REVISION NOTES
IGCSE Edexcel Biology
a
2.2 Cell Structure
2.2.1 Describe cell structures, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, chloroplasts, ribosomes and vacuole
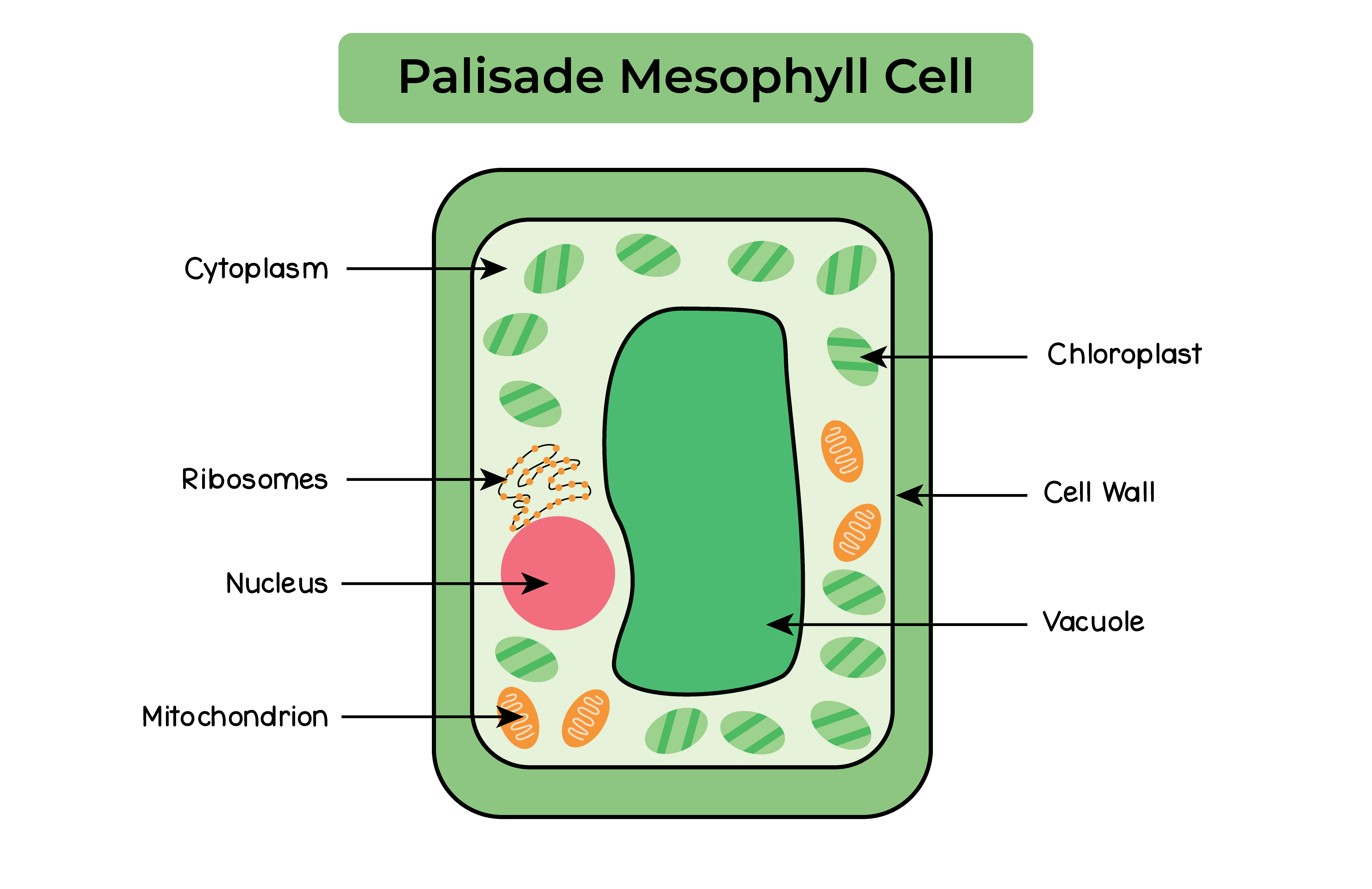
2.2.2 Describe the functions of the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, chloroplasts, ribosomes and vacuole
2.2.3 Know the similarities and differences in the structure of plant and animal cells
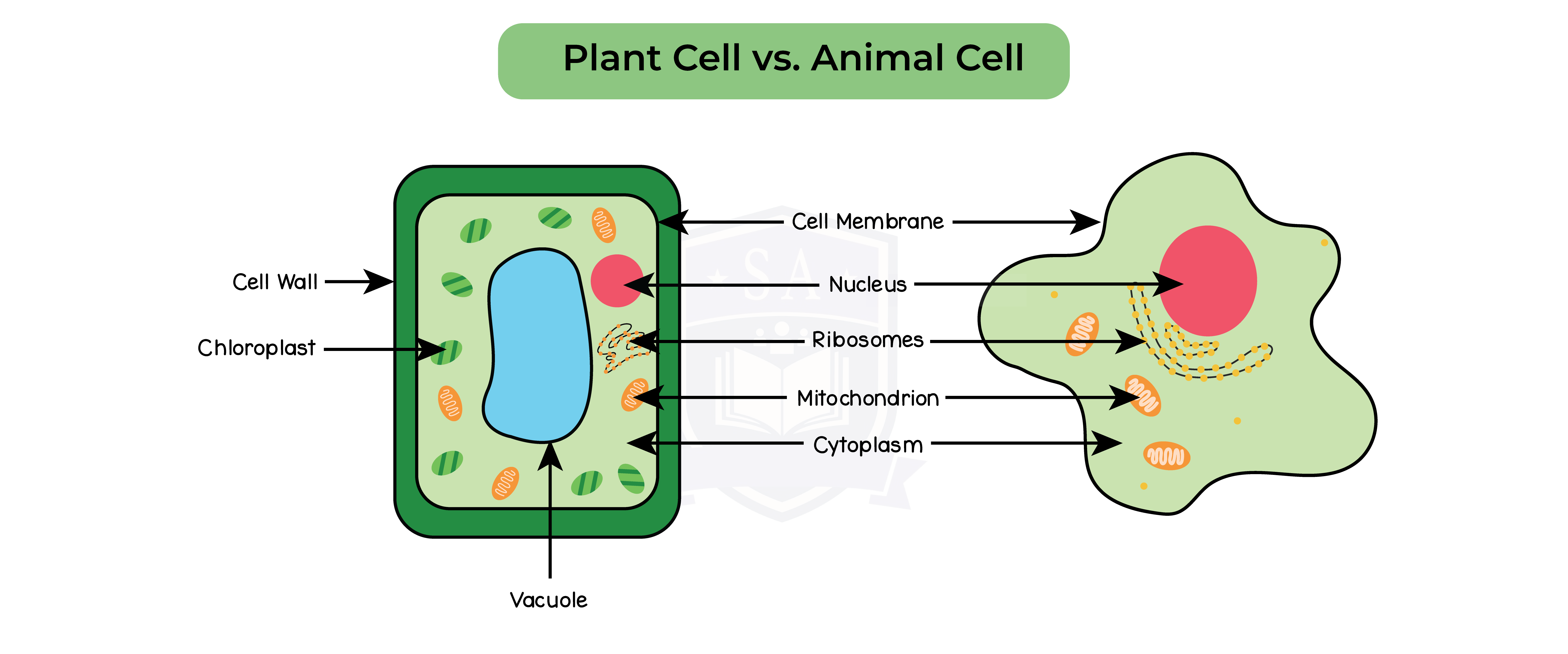
2.2.4B Know the similarities and differences in the structure of plant and animal cells
Specialised cells:
- Specialised cells have particular characteristics responsible for certain functions
- Formed by cell differentiation
- All cells contain the same genetic material
- Genes expressed dictate function of cell
Cell differentiation:
- The development of subcellular structures
- In animals most cells differentiate at early stages of development
- In plants cells differentiation can occur at any stage of development
2.2.5 Understand the advantages and disadvantages of using stem cells in medicine
Stem cells:
- An undifferentiated cell that has the ability to differentiate into any type of specialised cell
- Continue differentiating throughout the animals life
- Replace and repair cells
- Can divide by mitosis to produce more undifferentiated stem cells
Type of stem cells:
- Embryonic stem cell
- Undifferentiated cell
- Totipotent
- Can differentiate into all the different tissues and organs of the human body
- Formed in zygotes
- Adult stem cell:
- Can not differentiate into any cell
- Can form some specialised cells
- Used to replace damaged cells or produce new cells
- Meristem cell:
- Unspecialised cells
- Differentiate into cells required by plants
- Found at location of growth: root and shoot tips

