis is higher than rate of respiration
- At low intensity of light, rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration
- No net movement of gases in either direction
- Increase in net diffusion of CO2 into the plant
- Increase in net diffusion of O2 out of the plant
Night Time:
- Plants can only respire
- No light for photosynthesis to occur
- Rate of respiration is higher than rate of photosynthesis
- Increase in net diffusion of O2 into the plant
Increase in net diffusion of CO2 out of the plant
2.8.6B Practical: investigate the effect of light on net gas exchange from a leaf, using hydrogen-carbonate indicator
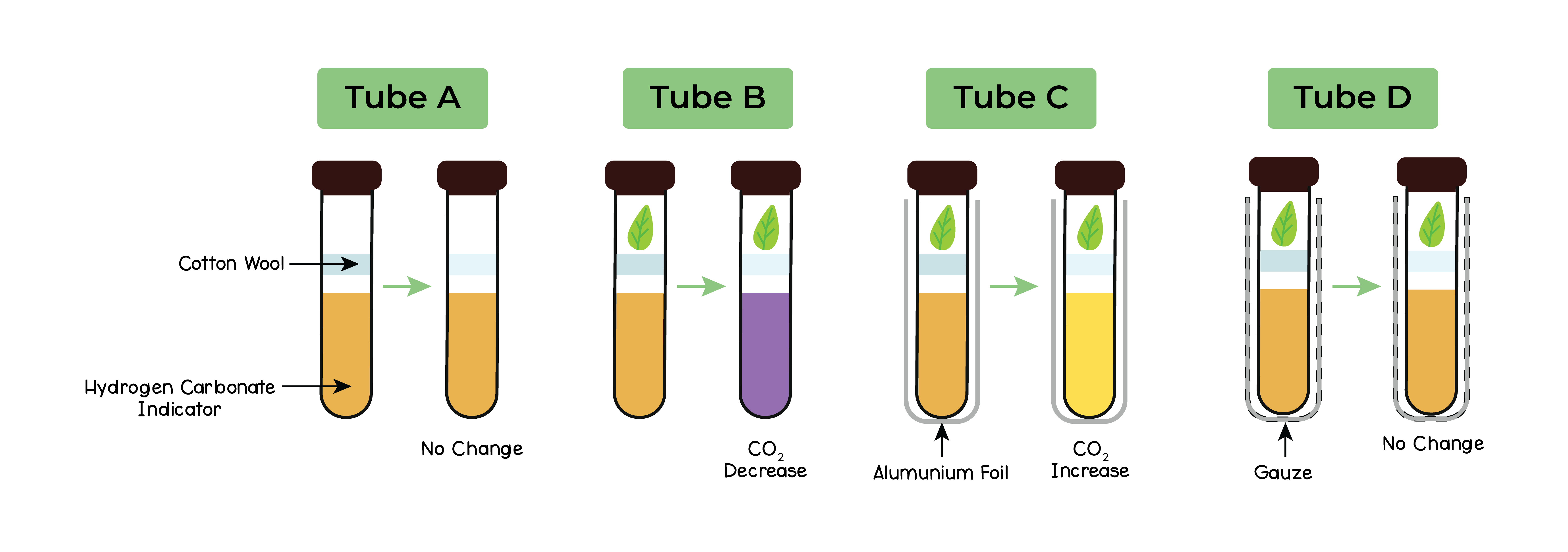
Method:
- Add 10cm3 of hydrogencarbonate indicator into 3 boiling tubes
- Add cotton wool into each tube and prepare samples accordingly:
- Tube 1 – control with no leaf
- Tube 2 – leaf
- Tube 3 – leaf wrapped in foil to block light
- Add a bung to the top of each tube and leave under light for 1 hour
Results:
- Tube 1 will remain orange/red showing CO2 at atmospheric levels
- Tube 2 will turn purple as the leaf would photosynthesize and respire
- Both processes displace the CO2 levels
- CO2 levels decrease from atmospheric levels
- Tube 3 will turn yellow as CO2 levels rise above atmospheric
- Photosynthesis cannot occur with light being blocked
- Respiration occurs releasing carbon dioxide